Java数据持久层
一、前言
1.持久层
Java数据持久层,其本身是为了实现与数据源进行数据交互的存在,其目的是通过分层架构风格,进行应用&数据的解耦。
我从整体角度,依次阐述JDBC、Mybatis、MybatisPlus。
前者总是后者的依赖。只有在了解前者,才可以更好地学习后者。
2.技术选型
ciwai ,还有Hibernate、SpringData、JPA等。
至于Hibernate作为知名框架,其最大的特点,是支持面向对象的数据管理。但成也萧何,败也萧何。Hibernate的该功能,导致其太重了。而大多数场景下,我们是不需要这个功能的。另外,Hibernate的该功能,使用起来过于复杂。其设计关联关系&映射关系,带来了太多复杂度。
SpringData,则是我看好的另一个Spring原生支持。但是目前主流还是Mybatis,其发展&主流的切换,还需要时间。就让子弹飞一会儿吧。
至于MybatisPlus,是我在工业物联网公司时所采用的一个技术方案。其符合“约定大于配置”的技术趋势,减少了Mybatis那样的配置成本,但是比JPA更加灵活。更棒的是,它支持stream这样的编码方式进行Sql支持(错误可以在编译期透出)。但如果是大型公司,个人的建议是,谨慎考虑,再进行使用。抛开技术方面的考量,MybatisPlus虽然是优秀的开源软件,但其开源社区&软件管理确实相对过于薄弱。对于大公司的技术生态而言,这是一个不得不重视的风险点。
3.文章脉络
不过,Mybatis作为现在最流行的ORM框架,还是值得大家相信的。所以经过考虑,这边文章虽然包含三块内容,但是JDBC更多作为一个依赖,进行了解。而MybatisPlus主要侧重于其核心功能-BaseMapper的实现,以及其扩展Mybatis得到的扩展实现方式。整篇文章的重点,还是落在Mybatis,对其投入较大的精力进行描述。
4.文章优势
又到了王婆卖瓜的阶段。
文章最大的两个优点:图&结构。
本篇文章采用了数十张图,用于展现对应关系。毕竟一图胜千言嘛。
而结构方面,文章采用MECE原则。文章分为JDBC、Mybatis、MybatisPlus。核心的Mybatis分为静态结构&运行流程。静态结构对Mybatis的架构,以及模块进行了展开。运行流程则是针对Mybatis的初始化&运行两个重要生命周期节点,进行展开。最后,通过Mybatis的核心Configuration的核心字段解析(作用、来源、去向)进行总结收纳。
5.文章遗憾
遗憾主要集中在两个方面:
- 由于是一个长文(接近6W字),最近事情又多(财年底,大家懂的),所以难免有一些疏漏。欢迎大家指出来哈。
- 战线拖得太长(写了快两个月)。虽然还有很多地方可以展开&深入,但是经过考虑后,还是放弃了。
文章中有很多补充部分,大家可以自行查阅,扩展知识面。虽然我查询了一些资料,但是有点整理不动(又不知大家是否感兴趣)。当然,如果大家对某部分感兴趣,可以提出来,我出个单章。
二、JDBC
1.简介
JDBC是一个规范,其分为两个部分:
- 厂商:完成数据库驱动
- Java开发者:调用统一接口

2.整体结构

对应组件:
- DriverManager:数据库驱动管理器
- Driver:数据库驱动的抽象接口,用于与数据库服务进行通信
- Connection:与数据库的连接
- Statement:用于提交SQL语句
- Statement:通用接口,继承自Wrapper。普通的不带参的查询SQL;支持批量更新,批量删除;
- PreparedStatement:预编译接口,继承自Statement。可变参数的SQL,编译一次,执行多次,效率高; 安全性好,有效防止Sql注入等问题;
- CallableStatement:继承自PreparedStatement。支持调用存储过程,提供了对输出和输入/输出参数(INOUT)的支持;
- ResultSet:用于保存数据库结果
- SQLException:数据库异常
3.生命周期
a.初始化过程
驱动注册&配置注入
b.执行过程

4.代码示例
原生JDBC较为原始,架构上的设计也是非常薄的。
所以,说得太多,还不如看看应用代码。
// 1. 注册驱动
// 使用java.sql.DriverManager类的静态方法registerDriver(Driver driver)
// Driver是一个接口,参数传递:MySQL驱动程序的实现类
// DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
// 查看驱动类源码,注册两次驱动,浪费资源
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获得连接
// uri:数据库地址 jdbc:mysql://连接主机ip:端口号//数据库名字
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/TEST";
// static Connection getConnection(String url, String user, String password)
// 返回值是java.sql.Connection接口的实现类,在MySQL驱动程序中
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "123456");
// conn.setAutoCommit(false); // 用于事务提交conn.commit(),conn.rollback()
System.out.println(conn);// com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@10d1f30
// 3. 获得语句执行平台,通过数据库连接对象,获取到SQL语句的执行者对象
//conn对象,调用方法 Statement createStatement() 获取Statement对象,将SQL语句发送到数据库
//返回的是Statement接口的实现类对象,在MySQL驱动程序中
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
System.out.println(statement);//com.mysql.jdbc.StatementImpl@137bc9
// 4. 执行sql语句
//通过执行者对象调用方法执行SQL语句,获取结果
//int executeUpdate(String sql) 执行数据库中的SQL语句,仅限于insert,update,delete
//返回值int,操作成功数据库的行数
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery("SELECT * from user where id = 1");
System.out.println(resultSet);
// 5. 释放资源
statement.close();
conn.close();
5.总结
关键词:简单、原始、看不到
现在基本没有人直接使用了。大多使用框架。我在生产级的使用,还是刚工作的时候,在前端使用了类似的东东。
三、Mybatis
1.整体框架

对应模块:
- 接口层
- SqlSession:应用程序与Mybatis的交互接口
- 核心处理层
- 配置解析:对Mybatis配置文件、映射文件,dao接口注解等进行配置解析,生成Configuration对象
- SQL解析:MyBatis 实现动态SQL 语句的功能,并提供了诸如where等SQL语句节点
- 参数映射:根据实参,解析动态SQLL节点,生成可执行SQL语句,处理占位符,绑定实参
- SQL执行:负责缓存,事务,JDBC等的调度。详见执行过程图
- 结果集映射:通过ResultSetHandler等,完成结果集的映射,得到结果对象并返回
- 插件:提供插件接口,便于用户扩展,甚至修改Mybatis默认行为
- 基础支持层
- 数据源模块:通过配置生成(可委托第三方数据源框架),包含目标数据库信息,向上支持连接生成等
- 事务管理模块:对数据库事务进行抽象,并提供简单实现。可与Spring集成,由Spring实现事务管理
- 缓存模块:为Mybatis的一二级缓存提供支持,从而优化数据库性能
- Binding模块:实现DAO接口文件与对应映射文件的关联
- 反射模块:对Java原生反射进行了封装与优化
- 类型转换:一方面实现JavaType与JDBCType的转换,另一方面支撑Mybatis的别名机制
- 日志模块:提供详细日志输出信息,并能够集成第三方日志框架(log4j,sel4j等)
- 资源加载:封装Java原生类加载器,提供类与其他资源文件的有序加载能力
- 解析器模块:一方面封装XPath,提供xml配置文件解析能力,另一方面为动态Sql占位符的处理,提供支持
数据源模块补充:即常用组件-DataSource。MyBatis 自身提供了相应的数据源实现(Pooled,UnPooled,Jndi),MyBatis 也提供第三方数据源集成的接口()。现在开源的数据源都提供了比较丰富的功能,如连接池功能、检测连接状态等
@Select注解,就可以省略对应的映射文件节点
DAO接口的实现类,是由Mybatis自动创建的动态代理对象(依赖于对应的映射文件节点)
Mybatis初始化阶段:加载Mybatis配置文件、映射文件,dao接口注解->保存到configuration对象中->创建SqlSessionFactory对象。Mybatis初始化阶段后,开发者可以通过SqlSessionFactory,获取对应的SqlSession。wdk-som的数据库配置就是直接配置生成DataSource与SqlSessionFactory。
a.解析模块
Mybatis的配置,有三种途径:
- XML:如Mybatis-config.xml
- 注解:如DAO接口方法上的@Select
- 注入:如MybatisConfiguration类
其中,XML是Mybatis配置的主要方式。XML配置则涉及XML文件解析。
XML常见解析方式,有一下三种:
- DOM:前端小伙伴,不要太熟悉。DOM 是基于树形结构的XML 解析方式,它会将整个XML 文档读入内存并构建一个DOM树,基于这棵树形结构对各个节点( Node )进行操作。DOM 解析方式的优点是易于编程,可以根据需求在树形结构的各节点之间导航。DOM 解析方式的缺点是在XML文件较大时,会造成较大的资源占用(因为需要构建DOM树)。
- SAX:SAX 是基于事件模型的XML 解析方式。当SAX 解析器解析到某类型节点时,会触发注册在该类型节点上的回调函数,开发人员可以根据自己感兴趣的事件注册相应的回调函数。由于在处理过程中井不会在内存中记录XML 中的数据,所以占用的资源比较小,这是其优点。其缺点是因为不存储XML 文挡的结构,所以需要开发人员自己负责维护业务逻辑涉及的多层节点之间的关系。
- StAX:StAX将XML 文档作为一个事件流进行处理。不同于SAX,在StAX 解析方式中,应用程序控制着整个解析过程的推进,可以简化应用处理XML 文档的代码,并且决定何时停止解析,而且StAX 可以同时处理多个XML 文档。
而Mybatis则是采用DOM解析方式,并结合XPath进行XML解析。
DOM 会将整个XML 文档加载到内存中并形成树状数据结构,而XPath 是一种为查询XML 文档而设计的语言,可以与DOM 解析方式配合使用,实现对XML 文档的解析。XPath 之于XML 就好比SQL 语言之于数据库。
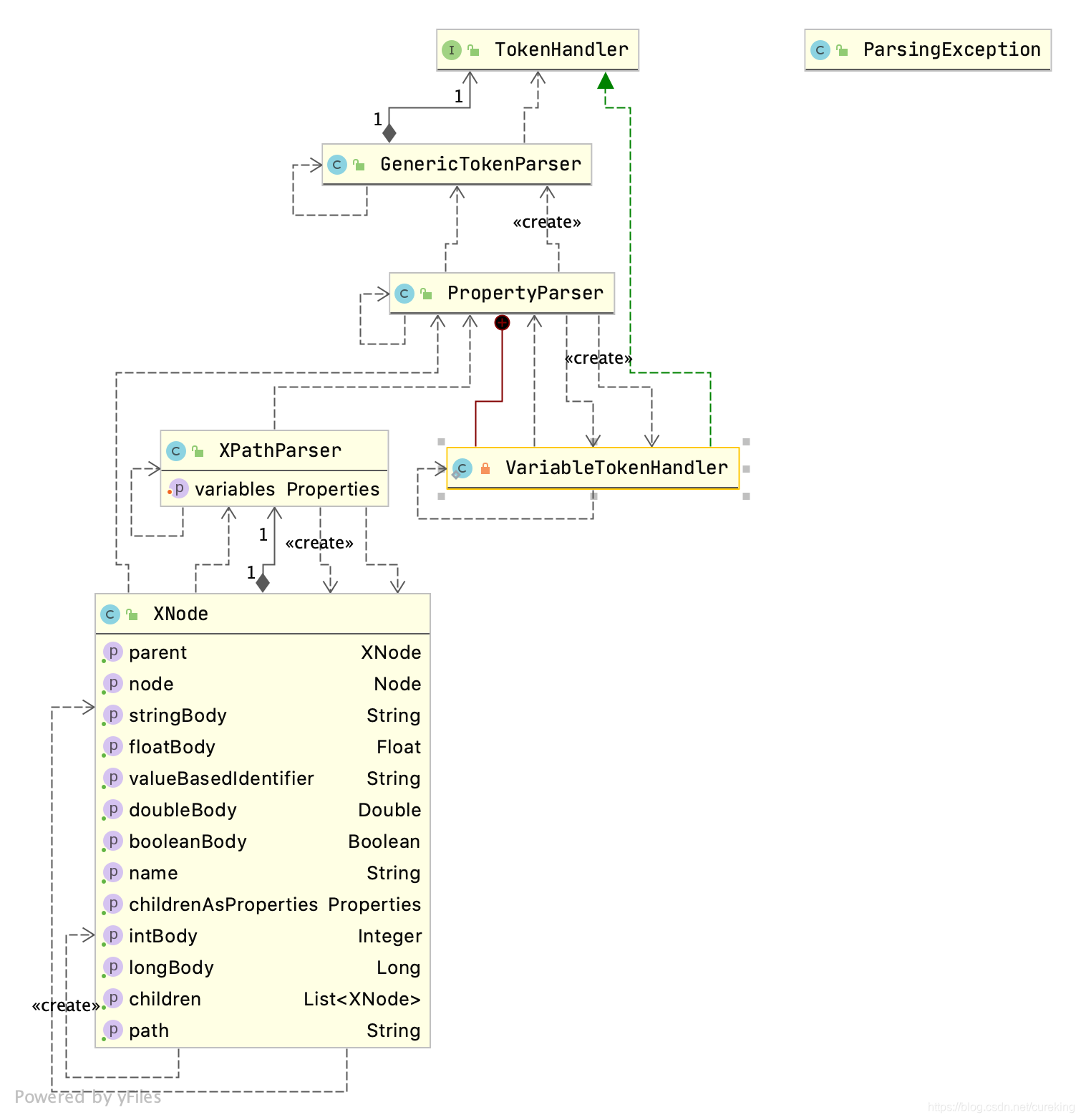
org.apache.ibatis.parsing.XPathParser#variables:mybatis-config.xml 中<propteries>标签定义的键位对集合。
XPathParser中提供了一系列的eval*方法用于解析boolean、short、long、int、String、Node等类型的信息,它通过调用XPath.evaluate方法查找指定路径的节点或属性,并进行相应的类型装换。
剩余部分,此处不再详解。
b.反射模块
Mybatis运行过程中,大量使用了反射(如生成DAO对应代理实现类)。Mybatis对Java原生的反射操作进行了进一步的封装,从而提供更加简洁的API。
Reflector 是MyBatis 中反射模块的基础,每个Reflector 对象都对应一个类,在Reflector 中缓存了反射操作需要使用的类的元信息。

从上图中,可以看出
- 核心类:
- Reflector:对于每个类,都有一个对应的Reflector,用于保存其类元信息。可以类比Spring中的Bean。但是其内部没有类之间的关联&依赖关系
- MetaClass:MetaClass 是MyBatis 对类级别的元信息的封装和处理。MetaClass 通过Reflector 和PropertyTokenizer 组合使用, 实现了对复杂的属性表达式的解析,并实现了获取指定属性描述信息的功能。
- MetaObject:ObjectWrapper实现的属性表达式解析功能,是委托给MetaObject实现的。
- 包:
- invoker:包含MethodInvoker、SetFieldInvoker等,用于实现目标方法反射调用,属性读取与设置等
- factory:包含ObjectFactory&DefaultObjectFactory,对象创建工厂。ObjectFactory提供实例创建接口,其默认实现为DefaultObjectFactory。在Mybatis源码的测试类中,存在对应测试。
- property:包含PropertyCopier、PropertyNamer、PropertyTokenizer,是类字段工具,提供如字段复制、字段是否为属性、字段与index转化(属性表达式&Sql占位符应用)等功能。
- wrapper:包含ObjectWrapperFactory、ObjectWrapper、BaseWrapper等。ObjectWrapper接口是对对象的包装,抽象了对象的属性信息,定义了一系列查询对象属性信息的方法,以及更新属性的方法。
TypeParameterResolver:进行类型解析。如TypeParameterResolver#resolveReturnType会返回对应类&方法的返回类型。在Mybatis源码的测试类中,存在对应测试。
Reflector
每个类,都有其对应等Reflector,用于保存其对应的类元信息(属性,字段等)
public class Reflector {
// 对应的Class 类型
private final Class<?> type;
// 可读属性的名称集合
private final String[] readablePropertyNames;
// 可写属性的名称集合
private final String[] writablePropertyNames;
// 属性相应的setter方法,key是属性名称,value是Invoker对象
private final Map<String, Invoker> setMethods = new HashMap<>();
// 属性相应的getter方法集合,key是属性名称,value是Invoker对象
private final Map<String, Invoker> getMethods = new HashMap<>();
// 属性相应的setter方法的参数值类型,key是属性名称,value是setter方法的参数类型
private final Map<String, Class<?>> setTypes = new HashMap<>();
// 属性相应的getter方法的返回位类型,key是属性名称,value是getter方法的返回位类型
private final Map<String, Class<?>> getTypes = new HashMap<>();
// 默认构造方法
private Constructor<?> defaultConstructor;
// 所有属性名称的集合,key是属性名称的大写形式,value是属性名称
private Map<String, String> caseInsensitivePropertyMap = new HashMap<>();
// 构造方法
public Reflector(Class<?> clazz) {
type = clazz;
addDefaultConstructor(clazz);
addGetMethods(clazz);
addSetMethods(clazz);
addFields(clazz);
// 学习一下:Collection.toArray()返回的是Object[],而Collection.toArray(T[] a)返回的是T[]
readablePropertyNames = getMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
writablePropertyNames = setMethods.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
for (String propName : readablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
for (String propName : writablePropertyNames) {
caseInsensitivePropertyMap.put(propName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH), propName);
}
}
// 其他方法
}
上述提到的都是”属性“,而不是字段。按照JavaBean的规范,类中定义的成员变量称为“ 宇段” ,属性则是通过ge阳r/setter 方法得到的,属性只与类中的方法有关,与是否存在对应成员变量没有关系。
所以,Mybatis与对应DO进行交互的依据是getter/setter方法。所以,可以通过自定义getter/setter方法进行字段转换。另外,DO中有字段,但没有对应getter/setter方法,则无法在对应mapper进行映射,最终导致报错。
MetaClass
MetaClass 是MyBatis 对类级别的元信息的封装和处理。
MetaClass 通过Reflector 和PropertyTokenizer 组合使用, 实现了对复杂的属性表达式的解析,并实现了获取指定属性描述信息的功能。
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class MetaClass {
private final ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory;
// class对应等Reflector
private final Reflector reflector;
private MetaClass(Class<?> type, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
this.reflectorFactory = reflectorFactory;
this.reflector = reflectorFactory.findForClass(type);
}
// 核心方法:解析属性表达式。委托给buildProperty方法实现
public String findProperty(String name) {
StringBuilder prop = buildProperty(name, new StringBuilder());
return prop.length() > 0 ? prop.toString() : null;
}
private StringBuilder buildProperty(String name, StringBuilder builder) {
// name即是属性表达式。如<result property= ”orders[0].items[1].name” column= ”item2” />
// PropertyTokenizer包含name、indexName、index、children
PropertyTokenizer prop = new PropertyTokenizer(name);
// 判断是否还有子表达式
if (prop.hasNext()) {
String propertyName = reflector.findPropertyName(prop.getName());
if (propertyName != null) {
// 返回结果,追加属性名(.name形式)
builder.append(propertyName);
builder.append(".");
// 为该属性,建立对应的MetaClass
MetaClass metaProp = metaClassForProperty(propertyName);
// 深度优先递归。创建所有MetaClass,并通过builder形成一个深度优先遍历的关系链
metaProp.buildProperty(prop.getChildren(), builder);
}
} else {
String propertyName = reflector.findPropertyName(name);
if (propertyName != null) {
builder.append(propertyName);
}
}
return builder;
}
}
ObjectWrapper
ObjectWrapper接口是对对象的包装,抽象了对象的属性信息,定义了一系列查询对象属性信息的方法,以及更新属性的方法。
其功能实现,是通过实现基础类-BaseObjectWrapper,委托给MetaObject实现。
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface ObjectWrapper {
// 如采Object Wrapper 中封装的是普通的Bean对象,则调用相应属性的相应getter 方法
// 如采封装的是集合类,则获取指定key或下标对应的value值
Object get(PropertyTokenizer prop);
void set(PropertyTokenizer prop, Object value);
// 查找属性表达式指定的属性,第二个参数表示是否忽略属性表达式中的下画线
String findProperty(String name, boolean useCamelCaseMapping);
String[] getGetterNames();
String[] getSetterNames();
// 解析属性表达式指定属性的setter 方法的参数类型。name为请求的属性表达式
Class<?> getSetterType(String name);
Class<?> getGetterType(String name);
boolean hasSetter(String name);
boolean hasGetter(String name);
// 为属性表达式指定的属性创建相应的MetaObject对象
MetaObject instantiatePropertyValue(String name, PropertyTokenizer prop, ObjectFactory objectFactory);
boolean isCollection();
void add(Object element);
<E> void addAll(List<E> element);
}
MetaObject
ObjectWrapper实现的属性表达式解析功能,是委托给MetaObject实现的。
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class MetaObject {
// 原生对象,即MetaObject所表示的对象
private final Object originalObject;
private final ObjectWrapper objectWrapper;
private final ObjectFactory objectFactory;
private final ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory;
private final ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory;
private MetaObject(Object object, ObjectFactory objectFactory, ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
this.originalObject = object;
this.objectFactory = objectFactory;
this.objectWrapperFactory = objectWrapperFactory;
this.reflectorFactory = reflectorFactory;
// 根据对象类型,使用不同的wrapper方法
if (object instanceof ObjectWrapper) {
this.objectWrapper = (ObjectWrapper) object;
} else if (objectWrapperFactory.hasWrapperFor(object)) {
this.objectWrapper = objectWrapperFactory.getWrapperFor(this, object);
} else if (object instanceof Map) {
this.objectWrapper = new MapWrapper(this, (Map) object);
} else if (object instanceof Collection) {
this.objectWrapper = new CollectionWrapper(this, (Collection) object);
} else {
this.objectWrapper = new BeanWrapper(this, object);
}
}
public static MetaObject forObject(Object object, ObjectFactory objectFactory, ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory, ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory) {
if (object == null) {
return SystemMetaObject.NULL_META_OBJECT;
} else {
return new MetaObject(object, objectFactory, objectWrapperFactory, reflectorFactory);
}
}
// 从MetaObject中,获取某个字段的属性值
public Object getValue(String name) {
PropertyTokenizer prop = new PropertyTokenizer(name);
if (prop.hasNext()) {
MetaObject metaValue = metaObjectForProperty(prop.getIndexedName());
if (metaValue == SystemMetaObject.NULL_META_OBJECT) {
return null;
} else {
return metaValue.getValue(prop.getChildren());
}
} else {
return objectWrapper.get(prop);
}
}
// 对MetaObject中某个字段进行赋值
public void setValue(String name, Object value) {
PropertyTokenizer prop = new PropertyTokenizer(name);
if (prop.hasNext()) {
MetaObject metaValue = metaObjectForProperty(prop.getIndexedName());
if (metaValue == SystemMetaObject.NULL_META_OBJECT) {
if (value == null) {
// don't instantiate child path if value is null
return;
} else {
metaValue = objectWrapper.instantiatePropertyValue(name, prop, objectFactory);
}
}
metaValue.setValue(prop.getChildren(), value);
} else {
objectWrapper.set(prop, value);
}
}
// 其他方法
c.类型转换
JDBC 数据类型与Java 语言中的数据类型井不是完全对应的,所以在PreparedStatement 为SQL 语句绑定参数时,需要从Java 类型转换成JDBC 类型,而从结果集中获取数据时,则需要从JDBC 类型转换成Java 类型。My Batis 使用类型模块完成上述两种转换。

TypeHandler
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
// 设置参数。在通过PreparedStatement 为SQL 语句绑定参数时,会将数据由Java 类型转换成JdbcType 类型
// 《Mybatis技术内幕》这部分的解释反了,详见入参与功能实现代码
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
// 获取结果。
// 从ResultSet 中获取数据时会调用此方法,会将数据由Java 类型转换成JdbcType 类型
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
BaseTypeHandler
public abstract class BaseTypeHandler<T> extends TypeReference<T> implements TypeHandler<T> {
@Deprecated
protected Configuration configuration;
@Deprecated
public void setConfiguration(Configuration c) {
this.configuration = c;
}
@Override
public void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
if (parameter == null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
throw new TypeException("JDBC requires that the JdbcType must be specified for all nullable parameters.");
}
try {
ps.setNull(i, jdbcType.TYPE_CODE);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different jdbcTypeForNull configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
} else {
try {
// 设置参数,该方法具体有子类实现
setNonNullParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Error setting non null for parameter #" + i + " with JdbcType " + jdbcType + " . "
+ "Try setting a different JdbcType for this parameter or a different configuration property. "
+ "Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(rs, columnName);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column '" + columnName + "' from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(rs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex + " from result set. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
@Override
public T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
try {
return getNullableResult(cs, columnIndex);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ResultMapException("Error attempting to get column #" + columnIndex + " from callable statement. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public abstract void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
public abstract T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
public abstract T getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}
实现子类的类型转换,最终还是会落到JDBC的PreparedStatement/ResultSet中对应的类型转换方法。
而PreparedStatement/ResultSet,是由入参带入的。
TypeHandlerRegistry&TypeAliasRegistry,主要是进行类型处理器&类型别名的管理(类似IOC容器对Bean的管理)。
d.数据源模块
Mybatis的数据源模块,采用了工厂方法设计模式。
如其中DataSourceFactory是工厂接口,而PooledDataSourceFactory等则是其工厂实现类。
Mybatis提供了三个工厂类实现方式:
- PooledDataSourceFactory
- UnpooledDataSourceFactory
- JndiDataSourceFactory

调用方举例:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.XMLConfigBuilder#dataSourceElement
DataSourceFactory
public interface DataSourceFactory {
void setProperties(Properties var1);
DataSource getDataSource();
}
UnpooledDataSourceFactory
public class UnpooledDataSourceFactory implements DataSourceFactory {
private static final String DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX = "driver.";
private static final int DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH = DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX.length();
protected DataSource dataSource;
public UnpooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource();
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
Properties driverProperties = new Properties();
// 利用基础层的配置解析模块,创建DataSource 相应的MetaObject
MetaObject metaDataSource = SystemMetaObject.forObject(dataSource);
for (Object key : properties.keySet()) {
// 遍历Properties,从而获取DataSource所需的配置信息
String propertyName = (String) key;
// 以”driver.”开头的配置项,是对DataSource的配置,记录到driverProperties中保存
if (propertyName.startsWith(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX)) {
String value = properties.getProperty(propertyName);
driverProperties.setProperty(propertyName.substring(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH), value);
} else if (metaDataSource.hasSetter(propertyName)) {
String value = (String) properties.get(propertyName);
Object convertedValue = convertValue(metaDataSource, propertyName, value);
metaDataSource.setValue(propertyName, convertedValue);
} else {
throw new DataSourceException("Unknown DataSource property: " + propertyName);
}
}
if (driverProperties.size() > 0) {
metaDataSource.setValue("driverProperties", driverProperties);
}
}
@Override
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
private Object convertValue(MetaObject metaDataSource, String propertyName, String value) {
Object convertedValue = value;
Class<?> targetType = metaDataSource.getSetterType(propertyName);
if (targetType == Integer.class || targetType == int.class) {
convertedValue = Integer.valueOf(value);
} else if (targetType == Long.class || targetType == long.class) {
convertedValue = Long.valueOf(value);
} else if (targetType == Boolean.class || targetType == boolean.class) {
convertedValue = Boolean.valueOf(value);
}
return convertedValue;
}
}
UnpooledDataSource
public class UnpooledDataSource implements DataSource {
// 进行驱动加载的classLoader,可参照JDBC相关处理
private ClassLoader driverClassLoader;
// 驱动配置
private Properties driverProperties;
// 驱动注册表(全量)
private static Map<String, Driver> registeredDrivers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 当前DataSource所采用的驱动,如mysqlDriver
private String driver;
// 数据源地址
private String url;
// 用户名
private String username;
// 密码
private String password;
// 是否自动提交(有关于事务),默认自动提交
private Boolean autoCommit;
// 默认事务隔离级别
private Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel;
// 默认网络超时时间
private Integer defaultNetworkTimeout;
// 驱动注册
static {
Enumeration<Driver> drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers();
while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) {
Driver driver = drivers.nextElement();
registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver);
}
}
// 方法略
}
e.事务管理模块
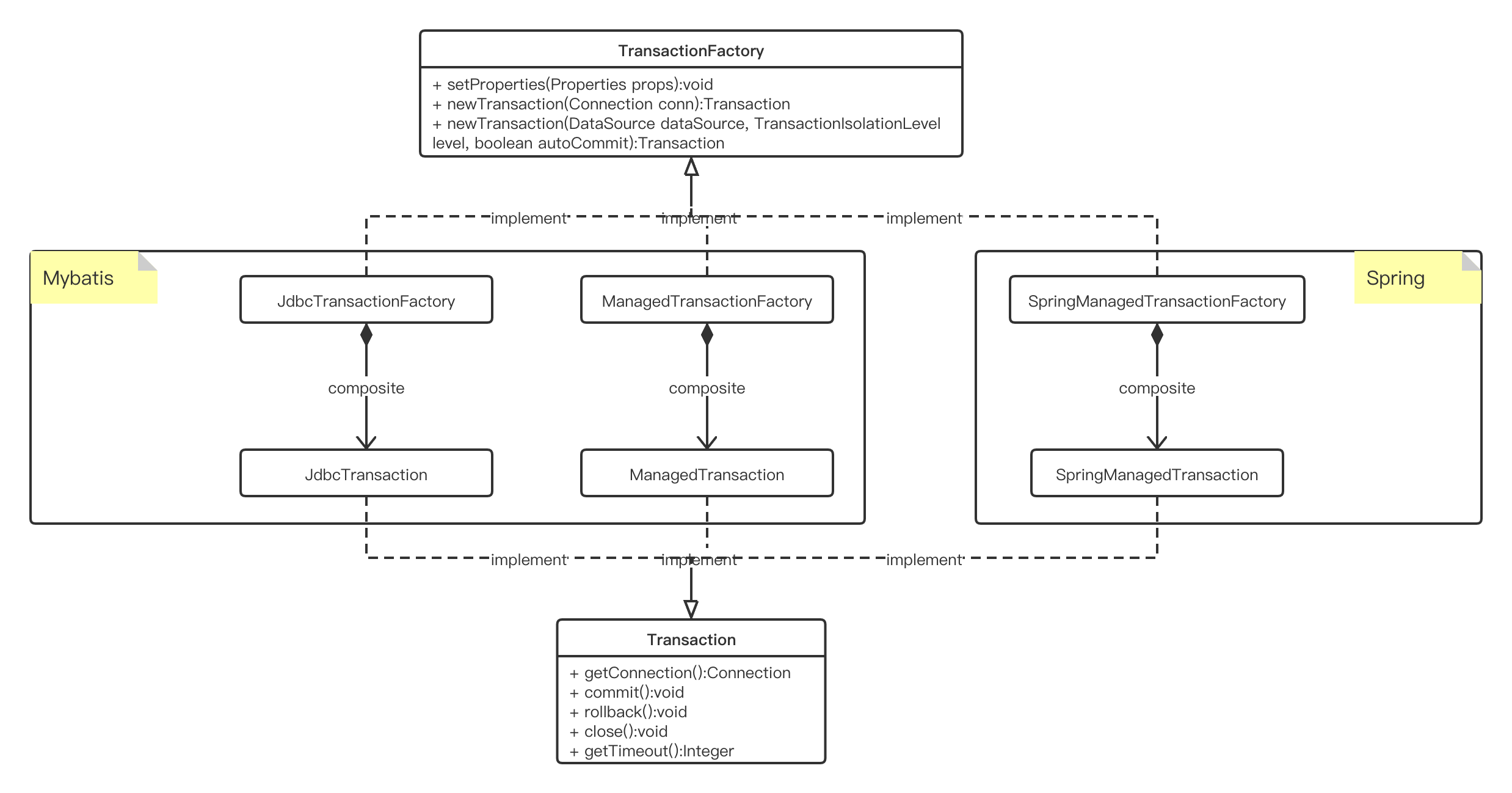
TransactionFactory
public interface TransactionFactory {
default void setProperties(Properties props) {
// NOP
}
Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn);
Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit);
}
Transaction
public interface Transaction {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
// 获取事务超时时间(Spring的SpringManagedTransaction,存在对应实现)
Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
}
SpringManagedTransaction
public class SpringManagedTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(SpringManagedTransaction.class);
private final DataSource dataSource;
private Connection connection;
// 当前连接是否为事务连接
private boolean isConnectionTransactional;
// 是否自动提交。如果是自动提交,也就不需要手动commit()了
private boolean autoCommit;
public SpringManagedTransaction(DataSource dataSource) {
Assert.notNull(dataSource, "No DataSource specified");
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection == null) {
this.openConnection();
}
return this.connection;
}
private void openConnection() throws SQLException {
this.connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(this.dataSource);
this.autoCommit = this.connection.getAutoCommit();
// DataSourceUtils获取对应的事务性ConnectionHolder,然后比对当前连接与ConnectionHolder
this.isConnectionTransactional = DataSourceUtils.isConnectionTransactional(this.connection, this.dataSource);
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "] will" + (this.isConnectionTransactional ? " " : " not ") + "be managed by Spring");
}
}
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection != null && !this.isConnectionTransactional && !this.autoCommit) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
// 事务提交
this.connection.commit();
}
}
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection != null && !this.isConnectionTransactional && !this.autoCommit) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
// 事务回滚
this.connection.rollback();
}
}
public void close() throws SQLException {
// 通过DataSourceUtils,释放当前连接。依旧涉及ConnectionHolder
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(this.connection, this.dataSource);
}
public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
// Connection没有对应的事务超时时间,这里直接调用底层实现,获取事务超时时间
ConnectionHolder holder = (ConnectionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(this.dataSource);
return holder != null && holder.hasTimeout() ? holder.getTimeToLiveInSeconds() : null;
}
}
这里的实现,涉及Connection的事务实现、DataSourceUtils、TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource三个点。
f.缓存模块
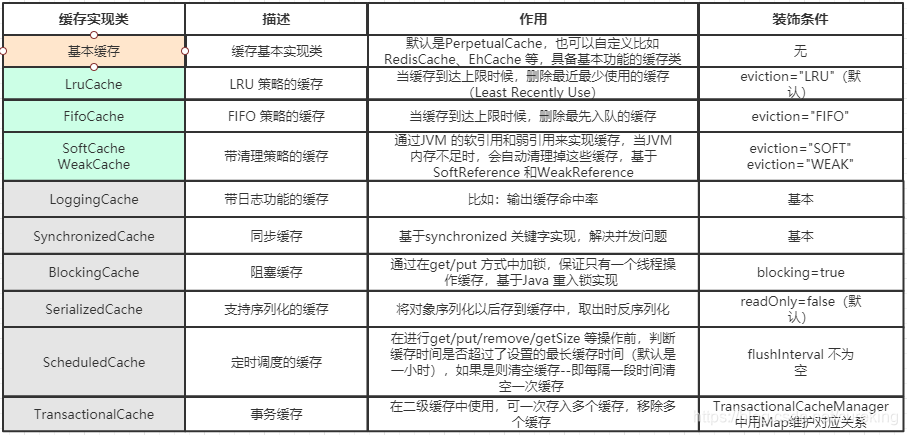
Cache:多种实现。如FIFO、LRU
CacheKey:应对SQL的可变参数
TransactionalCacheManager&TransactionalCache:事务缓存
缓存模块,是直接关联执行模块-Executor模块
- Mybatis的缓存:
- 一级缓存:默认开启。属于SqlSession级别的缓存。利用BaseExecute -> PerpetualCache -> HashMap<Obj,Obj>实现。
- 二级缓存:默认关闭。属于全局级别的缓存。利用CacheExecute -> TransactionalCacheManager -> HashMap<Cache, TransactionalCache> -> TransactionalCache
缓存实现,采用装饰器模式
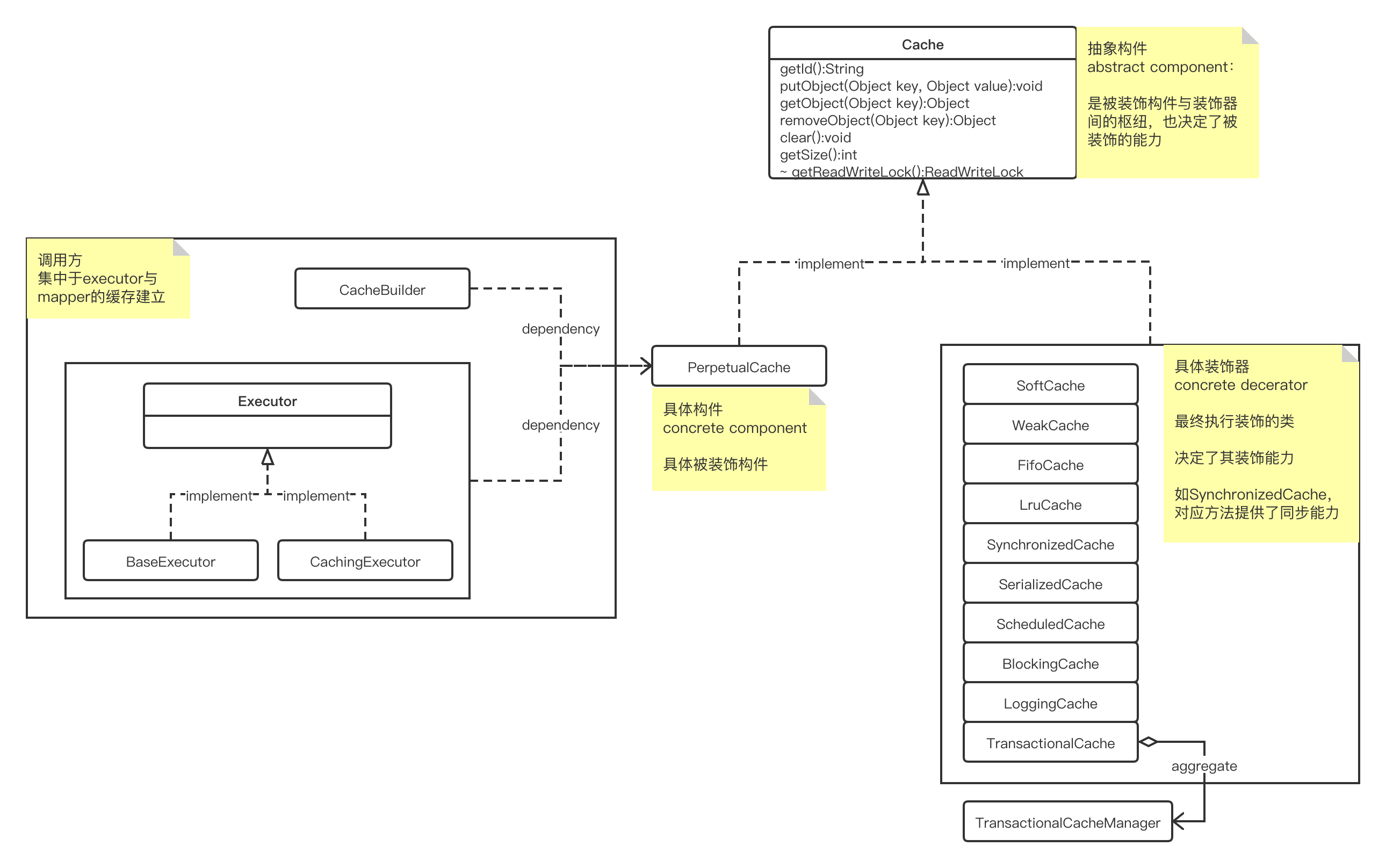
Cache
public interface Cache {
String getId();
void putObject(Object key, Object value);
Object getObject(Object key);
Object removeObject(Object key);
void clear();
int getSize();
default ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return null;
}
}
PerpetualCache
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private final String id;
private final Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
public PerpetualCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return cache.size();
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (!(o instanceof Cache)) {
return false;
}
Cache otherCache = (Cache) o;
return getId().equals(otherCache.getId());
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (getId() == null) {
throw new CacheException("Cache instances require an ID.");
}
return getId().hashCode();
}
}
SynchronizedCache
public class SynchronizedCache implements Cache {
private final Cache delegate;
public SynchronizedCache(Cache delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return delegate.getId();
}
@Override
public synchronized int getSize() {
return delegate.getSize();
}
@Override
public synchronized void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
delegate.putObject(key, object);
}
@Override
public synchronized Object getObject(Object key) {
return delegate.getObject(key);
}
@Override
public synchronized Object removeObject(Object key) {
return delegate.removeObject(key);
}
@Override
public synchronized void clear() {
delegate.clear();
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return delegate.hashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return delegate.equals(obj);
}
}
CacheKey
public class CacheKey implements Cloneable, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1146682552656046210L;
public static final CacheKey NULL_CACHE_KEY = new CacheKey() {
@Override
public void update(Object object) {
throw new CacheException("Not allowed to update a null cache key instance.");
}
@Override
public void updateAll(Object[] objects) {
throw new CacheException("Not allowed to update a null cache key instance.");
}
};
private static final int DEFAULT_MULTIPLIER = 37;
private static final int DEFAULT_HASHCODE = 17;
private final int multiplier;
private int hashcode;
private long checksum;
private int count;
private List<Object> updateList;
public CacheKey() {
this.hashcode = DEFAULT_HASHCODE;
this.multiplier = DEFAULT_MULTIPLIER;
this.count = 0;
this.updateList = new ArrayList<>();
}
public CacheKey(Object[] objects) {
this();
updateAll(objects);
}
public int getUpdateCount() {
return updateList.size();
}
public void update(Object object) {
int baseHashCode = object == null ? 1 : ArrayUtil.hashCode(object);
count++;
checksum += baseHashCode;
baseHashCode *= count;
hashcode = multiplier * hashcode + baseHashCode;
updateList.add(object);
}
public void updateAll(Object[] objects) {
for (Object o : objects) {
update(o);
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object) {
if (this == object) {
return true;
}
if (!(object instanceof CacheKey)) {
return false;
}
final CacheKey cacheKey = (CacheKey) object;
if (hashcode != cacheKey.hashcode) {
return false;
}
if (checksum != cacheKey.checksum) {
return false;
}
if (count != cacheKey.count) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < updateList.size(); i++) {
Object thisObject = updateList.get(i);
Object thatObject = cacheKey.updateList.get(i);
if (!ArrayUtil.equals(thisObject, thatObject)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return hashcode;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringJoiner returnValue = new StringJoiner(":");
returnValue.add(String.valueOf(hashcode));
returnValue.add(String.valueOf(checksum));
updateList.stream().map(ArrayUtil::toString).forEach(returnValue::add);
return returnValue.toString();
}
@Override
public CacheKey clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
CacheKey clonedCacheKey = (CacheKey) super.clone();
clonedCacheKey.updateList = new ArrayList<>(updateList);
return clonedCacheKey;
}
}
g.Binding模块
在mybatis的前身-iBatis,数据插入是这样的:
sqlSession.insert("insert", userDO);
或者,抽象一下:
public interface UserDAO {
void insertUser(UserDO userDO);
}
public class UserDAOImpl extends SqlMapDaoTemplate implements UserDAO {
public UserDAOImpl(DaoManager daoManager) {
super(daoManager);
}
public void insertUser(UserDO userDO) throws SQLException {
insert("insert", userDO);
}
}
两个实现,都涉及一个问题,需要手写
insert("insert", userDO);
那么写错,也是完全可能的嘛。但iBatis这部分,与Mybatis一样,是通过运行时的反射实现的。那么就无法快速失败,从而在启动时检索出问题。
如果一个不常用的方法实现的入参方法名写错了。Boom,线上故障+紧急发布。
所以,这里需要一个解决方案,可以在启动时,就检索出对应错误。
Mybatis给出的答案是,不再需要写上述实现。Mybatis直接通过Binding模块,直接关联DAO&对应Mapper。如果映射存在问题,则在启动时抛出相应问题。
举个栗子,如果在DAO的入参中没有String shopCode,而对应Mapper有对应入参注入,则会在启动时报错,提示“无法找到对应入参”。
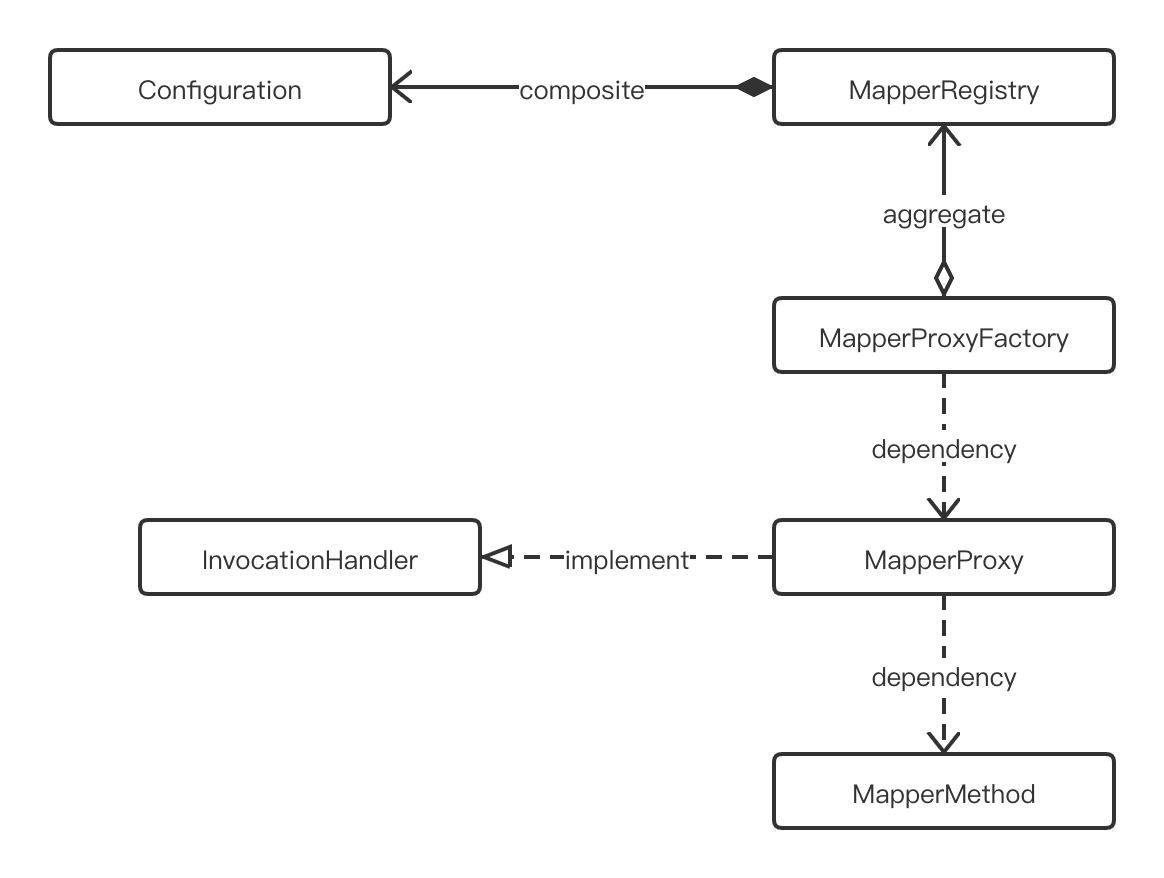
MapperRegistry
public class MapperRegistry {
// Mybatis全局Configuration,通过构造器注入
private final Configuration config;
// mapperInterface与相应MapperProxyFactory的映射表
// 如果是sqlSession.xxx的使用,则不经过这里。因为sqlSession在执行过程中,属于更底层的位置。详见后文:生命周期-执行过程
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
// 通过mapperInterface,获取对应的MapperProxy(type为接口类型)
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
public <T> boolean hasMapper(Class<T> type) {
return knownMappers.containsKey(type);
}
// 初始化过程中,用于添加mapperInterface。详见下述生命周期-初始化
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
// 检测type是否为接口类型,因为是针对mapperInterface
if (type.isInterface()) {
// 判断该接口是否已经注入到上面的映射表knownMappers中
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 进行对应mapper的解析,详见下述生命周期-初始化
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
// 失败,“回滚”
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
// 其他方法
}
MapperProxyFactory
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 该接口中,method与对应Invoker的映射表。
// MapperMethodInvoker与MapperMethod关系,详见org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy.PlainMethodInvoker
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
MapperProxy
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
// 核心字段
// 关联的SqlSession
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
// 当前Mapper,所对应的mapperInterface
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
// 当前Mapper中,Method与Invoker对应的映射表,作为缓存。此是由MapperProxyFactory给出
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache;
// 核心方法
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 如采目标方法继承自Object ,则直接调用目标方法。如toString()等方法
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// 其他的方法,则是Mapper相关的方法(非Object方法),则需要通过MapperMethodInvoker。具体可参照下面的PlainMethodInvoker
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
MapperMethodInvoker invoker = methodCache.get(method);
if (invoker != null) {
return invoker;
}
return methodCache.computeIfAbsent(method, m -> {
// 默认方法是公共非抽象的实例方法。也就是Interface的default方法
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
// 根据默认方法的判定,常用的MapperMethodInvoker是PlainMethodInvoker
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
// 核心内部类
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
// 通过MapperMethod.execute(),进行Sql语句的代理执行。详见MapperMethod
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
}
MapperMethod
MapperMethod 中封装了Mapper 接口中对应方法的信息,以及对应SQL 语句的信息
MapperMethod 对象。MapperMethod 对象会完成参数转换以及SQL语句的执行功能
MapperMethod 中并不记录任何状态相关的信息,所以可以在多个代理对象之间共享
public class MapperMethod {
// 当前Mapper下Method的Sql信息(SqlCommand)
// SqlCommand包含SQL语句的名称和类型
private final SqlCommand command;
// 当前Mapper下Method的方法签名,包括入参与返回值(类型&位置信息等)
private final MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
// 核心方法
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
// 根据SqlCommand的类型,执行不同的分支
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
// 参数关联,将传入实参数与方法形参关联起来。通过MethodSIgnature下的convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(),间接调用ParamNameResolver.getNamedParams(),从而获取Map<paramterName, paramterValue>
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 通过sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)进行执行,并将其返回值(effectLines),按照当前Method的返回值,返回对应类型的值(int、long、boolean)
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
// 根据返回值类型不同,调用不同执行方法,并返回不同结果
// 但其中executexxx()本质,还是调用sqlSession.xxx(),获取执行结果
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 这部分,个人认为也可以采用一个私有方法进行处理。
// 这里为什么不作为私有方法处理。个人猜测:一方面是命名(命名与语义关联);另一方面是为了更直观展示other的处理方式,提高代码可读性?
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
小结:
MapperRegistry.getMapper -> MapperProxyFactory.newInstance -> MapperProxy.invoke -> MapperMethod.execute -> Sqlsession.xxx(进入执行时)
h.资源加载模块
(暂略)
i.日志模块
(暂略)
2.生命周期
a.初始化过程
Mybatis初始化

Mybatis初始化-解析Mapper

mapper解析过程中,存在incompile 与 parsePending,很有意思。与
对MyBatis 初始化过程的分析可知, 映射配置文件中定义的SQL 节点会被解析成MappedStatement对象, 其中的SQL 语句会被解析成SqlSource 对象, SQL 语句中定义的动态SQL 节点、文本节点等,则由SqlNode 接口的相应实现表示。
MappedStatement包含SqlSource sqlSource。
SqlSource实现:DynamicSqlSource 负责处理动态SQL 语句,RawSqlSource 负责处理静态语句,两者最终都会将处理后的SQL 语句封装成StaticSqlSource返回。
DynamicSqlSource 与StaticSq!Source 的主要区别是:StaticSq!Source 中记录的SQL语句中可能含有“?”占位符,但是可以直接提交给数据库执行:DynamicSqlSourc e 中封装的SQL语句还需要进行一系列解析,才会最终形成数据库可执行的SQL 语句。
MyBatis 在处理动态SQL节点时,应用到了组合设计模式。MyBatis 会将动态SQL节点解析成对应的SqINode 实现,并形成树形结构。
DynamicContext 主要用于记录解析动态SQL 语句之后产生的SQL 语句片段,可以认为它是一个用于记录动态SQL 语句解析结果的容器。
SqlNode 接口有多个实现类,每个实现类对应一个动态SQL节点。如IfSqlNode,表示mapper映射文件中的if节点。
MapperBuilderAssistant

从上图,就可以看出MapperBuilderAssistant这个类的实际地位了。
BaseBuilder作为一个抽象类,提供了一个构建规约。
MapperBuilderAssistant则是实际提供构建能力的assistant。
而XMLStatementBuilder、XMLMapperBuilder等构建器,都是通过组合的方式,将通用能力,委托于MapperBuilderAssistant。
这个部分,这里只是点一下。
b.执行过程

SQL 语句的执行涉及多个组件,其中比较重要的是Executor 、StatementHandler 、ParameterHandler 和ResultSetHandler 。
Executor主要负责维护一级缓存和二级缓存,并提供事务管理的相关操作,它会将数据库相关操作委托给StatementHandler完成。
StatementHandler先通过ParameterHandler 完成SQL语句的实参绑定。然后通过java.sql.Statement 对象执行SQL 语句并得到结果集。最后通过ResultSetHandler 完成结果集的映射,得到结果对象并返回。
Mybatis最终是直接通过DataSource.getConnection(),获取对应Connnection,再进行联合Statement.execute进行操作。
Connection -> Transaction -> Executor -> StatementHandler
c.补充:初始化过程与执行过程的关联

3.Mybatis-Spring
这里不再详细展开Mybatis在SpringFramework集成时的配置。
主要针对Mybatis-Spring核心类的剖析,以及Mybatis在SpringBoot中的拆箱即用。
a.SqlSessionFactoryBean
在前面的Mybatis生命周期-初始化过程中,提到:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder会通过XMLConfigBuilder
等对象读取mybatis-config.xml配置文件以及映射配置信息,进而得到Configuration 对象,然后创建SqlSessionFactory 对象。
而在Mybatis-Spring中,SqlSessionFactoryBean取代了SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,进行SqlSessionFactory对象的生成。

这里对上述相关类,进行阐述:
- SqlSessionFactoryBean:Mybatis-Spring集成中,Spring初始化Mybatis的核心
- FactoryBean<>:声明该类为一个工厂类
- InitializingBean:利用Spring的生命周期接口,进行Mybatis对应Bean注入时间的时机控制(在配置注入完毕后)。详见Initialization Callbacks
- ApplicationListener<>:通过Spring下ApplicationContext的扩展能力,确保在上下文发生变化时,进行Mybatis配置的更新(主要针对Statement)。详见Additional Capabilities of the ApplicationContext
- SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:SqlSessionFactoryBean通过组合&委托的方式,调用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,从而构建SqlSessionFactory。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
private static final Log LOGGER = LogFactory.getLog(SqlSessionFactoryBean.class);
private Resource configLocation;
private Configuration configuration;
private SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//EnvironmentAware requires spring 3.1
private String environment = SqlSessionFactoryBean.class.getSimpleName();
// 是否采取快速失败,用于在上下文刷新时,进行statement刷新
private boolean failFast;
// Mybatis插件
private Interceptor[] plugins;
// 其他Mybatis-Configuration的字段(略)
// 各字段的getter/setter方法(略)
/**
* 核心方法,由Spring的生命周期进行控制(钩子函数-配置设置后,进行触发)
* 进行数据校验,然后调用构建方法-buildSqlSessionFactory()
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
/**
*
*/
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
// 各条件分支,对configuration进行配置的载入,以及不同级别日志的输出
// 略
// 委托给SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,进行实际的SqlSessionFactory的构建。后续流程就和Mybatis生命周期-初始化流程一致。详见前文Mybatis生命周期-初始化流程
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
@Override
public Class<? extends SqlSessionFactory> getObjectType() {
return this.sqlSessionFactory == null ? SqlSessionFactory.class : this.sqlSessionFactory.getClass();
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (failFast && event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
// fail-fast -> check all statements are completed
this.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getMappedStatementNames();
}
}
}
b.SpringManagedTransaction
有关Spring下Mybatis的事务,已经在Mybatis的事务模块,说明了。这里不再赘述。
提醒一下,只有在配置中未指定Mybatis事务管理,Spring才会采用默认事务管理-SpringManagedTransaction。
c.SqlSessionTemplate
SqlSessionTemplate实现了SqlSession接口,代替Mybatis原有的DefaultSqlSession,完成指定的数据库操作。
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(
SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class },
new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy.<T> selectOne(statement);
}
// 其他略
其通过委托的方式,调用其内部SqlSession sqlSessionProxy,从而完成对应功能。而此处的sqlSessionProxy,最终也是通过DefaultSqlSession实现,除非自定义实现SqlSessionFactory&SqlSession。
d.Mybatis-Starter
这部分涉及SpringBoot的自动注入,从而达到拆箱即用的效果。
首先,Spring根据配置,确定并注入DataSource等Bean。
然后,SpringBoot通过spring.factory,确定Mybatis的自动注入类MybatisAutoConfiguration。
最后,根据MybatisAutoConfiguration的@Bean方法,以及已有的配置Bean,进行Mybatis下SqlSessionFactory&SqlSessionTemplate的Bean注入。
spring.factory
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration
MybatisAutoConfiguration
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class })
@ConditionalOnBean(DataSource.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisAutoConfiguration.class);
private final MybatisProperties properties;
private final Interceptor[] interceptors;
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private final DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider;
private final List<ConfigurationCustomizer> configurationCustomizers;
public MybatisAutoConfiguration(MybatisProperties properties,
ObjectProvider<Interceptor[]> interceptorsProvider,
ResourceLoader resourceLoader,
ObjectProvider<DatabaseIdProvider> databaseIdProvider,
ObjectProvider<List<ConfigurationCustomizer>> configurationCustomizersProvider) {
this.properties = properties;
this.interceptors = interceptorsProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
this.databaseIdProvider = databaseIdProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.configurationCustomizers = configurationCustomizersProvider.getIfAvailable();
}
@PostConstruct
public void checkConfigFileExists() {
if (this.properties.isCheckConfigLocation() && StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation());
Assert.state(resource.exists(), "Cannot find config location: " + resource
+ " (please add config file or check your Mybatis configuration)");
}
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
Configuration configuration = this.properties.getConfiguration();
if (configuration == null && !StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
configuration = new Configuration();
}
if (configuration != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.configurationCustomizers)) {
for (ConfigurationCustomizer customizer : this.configurationCustomizers) {
customizer.customize(configuration);
}
}
factory.setConfiguration(configuration);
if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) {
factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors);
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) {
factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) {
factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) {
factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations());
}
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
if (executorType != null) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType);
} else {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
// 其他方法
}
4.总结
a.Configuration
以Mybatis的Configuration的核心字段,进行总结
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class Configuration {
// 核心:环境(特指数据源环境,同一个Mybatis中,可以存在多个环境)
// 来源:如mybatis-config.xml中<environments>下,多个<environment>节点信息
// 去向:DefaultSqlSessionFactory中提供数据源(DataSource)、AbstractBaseExecutor中提供数据源区分标识等
protected Environment environment;
// Mybatis的开关配置
// 如cacheEnabled决定是否采用一级缓存(详见MybatisConfiguration#newExecutor)
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
protected boolean shrinkWhitespacesInSql;
// 操作日志前缀
protected String logPrefix;
protected Class<? extends Log> logImpl;
protected Class<? extends VFS> vfsImpl;
protected Class<?> defaultSqlProviderType;
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<>(Arrays.asList("equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString"));
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
protected Integer defaultFetchSize;
protected ResultSetType defaultResultSetType;
// Mybatis默认执行器类型(SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH三种类型,详见newExecutor())
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
// Mybatis自动映射行为(NONE、PARTIAL(不对嵌套结果类型进行映射)、FULL三种类型)
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
// Mybatis对未识别对Column&type,进行对映射行为
protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE;
// 配置中变量列表。如mybatis-config.xml中<properties>节点信息
// 来源:XMLConfigBuilder.propertiesElement()解析获取
// 去向:作为Mybatis的配置项,如username、password等
protected Properties variables = new Properties();
// 默认反射工厂。详见反射模块部分
protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
// 默认对象构建工厂。详见反射模块部分
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory();
protected String databaseId;
protected Class<?> configurationFactory;
// 核心:Mapper方法的管理容器。详见Binding模块
// 来源:XMLConfigBuilder#mapperElement(针对xml配置)、XMLMapperBuilder#bindMapperForNamespace(针对xml配置)=》Configuration#addMapper
// 去向:SqlSessionManager#getMapper、DefaultSqlSession#getMapper =》Configuration#getMapper
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
// Mybatis插件实现,所依赖的责任链(暂不深入)
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
// 核心:Mybatis类型处理器管理容器。详见类型模块
// 来源:TypeHandlerRegistry#TypeHandlerRegistry =》 Configuration(默认类型注册)、TypeHandlerRegistry#register =》 XMLConfigBuilder#typeHandlerElement(自定义类型)
// 去向:DefaultParameterHandler#setParameters(形参注入)、DefaultResultSetHandler#prepareSimpleKeyParameter(返回结果的类型处理)
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry(this);
// Mybatis别名的管理容器
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
// 核心:唯一标识与对应MappedStatement的映射
// 来源:MapperAnnotationBuilder#handleSelectKeyAnnotation / XMLStatementBuilder#parseStatementNode =》 MapperBuilderAssistant#addMappedStatement =》 Configuration#addMappedStatement
// 去向:DefaultResultSetHandler#getNestedQueryConstructorValue / DefaultSqlSession#selectList / MapperMethod.SqlCommand#resolveMappedStatement =》 Configuration#getMappedStatement
// 注:唯一标识:可能包含namespace、前缀、自定mapperId(xml)/(typeName+methodName)(注解)
// 注:MappedStatement与Sql语句,是1:1关系(MappedStatement -> SqlSource -> BoundSql -> String sql)。所以,MappedStatement是针对接口方法的。
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection")
.conflictMessageProducer((savedValue, targetValue) ->
". please check " + savedValue.getResource() + " and " + targetValue.getResource());
// 重要:缓存映射表,进行命名空间与其下对应缓存的映射
// 来源:MapperAnnotationBuilder#parseCache / XMLMapperBuilder#cacheElement =》 MapperBuilderAssistant#useNewCache =》 Configuration#addCache
// 去向:XMLMapperBuilder#parsePendingCacheRefs =》 CacheRefResolver#resolveCacheRef =》 MapperBuilderAssistant#useCacheRef =》 Configuration#getCache(其中有关Incomplete,不用关注)
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<>("Caches collection");
// 核心:唯一标识和对应ResultMap的映射(类似于上面的mappedStatements)
// 来源&去向:类比上文mappedStatements。
// 注:mappedStatements关联Sql语句映射,resultMaps关联结果集映射
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<>("Result Maps collection");
// 核心:唯一标识和对应ParameterMap的映射(类似于上面的mappedStatements)
// 来源:XMLMapperBuilder#parameterMapElement =》 MapperBuilderAssistant#addParameterMap =》 Configuration#addParameterMap
// 去向:MapperBuilderAssistant#getStatementParameterMap =》 Configuration#getParameterMap
// 注:mappedStatements关联Sql语句映射,resultMaps关联结果集映射,ParameterMap关联参数集映射
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<>("Parameter Maps collection");
// 重要:唯一标识和对应KeyGenerator的映射(类似于上面的mappedStatements)
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<>("Key Generators collection");
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<>();
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
protected final Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = new LinkedList<>();
protected final Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList<>();
protected final Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList<>();
protected final Collection<MethodResolver> incompleteMethods = new LinkedList<>();
protected final Map<String, String> cacheRefMap = new HashMap<>();
}
四、Mybatis-Plus
1.简介
a.介绍

b.架构
c.特性:
- 无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑
- 损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作
- 强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求
- 支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错
- 支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题
- 支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操作
- 支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入( Write once, use anywhere )
- 内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用
- 内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List 查询
- 分页插件支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer 等多种数据库
- 内置性能分析插件:可输出 Sql 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询
- 内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作
2.实现
MP的实现,是基于Mybatis的。如果对Mybatis的源码有足够的认识,那么MP是很容易就入门的。
所以,这里不会对整个MP进行类似Mybatis的剖析。这里只针对其核心功能,进行实现的剖析。
a.BaseMapper默认模版
可以说,90%的小伙伴,都是冲着Mybatis-Plus基础mapper不用写的特点,入坑的。
那么Mybatis-Plus,是如何基于Mybatis,实现基础通用mapper呢?
答案,就是继承&覆写,Mybatis的MapperAnnotationBuilder。
Mybatis的MapperAnnotationBuilder,原先是为了提供对@Select等注解的解析。Mybatis-Plus通过继承&重写其中的parse方法,实现了Mybatis-Plus自身通用Mapper的注入。

有关MapperRegistry之前的流程,详见前文对Mybatis初始化流程中,mapper注入的部分。
MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder
/**
* 继承
* 只重写了 {@link MapperAnnotationBuilder#parse} 和 #getReturnType
* 没有XML配置文件注入基础CRUD方法
* @author Caratacus
* @since 2017-01-04
*/
public class MybatisMapperAnnotationBuilder extends MapperAnnotationBuilder {
@Override
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
String mapperName = type.getName();
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(mapperName);
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
InterceptorIgnoreHelper.InterceptorIgnoreCache cache = InterceptorIgnoreHelper.initSqlParserInfoCache(type);
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
InterceptorIgnoreHelper.initSqlParserInfoCache(cache, mapperName, method);
SqlParserHelper.initSqlParserInfoCache(mapperName, method);
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MybatisMethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
try {
if (GlobalConfigUtils.isSupperMapperChildren(configuration, type)) {
parserInjector();
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new InjectorResolver(this));
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
// 核心方法。进行定制化的通用mapper注入
void parserInjector() {
GlobalConfigUtils.getSqlInjector(configuration).inspectInject(assistant, type);
}
// 其他方法(略)
}
Insert
Mybatis-Plus下BaseMapper的通用Mapper方法,实现都在com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.injector.methods下。
这里,就以Insert为例,简单解析一下。
/**
* 插入一条数据(选择字段插入)
*
* @author hubin
* @since 2018-04-06
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class Insert extends AbstractMethod {
@Override
public MappedStatement injectMappedStatement(Class<?> mapperClass, Class<?> modelClass, TableInfo tableInfo) {
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = new NoKeyGenerator();
SqlMethod sqlMethod = SqlMethod.INSERT_ONE;
// 构建Sql的形参
String columnScript = SqlScriptUtils.convertTrim(tableInfo.getAllInsertSqlColumnMaybeIf(null),
LEFT_BRACKET, RIGHT_BRACKET, null, COMMA);
// 构建Sql的实参
String valuesScript = SqlScriptUtils.convertTrim(tableInfo.getAllInsertSqlPropertyMaybeIf(null),
LEFT_BRACKET, RIGHT_BRACKET, null, COMMA);
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
// 表包含主键处理逻辑,如果不包含主键当普通字段处理
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(tableInfo.getKeyProperty())) {
if (tableInfo.getIdType() == IdType.AUTO) {
/** 自增主键 */
keyGenerator = new Jdbc3KeyGenerator();
keyProperty = tableInfo.getKeyProperty();
keyColumn = tableInfo.getKeyColumn();
} else {
if (null != tableInfo.getKeySequence()) {
keyGenerator = TableInfoHelper.genKeyGenerator(getMethod(sqlMethod), tableInfo, builderAssistant);
keyProperty = tableInfo.getKeyProperty();
keyColumn = tableInfo.getKeyColumn();
}
}
}
// 按照格式要求,配合MethodType,构建对应的sql语句
String sql = String.format(sqlMethod.getSql(), tableInfo.getTableName(), columnScript, valuesScript);
// 获取对应SqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, sql, modelClass);
// 通过AbstractMethod,添加MappedStatement到Mybatis容器-Configuration下Mapper容器:MapperRegistry
return this.addInsertMappedStatement(mapperClass, modelClass, getMethod(sqlMethod), sqlSource, keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn);
}
}
b.lambda表达式
有关Mybatis-Plus的lambda表达式的实现,涉及的点比较多。这里给一些建议:首先对函数式编程&流式编程有足够的了解,其次需要对wrapper的使用有一定认识,最后剖析Mybatis-Plus中对应部分。
具体实现,详见:
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.AbstractLambdaWrapper
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.update.LambdaUpdateWrapper
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.LambdaUtils
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.support.SerializedLambda
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.conditions.query.LambdaQueryChainWrapper
com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.conditions.update.LambdaUpdateChainWrapper
最后,愿与诸君共进步。
五、附录
补充
- driver加载:jdbc下的driver加载分为三种方式:
- driverManager会在第一次调用时,会通过loadInitialDrivers()静态方法,对系统变量中的jdbc.drivers进行驱动注册
- 直接调用driverManager的register()方法,进行注册。
- 具体驱动,在初始化时,会调用driverManager的register()方法,进行注册。例:Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
- vfs:虚拟文件系统,Mybatis用于加载服务器相关资源。具体作用,需要继续查看。其由一个抽象类VFS与两个实现类:JBoss6VFS与DefaultVFS,允许自定义实现(Stripes cannot scan classpath correctly with Spring-Boot通过自定义VFS实现,解决springBoot的嵌套jar扫描问题)。
- SpringBoot默认数据库连接池:早期采用tomcat的连接池,2.0后改为HikariCP(位于spring-starter-jdbc下)。现在使用SpringBoot2+时,mybatis自动连接SpringBoot的默认数据源HikariCP。相关注入,详见:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration。其通过org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceConfiguration.Hikari上的@ConditionalOnMissingBean(DataSource.class)注解,实现优先级队列
- 工厂方法:DataSourceFactory 接口扮演工厂接口的角色。UnpooledDataSourceFactory和PooledDataSourceFactory 则扮演着具体工厂类的角色。而DataSource(Java)接口扮演产品接口的角色。UnpooledDataSource和HikariDataSource都扮演着具体产品类的角色。
- MyBatis的初始化可以有两种方式:
- 基于XML配置文件:基于XML配置文件的方式是将MyBatis的所有配置信息放在XML文件中,MyBatis通过加载并XML配置文件,将配置文信息组装成内部的Configuration对象
- 基于Java API:这种方式不使用XML配置文件,需要MyBatis使用者在Java代码中,手动创建Configuration对象,然后将配置参数set 进入Configuration对象中
- MyBatis和数据库的交互有两种方式:
- 使用传统的MyBatis提供的API:如SqlSession.selectOne(String statementId, T parameter);
- 使用Mapper接口
- 只有Mapper接口方式,才会经过MapperProxyFactory,MapperProxy,MapperMethod,最终都是调用sqlSession.xxx()
参考资料
- JDBC指南(W3C版)
- 老调重弹:JDBC系列 之 <驱动加载原理全面解析>
- 老调重弹:JDBC系列 之 <JDBC层次结构和基本构成>
- 《深入理解mybatis原理》 Mybatis初始化机制详解
- 面试:你知道MyBatis执行过程之初始化是如何执行的吗?
- JDBC层次结构和基本构成
- 《Mybatis技术内幕》
- 《深入理解mybatis原理》 MyBatis的架构设计以及实例分析
- Mybatis数据源
- Mybatis实现@Select等注解动态组合SQL语句
- Stripes cannot scan classpath correctly with Spring-Boot
- Github_HikariCP
- mybatis缓存机制
- SpringFramework-Core
- Github_Mybatis-3
- Github_Mybatis-redis-cache
- Github_Mybatis-Plus



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号