springboot中使用h2数据库(内存模式)
使用H2的优点,不需要装有服务端和客户端,在项目中包含一个jar即可,加上初始化的SQL就可以使用数据库了
在springboot中引入,我的版本是2.1.4,里面就包含有h2的版本控制
<!-- 集成h2数据库 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency>
在pom文件中,一般我都包含了下面一段
<build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <fork>true</fork> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> <resources> <resource> <directory>src/main/resources</directory> <includes> <include>**/**</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> <resource> <directory>src/main/java</directory> <includes> <include>**/*.properties</include> <include>**/*.xml</include> <include>**/*.tld</include> </includes> <filtering>false</filtering> </resource> </resources> </build>
截图:
h2数据库的配置:application-h2.properties
#spring.datasource.url = jdbc:h2:file:~/.h2/testdb spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:activiti;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=1000 spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver spring.datasource.username=sa spring.datasource.password= spring.datasource.schema=classpath:db/schema.sql spring.datasource.data=classpath:db/data.sql
如果数据文件有多个,使用逗号拼接就可以了,spring.datasource.data=classpath:db/data.sql,classpath:db/data2.sql
db/data.sql内容:
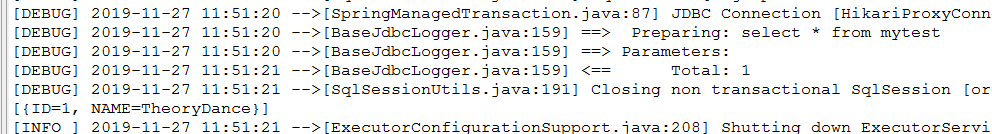
insert into mytest(name) values('TheoryDance');
schema.sql内容:
create table mytest(id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20) not null);
在测试类中添加一个测试方法
package com.grand.mysql_handler; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import javax.annotation.Resource; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner; import com.grand.mysql_handler.mapper.SystemMapper; @SpringBootTest @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) public class MyRestTest2 { @Resource private SystemMapper systemMapper; @Test public void testH2() { List<Map<String,Object>> list = systemMapper.selectBySql("select * from mytest"); System.out.println(list); } }
其中SysMapper.java内容如下(使用的Mybatis连接数据库):
package com.grand.mysql_handler.mapper; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update; @Mapper public interface SystemMapper { @Insert("${sql}") int insertBySql(@Param("sql")String sql); @Delete("${sql}") int deleteBySql(@Param("sql")String sql); @Update("${sql}") int updateBySql(@Param("sql")String sql); @Select("${sql}") List<Map<String,Object>> selectBySql(@Param("sql")String sql); @Select("${sql}") Map<String,Object> selectOneBySql(@Param("sql")String sql); }
测试结果: