负环(Negative Ring)
简介(Introduction)
一个图中,环的边权和 $ < 0$ ,进行无限次循环后,环上点的距离就会被更新成 \(-\infty\)
描述(Description)
- 判断方式:
- 统计每个点入队的次数如果某个点入队 \(n\) 次说明存在负环
- 统计当前每个点的最短路中所包含的边数,如果某个点的最短路所包含的边数 \(\ge n\) 说明存在负环(常用)
- 判读环出现 \(TLE\) 时:
- 将 \(queue\) 换成 \(stack\)
- 当更新超过 \(10^4\) 方次数时,可以默认该图存在负环
示例(Example)
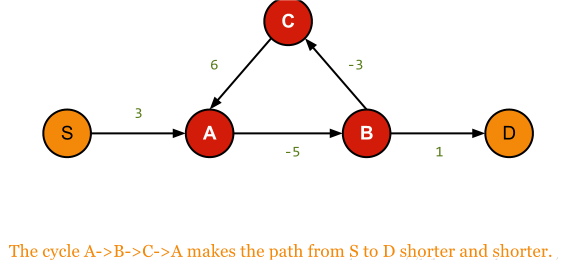
代码(Code)
// C++ Version
int dist[N], cnt[N];
bool st[N];
int q[N];
bool spfa() {
int hh = 0, tt = 0;
memset(dist, 0, sizeof dist);
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) {
q[tt ++ ] = i;
st[i] = true;
}
while (hh != tt) {
int t = q[hh ++ ];
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
st[t] = false;
for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]) {
dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i];
cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1;
if (cnt[j] >= n) return true; // 抽屉原理
if (!st[j]) {
q[tt ++ ] = j;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
st[j] = true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
应用(Application)
虫洞
农夫约翰在巡视他的众多农场时,发现了很多令人惊叹的虫洞。
虫洞非常奇特,它可以看作是一条 单向 路径,通过它可以使你回到过去的某个时刻(相对于你进入虫洞之前)。
农夫约翰的每个农场中包含 \(N\) 片田地,\(M\) 条路径(双向)以及 \(W\) 个虫洞。
现在农夫约翰希望能够从农场中的某片田地出发,经过一些路径和虫洞回到过去,并在他的出发时刻之前赶到他的出发地。
他希望能够看到出发之前的自己。
请你判断一下约翰能否做到这一点。
下面我们将给你提供约翰拥有的农场数量 \(F\),以及每个农场的完整信息。
已知走过任何一条路径所花费的时间都不超过 \(10000\) 秒,任何虫洞将他带回的时间都不会超过 \(10000\) 秒。
输入格式
第一行包含整数 \(F\),表示约翰共有 \(F\) 个农场。
对于每个农场,第一行包含三个整数 \(N,M,W\)。
接下来 \(M\) 行,每行包含三个整数 \(S,E,T\),表示田地 \(S\) 和 \(E\) 之间存在一条路径,经过这条路径所花的时间为 \(T\)。
再接下来 \(W\) 行,每行包含三个整数 \(S,E,T\),表示存在一条从田地 \(S\) 走到田地 \(E\) 的虫洞,走过这条虫洞,可以回到 \(T\) 秒之前。
输出格式
输出共 \(F\) 行,每行输出一个结果。
如果约翰能够在出发时刻之前回到出发地,则输出
YES,否则输出NO。数据范围
\(1 \le F \le 5\)
\(1 \le N \le 500\),
\(1 \le M \le 2500\),
\(1 \le W \le 200\),
\(1 \le T \le 10000\),
\(1 \le S,E \le N\)
输入样例:
2
3 3 1
1 2 2
1 3 4
2 3 1
3 1 3
3 2 1
1 2 3
2 3 4
3 1 8
输出样例:
NO
YES
-
题解:
// C++ Version #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 510, M = 5210; int n, m1, m2; int h[N], e[M], ne[M], w[M], idx; int dist[N], cnt[N]; bool st[N]; int q[N]; void add(int a, int b, int c) { e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ; } bool spfa() { int hh = 0, tt = 0; memset(dist, 0, sizeof dist); memset(st, 0, sizeof st); memset(cnt, 0, sizeof cnt); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { q[tt ++ ] = i; st[i] = true; } while (hh != tt) { int t = q[hh ++ ]; if (hh == N) hh = 0; st[t] = false; for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (dist[j] > dist[t] + w[i]) { dist[j] = dist[t] + w[i]; cnt[j] = cnt[t] + 1; if (cnt[j] >= n) return true; if (!st[j]) { q[tt ++ ] = j; if (tt == N) tt = 0; st[j] = true; } } } } return false; } int main() { int T; cin >> T; while (T -- ) { cin >> n >> m1 >> m2; memset(h, -1, sizeof h); idx = 0; while (m1 -- ) { int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; add(a, b, c), add(b, a, c); } while (m2 -- ) { int a, b, c; cin >> a >> b >> c; add(a, b, -c); } if (spfa()) puts("YES"); else puts("NO"); } return 0; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号