moectf-re WP
IntroducingRe
将下载的文件拉入IDA,f5运行一下:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { int v4; // [esp+17h] [ebp-19h] int v5; // [esp+1Bh] [ebp-15h] int v6; // [esp+1Fh] [ebp-11h] int v7; // [esp+23h] [ebp-Dh] int v8; // [esp+27h] [ebp-9h] int v9; // [esp+2Bh] [ebp-5h] char v10; // [esp+2Fh] [ebp-1h] sub_401F10(); puts("Welcome to the MoeCTF!"); v4 = 1667592045; v5 = 1148937844; v6 = 1868128048; v7 = 845897589; v8 = 1230993263; v9 = 2101297476; v10 = 0; sub_401500((char *)&v4); return system("pause"); }
根据(char *)考虑v4开始v10结束的应该是一串字符串,使用快捷键‘R’将其转换成字符,即得到flag:moectf{D0_You_k2ow_IDA?}
MoeRe
将文件拖入IDA,f5:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { int v3; // eax int result; // eax int j; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-A0h] int i; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-9Ch] int v7; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-98h] __int64 v8; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-90h] char v9[104]; // [rsp+40h] [rbp-70h] __int64 v10; // [rsp+A8h] [rbp-8h] scanf("%s", v9, envp); v3 = strlen(v9); v7 = v3; strcpy((char *)&v8, "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"); for ( i = 0; i < v3; ++i ) v9[i] ^= *((_BYTE *)&v8 + i % 26); for ( j = 0; j < v7; ++j ) printf("%d,", (unsigned int)v9[j]); result = 0; if ( __stack_chk_guard == v10 ) result = 0; return result; }
意思是:flag(v9)中的字符分别与26个字母(v8)做异或运算,其中:
v9[i] ^= *((_BYTE *)&v8 + i % 26);//取从v8开始的第一个字节,并+i%26,即与相应位置的字母异或
结果为题目中的这一大串输出结果:

于是尝试写脚本,如下:
import numpy #写文件: inf1 = input("") #题目中的运行结果 inf2 = inf1.split(',') #把读入的字符串以','分隔并存入列表inf2中 file1 = open("C:/Python27/Myprogrammes/test2.txt","w") N = len(inf2) for i in range(N): file1.write(str(inf2[i])) file1.write('\n') #按照每行一个数据的格式写入文件 file1.close() #读文件: file = open(r"C:/Python27/Myprogrammes/test2.txt") num = [] for line in file: line=line.strip('\n') #将\n去掉 num.append(line.split()) #把每一行中的数据加入num的list file.close() #处理读入的数据 num = numpy.array(num,dtype=int) #把num由list变成array str1 = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" n = len(num) flag = [] for i in range(n): flag.append(num[i]^ord(str1[i])) strlist = list(flag) for i in range(n): strlist[i]=chr(flag[i]) print("".join(strlist)) #输出flag
运行得到flag:moectf{Kn0wing_R3v3rs3_from_x0r_and_1da}
.pyc
利用在线反编译网站(有很多网站显示反编译失败,暂时不知原因),得到:
from binascii import b2a_hex from base64 import b32encode x = input y = print if b2a_hex(b32encode(x().encode())).decode() == '4e5658574b5933554d5a3558413452544d4d59473234444a4e525557345a5a4e4b4234574758334447525846364d44514f51595732324c324d55575647344254474e5348323d3d3d': y('congrats')
意思就是将flag先base32编码,再把每一个字符变成其ASCII码对应的十六进制形式。于是,先十六进制转成ASCII码对应的文本,再解码base32即可。得到flag:moectf{pr3c0mpiling-Pyc_c4n_0pt1mize-Sp33d}
补充:又把base家族编码看了一遍,再次总结:
16=2^4 32=2^5 64=2^6
∴base16是每4个字节一划分,对应0-9,A-F
base32是每5个字节一划分,对应2-7,A-Z,用0和=凑够成编码后的字符长度是八的整数倍
base64是每6个字节一划分,对应0-9,A-Z,a-z,+,/,用0和=凑够成编码后的字符长度是四的整数倍
EasyShell
由题目已经知道是upx加壳,下载了UpxUnpacker,但尝试无果,放入kali linux,输入
upx -d upx.exe
再拖入IDA,得到flag:moectf{upx_1s_a_K1nd_0F_sh21L}
#EasyDebugger
题目明显说明这道题应该用到调试器,于是下载windbg,配置symbol,开调试直接蹦出flag : moectf{Debuger_1s_@_Go04_tOoL_4_r2vers2}
#EasyGo
题目提示这道题的点在于Go语言的入口点,
资料如下:
Go 程序是通过 package 来组织的。
只有 package 名称为 main 的包可以包含 main 函数。
一个可执行程序有且仅有一个 main 包。
通过 import 关键字来导入其他非 main 包。
所以入口点为main_main函数,f5运行一下:
fmt_Fscanln(a1, a2, (__int64)&v28, (__int64)&unk_4AAF60, v11, v12, (__int64)&go_itab__os_File_io_Reader, os_Stdin); if ( *v24 == 1107LL ) { runtime_convTstring(a1, a2, v13, v14, v15, v16, (__int64)&unk_4D954E, 34LL); *(_QWORD *)&v27 = &unk_4B0720; *((_QWORD *)&v27 + 1) = &v28; fmt_Fprintln( a1, a2, v17, (__int64)&go_itab__os_File_io_Writer, v18, v19, (__int64)&go_itab__os_File_io_Writer, os_Stdout); }
直接跟进unk_4D954E,找到flag: moectf{G0_1Anguage_1s_1nT3r3st1ng}
#EasyJava
拿到题目,利用jd-gui反汇编class文件(BOX),得到关键代码:
public static boolean CHECK(int input) { if ((input > 10000000) && (input < 99999999)) { int v7 = 1; int v8 = 10000000; int v3 = 1; if ((Math.abs(input / 1000 % 100 - 80) == 3) && (input % 1000 % 927 == 0)) { int v5 = 0; while (v5 < 4) { if (input / v7 % 10 != input / v8 % 10) { v3 = 0; break; } v7 *= 10; v8 /= 10; v5++; } if (v3 != 1) { return false; } if (v3 == 1) { return true; } } } return false; }
条件:
(Math.abs(input / 1000 % 100 - 80) == 3) && (input % 1000 % 927 == 0)
表示输入的中间两位是83或77,最后三位是927;
条件:
while (v5 < 4) { if (input / v7 % 10 != input / v8 % 10) { v3 = 0; break; } v7 *= 10; v8 /= 10; v5++; }
判断输入是否是回文字符串,即:输入必须满足72977927,最后判断输出flag的代码:
if (e.getSource() == this.bt) { if (CHECK(Integer.parseInt(this.a))) { this.tx.setText("moectf{" + (char)(Integer.parseInt(this.a) / 1000000) + (char)(Integer.parseInt(this.a) / 10000 % 100) + (char)(Integer.parseInt(this.a) / 100 % 100) + "_he}"); } else { this.tx.setText("clear and try again!"); } }
意思是将该整数两位两位拆开转成字符,其中27对应Esc退出,所以得到flag : moectf{Hao_he}
#Mine Sweep
先找到main函数,
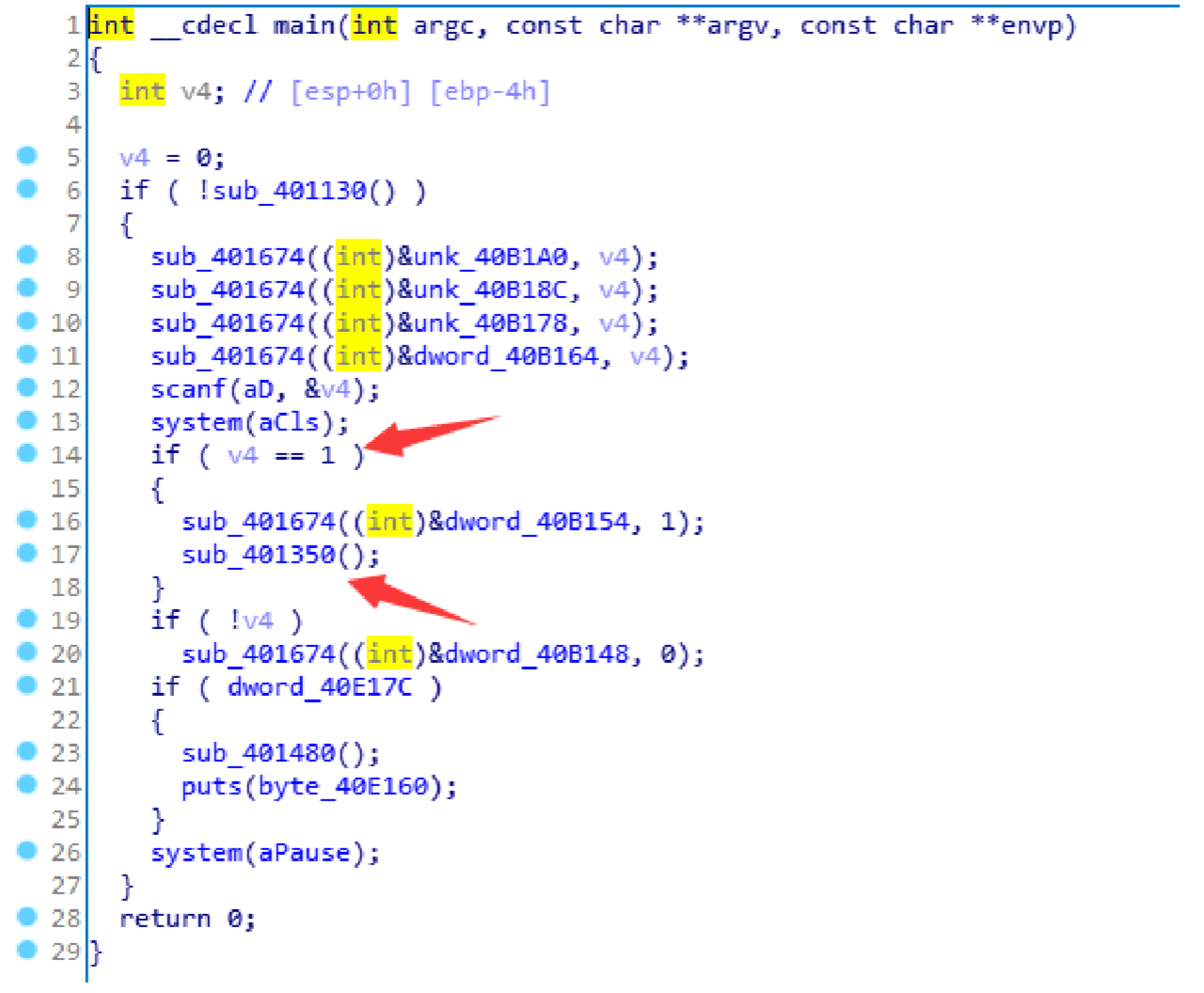
输入1执行程序,跟进下面这个函数,找到关键,发现显示的是字符串success:
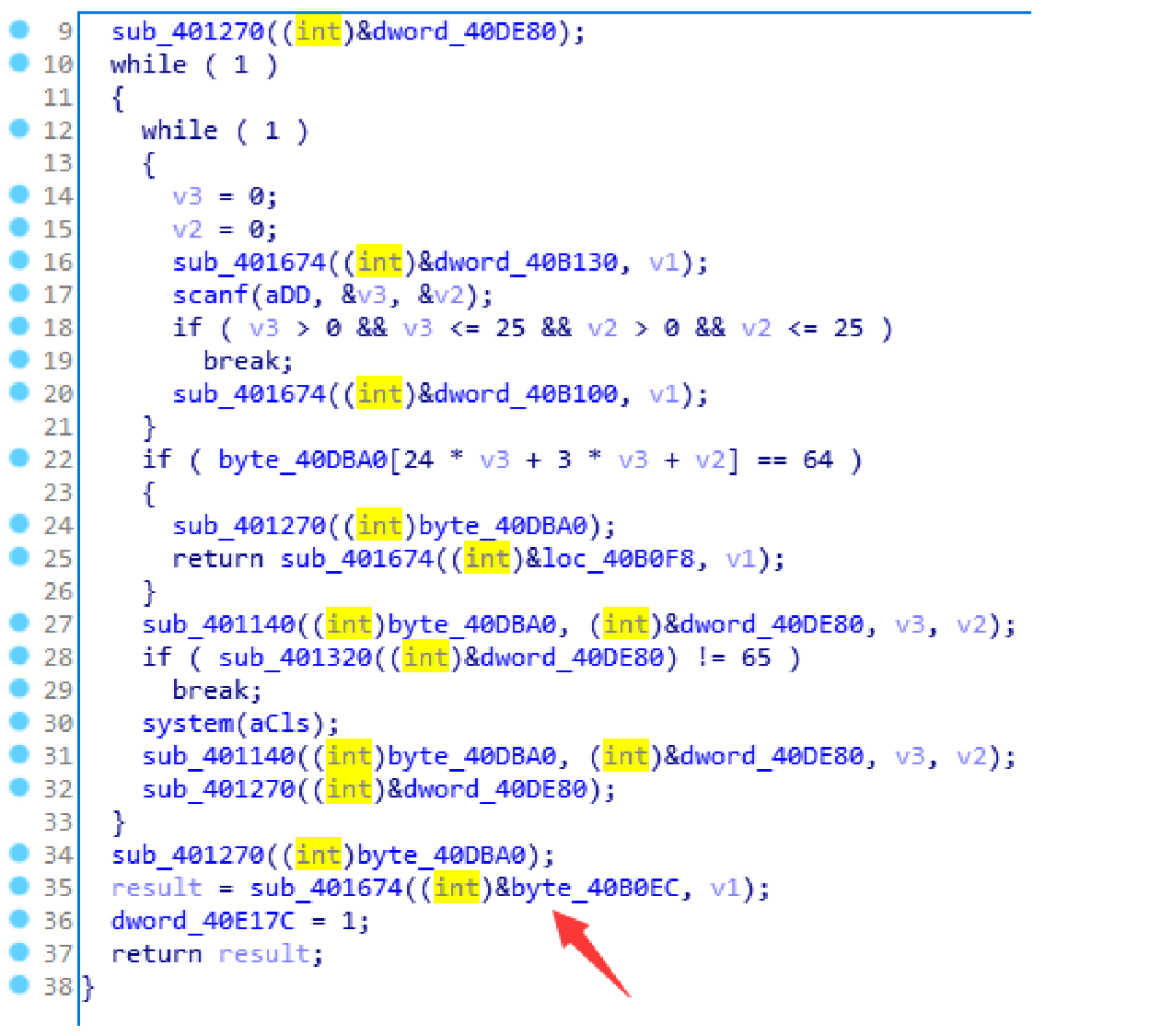
找到调用的地方:

可以看出是一个条件分支,将上面的jz改成jnz保存再执行程序即可得到flag:moectf{G00d_Min3_5w3eper}
#EasyRe
题目描述:You can decode the string or AntiAntiDebug(: Enjoy it~
打开题目,无壳ELF文件,拖入IDA,找到mian函数,
__int64 __fastcall main(__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3) { __int64 v4; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-30h] __int64 v5; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-28h] __int64 v6; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-20h] int v7; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-18h] __int16 v8; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-14h] char v9; // [rsp+2Eh] [rbp-12h] int v10; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h] int v11; // [rsp+3Ch] [rbp-4h] v11 = 0; sub_4011E0(); v10 = 1; v4 = 0x3A362B392E282274LL; v5 = 0x9123F393E123A7DLL; v6 = 0x3E7C127E297D2E79LL; v7 = 0x3E792812; v8 = 12340; v9 = 0x4D; printf(&byte_4040B0); sub_401270(&v4); sub_4012A0(); return 0LL; }
进入
__int64 sub_401360() { bool v0; // ST3B_1 bool v1; // ST2F_1 bool v2; // ST23_1 bool v3; // ST17_1 __int64 result; // rax bool v5; // ST0B_1 unsigned int v6; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-34h] unsigned int v7; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-28h] unsigned int v8; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-1Ch] unsigned int v9; // [rsp+2Ch] [rbp-10h] unsigned int v10; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-4h] v10 = 0; do { *(&format + (signed int)v10) ^= 0x1Au; v0 = v10++ < 0x1D; } while ( v0 ); v9 = 0; do { *(&byte_40406E + (signed int)v9) ^= 0x17u; v1 = v9++ < 2; } while ( v1 ); v8 = 0; do { byte_404080[v8] ^= 0x4Du; v2 = v8++ < 0x1E; } while ( v2 ); v7 = 0; do { *(&byte_40409F + (signed int)v7) ^= 0x1Au; v3 = v7++ < 4; } while ( v3 ); v6 = 0; do { *(&byte_4040B0 + (signed int)v6) ^= 0xBEu; result = v6 - 23; v5 = v6++ < 0x17; } while ( v5 ); return result; }
逐个追踪,发现byte_404080中存储的数据和主函数的相同,于是写exp实现一下,
#include <iostream> using namespace std; /* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */ typedef unsigned char Byte; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int v8=0; long long int a=0x3A362B392E282274LL; char t; do { t=(char)(*((Byte *)&a+v8)^0x4D); cout<<t; }while(v8++<7); return 0; }
跑出:9oectf{w0w_str_D4c0d3_1s_e4sy},把9改成m,得到flag.
补充:在unsigned char 为1个字节长度,unsigned int 为4个字节,在我的电脑中long long int是8个字节长度来储存整型,本题中以字节(两个十六进制数位)为单位逐个亦或,且exp中最多八个字节长度,否则数值溢出。
注:以上带有#标记的为赛后复现,tcl,tcl......



