[网络流24题] 最长k可重区间集
https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/3358
以区间(1,5),(2,6),(7,8)为例
建模方法一:
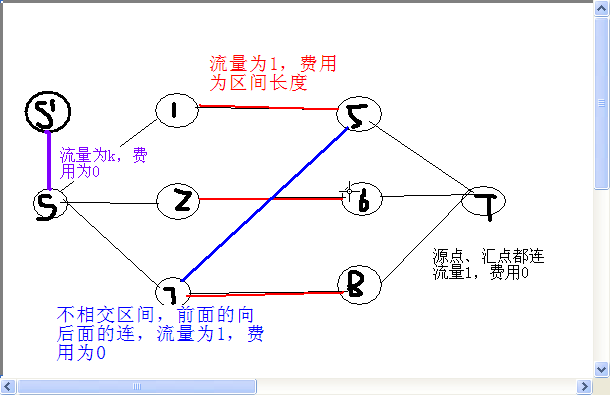
建模方法二:
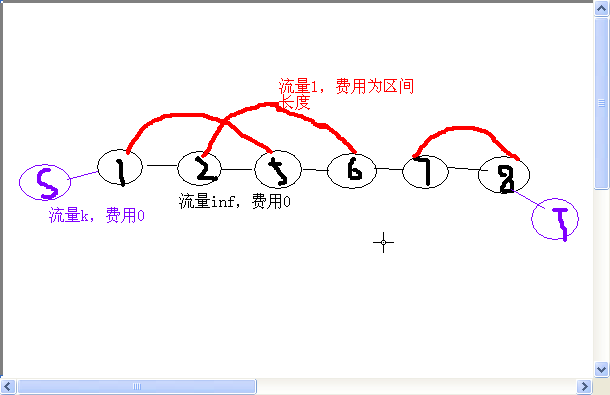
离散化区间端点
相当于找k条费用最大的不相交路径
#include<queue> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #define N 1011 #define M 3011 typedef long long LL; int h[N]; struct node { int l,r; }e[501]; int src,decc; int front[N],to[M<<1],nxt[M<<1],from[M<<1],cnt=1; int cap[M<<1]; LL cost[M<<1]; LL dis[N]; int path[N]; bool vis[N]; void read(int &x) { x=0; char c=getchar(); while(!isdigit(c)) c=getchar(); while(isdigit(c)) { x=x*10+c-'0'; c=getchar(); } } void add(int u,int v,int w,int val) { to[++cnt]=v; nxt[cnt]=front[u]; front[u]=cnt; from[cnt]=u; cap[cnt]=w; cost[cnt]=val; to[++cnt]=u; nxt[cnt]=front[v]; front[v]=cnt; from[cnt]=v; cap[cnt]=0; cost[cnt]=-val; } bool spfa() { queue<int>q; memset(dis,128,sizeof(dis)); dis[src]=0; vis[src]=true; q.push(src); int now; while(!q.empty()) { now=q.front(); q.pop(); vis[now]=false; for(int i=front[now];i;i=nxt[i]) { if(cap[i]>0 && dis[to[i]]<dis[now]+cost[i]) { dis[to[i]]=dis[now]+cost[i]; path[to[i]]=i; if(!vis[to[i]]) { q.push(to[i]); vis[to[i]]=true; } } } } return dis[decc]>0; } int main() { freopen("interv.in","r",stdin); freopen("interv.out","w",stdout); int n,k; read(n); read(k); int tot=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) { read(e[i].l); read(e[i].r); if(e[i].l>e[i].r) swap(e[i].l,e[i].r); h[++tot]=e[i].l; h[++tot]=e[i].r; } sort(h+1,h+tot+1); tot=unique(h+1,h+tot+1)-h-1; for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) { e[i].l=lower_bound(h+1,h+tot+1,e[i].l)-h; e[i].r=lower_bound(h+1,h+tot+1,e[i].r)-h; } for(int i=1;i<tot;++i) add(i,i+1,1e9,0); decc=tot+1; add(src,1,k,0); add(tot,decc,k,0); for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) add(e[i].l,e[i].r,1,h[e[i].r]-h[e[i].l]); LL ans=0; int now,j; while(spfa()) { ans+=dis[decc]; now=decc; while(now!=src) { j=path[now]; cap[j]--; cap[j^1]++; now=from[path[now]]; } } cout<<ans; }
题目描述

对于给定的开区间集合 I 和正整数 k,计算开区间集合 I 的最长 k可重区间集的长度。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
的第 1 行有 2 个正整数 n和 k,分别表示开区间的个数和开区间的可重迭数。接下来的 n行,每行有 2 个整数,表示开区间的左右端点坐标。
输出格式:
将计算出的最长 k可重区间集的长度输出
输入输出样例
说明
对于100%的数据,1\le n\le 5001≤n≤500,1\le k\le 31≤k≤3


