设计模式——从HttpServletRequestWrapper了解装饰者模式
从一个业务开始
最近项目上紧急需要,为了应付一个不知道啥的安全检测,我们要给系统追加防XSS注入的功能,这里有经验的JavaWeb开发就会想到,用过滤器或者基于项目框架的拦截器来做,但是顺着这个思路下去,我们会发现一个很尴尬的问题,如果我们在过滤器里把Request对象的参数拿处理校验(即表明使用了Reuqest的参数),那么后续的过滤器或者Controller都将得到一个“失效”的Request对象,后面的逻辑全线垮掉……
于是,爱好学习的你就去了某度,某度经过检索,给了你一个页面……,又经过重重查询和阅读,你终于有了解决方案:
我们可以利用HttpServletRequestWrapper包装HttpServletRequest,在Wrapper中实现参数的修改,然后用HttpServletRequestWrapper替换HttpServletRequest,这样就实现了参数的修改设置。
这时候,喜欢刨根问底的你,就想看看这个HttpServletRequestWrapper究竟是什么,于是好奇之旅开始。
HttpServletRequestWrapper源码
说白了HttpServletRequestWrapper是HttpServletRequest装饰类,什么是装饰类,我们后面再说,这一节里,先来看看它的落地实现,也就是源码。
整体关系
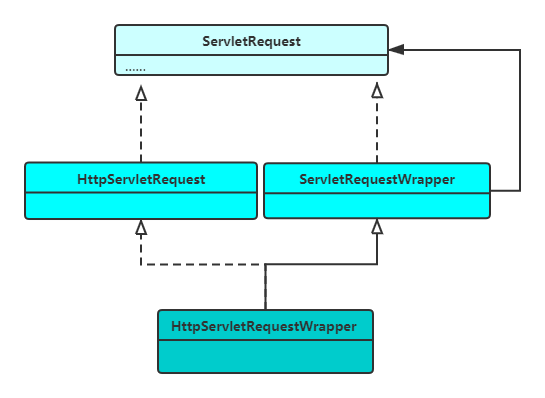
这里我就先说结论吧:
- HttpServletRequestWrapper继承了ServletRequestWrapper,实现了HttpServletRequest接口;
- ServletRequestWrapper和HttpServletRequest都实现了ServletRequest接口;
- ServletRequestWrapper是对ServletRequest的包装;
- HttpServletRequestWrapper是对HttpServletRequest的包装;
实际的继承关系如下图:
ServletRequestWrapper的源码:
package javax.servlet; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; /** * ServletRequestWrapper提供了一个简便实现类,在对ServletRequest有改动需求的时,可以重写此类,之后Request的操作都会经过重写的类. */ public class ServletRequestWrapper implements ServletRequest { /** * ServletRequestWrapper持有ServletRequest的实例. */ private ServletRequest request; /** * 构建ServletRequestWrapper,传入ServletRequest的值. */ public ServletRequestWrapper(ServletRequest request) { if (request == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Request cannot be null"); } this.request = request; } /** * 获取ServletRequest实例. */ public ServletRequest getRequest() { return this.request; } /** * 设置ServletRequest实例. * @param request ServletRequest. */ public void setRequest(ServletRequest request) { if (request == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Request cannot be null"); } this.request = request; } /** * 获取Servlet的属性. */ public Object getAttribute(String name) { return this.request.getAttribute(name); } /** * 获取所有属性枚举格式. */ public Enumeration getAttributeNames() { return this.request.getAttributeNames(); } /** * 返回请求中输入内容的字符编码类型,如果没有定义字符编码类型就返回空值. * @return 字符编码. */ public String getCharacterEncoding() { return this.request.getCharacterEncoding(); } /** * 设置输入内容的字符编码类型. * @param env 字符编码类型. * @throws java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException . */ public void setCharacterEncoding(String enc) throws java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException { this.request.setCharacterEncoding(enc); } /** * 请求内容的长度,如果长度未知就返回-1. * @return 请求内容长度. */ public int getContentLength() { return this.request.getContentLength(); } /** * 返回请求数据体的MIME类型CONTENT-TYPE,如果类型未知返回空值. * @return */ public String getContentType() { return this.request.getContentType(); } /** * 返回一个输入流,使用该输入流以二进制方式读取请求正文的内容. * javax.servlet.ServletInputStream是一个抽象类,继承自InputStream. * @return . * @throws IOException . */ public ServletInputStream getInputStream() throws IOException { return this.request.getInputStream(); } /** * 根据指定参数名获取参数值. * @param name 参数名. * @return 参数值. */ public String getParameter(String name) { return this.request.getParameter(name); } /** * 获取参数的Map形式,包括所有参数. * @return 参数Map. */ public Map getParameterMap() { return this.request.getParameterMap(); } /** * 获取所有参数名的枚举. * @return 参数名枚举. */ public Enumeration getParameterNames() { return this.request.getParameterNames(); } /** * 根据指定属性名获取参数值数组. * @param name 参数名. * @return 参数值数组. */ public String[] getParameterValues(String name) { return this.request.getParameterValues(name); } /** * 返回请求使用的协议信息.格式为:协议/主版本号.次版本号.例如:http/1.0. * @return */ public String getProtocol() { return this.request.getProtocol(); } /** * 返回请求所使用的URL的模式.若http、https等. * @return 模式. */ public String getScheme() { return this.request.getScheme(); } /** * 返回请求发送到的服务器的主机名. * @return 主机名. */ public String getServerName() { return this.request.getServerName(); } /** * 返回请求发送到的服务器的端口号. * @return 端口号. */ public int getServerPort() { return this.request.getServerPort(); } /** * 返回BufferedReader对象,以字节数据方式读取请求正文. * @return . * @throws IOException . */ public BufferedReader getReader() throws IOException { return this.request.getReader(); } /** * 返回发送请求的客户端或最后一个代理服务器的IP地址. * @return IP地址. */ public String getRemoteAddr() { return this.request.getRemoteAddr(); } /** * 返回发送请求的客户端或最后一个代理服务器的主机名. * @return 主机名. */ public String getRemoteHost() { return this.request.getRemoteHost(); } /** * 根据传递的属性名和属性值设置Request属性. * @param name 属性名. * @param o 属性值. */ public void setAttribute(String name, Object o) { this.request.setAttribute(name, o); } /** * 从Request中删除指定的属性名对应的值.一般使用此方法. * @param name 属性名. */ public void removeAttribute(String name) { this.request.removeAttribute(name); } /** * 根据客户端传递的Accept-Language对应的区域设置. * 若客户端未指定Accept-Language,则返回服务器默认语言环境. * @return */ public Locale getLocale() { return this.request.getLocale(); } /** * 返回Locale对象的枚举,从首选区域开始按降序返回基于Accept-Language头的客户端可接受的区域. * 如果客户机请求不提供Accept-Language头,此方法返回包含一个Locale的枚举,即是服务器默认语言环境对应的Locale. * @return */ public Enumeration getLocales() { return this.request.getLocales(); } /** * 指示是否使用安全通道(如HTTPS)发出此请求. */ public boolean isSecure() { return this.request.isSecure(); } /** * 返回RequestDispatcher对象,作为path所定位的资源的封装. * RequestDispatcher用于服务器请求转发. * @param path 相对路径或绝对路径. * @return RequestDispatcher. */ public RequestDispatcher getRequestDispatcher(String path) { return this.request.getRequestDispatcher(path); } /** * @deprecated * Servlet API 2.1开始已不推荐使用此API. * 取得文件在服务器上的绝对路径. * @param path 相对路径. * @return 绝对路径. */ public String getRealPath(String path) { return this.request.getRealPath(path); } /** * 返回发送请求的客户端或者最后一个代理服务器的IP源端口, 这个方法是在Servlet 2.4规范中新增的方法. * @return 端口号. */ public int getRemotePort() { return this.request.getRemotePort(); } /** * 返回接收到请求的IP接口的主机名,这个方法是在Servlet 2.4规范中新增的方法. * @return 主机名. */ public String getLocalName() { return this.request.getLocalName(); } /** * 返回接收到请求的网络接口的IP地址,这个方法是在Servlet 2.4规范中新增的方法. * @return IP地址. */ public String getLocalAddr() { return this.request.getLocalAddr(); } /** * 返回接收到请求的网络接口的IP端口号,这个方法是在Servlet 2.4规范中新增的方法. * @return 端口号. */ public int getLocalPort() { return this.request.getLocalPort(); } }
HttpServletRequestWrapper的源码:
package javax.servlet.http; import javax.servlet.ServletRequestWrapper; import java.util.Enumeration; /** * HttpServletRequestWrapper提供了一个简便实现不了,在对HttpServletRequest有改动需求的时,可以重写此类,之后Request的操作都会经过重写的类. */ public class HttpServletRequestWrapper extends ServletRequestWrapper implements HttpServletRequest { /** * Constructs. */ public HttpServletRequestWrapper(HttpServletRequest request) { super(request); } /** * 获取HttpServletRequest. * @return HttpServletRequest. */ private HttpServletRequest _getHttpServletRequest() { return (HttpServletRequest) super.getRequest(); } /** * 返回认证类型. * 所有Servlet容器都支持basic、form、client_cert,digest不一定支持. * 若不支持,则返回null. */ public String getAuthType() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getAuthType(); } /** * 获取请求中带有的Cookie信息. */ public Cookie[] getCookies() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getCookies(); } /** * 以长整数形式返回一个特定的请求头,该长整数代表一个Date对象. * 该方法可以用在包含时间信息的header中,如:If-Modified-Since. * @param name 头名称. * @return 头值. */ public long getDateHeader(String name) { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getDateHeader(name); } /** * 根据指定的头名称获取头的值. * 若存在多个,则返回第一个. * @param name 头名称. * @return 头值. */ public String getHeader(String name) { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getHeader(name); } /** * 根据指定的头名称获取头值的枚举. * 若没有找到,则返回空的枚举. * @param name 头名称. * @return 头值. */ public Enumeration getHeaders(String name) { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getHeaders(name); } /** * 获取所有的头的枚举. * @return 头的枚举. */ public Enumeration getHeaderNames() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getHeaderNames(); } /** * 根据指定头名称获取int类型的值.若未找到则返回-1,如不是int类型,则会抛出NumberFormatException异常. * @param name 头名称. * @return 头值. */ public int getIntHeader(String name) { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getIntHeader(name); } /** * 获取HTTP方法,如:GET、POST、PUT等. * @return 方法名. */ public String getMethod() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getMethod(); } /** * 官网解释: * 返回与客户端发出此请求时发送的URL相关联的任何额外路径信息. * 额外的路径信息跟随servlet路径,但位于查询字符串之前,并以"/"字符开头. * 例如:url-pattern配置为/demo/*,请求URL为http://localhost/Pro/demo/htm/index.html,则pathInfo为/htm/index.html. * @return */ public String getPathInfo() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getPathInfo(); } /** * 返回servlet名称之后、 * 查询字符串之前的任何额外路径信息,并将其转换为实际路径. * 与转换的CGI变量PATH U的值相同 * @return */ public String getPathTranslated() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getPathTranslated(); } /** * 返回项目根路径. * 例如:url-pattern配置为/demo/*,请求URL为http://localhost/Pro/demo/htm/index.html,则contextPath为/demo. * @return 项目根路径. */ public String getContextPath() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getContextPath(); } /** * 获得请求中的查询字符串,例如a=1&b=2这样的格式. * @return 查询字符串. */ public String getQueryString() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getQueryString(); } /** * 如果用户已经过验证,则返回发出此请求的用户的登录信息,如果用户未经过验证,则返回 null. * 用户名是否随每个后续请求发送取决于浏览器和验证类型,返回的值与 CGI变量REMOTE_USER的值相同. * @return 用户信息. */ public String getRemoteUser() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getRemoteUser(); } /** * 返回一个 boolean值,指示指定的逻辑"角色"中是否包含经过验证的用户. * 角色和角色成员关系可使用部署描述符定义. * 如果用户没有经过验证,则该方法返回 false. * @param role 角色. * @return 已验证用户是否属于某种角色. */ public boolean isUserInRole(String role) { return this._getHttpServletRequest().isUserInRole(role); } /** * 返回包含当前已经过验证的用户的名称的 java.security.Principal对象. * 如果用户没有经过验证,则该方法返回 null. * @return java.security.Principal或null. */ public java.security.Principal getUserPrincipal() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getUserPrincipal(); } /** * 获取请求对应的sessionId. * @return sessionId.会话ID. */ public String getRequestedSessionId() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getRequestedSessionId(); } /** * 请求URL的相对地址,包括服务器路径,不包括查询参数. * @return 请求URL的相对地址. */ public String getRequestURI() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getRequestURI(); } /** * 请求的URL地址,包含协议、主机名、端口和服务器路径,但是不包括查询参数. * @return 请求URL地址. */ public StringBuffer getRequestURL() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getRequestURL(); } /** * 官方解释: * 返回此请求的URL中调用servlet的部分. * 此路径以"/"字符开头,包含servlet名称或到servlet的路径,但不包含任何额外的路径信息或查询字符串. * 与CGI变量SCRIPT_NAME的值相同. * 其实真是的意思就是,在配置webx.xml或编程式配置时,配置了url-pattern,请求的URL与url-pattern的有效部分重合部分就是servletPath, * 也可以理解为url-pattern的有效部分就是servletPath. * 例如:url-pattern配置为/demo/*,请求URL为http://localhost/Pro/demo/htm/index.html,则servletPath为/demo. * @return */ public String getServletPath() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getServletPath(); } /** * 获得请求对应的当前sesson. * 在没有session的情况下: * 若create=true,则新创建一个session. * 若create=false,则不创建session,返回null. * @param create session失效的情况下,是否创建session. * @return HttpSession实例. */ public HttpSession getSession(boolean create) { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getSession(create); } /** * 获得请求对应的当前sesson. * 若没有session,则创建一个session. * @return HttpSession实例. */ public HttpSession getSession() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().getSession(); } /** * 返回session是否有效. * @return session是否有效. */ public boolean isRequestedSessionIdValid() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().isRequestedSessionIdValid(); } /** * sessionId是否从Cookie中获得. * @return 若是从Cookie中获得,返回true,否则返回false. */ public boolean isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().isRequestedSessionIdFromCookie(); } /** * sessionId是否从URL中获得. * @return 若是从URL中获得,返回true,否则返回false. */ public boolean isRequestedSessionIdFromURL() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().isRequestedSessionIdFromURL(); } /** * @deprecated * sessionId是否从URL中获得. * @return 若是从URL中获得,返回true,否则返回false. */ public boolean isRequestedSessionIdFromUrl() { return this._getHttpServletRequest().isRequestedSessionIdFromUrl(); } }
其实查看源码后会发现,ServletRequestWrapper和HttpServletRequestWrapper提供的API完全调用的ServletRequest和HttpServletRequest的API进行实现。在我们进行应用时,使用HttpServletRequestWrapper即可,它同时拥有ServletRequestWrapper和HttpServletRequestWrapper的功能。
装饰者模式
我们来分析一下,HttpServletRequestWrapper的实现流程,首先,所有的源头,都是ServletRequest这个接口,这个接口其实就是定义来请求功能的;然后HttpServletRequest实现了ServletRequest,它的对象就是我们在Filter常用的Request,ServletRequestWrapper也实现了ServletRequest这个接口,同时它内部又引用了ServletRequest作为成员变量,它和HttpServletRequest就有同样了API,属于同一层级,这时候,HttpServletRequestWrapper继承了ServletRequestWrapper同时实现了HttpServletRequest,也就是集两家之长,又能代替两家,所以可以满足我们一开始的场景需求(替换掉HttpServletRequest对象)。
以上这段分析描述,也就是装饰模式的实现思路,下面开始介绍一下何为装饰模式。
装饰模式的定义与特点
装饰(Decorator)模式的定义:指在不改变现有对象结构的情况下,动态地给该对象增加一些职责(即增加其额外功能)的模式,它属于对象结构型模式。
装饰(Decorator)模式的主要优点有:
-
- 装饰器是继承的有力补充,比继承灵活,在不改变原有对象的情况下,动态的给一个对象扩展功能,即插即用
- 通过使用不用装饰类及这些装饰类的排列组合,可以实现不同效果
- 装饰器模式完全遵守开闭原则
其主要缺点是:装饰模式会增加许多子类,过度使用会增加程序得复杂性。
装饰模式的结构与实现
通常情况下,扩展一个类的功能会使用继承方式来实现。但继承具有静态特征,耦合度高,并且随着扩展功能的增多,子类会很膨胀。如果使用组合关系来创建一个包装对象(即装饰对象)来包裹真实对象,并在保持真实对象的类结构不变的前提下,为其提供额外的功能,这就是装饰模式的目标。下面来分析其基本结构和实现方法。
模式的结构
装饰模式主要包含以下角色。
- 抽象构件(Component)角色:定义一个抽象接口以规范准备接收附加责任的对象。
- 具体构件(ConcreteComponent)角色:实现抽象构件,通过装饰角色为其添加一些职责。
- 抽象装饰(Decorator)角色:继承抽象构件,并包含具体构件的实例,可以通过其子类扩展具体构件的功能。
- 具体装饰(ConcreteDecorator)角色:实现抽象装饰的相关方法,并给具体构件对象添加附加的责任。
模板的UML实现关系为:
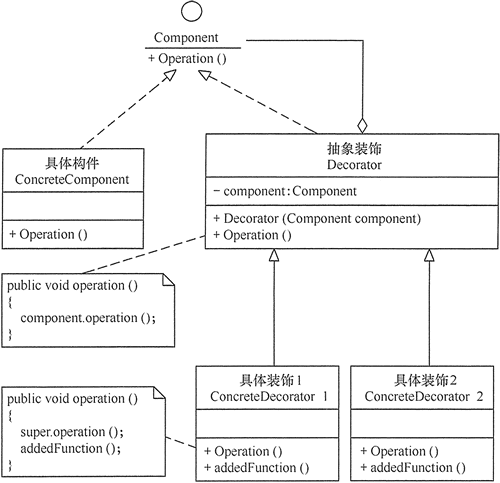
细品之后,是不是发现这个UML和HttpServletRequestWrapper那个很相似 !!!!!其实ServletRequest充当了这里抽象构件的角色,ServletRequestWrapper冲到了抽象装饰的角色,而HttpServletRequest就是具体构件的位置。
下面看一个简单的装饰者实现例子:
package decorator; public class DecoratorPattern { public static void main(String[] args) { Component p = new ConcreteComponent(); p.operation(); System.out.println("---------------------------------"); Component d = new ConcreteDecorator(p); d.operation(); } } //抽象构件角色 interface Component { public void operation(); } //具体构件角色 class ConcreteComponent implements Component { public ConcreteComponent() { System.out.println("创建具体构件角色"); } public void operation() { System.out.println("调用具体构件角色的方法operation()"); } } //抽象装饰角色 class Decorator implements Component { private Component component; public Decorator(Component component) { this.component = component; } public void operation() { component.operation(); } } //具体装饰角色 class ConcreteDecorator extends Decorator { public ConcreteDecorator(Component component) { super(component); } public void operation() { super.operation(); addedFunction(); } public void addedFunction() { System.out.println("为具体构件角色增加额外的功能addedFunction()"); } }
装饰模式的应用场景
前面讲解了关于装饰模式的结构与特点,下面介绍其适用的应用场景,装饰模式通常在以下几种情况使用。
-
- 当需要给一个现有类添加附加职责,而又不能采用生成子类的方法进行扩充时。例如,该类被隐藏或者该类是终极类或者采用继承方式会产生大量的子类。
- 当需要通过对现有的一组基本功能进行排列组合而产生非常多的功能时,采用继承关系很难实现,而采用装饰模式却很好实现。
- 当对象的功能要求可以动态地添加,也可以再动态地撤销时。
装饰模式在Java中的最著名的应用莫过于 Java I/O 标准库的设计了。例如,InputStream 的子类 FilterInputStream,OutputStream 的子类 FilterOutputStream,Reader 的子类 BufferedReader 以及 FilterReader,还有 Writer 的子类 BufferedWriter、FilterWriter 以及 PrintWriter 等,它们都是抽象装饰类。
下面代码是为 FileReader 增加缓冲区而采用的装饰类 BufferedReader 的例子:
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("filename.txt")); String s = in.readLine();
装饰模式的扩展
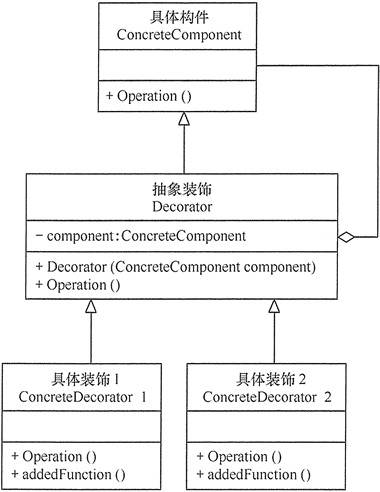
(1) 如果只有一个具体构件而没有抽象构件时,可以让抽象装饰继承具体构件,其结构图如图
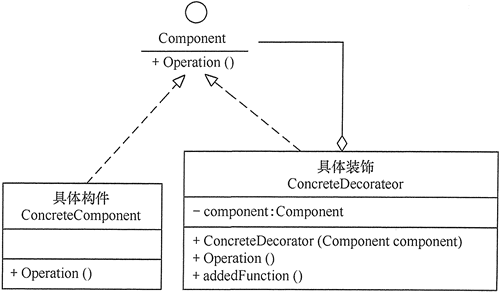
(2) 如果只有一个具体装饰时,可以将抽象装饰和具体装饰合并,其结构图如图
该类型文章目录:设计模式汇总



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号