利用TensorFlow识别手写的数字---基于两层卷积网络
1 为什么使用卷积神经网络
Softmax回归是一个比较简单的模型,预测的准确率在91%左右,而使用卷积神经网络将预测的准确率提高到99%。
2 卷积网络的流程
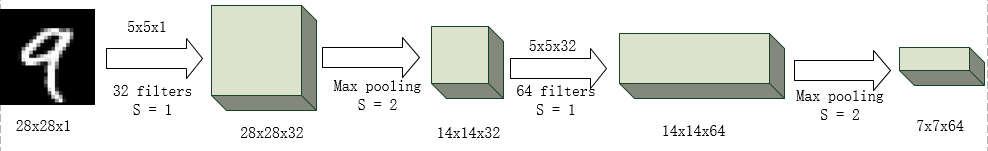
3 代码展示
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#读入数据
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot=True)
#x为训练图像的占位符,y_为训练图像标签的占位符
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
#将单张图片从784维向量重新还原为28*28的矩阵图片
x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) #-1 表示任意的数,由实际输入的图像个数决定
# 定义卷积过程中用到的函数
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1) #产生正太分布
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x,w):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x,w,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME")
# 第一层卷积
w_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image,w_conv1)+b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
# 第二层卷积
w_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1,w_conv2)+b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
# 第一层全连接层,输出1024维的向量
w_fc1 = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2,[-1,7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat,w_fc1)+b_fc1)
#使用Dropout ,keep_prob 是一个占位符,训练是0.5,测试时为1
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1,keep_prob)
# 第二层全连接层,输出1024维的向量
w_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop,w_fc2)+b_fc2
# 不采用先softmax再计算交叉熵的办法
#采用tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits直接计算
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_,logits=y_conv))
#定义train_step
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
#定义准确率
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1),tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
# 训练
# 创建Session,对变量初始化
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#训练2000步
for i in range(2000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
# 每一百步报告一次在验证集上的准确率
if i % 100 == 0 :
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:batch[0],y_:batch[1],keep_prob:1})
print("step %d,training accuracy %g" % (i,train_accuracy))
train_step.run(feed_dict={x:batch[0],y_:batch[1],keep_prob:0.5})
# 训练结束后报告在测试集上的准确率
print("test_accuracy %g" % accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y_:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0}))
4 补充
步长stride是一个一维的向量,长度为4。形式是[a,x,y,z],分别代表[batch滑动步长,水平滑动步长,垂直滑动步长,通道滑动步长]。在tensorflow中,stride的一般形式是[1,x,y,1]
- 第一个1表示:在batch维度上的滑动步长为1,即不跳过任何一个样本
- x表示:卷积核的水平滑动步长
- y表示:卷积核的垂直滑动步长
- 最后一个1表示:在通道维度上的滑动步长为1,即不跳过任何一个颜色通道


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号