Android 小项目之--数据存储【Files】(附源码)
2010-06-20 11:34 Terry_龙 阅读(3631) 评论(5) 编辑 收藏 举报继上篇数据存储,现在我们来讲讲另外一种数据存储,Files。本篇讲述步骤如下:
- 1、温故而知新,复习四种数据存储的区别。
- 2、什么是 Files 数据存储。
- 3、什么是 Properties ?
- 4、Properties 重要方法和属性讲解。
- 5、模拟用户设置参数。
- 6、查看 Files 产生的文件。
1、温故而知新,复习四种数据存储的区别
Android 总共有4种数据存储方式,具体解释和列表如下:
- Shared Preferences
用来存储“键-值”对的格式数据。是一个轻量级的键值对存储机制,只可以存储基本数据类型。
你可以参考上篇文章了解和使用它的用法:Android 小项目之--数据存储【Shared Preferences】(附源码) - Files
它通过 FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 对文件进行操作。本篇将讲述如何使用Files 数据存储。 - SQLite
Android 提供的一个标准数据库,支持SQL语句。
你可以参考这篇文章大致了解和使用它的用法:Android 小项目之--SQLite 使用法门 (附源码) - NetWork
通过网络来存储和获得数据。
2、什么是 Files 数据存储
- File 就是把需要保存的东西通过文件的形式讯录下来,当需要这些数据时,通过读取这个文件来获取这些数据。因为 Android 采用了 Linux 核心,所以在Android 系统中,文件也是Linux 的形式。
- Android 中可以在设备本身的的存储或者外接的存储设备中创建用于保存数据的文件。同时,在默认状态下,文件是不能在不同的程序间共享的。
3、什么是 Properties ?
Properties(属性),可以把Properties继承自Hashtable,理解成一个Hashtable ,不过唯一不同的是,Properties对应的“键-值”必须是字符串形式的数据类型。Files 数据存储主要是使用 Properties 配合 FileInputStream或者FileOutputStream对文件写入操作。
4、Properties 重要方法和属性讲解
公用方法:
- 返回值:String
方法:getProperty(String name, String defaultValue)
解释:通过指定的 “name“ 即Key,搜索属性,参数二为默认值,即通过Key找不到文件中的属性时,要返回的默认值。 - 返回值:String
方法:getProperty(String name)
解释:通过指定的 ”name“ 即为 Key,搜索属性,没有返回默认值。 - 无返回值:void
方法:list(PrintStream out)
解释:通过PrintStream 列出可读的属性列表 - 无返回值:void
方法:list(PrintWriter writer)
解释:通过PrintStream 列出可写的属性列表 - 无返回值:synchronized void
方法:load(InputStream in)
解释:从指定的 ”inputStream “ 即输出流,加载properties - 无返回值:synchronized void
方法:loadFromXML(InputStream in)
解释:从指定的 "InputStream" 即输出流,加载一个以XML形式的 Properties - 返回值:Enumeration<?>
方法:propertyNames()
解释:返回所有包含在文件里面的属性名称 - 无返回值:void
方法:save(OutputStream out, String comment)
解释:注意,这种保存方法己经过时,Google 不推荐使用此种写法,这种方法忽略任何IO 异常,所以在实际操作过程中,可能会发生不必要的异常。 - 返回值:object
方法:setProperty(String name, String value)
解释:设置属性,保存一个”键-值“对的属性。 - 无返回值:synchronized void
方法:store(OutputStream out, String comment)
解释:通过 FileOutputStream 打开对应的程序文件,然后通过Store 保存之前 Properties 打包好的数据。这里备注可以为空。 - 无返回值:void
方法:storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment)
解释:通过FileOutputStream 打开对应的程序文件,将打包好的数据写入到XML文件。 - 无返回值:synchronized void
方法:storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment, String encoding)
解释:通过FileOutputStream 打开对应的程序文件,将打包好的数据写入到XML文件,第三个参数可以指定编码。
5、模拟用户设置参数
本篇还是以上篇例子为基础,还是以保存音乐播放状态来对Properties的使用进行大概的了解。本例中,实现了load方法,即加载用户之前保存的属性文件,然后通过获取对应的KEY值为状态赋值。此外还有一个save方法用来保存用户退出程序时的播放状态。
load方法代码如下:
 本篇Load方法代码参考
本篇Load方法代码参考
{
Properties properties=new Properties();
try {
FileInputStream stream =this.openFileInput("music.cfg");
properties.load(stream);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return;
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
return;
}
isplay=Boolean.valueOf(properties.get("isplay").toString());
}
注意:
- 1、 properties.load方法如果遇到错误将抛出 IOException 异常,并且使用的编码为:ISO8859 - 1
- 2、加载的数据出现空格将会被忽略。
- 3、不要在你的Files 文件中加注释 ,因为load的时候将会忽略你的注释符号。
- 4、公认的转义序列:“\”,“\ \”,“\ r”开始,“\ ñ”,“\!”,“\#”,“\ t”的,“\ b”与“\ f”的,和“\ uXXXX”(Unicode字符)。
save方法代码参考:
 Save 方法代码参考
Save 方法代码参考
{
Properties properties =new Properties();
properties.put("isplay", String.valueOf(isplay));
try {
FileOutputStream stream=this.openFileOutput("music.cfg", Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE);
properties.store(stream, "");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return false;
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return false;
}
return true;
}
注意:
- 1、 properties.store方法如果出现错误将会抛出IOException异常。
- 2、properties 的KEY和value必须为 String 类型,如果不是String 类型将会抛出ClassCastException异常,请注意这点。
本篇全部代码参考如下:
 Files 文件操作代码参考
Files 文件操作代码参考
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.KeyEvent;
import android.widget.CheckBox;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener;
public class sharedPreActivity extends Activity {
private TextView myTextView;
private CheckBox myBox;
private playMusic PLAYER=null;
private boolean isplay=false;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
myTextView=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.TextView01);
myBox=(CheckBox)findViewById(R.id.CheckBox01);
PLAYER=new playMusic(this);
/*
* 文件创建模式:Activity.MODE_APPEND
* 如果该文件已经存在,然后将数据写入,而不是抹掉它现有文件的末尾。
*/
/*
* 文件创建模式:MODE_PRIVATE
* 默认模式,在那里创建的文件只能由应用程序调用,即为私有的
*/
/*
* 文件创建模式:Activity.MODE_WORLD_READABLE
* 允许所有其他应用程序有读取和创建文件的权限。
*/
/*
* 文件创建模式:Activity.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE
* 允许所有其他应用程序具有写入、访问和创建的文件权限。
*/
/*
* SharedPreferences---数据存储之获取
SharedPreferences settings=getPreferences(Activity.MODE_PRIVATE);
isplay=settings.getBoolean("isplay", false); //通过key值找到value,如果不存在即返回false
*/
load();
myBox.setChecked(isplay);
if(isplay){
myTextView.setText("当前音乐的播放状态:开");
isplay=true;
PLAYER.Play();
}
else{
myTextView.setText("当前音乐的播放状态:关");
}
myBox.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(isChecked)
{
myTextView.setText("当前音乐的播放状态:开");
isplay=true;
PLAYER.Play();
}
else{
myTextView.setText("当前音乐的播放状态:关");
isplay=false;
PLAYER.FreeMusc();
}
}
});
}
@Override
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(keyCode==KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK){
/*
* SharedPreferences --数据存储之保存
SharedPreferences uiState=getPreferences(0);
SharedPreferences.Editor editor=uiState.edit();
editor.putBoolean("isplay", isplay);
editor.commit();
*/
save();
if(isplay)
{
PLAYER.FreeMusc();
}
this.finish();
return true;
}
return super.onKeyDown(keyCode, event);
}
void load()
{
Properties properties=new Properties();
try {
FileInputStream stream =this.openFileInput("music.cfg");
properties.load(stream);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return;
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
return;
}
isplay=Boolean.valueOf(properties.get("isplay").toString());
}
boolean save()
{
Properties properties =new Properties();
properties.put("isplay", String.valueOf(isplay));
try {
FileOutputStream stream=this.openFileOutput("music.cfg", Context.MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE);
properties.store(stream, "");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return false;
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO: handle exception
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
6、查看 Files 产生的文件
上篇preferences 存储数据时,文件保存在shared_prefs文件夹下,如果我们在 Files产生文件的时候没有为其指定绝对路径,那么系统就会在 shared_prefs 相同的目录中产生一个名为files 的文件夹,里面就有我们写入的数据。如图:

运行效果如下:
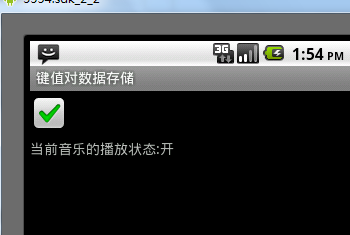
Tip:如果你需要用一个文件来加载初始化程序 ,可以事先在目录下res/raw/tempFile中建立一个静态文件,这样就可以通过Resources.openRawResource(R.raw.文件名)来返回一个文件流,直读读取文件。
就到这里。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架