题目:http://acm.timus.ru/problem.aspx?space=1&num=1748
题意:求n范围内约数个数最多的那个数。
Roughly speaking, for a number to be highly composite it has to have prime factors as small as possible, but not too many of the same. If we decompose a number n in prime factors like this:
where 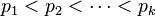 are prime, and the exponents
are prime, and the exponents  are positive integers, then the number of divisors of n is exactly
are positive integers, then the number of divisors of n is exactly
Hence, for n to be a highly composite number,
- the k given prime numbers pi must be precisely the first k prime numbers (2, 3, 5, ...); if not, we could replace one of the given primes by a smaller prime, and thus obtain a smaller number than n with the same number of divisors (for instance 10 = 2 × 5 may be replaced with 6 = 2 × 3; both have four divisors);
- the sequence of exponents must be non-increasing, that is
![c_1 \geq c_2 \geq \cdots \geq c_k]() ; otherwise, by exchanging two exponents we would again get a smaller number than n with the same number of divisors (for instance 18 = 21 × 32 may be replaced with 12 = 22 × 31; both have six divisors).
; otherwise, by exchanging two exponents we would again get a smaller number than n with the same number of divisors (for instance 18 = 21 × 32 may be replaced with 12 = 22 × 31; both have six divisors).
c++ 代码

#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; #define ll long long ll n, ansa, ansb; int p[] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47}; void dfs(int pos, ll num, int div, int limit ) { if ( div>ansb || (div==ansb && num<ansa) ){ ansa = num; ansb = div; } if (pos == 15) return ; for ( int i=1; i<=limit; ++i ) { if ( n/num < p[pos]) break; num *= p[pos]; dfs(pos+1, num, div*(i+1), i); } } int main(int argc, char**argv) { int T; scanf("%d", &T); while ( T-- ){ //scanf("%lld", &n); cin >> n; if (n==1) { puts("1 1"); continue; } ansa = ansb = -1; dfs(0, 1, 1, 60); //printf("%lld %lld\n", ansa, ansb); cout << ansa << ' ' << ansb << endl; } return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
python 代码 注意这代码会TLE,具体是什嘛原因,我没有具体查了。貌似测试10^18都很快的。
p= [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47] ansa=0; ansb=0 def dfs(pos, num, div, limit, n): global ansa, ansb if div>ansb or ( div==ansb and ansa>num ): ansa = num; ansb = div if pos == 15: return for i in xrange(1, limit+1): if (n/num) < p[pos] : return num *= p[pos] dfs(pos+1, num, div*(i+1), i, n) if __name__ == '__main__': T = input() while T: T -= 1 n = input() if n == 1: print 1, 1; continue ansa = ansb = -1 dfs(0, 1, 1, 60, n) print ansa, ansb
这种数有点类似与丑数,对于丑数的求法。
丑数:因子只含2,3,5的数。 例如求第n个丑数。
bruteforce 是有用的。效率太低了。
如果有一个丑数数组,那么这个数组接下来一个丑数会是哪个数呢?毫无疑问这个数是有数组里的元素乘上2,3,5里的某一个数,这个数满足大于当前丑数数组最后一个元素,最小的满足这个条件的数就是下一个丑数。即求min( 2*a, 3*b, 5*c ) ,枚举求2a,3b5c是可行的。但二分会是很不错的选择, 复杂度为o(n*3logn)。
def find(p, x): l = 0; r = len(p)-1 while l<=r: mid = (l+r)>>1 if x*p[mid]>p[-1]: r = mid-1 else : l = mid+1 return x*p[l] def solve(n): p=[1]; cnt = 0 # cnt while cnt < n: cnt += 1 a = find(p, 2) b = find(p, 3) c = find(p, 5) p.append(min(a, b, c) ) print p[-1] if __name__ == '__main__': n = input() solve(n)




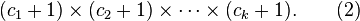
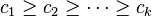 ; otherwise, by exchanging two exponents we would again get a smaller number than n with the same number of divisors (for instance 18 = 21 × 32 may be replaced with 12 = 22 × 31; both have six divisors).
; otherwise, by exchanging two exponents we would again get a smaller number than n with the same number of divisors (for instance 18 = 21 × 32 may be replaced with 12 = 22 × 31; both have six divisors).

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号