问题描述:给定一个迷宫,给定入口和出口,找到从入口到出口的一条路径(任何一条路径都可以),迷宫为0表示可走,为1表示墙。用1将迷宫围起来避免边界问题。
实现思路:1.DFS搜索(递归)
2.采用栈的数据结构
下面分别用这两种方法来解决这个问题。
DFS搜索(即递归+回溯)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define ROW 9
#define COL 9
int integer[ROW][COL]={
{1,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1},
{1,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,1},
{1,0,1,1,1,1,1,0,0},
{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1}
};
int print(int integer[ROW][COL],int x,int y);
int dir[4][2]={
{1,0},{-1,0},
{0,1},{0,-1},
} ;
int visted[120][120] ;
int check(int x,int y)
{
if(x< 0 || y<0 || x>= ROW || y>= COL)
return 0;
if(visted[x][y])
return 0;
if(integer[x][y] != 0 )
return 0;
return 1;
}
int dfs(int x,int y)
{
int xx,yy ,i ;
usleep(100000);
printf("\033c");
print(integer,x,y);
if(x == 7 && y == 8 )
exit(0);
for(i= 0;i< 4 ;i++)
{
xx = x + dir[i][0];
yy = y + dir[i][1];
if(check(xx,yy))
{
visted[xx][yy]= 1;
dfs(xx,yy) ;
visted[xx][yy] = 0 ;
}
}
usleep(100000);
printf("\033c");
print(integer,x,y);
return 0;
}
int print(int integer[ROW][COL],int x,int y)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<ROW ;i++)
{
for(j=0 ;j<COL ;j++)
{
if(visted[i][j])
printf("\033[41;32m * \033[0m") ;
else
printf(" %d ",integer[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
}
int main(void)
{
int i,j ;
memset(visted,0,sizeof(visted));
visted[0][1]=1;
dfs(0,1) ;
}
运行截图:

PS 1.这是一个动态演示的程序,可以清晰的看到移动的动作,所以运行有奇效
2. 回溯之后要再打印一次,才能有回溯的效果,并且必须有sleep 函数,否则会因为程序运行太快而导致看不到回溯的效果。
3. 如果对于DFS搜索还不太懂的–>点这里,文中提到的马踏棋盘我会在下一篇博客中提到。
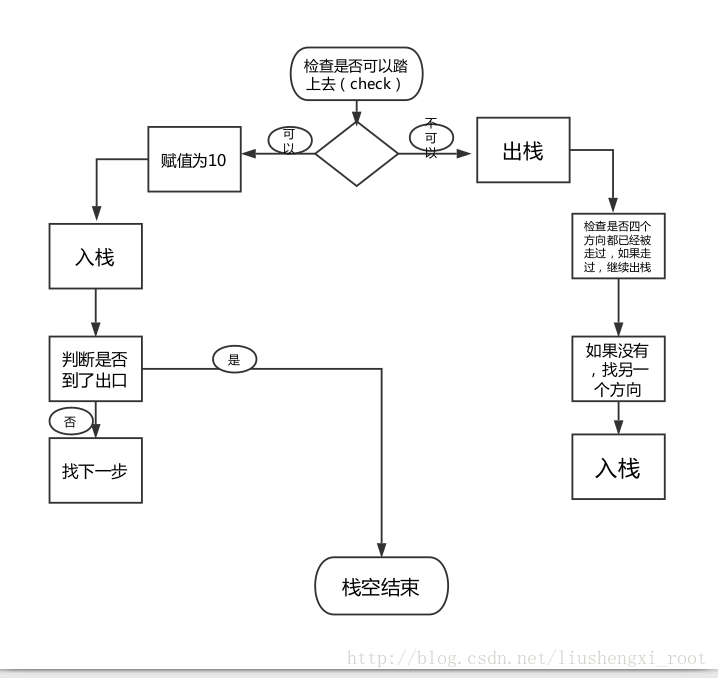
采用栈的数据结构
先来提出几个问题
1.为什么要用栈来实现?有什么好的地方?
2.di 有什么作用?为什么要它?
3.栈空与栈不空,有什么用?
4.大体思路是什么?
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAXSTACKSIZE 100
#define N 10
#define Entrance_row 0
#define Entrance_col 1
#define Exit_row 8
#define Exit_col 9
typedef struct position{
int x;
int y;
}position ;
typedef struct SElement {
position p;
int di;
}SElement ;
typedef struct Mystack{
SElement *top;
SElement *base;
int stackSize ;
}Mystack ;
int Maze[N][N]={
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,0,2,0,0,0,2,0,2},
{2,0,0,2,0,0,0,2,2,2},
{2,0,0,0,0,2,2,0,0,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,0,2,0,2,2},
{2,0,0,0,2,0,0,0,0,2},
{2,0,2,0,0,0,2,0,0,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,0,2,2,0,2},
{2,2,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2}
};
int IsEmptyStack(Mystack *path);
int InitStack(Mystack *path)
{
path->top = path->base =(SElement *)malloc(sizeof(SElement)*MAXSTACKSIZE);
if(path->top == NULL )
{
printf("Init stack is failed !!! \n");
return -1;
}
path->stackSize = MAXSTACKSIZE;
return 0;
}
int pop(Mystack *path ,SElement *t)
{
if(IsEmptyStack(path) == 1)
return 0;
*t = *(path->top-1);
path->top-- ;
return 1;
}
int push(Mystack *path ,SElement p)
{
*(path->top) = p ;
path->top++;
}
int IsEmptyStack(Mystack *path)
{
if(path->top == path->base ) return 1;
else return 0 ;
}
int print_MAZE(int Maze[N][N])
{
int i,j;
for(i= 0 ;i< N;i++)
{
for(j= 0 ;j< N ;j++)
{
if(Maze[i][j] == 10) printf("\033[31m * \033[0m") ;
else printf(" %d ",Maze[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\n");
}
}
int check(position now_try)
{
if(Maze[now_try.x][now_try.y] != 0)
return 0;
if(now_try.x < 0 && now_try.x >= N )
return 0;
if(now_try.y < 0 && now_try.y >= N )
return 0;
return 1;
}
position NextPosition(position now_try ,int direction)
{
position next ;
next.x= now_try.x;
next.y = now_try.y;
switch(direction)
{
case 4:next.y+=1;break;
case 3:next.x+=1;break;
case 1:next.x-=1;break;
case 2:next.y-=1;break;
}
return next ;
}
int main(void)
{
print_MAZE(Maze) ;
Mystack path ;
InitStack(&path);
position now_try ;
now_try.x= Entrance_row;
now_try.y= Entrance_col;
do{
if(check(now_try))
{
Maze[now_try.x][now_try.y] =10 ;
SElement temp ;
temp.p.x= now_try.x;
temp.p.y= now_try.y;
push(&path,temp);
if(now_try.x == Exit_row && now_try.y == Exit_col )
break;
now_try = NextPosition(now_try,1);
printf("\033c");
print_MAZE(Maze);
usleep(800000);
}
else
{
if(IsEmptyStack(&path) != 1)
{
SElement t ;
pop(&path,&t);
while(t.di == 4 && IsEmptyStack(&path) != 1){
Maze[t.p.x][t.p.y] = 9 ;
pop(&path,&t);
}
if(t.di < 4)
{
now_try = NextPosition(t.p,t.di+1);
t.di++;
push(&path,t);
}
}
}
}while( IsEmptyStack(&path) == 0 );
printf("\033c");
print_MAZE(Maze);
return 0;
}
运行截图:
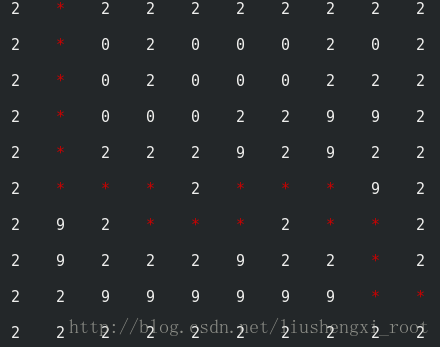
问题解答:
1.首先我们都知道栈有先进后出的特点,那么我们的迷宫是否需要这种特点呐。如果走的通,那么就走,如果走不通,那是不是要回到前一步,找另外一个方向走。那么前一步怎么存储?是不是符合一个先存后取的顺序!OK !这不正好与我们的栈的特点重合吗。
2.di 的作用有两个。一是表示方向,二是表示走了几个方向了。是不是感觉很拗口。那么我来简单解释一下。用1,2,3,4来表示东南西北,如果di==3,那么就说明北面还没有走,如果di == 4,那么就说明四个方向都已经走过了。
3.栈空与栈不空,有什么用?假如我们将迷宫改成了这样,那么会发生什么?
int Maze[N][N]={
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,0,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2},
{2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2}
};
是不是会依次入栈,然后依次出栈,出栈之后是不是会栈空,如果不判断栈空的话是不是会陷入一种死循环的状态呐。
4.核心代码:
now_try.x= Entrance_row;
now_try.y= Entrance_col;
do{
if(check(now_try))
{
Maze[now_try.x][now_try.y] =10 ;
SElement temp ;
temp.p.x= now_try.x;
temp.p.y= now_try.y;
push(&path,temp);
if(now_try.x == Exit_row && now_try.y == Exit_col )
break;
now_try = NextPosition(now_try,1);
printf("\033c");
print_MAZE(Maze);
usleep(800000);
}
else
{
if(IsEmptyStack(&path) != 1)
{
SElement t ;
pop(&path,&t);
while(t.di == 4 && IsEmptyStack(&path) != 1){
Maze[t.p.x][t.p.y] = 9 ;
pop(&path,&t);
}
if(t.di < 4)
{
now_try = NextPosition(t.p,t.di+1);
t.di++;
push(&path,t);
}
}
}
}while( IsEmptyStack(&path) == 0 );
大体思路: