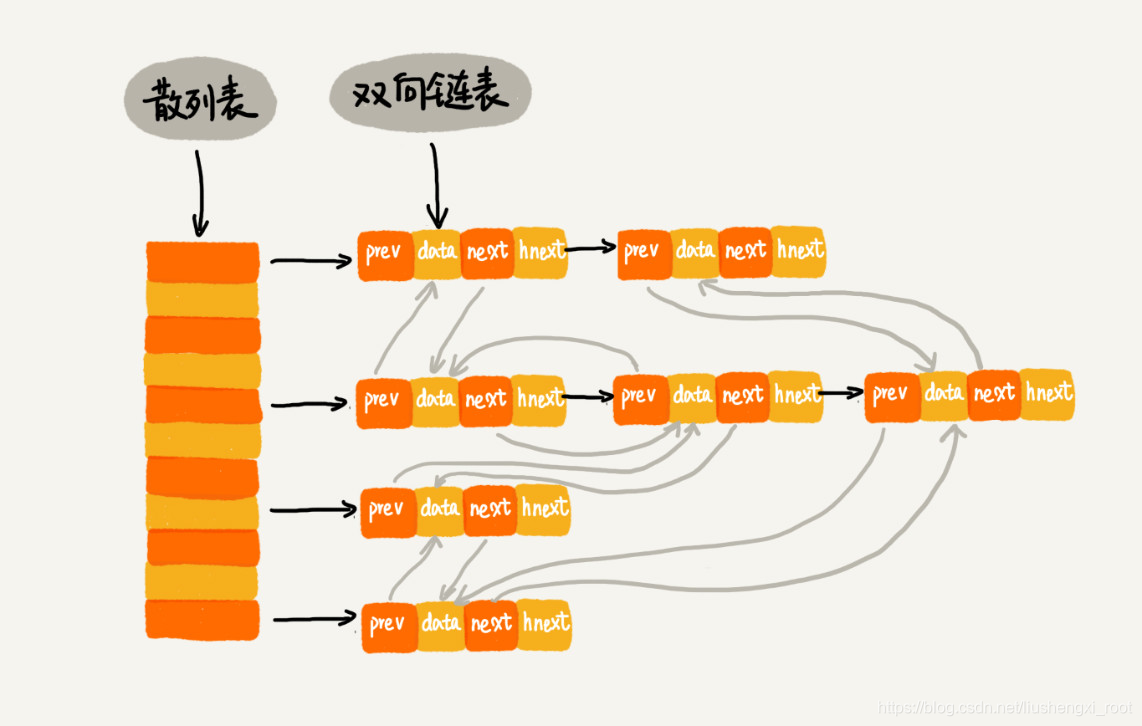
使用散列表和链表实现LRU缓存淘汰算法
LRU和LFU
LRU是最近最少使用页面置换算法(Least Recently Used),也就是首先淘汰最长时间未被使用的页面!
LFU是最近最不常用页面置换算法(Least Frequently Used),也就是淘汰一定时期内被访问次数最少的页!
frist,如何使用链表实现LRU(简单)
我们维护一个有序单链表,越靠近链表尾部的结点是越早之前访问的。当有一个新的数据被访问时,我们从链表头开始顺序遍历链表。
-
如果此数据之前已经被缓存在链表中了,我们遍历得到这个数据对应的结点,并将其从原来的位置删除,然后再插入到链表的头部。
-
如果此数据没有在缓存链表中,又可以分为两种情况:
- 如果此时缓存未满,则将此结点直接插入到链表的头部
- 如果此时缓存已满,则链表尾结点删除,将新的数据结点插入链表的头部。 这样我们就用链表实现了一个 LRU 缓存,是不是很简单?
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print(list<int> &physical_block)
{
for (auto tmp : physical_block)
cout << tmp << " ";
cout << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
// 規定缓存中放置的页面不超过 4 (也就是list不超过 4)
list<int> physical_block;
vector<int> pages = {7, 0, 1, 2, 0, 3, 0, 4, 2, 3,
0, 3, 2, 1, 2, 0, 1, 7, 0, 1};
for (auto i : pages) //依次访问页面
{
/*先看在没在缓存中*/
auto it = std::find(physical_block.begin(), physical_block.end(), i);
if (it != physical_block.end())
{
cout << i << "在缓存中" << endl;
physical_block.erase(it);
physical_block.push_front(i);
}
/*没在*/
else
{
cout << i << "不在缓存中" << endl;
/*页面满了就得删除并添加*/
if (physical_block.size() >= 4)
physical_block.pop_back();
physical_block.push_front(i);
}
/*打印缓存中的页面*/
print(physical_block);
cout << "********************************" << endl;
}
}
second,结合散列表实现LRU(优化)
使用STL hash_map(即unordered_map)实现
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
Node(std::string str)
: data_(str) {}
std::string data_;
};
namespace std
{
template <>
class hash<Node>
{
public:
int operator()(const Node &s) const
{
return stoi(s.data_);
}
};
} // namespace std
class LruCache
{
public:
LruCache() : capacity_(0) {}
// cpu 访问数据,需要动态更新缓存
bool PutCache(std::string &str)
{
Node node(str);
int key = hash_fn_(node);
auto it = hash_table_.find(key);
if (it != hash_table_.end())
{
auto list_iter = it->second;
cout << node.data_ << "数据已经在内存中...." << endl;
double_list_.splice(double_list_.begin(), double_list_, list_iter);
}
else
{
cout << node.data_ << "数据未在内存中...." << endl;
/*页面满了就得删除并添加*/
if (capacity_ >= 4)
{
int key = hash_fn_(double_list_.back());
double_list_.pop_back();
hash_table_.erase(key);
capacity_--;
}
double_list_.push_front(node);
hash_table_.insert({key, double_list_.begin()});
capacity_++;
}
for (auto &tt : double_list_)
cout << tt.data_ << " ";
cout << endl;
}
private:
std::hash<Node> hash_fn_;
int capacity_ = 0; //cache capacity,其实就是 list 的容量
//注意是:只用了一条 std::list
//对于list中只有元素的删除操作会导致指向该元素的迭代器失效,其他元素迭代器不受影响,当删除元素时,将迭代器置为空就行了
//或者直接在 hash_map 中 erase 即可
std::list<Node> double_list_;
std::unordered_map<int, std::list<Node>::iterator> hash_table_;
};
int main(void)
{
std::string str[] = {"7", "0", "1", "2", "0", "3", "0", "4", "2", "3", "0", "3", "2", "1", "2", "0", "1", "7", "0"};
std::vector<std::string> pages(str, str + 19);
LruCache lru;
for (auto tt : pages)
{
lru.PutCache(tt);
}
}
组织结构如下: