使用system V实现读者写者问题
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <sys/sem.h> 3 #include <sys/ipc.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <errno.h> 6 #include <unistd.h> 7 #include <pthread.h> 8 #include <sys/types.h> 9 #include <sys/wait.h> 10 11 typedef int semophore; 12 semophore mutex = 0; 13 semophore cnt = 0; 14 semophore db = 1; 15 //char mutex[] = "mutex"; 16 //char db[] = "db"; 17 int semId; 18 void read(int cnt) 19 { 20 fprintf(stdout, "NO.%d reading...\n",cnt); 21 //for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++); 22 sleep(1); 23 fprintf(stdout, "NO.%d read finished.\n",cnt); 24 25 } 26 void write() 27 { 28 fprintf(stdout, "writing...\n"); 29 //for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++); 30 sleep(1); 31 fprintf(stdout, "write finished.\n"); 32 } 33 34 union semun { 35 int val; 36 struct semid_ds *buf; 37 unsigned short int *array; 38 struct seminfo *__buf; 39 }; 40 /* 41 struct sembuf{ //结构定义在 linux/sem.h,无需重复定义 42 unsigned short sem_num; //信号在信号集中的索引,0代表第一个信号,1代表第二个信号 43 short sem_op; //操作类型 44 short sem_flg; //操作标志 45 }; 46 */ 47 48 /* 49 void p(const char *s) 50 { 51 /* 52 semun arg; 53 int tmp; 54 int r; 55 if (strcmp(s, mutex) == 0) 56 { 57 //fprintf(stdout,"mutex:%d\n",semctl(semId, 0, GETVAL, arg)); 58 while(1){ 59 if(semctl(semId, 0, GETVAL, arg)<=0) 60 wait(&r); 61 else break; 62 } 63 tmp = semctl(semId, 0, GETVAL, arg); 64 //if(tmp<=0) waitpid(); 65 arg.val = tmp - 1; 66 semctl(semId, 0, SETVAL, arg); 67 } 68 else if (strcmp(s, db) == 0) 69 { 70 //fprintf(stdout,"db:%d\n",semctl(semId, 1, GETVAL, arg)); 71 while(1){ 72 if(semctl(semId, 1, GETVAL, arg)<=0) 73 wait(&r); 74 else break; 75 } 76 tmp = semctl(semId, 1, GETVAL, arg); 77 arg.val = tmp - 1; 78 semctl(semId, 1, SETVAL, arg); 79 } 80 81 sembuf arg; 82 arg.sem_op = 1; 83 arg.sem_flg = IPC_UNDO; 84 if(strcmp(s, mutex)==0) 85 { 86 arg.sem_num = 0; 87 semop(semId,&arg,1); 88 } 89 else if(strcmp(s, db)==0) 90 { 91 arg.sem_num = 1; 92 semop(semId,&arg,1); 93 } 94 95 } 96 */ 97 /* 98 void v(const char *s) 99 { 100 /* 101 semun arg; 102 int tmp; 103 if (strcmp(s, mutex) == 0) 104 { 105 tmp = semctl(semId, 0, GETVAL, arg); 106 arg.val = tmp + 1; 107 semctl(semId, 0, SETVAL, arg); 108 } 109 else if (strcmp(s, db) == 0) 110 { 111 tmp = semctl(semId, 1, GETVAL, arg); 112 arg.val = tmp + 1; 113 semctl(semId, 1, SETVAL, arg); 114 } 115 116 sembuf arg; 117 arg.sem_op = -1; 118 arg.sem_flg = IPC_UNDO; 119 if(strcmp(s, mutex)==0) 120 { 121 arg.sem_num = 0; 122 semop(semId,&arg,1); 123 } 124 else if(strcmp(s, db)==0) 125 { 126 arg.sem_num = 1; 127 semop(semId,&arg,1); 128 } 129 } 130 */ 131 132 //P操作函数 133 int p(int index) 134 { 135 struct sembuf buf = {0, -1}; 136 137 if (index < 0) 138 { 139 perror("index of array cannot equals a minus value!\n"); 140 return -1; 141 } 142 buf.sem_num = index; 143 if (semop(semId, &buf, 1) == -1) 144 { 145 perror(" a wrong operation to semaphore occurred!\n"); 146 return -1; 147 } 148 return 0; 149 } 150 151 //V操作函数 152 int v(int index) 153 { 154 struct sembuf buf = {0, 1}; 155 156 if (index < 0) 157 { 158 perror("index of array cannot equals a minus value!\n"); 159 return -1; 160 } 161 buf.sem_num = index; 162 if (semop(semId, &buf, 1) == -1) 163 { 164 perror(" a wrong operation to semaphore occurred!\n"); 165 return -1; 166 } 167 return 0; 168 } 169 void* reader(void* args) 170 { 171 p(mutex); 172 cnt++; 173 if (cnt == 1) 174 { 175 p(db); 176 } 177 v(mutex); 178 179 read(cnt); 180 181 p(mutex); 182 cnt--; 183 if (cnt == 0) 184 { 185 v(db); 186 } 187 v(mutex); 188 } 189 void* writer(void* args) 190 { 191 p(db); 192 write(); 193 v(db); 194 } 195 196 int main() 197 { 198 semun arg; 199 200 key_t key = 1234; 201 if ((key = ftok(".", 11)) == -1) 202 { 203 perror("ftok error:"); 204 _exit(1); 205 } 206 semctl(semId, 0, IPC_RMID, arg); 207 208 //semid = semget(key, 1, IPC_CREAT|0660); 209 210 if ((semId = semget(key, 2, IPC_CREAT | IPC_EXCL | 0666)) >= 0) 211 { 212 arg.val = 1; 213 if (semctl(semId, 0, SETVAL, arg) < 0) 214 { 215 fprintf(stdout, "semctl error %s\n", strerror(errno)); 216 return -1; 217 } 218 if (semctl(semId, 1, SETVAL, arg) < 0) 219 { 220 fprintf(stdout, "semctl error %s\n", strerror(errno)); 221 return -1; 222 } 223 224 } 225 else if (errno == EEXIST) 226 { 227 semId = semget(key, 2, 0666); 228 //fprintf(stdout,"Taskr :: errno==EEXIST\n"); 229 arg.val = 1; 230 if (semctl(semId, 0, SETVAL, arg) < 0) 231 { 232 fprintf(stdout, "semctl error %s\n", strerror(errno)); 233 return -1; 234 } 235 if (semctl(semId, 1, SETVAL, arg) < 0) 236 { 237 fprintf(stdout, "semctl error %s\n", strerror(errno)); 238 return -1; 239 } 240 } 241 else 242 { 243 fprintf(stdout, "semget error %s\n", strerror(errno)); 244 return -1; 245 } 246 pthread_t tids[5]; 247 for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) 248 { 249 250 //参数依次是:创建的线程id,线程参数,调用的函数,传入的函数参数 251 if(i==0 || i==2 || i==4) 252 { 253 fprintf(stdout,"turn NO.%d want to read.\n",i); 254 int ret = pthread_create(&tids[i], NULL, reader, NULL); 255 if (ret != 0) 256 { 257 fprintf(stdout, "reading error\n"); 258 } 259 } 260 else{ 261 fprintf(stdout,"turn NO.%d want to write.\n",i); 262 int ret = pthread_create(&tids[i], NULL, writer, NULL); 263 if (ret != 0) 264 { 265 fprintf(stdout, "writing error\n"); 266 } 267 } 268 } 269 270 pthread_exit(NULL); 271 return 0; 272 }
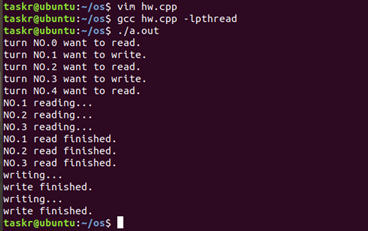
结果如图(读者优先):
非常感谢 @神一城 老师的指点,之前自己没有学清楚 system V 中关于信号量的内容,使用了 semctl 这种直接赋值的操作,其实这样和直接使用 int 变量再加一些条件判断实现一样,而这样就等同于没有原子性,完全没有体现出信号量的作用,只是把信号量当作了一个普通变量。
这里向之前受到错误博客内容误导的朋友道歉。
日后若能有更好的想法,再来完善。
希望看到的大神不吝赐教 orz


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号