HDU-5738
Eureka
Time Limit: 8000/4000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
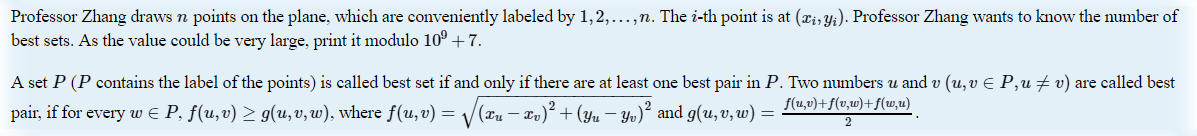
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of input contains an integer T, indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first line contains an integer n (1≤n≤1000) -- then number of points.
Each of the following n lines contains two integers xi and yi (−109≤xi,yi≤109) -- coordinates of the i-th point.
The first line contains an integer n (1≤n≤1000) -- then number of points.
Each of the following n lines contains two integers xi and yi (−109≤xi,yi≤109) -- coordinates of the i-th point.
Output
For each test case, output an integer denoting the answer.
Sample Input
3
3
1 1
1 1
1 1
3
0 0
0 1
1 0
1
0 0
Sample Output
4
3
0
Source
题解:给出n个整点,定义f(u,v)为u和v的距离,g(u,v,w)=((f(u,v)+f(u,w)+f(v,w))/2,定义这n个点的非空子集P是最好的当且仅当P中含有一个最好点对(u,v),最好点对定义是,对集合P中任一点w,(u,v)满足f(u,v)>=g(u,v,w),问有多少种不同的最好集合 .
思路:由f(u,v)>=g(u,v,w)知f(u,v)>=f(u,w)+f(v,w),显然w需要在以u和v为端点的线段上,故问题转变为这n个点能构成多少种不同的线段(此处不同指的是两个端点的编号不同时相同,线段可以左右端点相同),首先去重,将所有重点去掉只留一个同时记录其数量,枚举线段左端点,将其他所有点与此点的横纵坐标差值(x,y)化成即约形式后存在map中,那么最后这个map中存的就是以该点为左端点,其他点为右端点构成线段的所有可能斜率以及每个斜率对应的点数,假设斜率为k的有res个点,该点重复次数是num,之后就可以开始计数,即求以该点为左端点,斜率为k的线段有多少个,即从num个重复的端点中任选不少于一个点,简单推导可得共有(2^num-1)*(2^res-1)种,从res个点中任选不少于一个点的方法数,这样枚举完左端点后就得到了所有左右端点不同的线段的数量,但还要把左右端点相同的线段加到答案中,这个只需要枚举每个重点,例如某个点重复了num次,那么其对答案的贡献就是从中选取不少于两个点的方法数,即2^num-num-1,上面的贡献全部累加起来即为答案.
(转载:http://blog.csdn.net/v5zsq/article/details/52045420)
代码:
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<map> 6 using namespace std; 7 typedef long long ll; 8 #define maxn 1111 9 #define mod 1000000007ll 10 struct node 11 { 12 int x,y,num; 13 }a[maxn]; 14 int T,n; 15 typedef pair<int,int>P; 16 map<P,int>m; 17 map<P,int>::iterator it; 18 ll f[maxn]; 19 int cmp(node a,node b) 20 { 21 if(a.x!=b.x)return a.x<b.x; 22 if(a.y!=b.y)return a.y<b.y; 23 return a.num>b.num; 24 } 25 int gcd(int a,int b) 26 { 27 return b?gcd(b,a%b):a; 28 } 29 int main() 30 { 31 f[0]=1; 32 for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++)f[i]=f[i-1]*2ll%mod; 33 scanf("%d",&T); 34 while(T--) 35 { 36 37 scanf("%d",&n); 38 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 39 scanf("%d%d",&a[i].x,&a[i].y); 40 sort(a,a+n,cmp); 41 int cnt=0; 42 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 43 { 44 int num=1; 45 while(i<n-1&&a[i].x==a[i+1].x&&a[i].y==a[i+1].y)num++,i++; 46 a[cnt].x=a[i].x,a[cnt].y=a[i].y,a[cnt++].num=num; 47 } 48 sort(a,a+cnt,cmp); 49 ll ans=0; 50 for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) 51 { 52 ll temp=(f[a[i].num]-a[i].num-1)%mod; 53 ans=(ans+temp+mod)%mod; 54 } 55 for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++) 56 { 57 m.clear(); 58 for(int j=i+1;j<cnt;j++) 59 { 60 int x=a[j].x-a[i].x,y=a[j].y-a[i].y; 61 int g=gcd(abs(x),abs(y)); 62 x/=g,y/=g; 63 P p=make_pair(x,y); 64 m[p]+=a[j].num; 65 } 66 for(it=m.begin();it!=m.end();it++) 67 { 68 ll temp=(f[a[i].num]-1)*(f[it->second]-1)%mod; 69 ans=(ans+temp+mod)%mod; 70 } 71 } 72 printf("%I64d\n",ans); 73 } 74 return 0; 75 }

