TensorRT——INT8推理
原理
- 为什么要使用INT8推理:更高的吞吐量/处理的fps提高以及更低的内存占用(8-bit vs 32-bit)
- 将FP32模型转换成INT8模型存在的挑战:更低的动态范围和精度
Consider that 32-bit floating-point can represent roughly 4 billion numbers in the interval [-3.4e38, 3.40e38]. This interval of representable numbers is also known as the dynamic-range. The distance between two neighboring representable numbers is the precision of the representation. ——《Achieving FP32 Accuracy for INT8 Inference Using Quantization Aware Training with NVIDIA TensorRT》
- 如何将FP32量化成INT8:最简单的一种方式是Symmetric Linear Quantization,每个Tensor都可以用一个和它关联的scalar factor乘以量化后的INT8值。那么如何确定这个scalar factor呢?
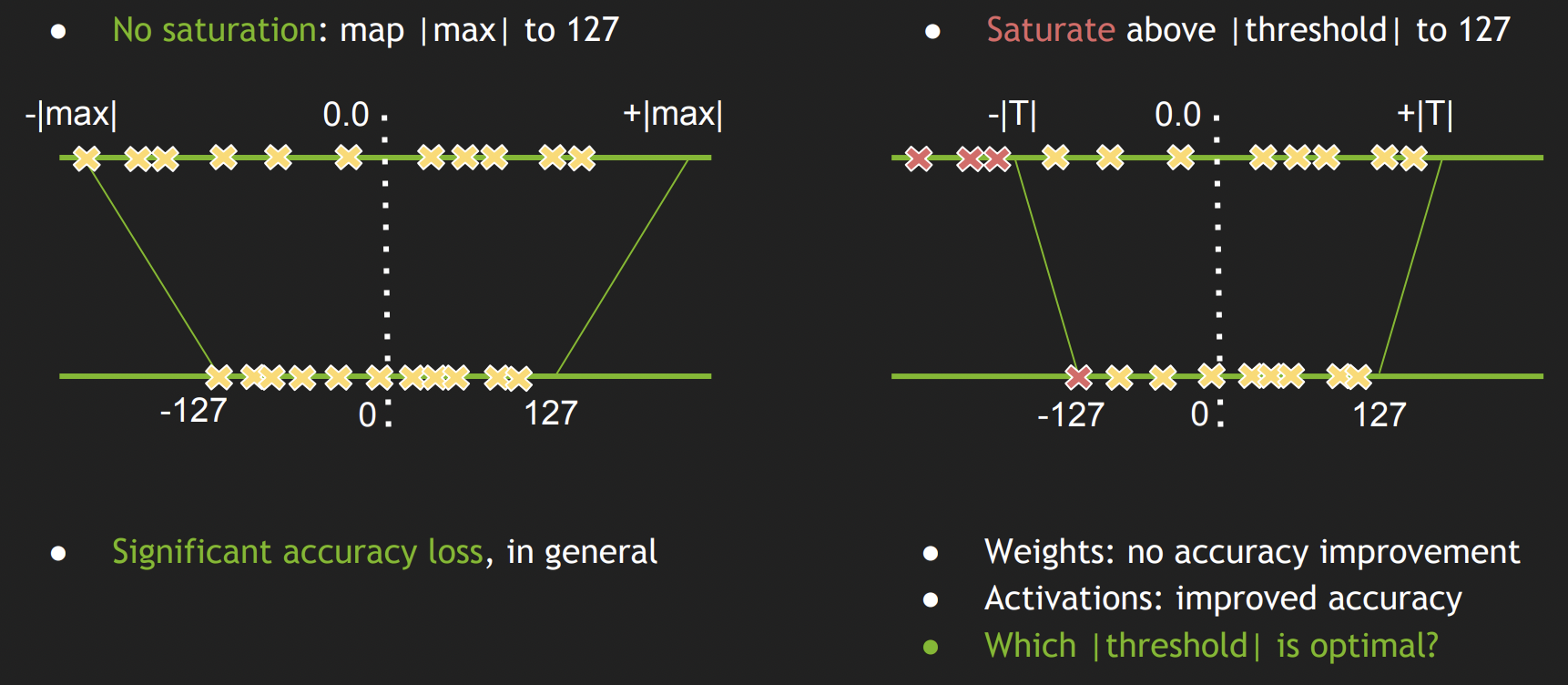
对于weights,TensorRT采用左图的方式进行映射,这样不会带来accuracy drop;对于activations,TensorRT采用上图右边这种方式进行INT8量化,这面临一个新的问题,如何为每个activation tensor选取最佳的|threshold|呢?(这个其实就是calibration的过程)
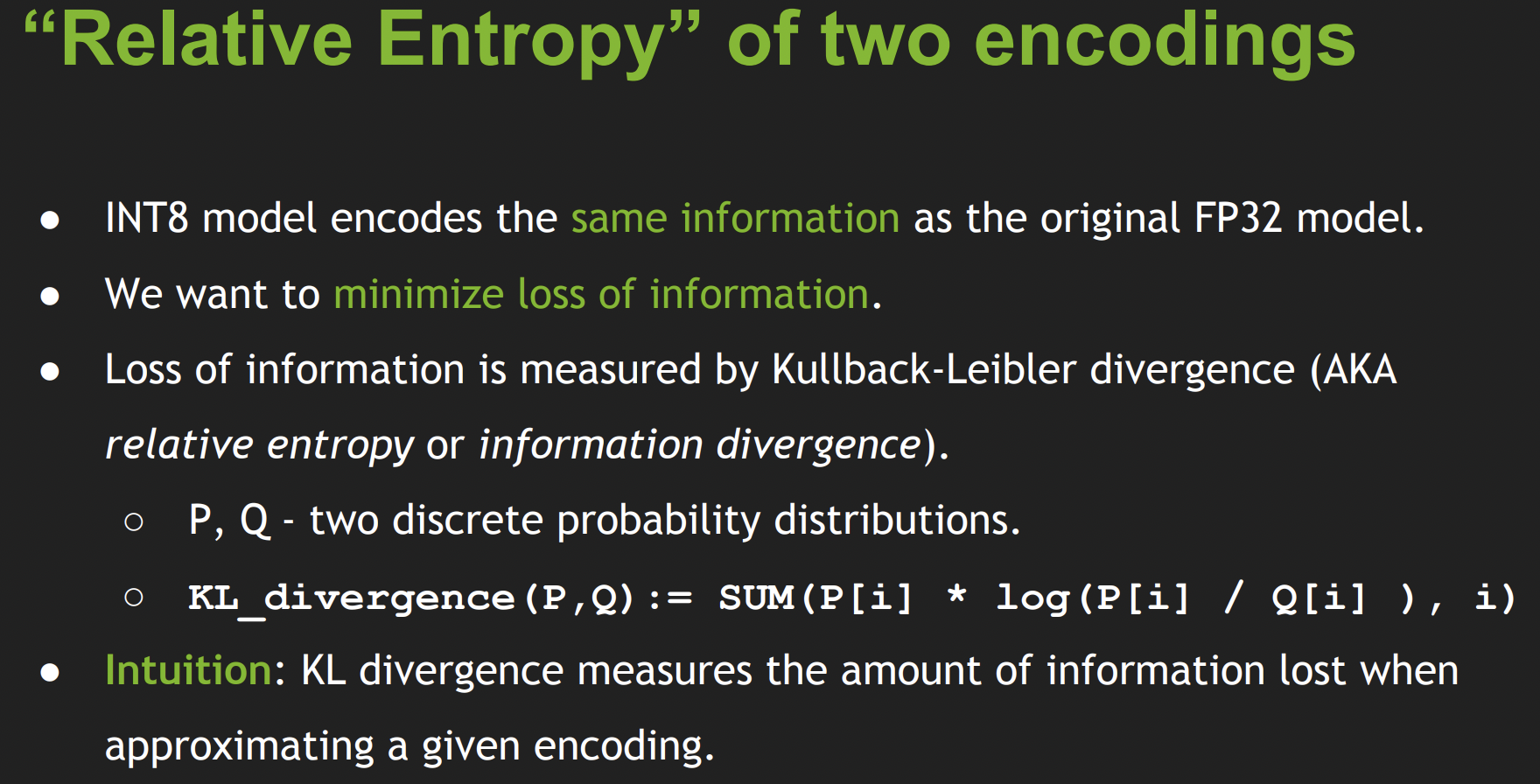
选取不同的threshold,相当于是不同的编码方式。从信息论的角度看,我们希望选取一种编码方式,使得编码前后的信息损失最小,我们可以用KL散度来衡量这个信息损失。
- 对activations的calibration
实践
为了使用TensorRT的INT8推理,我们需要编写一个自己的calibrator类,然后通过builder->setInt8Calibrator(calibrator)告诉builder使用这个calibrator来做数据标定,从而减小量化误差。
至于builder具体是怎么去做标定的,builder类实现了以下功能:
- builder首先调用calibrator类的
getBatchSize()来获取input batch的大小 - 然后builder不断调用
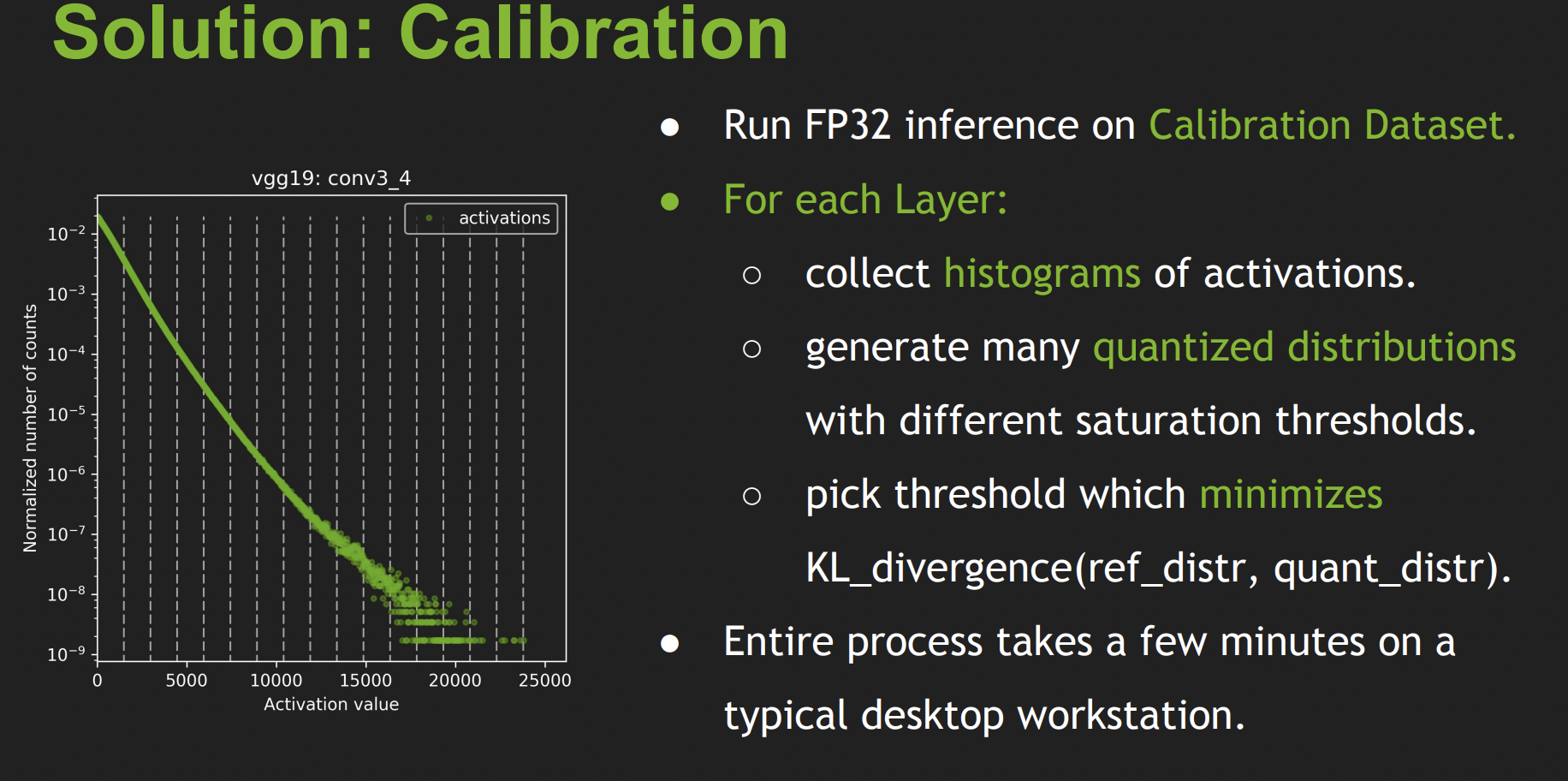
getBatch()来获取用于标定的输入数据,读入的batch data的大小必须和getBatchSize()得到的大小一致,如果没有input batch数据了,getBatch()返回false - builder会先建立一个32-bit的Engine,对calibration set进行前向推理,并记录下每层activations的直方图
- 根据获得的直方图建立一个calibration table
- 基于得到的calibration table和network definition来创建8-bit的Engine
而calibration的过程是比较耗时的,通过对calibration table进行缓存,可以高效地对同一网络build多次。要实现对calibration table的缓存功能,需要实现calibrator类中的writeCalibrationCache()和readCalibrationCache()两个函数。
综上所述,要实现一个INT8的Engine,开发人员需要实现一个calibrator类,这个类需override下面几个函数:
- getBatchSize
- getBatch
- writeCalibrationCache(optional)
- readCalibrationCache(optional)
这个calibrator类是一个IInt8Calibrator,TensorRT提供了4个IInt8Calibrator的派生类(IInt8EntropyCalibrator、IInt8EntropyCalibrator2、IInt8MinMaxCalibrator、IInt8LegacyCalibrator,我们例子中的calibrator继承自IInt8EntropyCalibrator.
#include <algorithm>
#include <assert.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <cuda_runtime_api.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include "NvInfer.h"
#include "NvOnnxParser.h"
#include "argsParser.h"
#include "logger.h"
#include "common.h"
#include "image.hpp"
#define DebugP(x) std::cout << "Line" << __LINE__ << " " << #x << "=" << x << std::endl
using namespace nvinfer1;
Logger gLogger;
// LogStreamConsumer gLogError;
static const int INPUT_H = 224;
static const int INPUT_W = 224;
static const int INPUT_C = 3;
static const int OUTPUT_SIZE = 1000;
const char* INPUT_BLOB_NAME = "input";
const char* OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME = "output";
const std::string gSampleName = "TensorRT.sample_onnx_image";
const std::string onnxFile = "resnet50.onnx";
const std::string engineFile = "../data/resnet50_int8.trt"
const std::string calibFile = "../data/calibration_img.txt"
samplesCommon::Args gArgs;
std::vector<float> prepareImage(cv::Mat &img) {
int c = 3;
int h = INPUT_H;
int w = INPUT_W;
// 1 Resize the source Image to a specific size(这里保持原图长宽比进行resize)
float scale = std::min(float(w) / img.cols, float(h) / img.rows);
auto scaleSize = cv::Size(img.cols * scale, img.rows * scale);
// Convert BGR to RGB
cv::Mat rgb;
cv::cvtColor(img, rgb, CV_BGR2RGB);
cv::Mat resized;
cv::resize(rgb, resized, scaleSize, 0, 0, cv::INTER_CUBIC);
// 2 Crop Image(将resize后的图像放在(H, W, C)的中心, 周围用127做padding)
cv::Mat cropped(h, w, CV_8UC3, 127)
// Rect(left_top_x, left_top_y, width, height)
cv::Rect rect((w - scaleSize.width) / 2, (h - scaleSize.height) / 2, scaleSize.width, scaleSize.height);
resize.copyTo(cropped(rect));
// 3 Type conversion, convert unsigned int 8 to float 32
cv::Mat img_float;
cropped.convertTo(img_float, CV_32FC3, 1.f / 255.0);
// HWC to CHW, and convert Mat to std::vector<float>
std::vector<cv::Mat> input_channels(c);
cv::split(cropped, input_channels);
std::vector<float> result(h * w * c);
auto data = result.data();
int channelLength = h * w;
for (int i = 0; i < c; ++i) {
memcpy(data, input_channels[i].data, channelLength * sizeof(float));
data += channelLength;
}
return result;
}
// 实现自己的calibrator类
namespace nvinfer1 {
class int8EntropyCalibrator: public nvinfer1::IInt8EntropyCalibrator {
public:
int8EntropyCalibrator(const int &batchSize,
const std::string &imgPath,
const std::string &calibTablePath);
virtual ~int8EntropyCalibrator();
int getBatchSize() const override { return batchSize; }
bool getBatch(void *bindings[], const char *names[], int nbBindings) override;
const void *readCalibationCache(std::size_t &length) override;
void writeCalibrationCache(const void *ptr, std::size_t length) override;
private:
int batchSize;
size_t inputCount;
size_t imageIndex;
std::string calibTablePath;
std::vector<std::string> imgPaths;
float *batchData { nullptr };
void *deviceInput { nullptr };
bool readCache;
std::vector<char> calibrationCache;
};
int8EntropyCalibrator::int8EntropyCalibrator(const int &batchSize, const std::string &imgPath,
const std::string &calibTablePath) : batchSize(batchSize), calibTablePath(calibTablePath), imageIndex(0) {
int inputChannel = 3;
int inputH = 256;
int inputW = 256;
inputCount = batchSize * inputChannel * inputH * inputW;
std::fstream f(imgPath);
if (f.is_open()) {
std::string temp;
while( std::getline(f, temp) ) imgPaths.push_back(temp);
}
int len = imgPaths.size();
for( int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
std::cout << imgPaths[i] << std::endl;
}
// allocate memory for a batch of data, batchData is for CPU, deviceInput is for GPU
batchData = new flowt[inputCount];
CHECK(cudaMalloc(&deviceInput, inputCount * sizeof(float)));
}
IInt8EntropyCalibrator::~IInt8EntropyCalibrator() {
CHECK(cudaFree(deviceInput));
if (batchData) {
delete[] batchData;
}
}
bool int8EntropyCalibrator::getBatch(void **bindings, const char **names, int nbBindings) {
std::cout << imageIndex << " " << batchSize << std::endl;
std::cout << imgPaths.size() << std::endl;
if (imageIndex + batchSize > ing(imgPaths.size()))
return false;
// load batch
float *ptr = batchData;
for (size_t j = imageIndex; j < imageIndex + batchSize; ++j) {
cv::Mat img = cv::imread(imgPaths[j]);
std::vector<float> inputData = prepareImage(img);
if (inputData.size() != inputCount) {
std::cout << "InputSize Error" << std::endl;
return false;
}
assert(inputData.size() == inputCount);
memcpy(ptr, inputData.data(), (int)(inputData.size()) * sizeof(float));
ptr += inputData.size();
std::cout << "load image " << imgPaths[j] << " " << (j + 1) * 100. / imgPaths.size() << "%" << std::endl;
}
imageIndex += batchSize;
// copy bytes from Host to Device
CHECK(cudaMemcpy(deviceInput, batchData, inputCount * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice));
bindings[0] = deviceInput;
return true;
}
const void* int8Entropycalibrator::readCalibrationCache(std::size_t &length) {
calibrationCache.clear();
std::ifstream input(calibTablePath, std::ios::binary);
input >> std::noskipws;
if (readCache && input.good()) {
std::copy(std::istream_iterator<char>(input), std::istream_iterator<char>(),
std::back_inserter(calibrationCache));
}
length = calibrationCache.size();
return length ? &calibrationCache[0] : nullptr;
}
void int8EntropyCalibrator::writeCalibrationCache(const void *cache, std::size_t length) {
std::ofstream output(calibTablePath, std::ios::binary);
output.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(cache), length);
}
}
bool onnxToTRTModel(const std::string& modelFile, // name of the onnx model
unsigned int maxBatchSize, // batch size - NB must be at least as large as the batch we want to run with
IHostMemory*& trtModelStream, // output buffer for the TensorRT model
const std::string& engineFile)
// create the builder
IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger.getTRTLogger());
assert(builder != nullptr);
// create the config
auto config = builder->createBuilderConfig();
assert(config != nullptr);
if (! builder->platformHasFastInt8()) {
std::cout << "builder platform do not support Int8" << std::endl;
return false;
}
const auto explicitBatch = 1U << static_cast<uint32_t>(NetworkDefinitionCreationFlag::kEXPLICIT_BATCH);
std::cout << "explicitBatch is: " << explicitBatch << std::endl;
nvinfer1::INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(explicitBatch);
auto parser = nvonnxparser::createParser(*network, gLogger.getTRTLogger());
//Optional - uncomment below lines to view network layer information
//config->setPrintLayerInfo(true);
//parser->reportParsingInfo();
if ( !parser->parseFromFile( locateFile(modelFile, gArgs.dataDirs).c_str(), static_cast<int>(gLogger.getReportableSeverity()) ) )
{
gLogError << "Failure while parsing ONNX file" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// config
config->setAvgTimingIterations(1);
config->setMinTimingIterations(1);
config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1_GiB);
// Build the engine
builder->setMaxBatchSize(maxBatchSize);
//builder->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20);
builder->setMaxWorkspaceSize(10 << 20);
nvinfer1::int8EntropyCalibrator *calibrator = nullptr;
if (calibFile.size() > 0 ) calibrator = new nvinfer1::int8EntropyCalibrator(maxBatchSize, calibFile, "");
// builder->setFp16Mode(gArgs.runInFp16);
// builder->setInt8Mode(gArgs.runInInt8);
// 对builder进行设置, 告诉它使用Int8模式, 并利用编写好的calibrator类进行calibration
builder->setInt8Mode(true);
builder->setInt8Calibrator(calibrator);
// if (gArgs.runInInt8)
// {
// samplesCommon::setAllTensorScales(network, 127.0f, 127.0f);
// }
config->setFlag(BuiderFlag::kINT8);
config->setInt8Calibrator(calibrator);
// 如果使用了calibrator, 应该参考https://github.com/enazoe/yolo-tensorrt/blob/dd4cb522625947bfe6bfbdfbb6890c3f7558864a/modules/yolo.cpp, 把下面这行注释掉,使用数据集校准得到dynamic range;否则使用下面这行手动设置dynamic range。
// setAllTensorScales函数在官方TensorRT开源代码里有
samplesCommon::setAllTensorScales(network, 127.0f, 127.0f);
// samplesCommon::enableDLA(builder, gArgs.useDLACore);
ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildCudaEngine(*network);
assert(engine);
if (calibrator) {
delete calibrator;
calibrator = nullptr;
}
// we can destroy the parser
parser->destroy();
// serialize the engine, then close everything down
trtModelStream = engine->serialize();
std::ofstream file;
file.open(engineFile, std::ios::binary | std::ios::out);
file.write((const char*)data->data(), data->size());
file.close();
engine->destroy();
config->destroy();
network->destroy();
builder->destroy();
return true;
}
void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize)
{
const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine();
// input and output buffer pointers that we pass to the engine - the engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings(),
// of these, but in this case we know that there is exactly one input and one output.
assert(engine.getNbBindings() == 2);
void* buffers[2];
// In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors.
// note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings()
const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(INPUT_BLOB_NAME);
const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex(OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME);
DebugP(inputIndex); DebugP(outputIndex);
// create GPU buffers and a stream
CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * INPUT_C * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float)));
CHECK(cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float)));
cudaStream_t stream;
CHECK(cudaStreamCreate(&stream));
// DMA the input to the GPU, execute the batch asynchronously, and DMA it back:
CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * INPUT_C * INPUT_H * INPUT_W * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream));
context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr);
CHECK(cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream));
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
// release the stream and the buffers
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]));
CHECK(cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]));
}
//!
//! \brief This function prints the help information for running this sample
//!
void printHelpInfo()
{
std::cout << "Usage: ./sample_onnx_mnist [-h or --help] [-d or --datadir=<path to data directory>] [--useDLACore=<int>]\n";
std::cout << "--help Display help information\n";
std::cout << "--datadir Specify path to a data directory, overriding the default. This option can be used multiple times to add multiple directories. If no data directories are given, the default is to use (data/samples/mnist/, data/mnist/)" << std::endl;
std::cout << "--useDLACore=N Specify a DLA engine for layers that support DLA. Value can range from 0 to n-1, where n is the number of DLA engines on the platform." << std::endl;
std::cout << "--int8 Run in Int8 mode.\n";
std::cout << "--fp16 Run in FP16 mode." << std::endl;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
bool argsOK = samplesCommon::parseArgs(gArgs, argc, argv);
if (gArgs.help)
{
printHelpInfo();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
if (!argsOK)
{
std::cout << "Invalid arguments" << std::endl;
// gLogError << "Invalid arguments" << std::endl;
printHelpInfo();
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
if (gArgs.dataDirs.empty())
{
gArgs.dataDirs = std::vector<std::string>{"data/"};
}
auto sampleTest = gLogger.defineTest(gSampleName, argc, const_cast<const char**>(argv));
gLogger.reportTestStart(sampleTest);
// create a TensorRT model from the onnx model and serialize it to a stream
nvinfer1::IHostMemory* trtModelStream{nullptr};
if (!onnxToTRTModel(onnxFile, 1, trtModelStream))
gLogger.reportFail(sampleTest);
assert(trtModelStream != nullptr);
std::cout << "Successfully parsed ONNX file!!!!" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Start reading the input image!!!!" << std::endl;
cv::Mat image = cv::imread(locateFile("test.jpg", gArgs.dataDirs), cv::IMREAD_COLOR);
if (image.empty()) {
std::cout << "The input image is empty!!! Please check....."<<std::endl;
}
DebugP(image.size());
cv::cvtColor(image, image, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
cv::Mat dst = cv::Mat::zeros(INPUT_H, INPUT_W, CV_32FC3);
cv::resize(image, dst, dst.size());
DebugP(dst.size());
float* data = normal(dst);
// deserialize the engine
IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger);
assert(runtime != nullptr);
if (gArgs.useDLACore >= 0)
{
runtime->setDLACore(gArgs.useDLACore);
}
ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream->data(), trtModelStream->size(), nullptr);
assert(engine != nullptr);
trtModelStream->destroy();
IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext();
assert(context != nullptr);
float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE];
typedef std::chrono::high_resolution_clock Time;
typedef std::chrono::duration<double, std::ratio<1, 1000>> ms;
typedef std::chrono::duration<float> fsec;
double total = 0.0;
// run inference and cout time
auto t0 = Time::now();
doInference(*context, data, prob, 1);
auto t1 = Time::now();
fsec fs = t1 - t0;
ms d = std::chrono::duration_cast<ms>(fs);
total += d.count();
// destroy the engine
context->destroy();
engine->destroy();
runtime->destroy();
std::cout << std::endl << "Running time of one image is:" << total << "ms" << std::endl;
std::cout << "Output:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < OUTPUT_SIZE; i++)
{
gLogInfo << prob[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return gLogger.reportTest(sampleTest, true);
}
除了上面这个实现外,官方的sampleINT8.cpp也非常值得参考。
参考资料:




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端