【学习笔记】AC自动机
AC自动机
其实我将近三个月前就准备写这个并且随笔都建好了,但是一直咕咕到现在才写。其实记忆力好的同学应该意识到这篇其实8月份已经发过了,这次只是更新了一下发布日期而已
概述
AC自动机是 以 Trie 的结构为基础,结合 KMP 的思想建立的。
所以,建立AC自动机一般有两个步骤:
- 将所有的模式串构成一棵Trie。
- 对Trie树上的所有节点构造失配指针。
然后就可以利用它进行多模式串匹配了。
至于多模式串匹配,用不怎么专业的话概述就是:
对于给定的文本串,找出每个模式串在其中各出现了几次。
构建字典树
和Trie树的插入一模一样,就建立一棵普通的Trie树就行。注意当模式串有相同的时候,要对其标记“去重”。
Code
void Insert(char *s, int id){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a';
if(!ch[u][v]) ch[u][v] = ++sz;
u = ch[u][v];
}
if(!val[u]) val[u] = id; //上文提及的“去重”
pos[id] = val[u];
}
失配指针
AC自动机利用 \(fail\) 指针来辅助多模式串的匹配。
那 \(fail\) 指针的含义是?
设 \(root\) 到点 \(i\) 的字符串为 \(S\),点 \(i\) 的 \(fail\) 指针指向 \(j\),\(root\) 到点 \(j\) 的字符串为 \(T\)。那 \(T\) 是 \(S\) 的最长后缀。所以,\(fail\) 指针是 当前字符串最长的后缀的末尾编号。
反正记住AC自动机的失配指针指向当前状态的最长后缀状态即可。
构建
构建 \(fail\) 指针的 基础思想 (别真的这么写,会T飞的):
参考KMP构建 \(next\) 指针的思想。考虑字典树中当前节点为 \(u\),其父节点为 \(p\),\(p\) 通过字符 \(v\) 的边指向 \(u\),即 \(trie[p][v] = u\),假设所有深度小于等于 \(u\) 的节点的 \(fail\) 指针都已求得。
- 如果 \(trie[fail[p]][v]\) 存在,使得 \(fail[u]\) 指向 \(trie[fail[p]][v]\),相当于在 \(p\) 和 \(fail[p]\) 之后都缀上一个字符 \(v\),分别对应 \(u\) 和 \(fail[u]\)。
- 如果 \(trie[fail[p]][v]\) 不存在,那一直找 \(trie[fail[fail[p]]][v]\),继续判断,直到跳到 \(root\)。
- 真的不存在,啥也没有,让 \(fail\) 指针跳到根节点。
放个OI-Wiki上偷来的例子:
对于模式串 i he his she hers 构建 \(fail\) 指针:
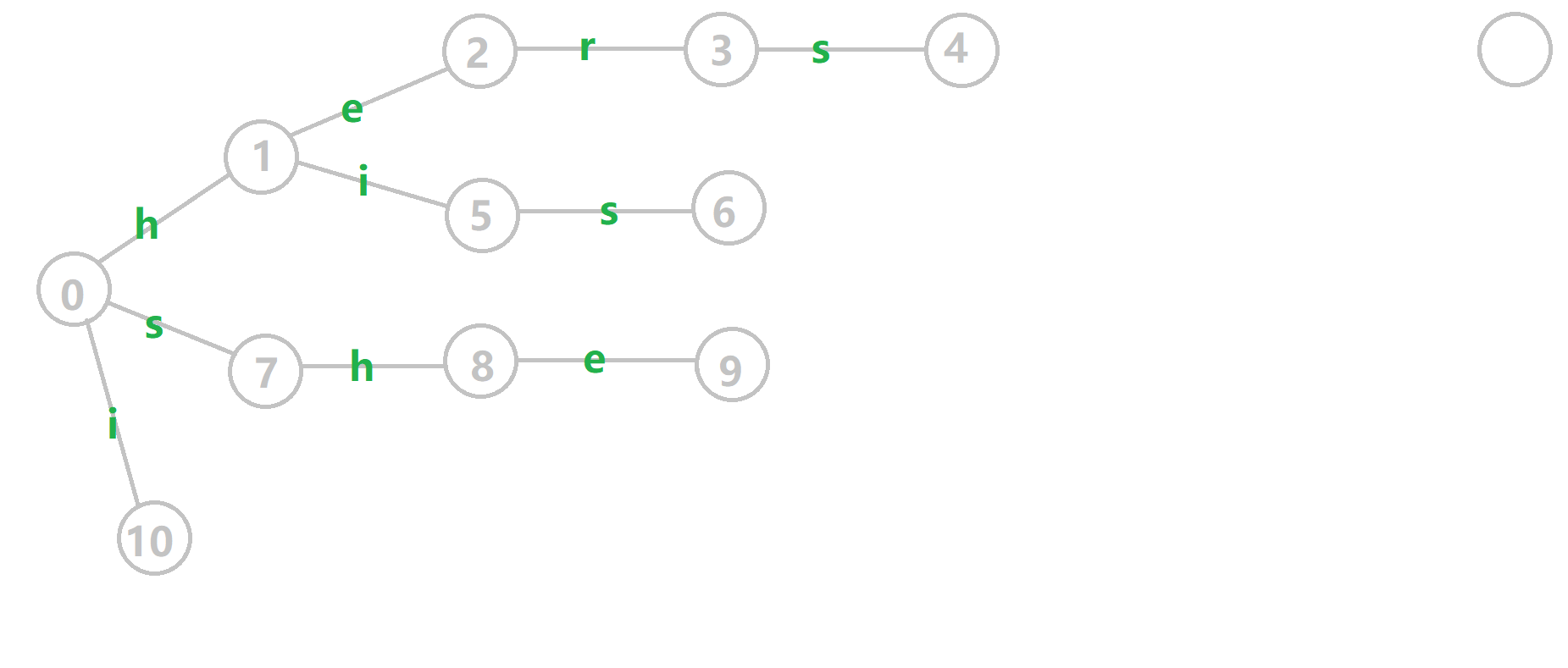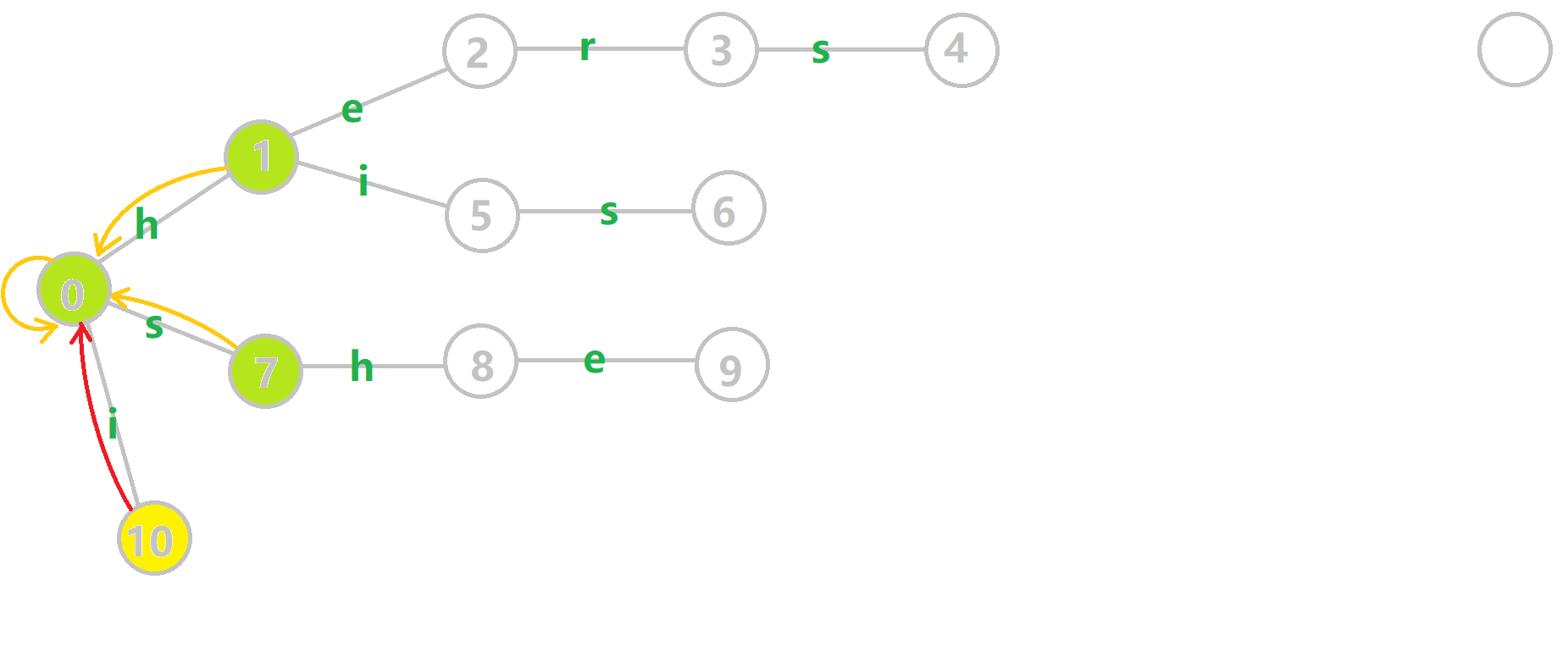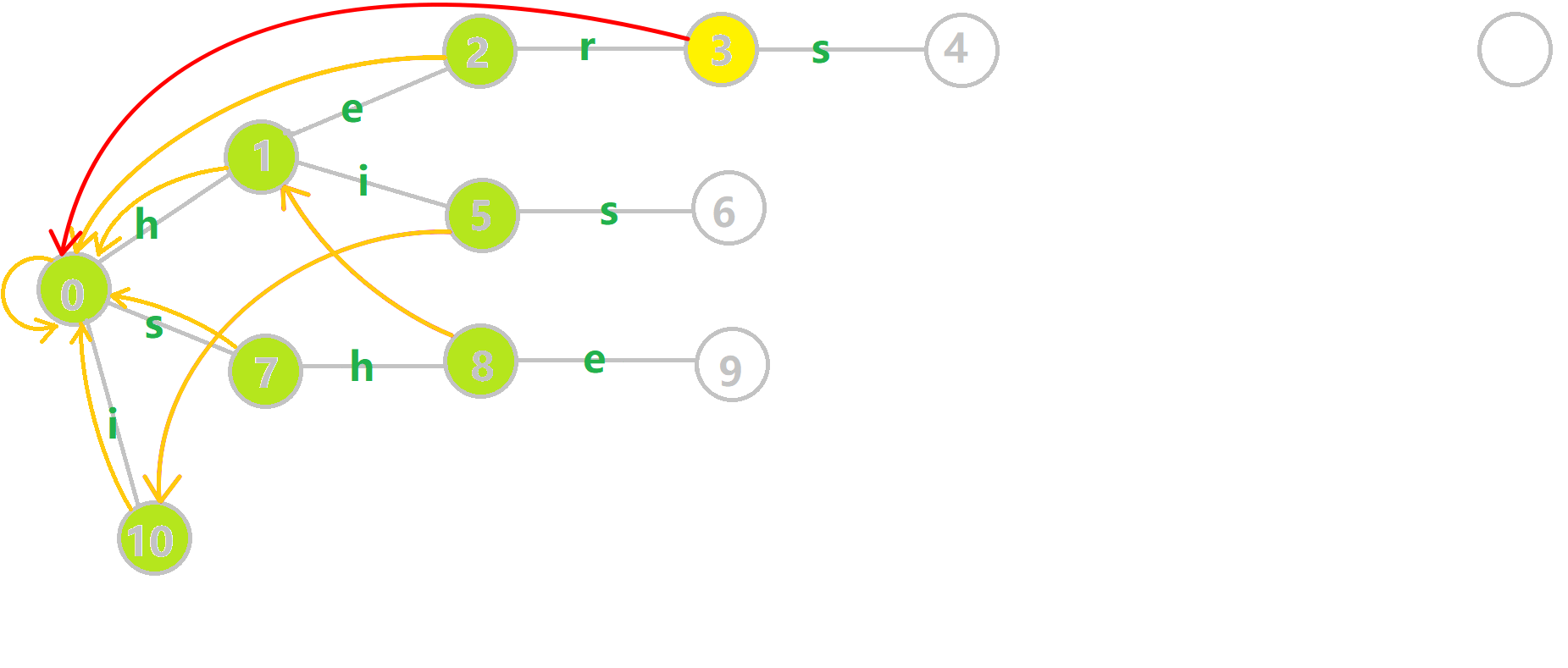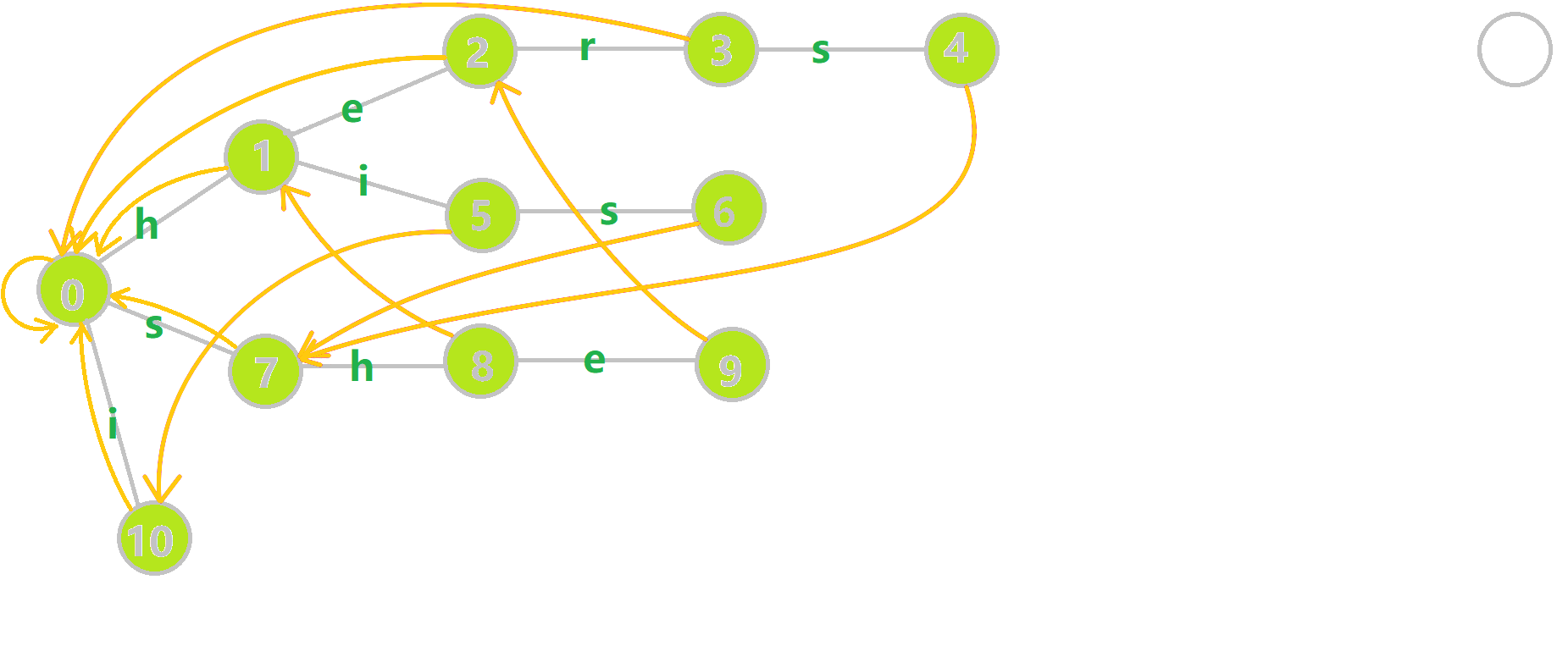
- 黄色结点:当前的结点 。
- 绿色结点:表示已经 BFS 遍历完毕的结点。
- 橙色的边:\(fail\) 指针。
- 红色的边:当前求出的 \(fail\) 指针。
我们重点分析结点 \(6\) 的 \(fail\) 指针构建:
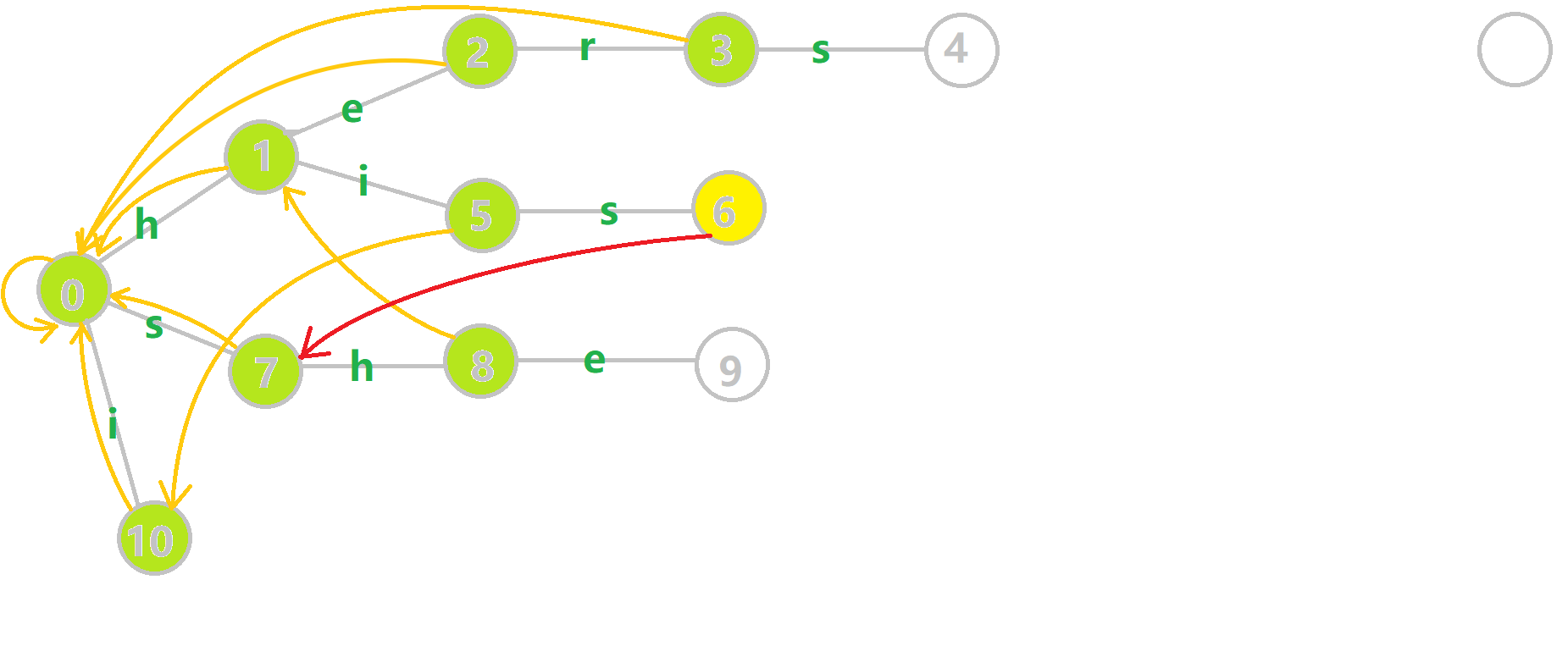
找到 \(6\) 的父结点 \(5\),\(fail[5] = 10\)。然而 \(10\) 结点没有字母 \(s\) 连出的边;继续跳到 \(10\) 的 \(fail\) 指针,\(fail[10] = 0\)。发现 \(0\) 结点有字母 \(s\) 连出的边,指向 \(7\) 结点;所以 \(fail[6] = 7\) 。最后放一张建出来的图
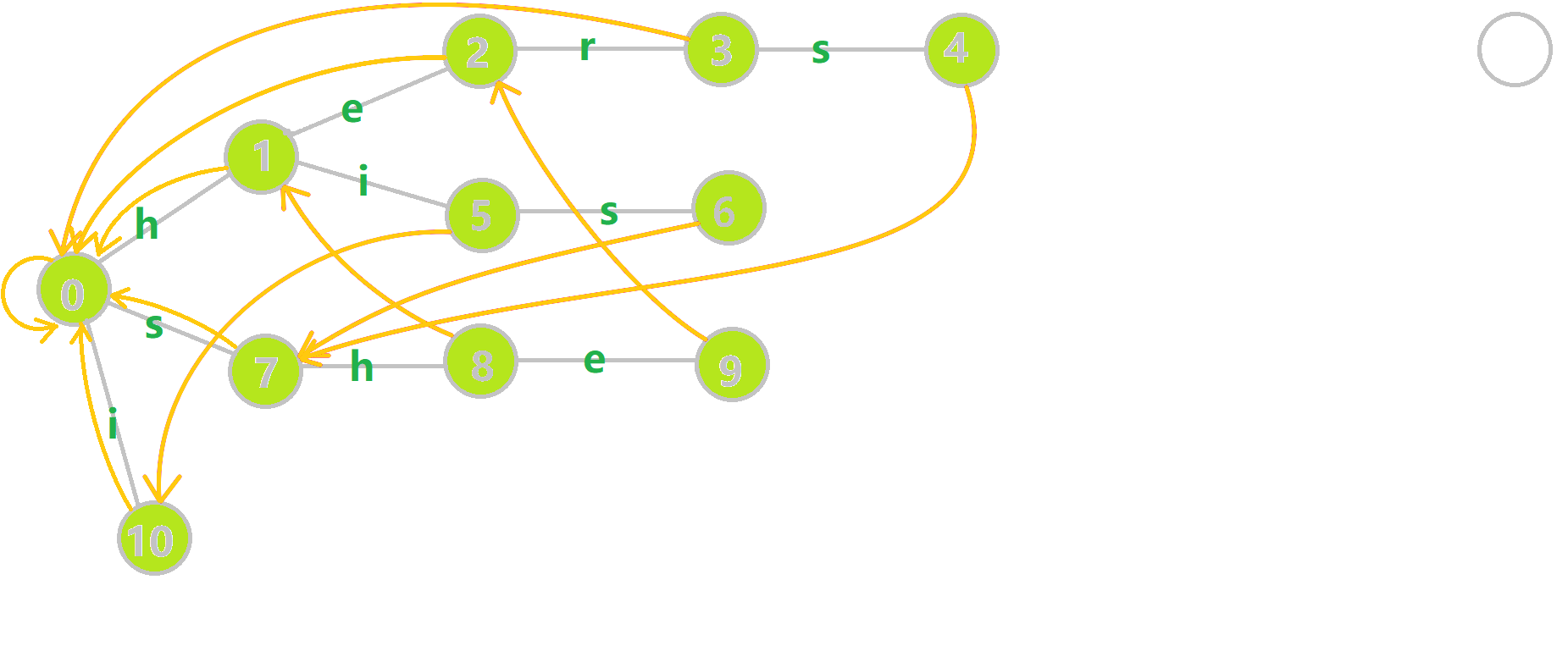
当然,这只是基本思想,真这么一个个递归找 \(fail\) 指针复杂度直接爆炸。
可以想到 \(fail\) 指针一定指向深度小于等于它的节点,并且要靠父节点来找自己的 \(fail\) 指针,所以考虑 BFS 来实现这个逐层扩展。
实现:
- 预处理出第二层(根节点下第一层) 的 \(fail\) 指针,压入队列。
- 广搜,枚举队列中节点的每个子节点。
- 如果子节点存在,子节点的 \(fail\) 指针指向父节点的 \(fail\) 指针对应的节点的相同子节点,让子节点入队。
- 如果子节点不存在,当前子节点指向父节点的 \(fail\) 指针对应的节点的相同子节点。
可能 \(4\) 操作较难理解一些,个人的理解是可以类比并查集的路径压缩,这样如果有其他节点的 \(fail\) 指针找到了一个空节点,就不用一下一下的跳 \(fail\) 指针了,保证了时间复杂度。
继续偷 OI-Wiki 的图来感受一下:
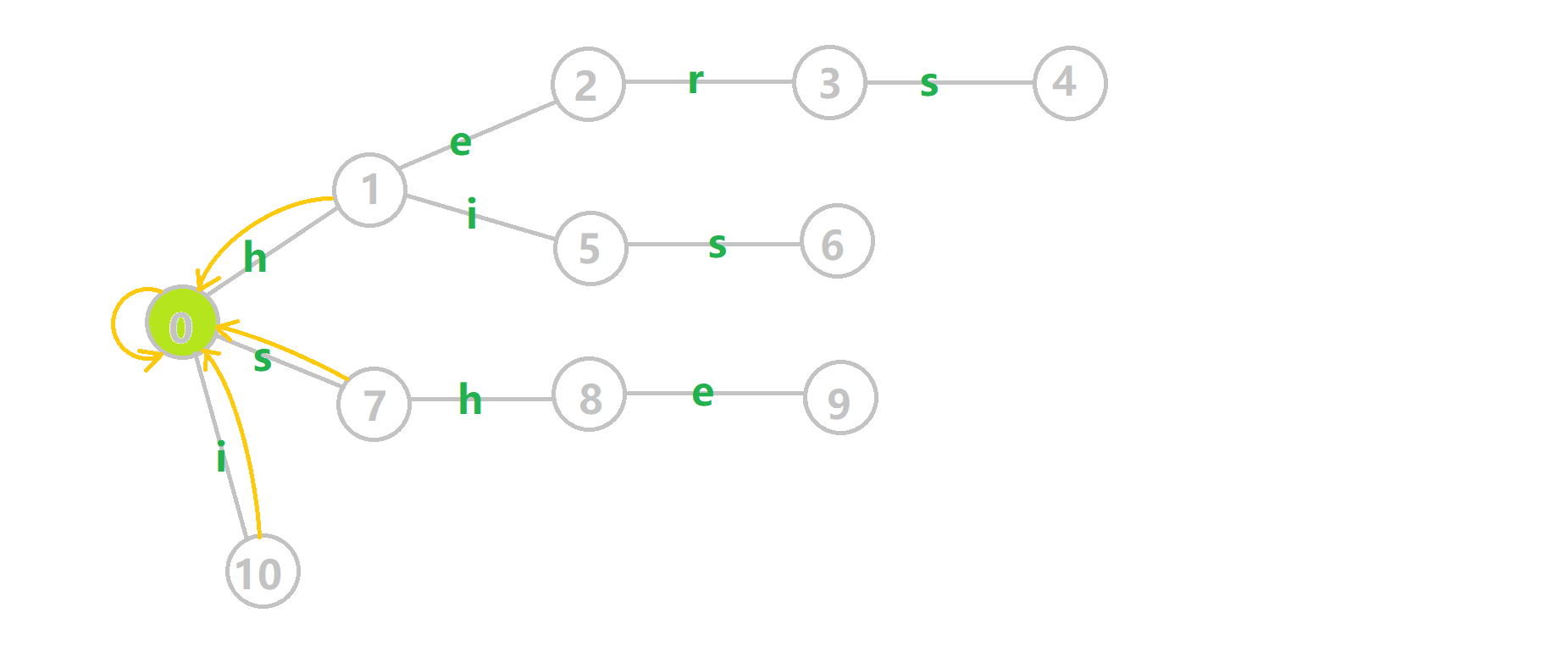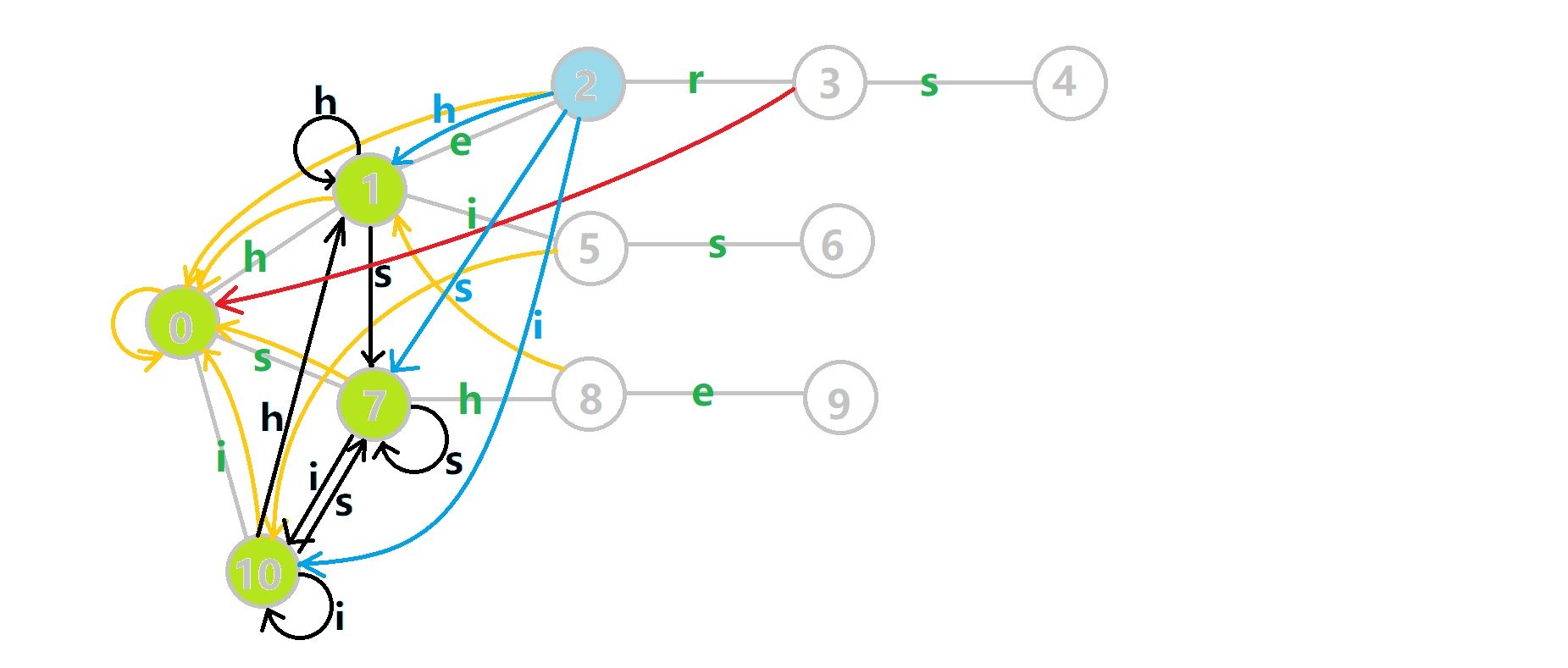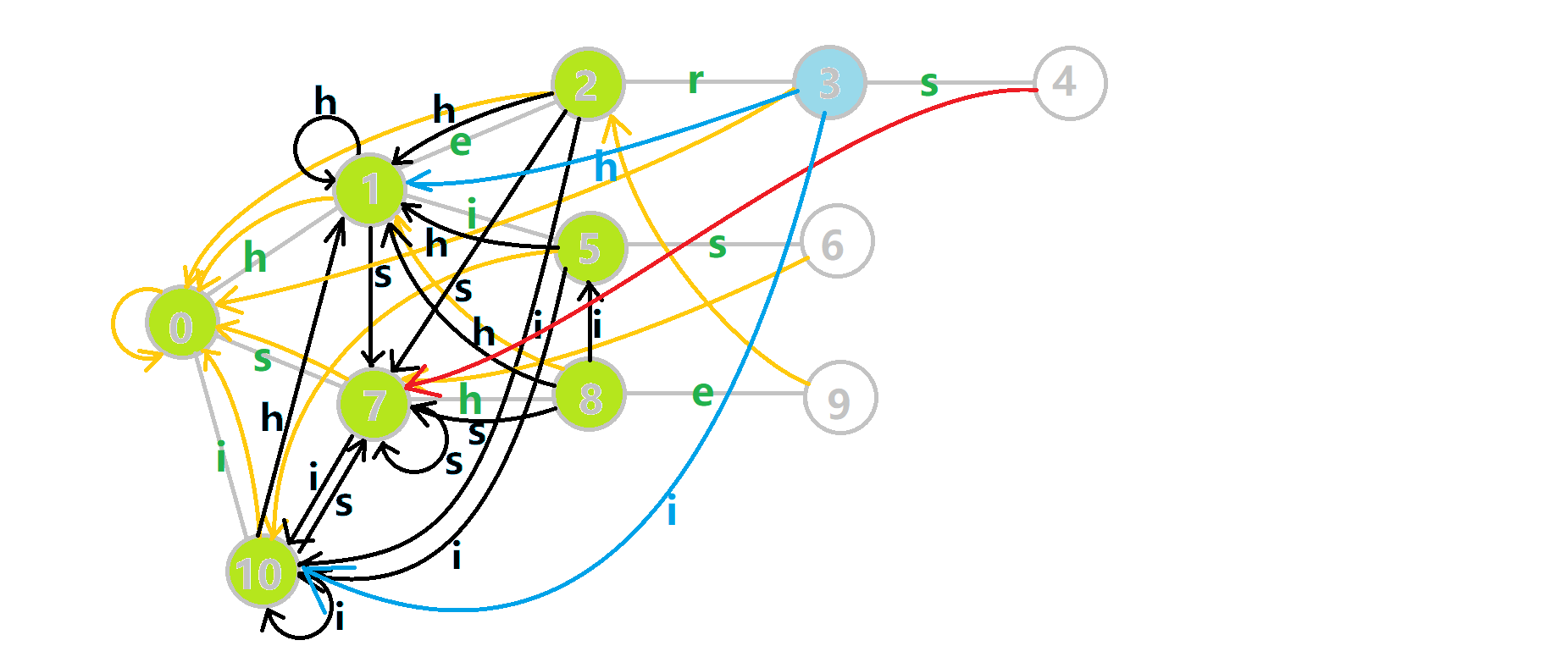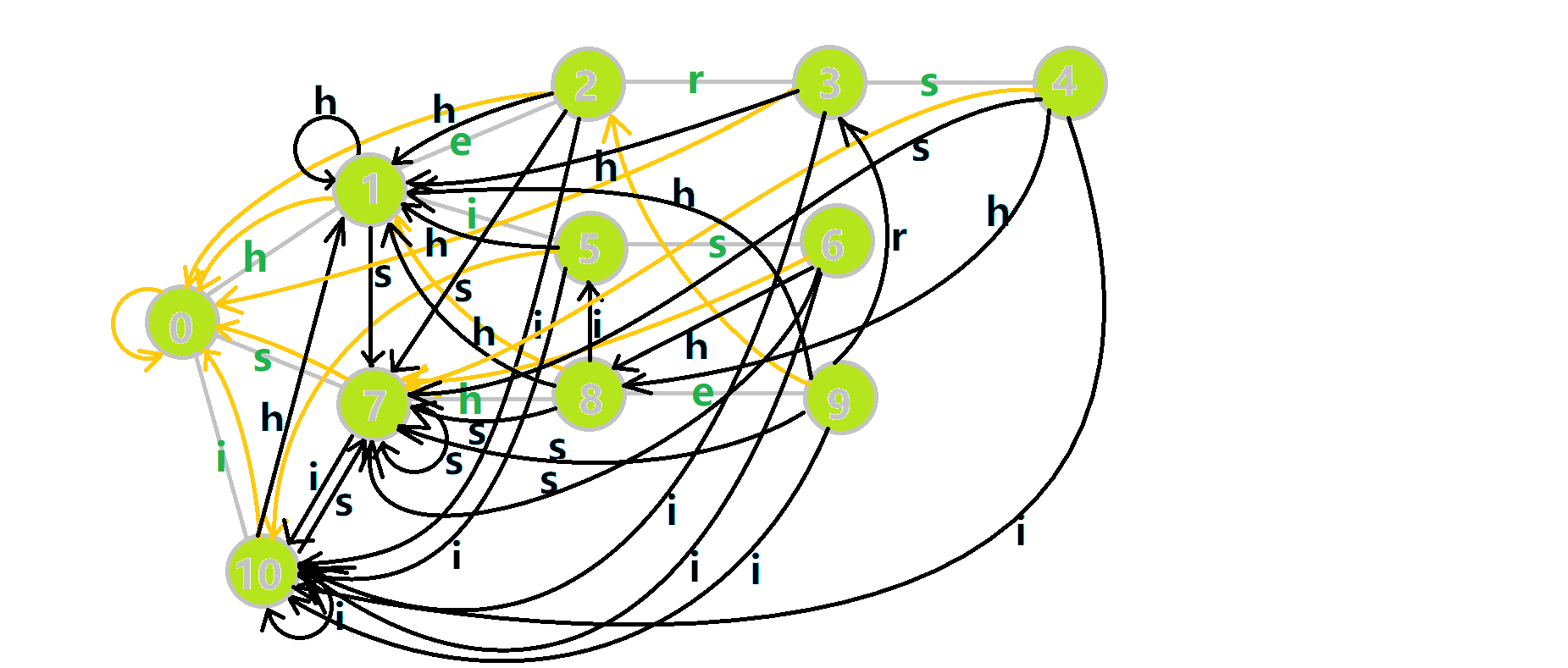
- 蓝色结点:BFS 遍历到的结点 \(u\)。
- 蓝色的边:当前结点下,AC自动机修改字典树结构连出的边。
- 黑色的边:AC自动机修改字典树结构连出的边。
- 红色的边:当前结点求出的 \(fail\) 指针。
- 黄色的边:fail 指针。
- 灰色的边:字典树的边。
可以发现,众多交错的黑色边将字典树变成了字典图。
Code
void Build(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
if(ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]), fail[ch[0][i]] = 0; //第一层的fail指针指向根节点
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){ //枚举每个子节点
if(ch[u][i]){
q.push(ch[u][i]);
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
查询
查询就简单一些了,考虑到 \(fail\) 指针指向当前状态的最长的后缀,如果当前状态匹配成功的话,它的最长后缀肯定也能匹配成功,所以跳 \(fail\) 指针就能找到以当前节点为结尾的模式串的出现次数。
继续用 OI-Wiki 的图来举例(匹配文本串 ushersheishis):
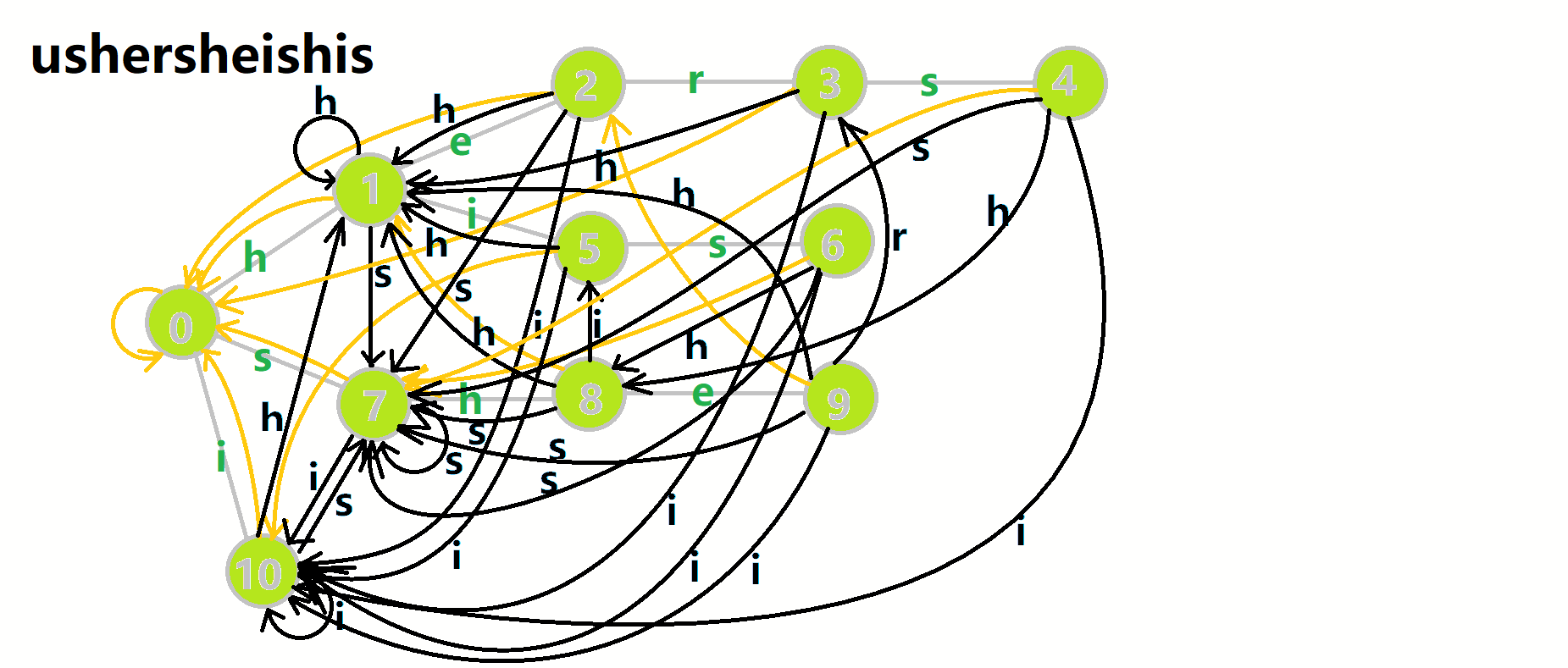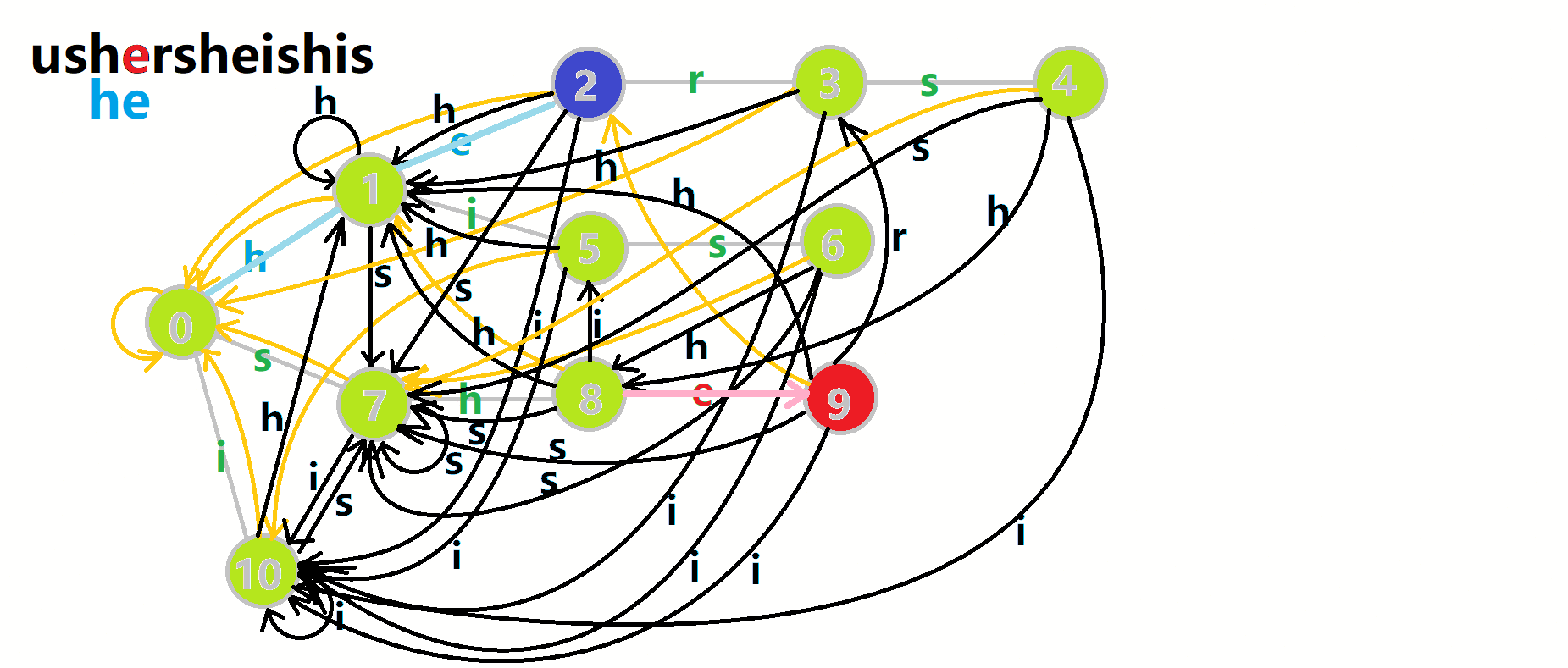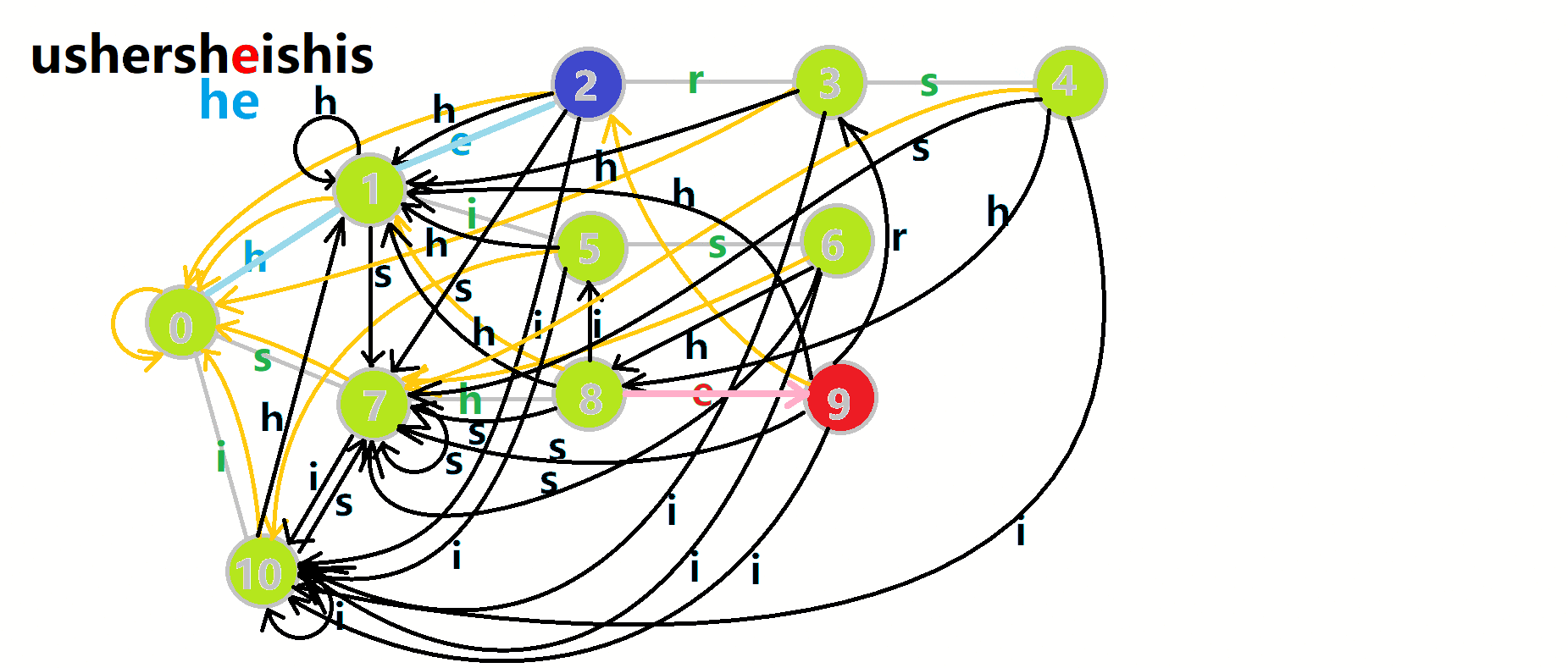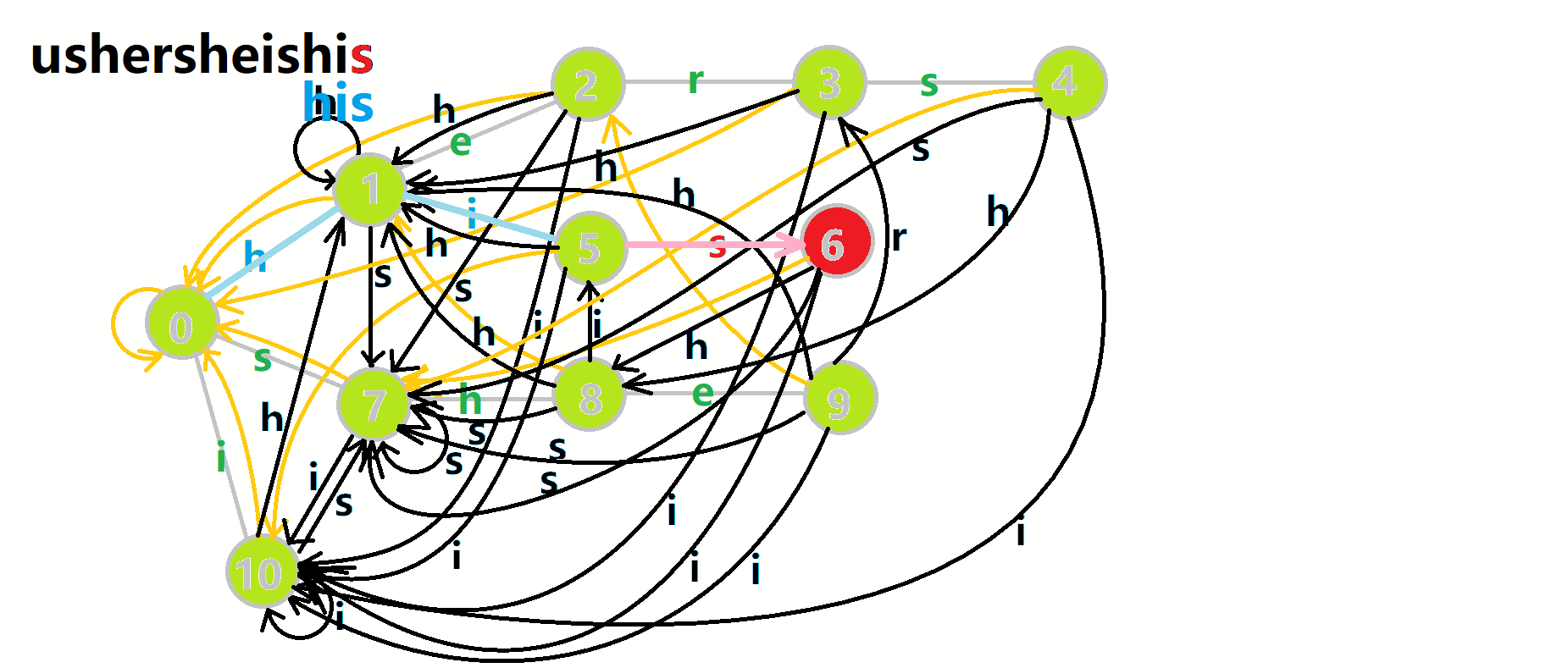
- 红色结点:\(p\) 结点。
- 粉色箭头:\(p\) 在自动机上的跳转。
- 蓝色的边:成功匹配的模式串。
- 蓝色结点:示跳 \(fail\) 指针时的结点(状态)。
Code
void Query(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a'; u = ch[u][v];
for(register int t = u; t; t = fail[t]) ++ans[val[t]];
}
}
时间复杂度
设 \(|S|\) 为模式串的长度,\(|T|\) 为文本串的长度,\(|Σ|\) 为字符集的大小,如果连了 trie 图,时间复杂度为 \(O(\sum|S| + n|Σ| + |T|)\),其中 \(n\) 为AC自动机中节点的数目。如果不连 trie 图,并且在构建 \(fail\) 指针的时候避免遍历到空儿子,时间复杂度就是 \(O(\sum|S| + |T|)\)。
例题
P3808 【模板】AC 自动机(简单版)
模板题,不过这道题只要求模式串出现过没有,所以每个模式串的结尾只用访问一遍,不然 #1 直接T飞,打个标记就行了。
Code
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 10;
const int SIZE = 26;
int n, tot;
int pos[MAXN], ans[MAXN];
char s[MAXN], t[MAXN];
struct Aho_Corasick_Automaton{
int sz;
int val[MAXN * 25];
int fail[MAXN * 25];
int ch[MAXN * 25][SIZE];
void Insert(char *s, int id){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a';
if(!ch[u][v]) ch[u][v] = ++sz;
u = ch[u][v];
}
if(!val[u]) val[u] = id;
pos[id] = val[u];
}
void Build(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
if(ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]), fail[ch[0][i]] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){
if(ch[u][i]){
q.push(ch[u][i]);
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
void Query(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a'; u = ch[u][v];
for(register int t = u; t && val[t] != -1; t = fail[t])
++ans[val[t]], val[t] = -1;
}
}
}A;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%s", s + 1);
A.Insert(s, i);
}
scanf("%s", t + 1);
A.Build(), A.Query(t);
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(ans[pos[i]]) ++tot;
printf("%d", tot);
return 0;
}
P3796 【模板】AC 自动机(加强版)
简简单单的查询,查询出来后给模式串排个序就行了。
Code
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e6 + 10, MAXM = 155;
const int SIZE = 26, LENTH = 75;
int n, maxn;
char t[MAXN];
char s[MAXM][LENTH];
struct Anser{
int pos, num;
}ans[MAXM];
bool cmp(const Anser &a, const Anser &b){
if(a.num != b.num) return a.num > b.num;
return a.pos < b.pos;
}
struct Aho_Corasick_Automaton{
int sz;
int val[MAXN];
int fail[MAXN];
int ch[MAXN][SIZE];
void Insert(char *s, int id){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a';
if(!ch[u][v]) ch[u][v] = ++sz;
u = ch[u][v];
}
val[u] = id;
}
void Build(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
if(ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]), fail[ch[0][i]] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){
if(ch[u][i]) q.push(ch[u][i]), fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
void Query(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a'; u = ch[u][v];
for(register int t = u; t; t = fail[t]) ++ans[val[t]].num;
}
}
}A;
void Clear(){
A.sz = 0;
memset(A.ch, 0, sizeof(A.ch));
memset(A.val, 0, sizeof(A.val));
memset(A.fail, 0, sizeof(A.fail));
}
int main(){
while(true){
Clear();
scanf("%d", &n);
if(n == 0) break;
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%s", s[i] + 1);
ans[i].pos = i, ans[i].num = 0;
A.Insert(s[i], i);
}
scanf("%s", t + 1);
A.Build();
A.Query(t);
sort(ans + 1, ans + 1 + n, cmp);
maxn = ans[1].num;
printf("%d\n", maxn);
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(ans[i].num != maxn) break;
else puts(s[ans[i].pos] + 1);
}
}
return 0;
}
拓扑排序优化
其实暴力跳 \(fail\) 指针的最坏时间复杂度是 \(O(\sum|S| \times |T|)\) 的。当我们构造出一组数据使得每次跳 \(fail\) 指针只使得深度减 \(1\),那每一次跳都要跳深度次,直接T飞。
那怎么才能在统计次数的时候让 trie 上的每个节点都只经过一次?
考虑把 \(fail\) 指针看做一条条的有向边,对一个点进行操作,沿着这个点连出去的点也会进行操作,其实就是跳 \(fail\)。
那可不可以给找到的点打一个标记,最后一次性将全部的标记上传来更新路径上的点。答案是肯定的。不难发现这种统计方法和暴力跳 \(fail\) 得到的答案一样。然后去考虑用什么方法统计。
明显,打标记后要从深度大的点开始更新,所以使用拓扑排序。同时由于 \(fail\) 指针指向的是当前状态的最长后缀,所以整个字典图其实是个 \(DAG\),可以跑拓扑排序。
由于视 \(fail\) 指针为有向边,所以一个点的入度可能很多,但出度最多就是 \(1\),所以不用再另建图了,直接按照 \(fail\) 指针跑就行。
实现:
构建 \(fail\) 指针的时候我们顺便记录一下入度。
查询的时候只要记录当前节点被文本串经过了几次。
最后再跑一遍拓扑排序就行了。
Code
void Build(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
if(ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]), fail[ch[0][i]] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){
if(ch[u][i]){
q.push(ch[u][i]);
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
++in[fail[ch[u][i]]]; //记录入度,其余的都相同
}
else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
void Query(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a'; u = ch[u][v];
++cnt[u]; //仅仅记录该节点被经过了几次就行
}
}
void Topsort(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i <= sz; i++)
if(!in[i]) q.push(i); //没有入度的节点深度一定最深
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
ans[val[u]] = cnt[u]; //统计答案
int v = fail[u]; --in[v];
cnt[v] += cnt[u]; //累加被经过的次数
if(!in[v]) q.push(v);
}
}
P5357 【模板】AC 自动机(二次加强版)
粘板子就能过。
Code
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10, MAXM = 2e6 + 10;
const int SIZE = 26;
int n;
int ans[MAXN], pos[MAXN];
char t[MAXN], s[MAXM];
struct Aho_Corasick_Automaton{
int sz;
int in[MAXN * 25];
int val[MAXN * 25], cnt[MAXN * 25];
int fail[MAXN * 25];
int ch[MAXN * 25][SIZE];
void Insert(char *s, int id){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a';
if(!ch[u][v]) ch[u][v] = ++sz;
u = ch[u][v];
}
if(!val[u]) val[u] = id;
pos[id] = val[u];
}
void Build(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
if(ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]), fail[ch[0][i]] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){
if(ch[u][i]){
q.push(ch[u][i]);
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
++in[fail[ch[u][i]]];
}
else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
void Query(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a'; u = ch[u][v];
++cnt[u];
}
}
void Topsort(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i <= sz; i++)
if(!in[i]) q.push(i);
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
ans[val[u]] = cnt[u];
int v = fail[u]; --in[v];
cnt[v] += cnt[u];
if(!in[v]) q.push(v);
}
}
}A;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%s", t + 1);
A.Insert(t, i);
}
scanf("%s", s + 1);
A.Build(), A.Query(s), A.Topsort();
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[pos[i]]);
return 0;
}
P3966 [TJOI2013]单词
也很板,把所有的模式串插进去,每个文本串都在AC自动机里跑一遍,最后再跑一遍拓扑排序统计答案即可。
Code
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 210, MAXM = 1e6 + 10;
const int SIZE = 26;
int n;
int ans[MAXN], pos[MAXN];
char s[MAXN][MAXM];
struct Aho_Corasick_Automaton{
int sz;
int in[MAXM * 25];
int val[MAXM * 25], cnt[MAXM * 25];
int fail[MAXM * 25];
int ch[MAXM * 25][SIZE];
void Insert(char *s, int id){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a';
if(!ch[u][v]) ch[u][v] = ++sz;
u = ch[u][v];
}
if(!val[u]) val[u] = id;
pos[id] = val[u];
}
void Build(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
if(ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]), fail[ch[0][i]] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){
if(ch[u][i]){
q.push(ch[u][i]);
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
++in[fail[ch[u][i]]];
}
else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
void Query(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = s[i] - 'a'; u = ch[u][v];
++cnt[u];
}
}
void Topsort(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 1; i <= sz; i++)
if(!in[i]) q.push(i);
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
ans[val[u]] = cnt[u];
int v = fail[u]; --in[v];
cnt[v] += cnt[u];
if(!in[v]) q.push(v);
}
}
}A;
int main(){
scanf("%d", &n);
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
scanf("%s", s[i] + 1);
A.Insert(s[i], i);
}
A.Build();
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) A.Query(s[i]);
A.Topsort();
for(register int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("%d\n", ans[pos[i]]);
return 0;
}
P5231 [JSOI2012]玄武密码
稍微需要想一下的板子题,我们视文字段为模式串,母串为文本串,建出AC自动机。在匹配文本串时遍历过的节点 \(u\) 代表的状态一定存在于文本串上,所以我们可以给节点 \(u\) 打上标记,再重新遍历每个模式串在AC自动机里的节点,有标记即可更新答案。
Code
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 1e7 + 10, MAXM = 1e5 + 10;
const int SIZE = 4, LENTH = 110;
int n, m;
char s[MAXN];
char t[MAXM][LENTH];
int Calc(char c){
if(c == 'E') return 0;
if(c == 'S') return 1;
if(c == 'W') return 2;
if(c == 'N') return 3;
}
struct Aho_Corasick_Automaton{
int sz;
int val[MAXN * 25], cnt[MAXN * 25];
int fail[MAXN * 25];
int ch[MAXN * 25][SIZE];
void Insert(char *s, int id){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = Calc(s[i]);
if(!ch[u][v]) ch[u][v] = ++sz;
u = ch[u][v];
}
val[u] = id;
}
void Build(){
queue<int> q;
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++)
if(ch[0][i]) q.push(ch[0][i]), fail[ch[0][i]] = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for(register int i = 0; i < SIZE; i++){
if(ch[u][i]){
q.push(ch[u][i]);
fail[ch[u][i]] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
else ch[u][i] = ch[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
void Query(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = Calc(s[i]); u = ch[u][v];
for(register int t = u; t && val[t] != -1; t = fail[t])
cnt[t] = 1, val[t] = -1;
}
}
int Find(char *s){
int len = strlen(s + 1), u = 0, ans = 0;
for(register int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int v = Calc(s[i]); u = ch[u][v];
if(cnt[u]) ans = i;
}
return ans;
}
}A;
int main(){
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
scanf("%s", s + 1);
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
scanf("%s", t[i] + 1), A.Insert(t[i], i);
A.Build(), A.Query(s);
for(register int i = 1; i <= m; i++) printf("%d\n", A.Find(t[i]));
return 0;
}
以下为博客签名,与博文无关。
只要你们不停下来,那前面就一定有我。所以啊,不要停下来~
本文来自博客园,作者:TSTYFST,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/TSTYFST/p/16875307.html


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号