动态规划-最长公共子序列与最长公共子串
1.最长公共子序列
参考博客:
http://blog.csdn.net/hrn1216/article/details/51534607
http://blog.csdn.net/u013074465/article/details/45392687
代码:

#include <stdio.h> #include <memory.h> #include <math.h> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #define I scanf #define OL puts #define O printf #define F(a,b,c) for(a=b;a<c;a++) #define FF(a,b) for(a=0;a<b;a++) #define FG(a,b) for(a=b-1;a>=0;a--) #define LEN 101 #define MAX 1<<30 #define V vector<int> using namespace std; int a[LEN],b[LEN]; int dp[LEN][LEN]; int N,M; vector<vector<int> > ans; void printDP(){ int i,j; F(i,1,N+1){ F(j,1,M+1){ O("%d\t",dp[i][j]); } OL("\n"); } } void buildLCS(int x,int y,V vec){ while(x>0 && y>0){ if(a[x]==b[y]){ vec.push_back(a[x]); x--;y--; }else{ if(dp[x-1][y]>dp[x][y-1]){ x--; }else if(dp[x-1][y]<dp[x][y-1]){ y--; }else{ buildLCS(x,y-1,vec); x--; } } } int i=vec.size()-1; while(i>=0){ O("%d ",vec[i]); i--; } OL(""); } int main(){ freopen("LCS.txt","r",stdin); int i,j; scanf("%d",&N); F(i,1,N+1) I("%d",&a[i]); scanf("%d",&M); F(i,1,M+1) I("%d",&b[i]); F(i,1,N+1){ F(j,1,M+1){ if(a[i]==b[j]) dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1; else dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]); } } printDP(); O("最长公共子序列长度: %d\n",dp[N][M]); V vec; buildLCS(N,M,vec); return 0; }
测试数据:
9 3 5 7 4 8 6 7 8 2 8 1 3 4 5 6 7 7 8
2.最长公共子串
代码:

#include <stdio.h> #include <memory.h> #include <math.h> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #define I scanf #define OL puts #define O printf #define F(a,b,c) for(a=b;a<c;a++) #define FF(a,b) for(a=0;a<b;a++) #define FG(a,b) for(a=b-1;a>=0;a--) #define LEN 101 #define MAX 1<<30 #define V vector<int> using namespace std; int a[LEN],b[LEN]; int dp[LEN][LEN]; int N,M; vector<vector<int> > ans; void printDP(){ int i,j; F(i,1,N+1){ F(j,1,M+1){ O("%d\t",dp[i][j]); } OL("\n"); } } int main(){ freopen("最长公共子串.txt","r",stdin); int i,j; scanf("%d",&N); F(i,1,N+1) I("%d",&a[i]); scanf("%d",&M); F(i,1,M+1) I("%d",&b[i]); int mx,my,mlen=0; F(i,1,N+1){ F(j,1,M+1){ if(a[i]==b[j]){ dp[i][j]=dp[i-1][j-1]+1; if(mlen<dp[i][j]){ mlen=dp[i][j]; mx=i; my=j; } } else dp[i][j]=0; } } printDP(); O("最长公共子序列长度: %d\n",mlen); V ans; while(dp[mx][my]){ ans.insert(ans.begin(),a[mx]); mx--;my--; } FF(i,ans.size()){ printf("%d ",ans[i]); } return 0; }
测试数据:
9 3 5 7 4 8 6 7 8 2 8 1 3 4 8 6 7 7 8
3.相似基因
代码:

#include <stdio.h> #include <memory.h> #include <math.h> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <queue> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #define I scanf #define OL puts #define O printf #define F(a,b,c) for(a=b;a<c;a++) #define FF(a,b) for(a=0;a<b;a++) #define FG(a,b) for(a=b-1;a>=0;a--) #define LEN 110 #define MAX 1<<30 #define V vector<int> using namespace std; int dp[LEN][LEN]; int mat[5][5]={ {5,-1,-2,-1,-3}, {-1,5,-3,-2,-4}, {-2,-3,5,-2,-2}, {-1,-2,-2,5,-1}, {-3,-4,-2,-1,0}}; int to(char ch){ if(ch=='A') return 0; else if(ch=='C') return 1; else if(ch=='G') return 2; else if(ch=='T') return 3; else return 4; } int main(){ // freopen("相似基因.txt","r",stdin); int an,bn,i,j; char buf[LEN]; string a,b; I("%d",&an); I("%s",buf); a=buf; a.insert(0,"#"); I("%d",&bn); I("%s",buf); b=buf; b.insert(0,"#"); memset(dp,-127,sizeof(dp)); dp[0][0]=0; for(i=0;i<=an;i++){ for(j=0;j<=bn;j++){ if(i && j) dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][j-1] + mat[to(a[i])][to(b[j])] ); if(i) dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j],dp[i-1][j] + mat[to(a[i])][4] ); if(j) dp[i][j]=max(dp[i][j],dp[i][j-1] + mat[4][to(b[j])] ); } } printf("%d",dp[an][bn]); return 0; }
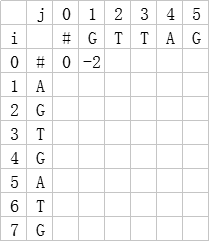
理解: 在边界条件的限制下,有三种情况:
1. 当前基因与对象基因进行匹配, =dp[i-1][j-1]+f(i,j)
2. 当前基因放弃匹配,插入一个“-”(空符号) =dp[i-1][j]+f(i,∅)
3. 对象基因放弃匹配,插入一个“-”(空符号) =dp[i][j-1]+f(∅,j)
基本思路与LCS相同




