Prim算法
今天学习了prim算法。严奶奶的代码我没看懂,毕竟她都80岁了。算了,我自己按照书上的描述写了一个。
今天学习的Java知识点:调用类中的类进行变量声明可以使用 className.innerClassName objectName 这种声明方式。
解题所用数据结构:邻接矩阵。
可视化:
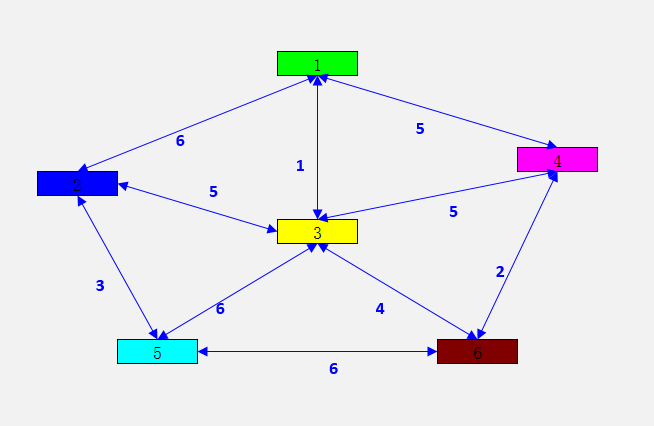
邻接矩阵prim.txt:(-1代表 ∞ )
-1 6 1 5 -1 -1
6 -1 5 -1 3 -1
1 5 -1 5 6 4
5 -1 5 -1 -1 2
-1 3 6 -1 -1 6
-1 -1 4 2 6 -1
解题代码:(Java)
1 void prim(){ 2 int i,j; 3 List<Integer> V=new ArrayList<Integer>();//集合V 4 List<Integer> U=new ArrayList<Integer>();//集合U 5 for(i=1;i<vexnum;i++) V.add(i); //V初始化 6 U.add(0); //U初始化 7 while(V.size()>0){ 8 int min=10000; 9 int a=0;//源点 10 int b=0;//目标点 11 for(i=0;i<U.size();i++){//取出U中每一个元素 12 int u=U.get(i);//每一次取出的元素 13 for(j=0;j<V.size();j++){//j 14 int v=V.get(j); 15 int value=adjMatrix[u][v];//取出的元素 16 if(value!=-1 && value<min){ 17 min=value; 18 a=u; 19 b=v; 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 U.add(b); 24 V.remove(V.indexOf(b)); 25 System.out.println(a+"->"+b); 26 } 27 }
输出:
0->2
2->5
5->3
2->1
1->4
今天编写的完整代码:(Java)
1 import java.io.*; 2 import java.util.*; 3 4 public class demo { 5 public static void main(String args[]){ 6 Graph grath=new Graph("D:/JavaWorkspace/图状结构/prim.txt"); 7 System.out.println("邻接矩阵:"); 8 System.out.println(grath); 9 System.out.println("邻接链表:"); 10 System.out.println(grath.getListStr()); 11 System.out.println("最小生成树:"); 12 grath.prim(); 13 } 14 } 15 16 class Graph{ 17 int [][] adjMatrix;//adjacency matrix 邻接矩阵数据结构 18 int vexnum=0; //顶点数目 19 AdjList adjList=null; 20 class AdjList{ //邻接表 21 class VNode{ //顶点节点。头节点 22 int index=0;//顶点编号 23 ANode firstArc=null;//第一个弧节点 24 } 25 class ANode{ //弧节点 26 int adjVex=0; //所指向顶点位置 27 ANode nextArc=null; //下一条弧 28 } 29 VNode vnodes[]=null; 30 AdjList(){ 31 } 32 AdjList(int [][] nums,int v){//用二维数组进行构造 33 vnodes=new VNode[v]; 34 int i,j; 35 for(i=0;i<v;i++){ 36 vnodes[i]=new VNode(); 37 vnodes[i].index=i+1;//顶点数组初始化 38 } 39 for(i=0;i<v;i++){ 40 for(j=0;j<v;j++){ //对邻接矩阵进行遍历 41 if(nums[i][j]!=-1){ //有元素 42 ANode arc=new ANode(); 43 arc.adjVex=j; 44 if(vnodes[i].firstArc==null) vnodes[i].firstArc=arc; 45 else{ 46 ANode node=vnodes[i].firstArc; 47 while(node.nextArc!=null) node=node.nextArc; 48 node.nextArc=arc; //勾链 49 } 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 String getListStr(){//打印邻接链表 56 int i; 57 String str=new String(); 58 for(i=0;i<vexnum;i++){ 59 str+=Integer.toString(adjList.vnodes[i].index); 60 str+=":"; 61 AdjList.ANode node=adjList.vnodes[i].firstArc; 62 while(node!=null){ 63 str+=Integer.toString(node.adjVex); 64 str+="->"; 65 node=node.nextArc; 66 } 67 str+="∧\n"; 68 } 69 return str; 70 } 71 public String toString(){ 72 String str=new String(); 73 int i,j; 74 for(i=0;i<vexnum;i++){ 75 for(j=0;j<vexnum;j++){ //对邻接矩阵进行遍历 76 str+=Integer.toString(adjMatrix[i][j]); 77 str+=" "; 78 } 79 str+="\n"; 80 } 81 return str; 82 } 83 Graph(String path){//通过文件路径,输入文件来读取邻接矩阵 84 String content=MyFile.readFile(path);//读取文件内容 85 String lines[]=content.split("\n"); 86 String probe[]; 87 vexnum=lines.length; 88 adjMatrix=new int[vexnum][vexnum];//刻画邻接矩阵大小 89 90 int i,j; 91 for(i=0;i<lines.length;i++){ 92 probe=lines[i].split(" "); 93 for(j=0;j<probe.length;j++){ 94 adjMatrix[i][j]=Integer.valueOf(probe[j]).intValue();//要对integer进行拆包 95 } 96 } 97 adjList=new AdjList(adjMatrix,lines.length);//构造本类中的邻接链表 98 } 99 /* class CloseEdge{ //记录 U-V 中各顶点到 U 中权值最小的边 100 int adjvex=0; //边所依附于 U 中的顶点 101 int lowcost=0; //这条边的权值(代价最小) 102 } 103 CloseEdge closedge[]=new CloseEdge[vexnum];//构建数组 104 */ 105 void prim(){ 106 int i,j; 107 List<Integer> V=new ArrayList<Integer>();//集合V 108 List<Integer> U=new ArrayList<Integer>();//集合U 109 for(i=1;i<vexnum;i++) V.add(i); //V初始化 110 U.add(0); //U初始化 111 while(V.size()>0){ 112 int min=10000; 113 int a=0;//源点 114 int b=0;//目标点 115 for(i=0;i<U.size();i++){//取出U中每一个元素 116 int u=U.get(i);//每一次取出的元素 117 for(j=0;j<V.size();j++){//j 118 int v=V.get(j); 119 int value=adjMatrix[u][v];//取出的元素 120 if(value!=-1 && value<min){ 121 min=value; 122 a=u; 123 b=v; 124 } 125 } 126 } 127 U.add(b); 128 V.remove(V.indexOf(b)); 129 System.out.println(a+"->"+b); 130 } 131 } 132 private boolean findInNum(int[] arr,int obj){ 133 for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) if(arr[i]==obj) return true; 134 return false; 135 } 136 137 138 } 139 140 class MyFile{ 141 142 /** 143 * 创建文件 144 * @param fileName 文件名称 145 * @param filecontent 文件内容 146 * @return 是否创建成功,成功则返回true 147 */ 148 public static boolean createFile(String fileName){ 149 boolean bool = false; 150 File file = new File(fileName); 151 try { 152 //如果文件不存在,则创建新的文件 153 if(!file.exists()){ 154 file.createNewFile(); 155 bool = true; 156 System.out.println("success create file,the file is "+fileName); 157 } 158 } catch (Exception e) { 159 e.printStackTrace(); 160 } 161 return bool; 162 } 163 164 /** 165 * 向文件中写入内容 166 * @param filepath 文件路径与名称 167 * @param newstr 写入的内容 168 * @return 169 * @throws IOException 170 */ 171 public static boolean writeFile(String filepath,String newstr) throws IOException{ 172 boolean bool = false; 173 String filein = newstr+"\r\n";//新写入的行,换行 174 String temp = ""; 175 176 FileInputStream fis = null; 177 InputStreamReader isr = null; 178 BufferedReader br = null; 179 FileOutputStream fos = null; 180 PrintWriter pw = null; 181 try { 182 File file = new File(filepath);//文件路径(包括文件名称) 183 //将文件读入输入流 184 fis = new FileInputStream(file); 185 isr = new InputStreamReader(fis); 186 br = new BufferedReader(isr); 187 StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(); 188 189 //文件原有内容 190 for(int i=0;(temp =br.readLine())!=null;i++){ 191 buffer.append(temp); 192 // 行与行之间的分隔符 相当于“\n” 193 buffer = buffer.append(System.getProperty("line.separator")); 194 } 195 buffer.append(filein); 196 197 fos = new FileOutputStream(file); 198 pw = new PrintWriter(fos); 199 pw.write(buffer.toString().toCharArray()); 200 pw.flush(); 201 bool = true; 202 } catch (Exception e) { 203 // TODO: handle exception 204 e.printStackTrace(); 205 }finally { 206 //不要忘记关闭 207 if (pw != null) { 208 pw.close(); 209 } 210 if (fos != null) { 211 fos.close(); 212 } 213 if (br != null) { 214 br.close(); 215 } 216 if (isr != null) { 217 isr.close(); 218 } 219 if (fis != null) { 220 fis.close(); 221 } 222 } 223 return bool; 224 } 225 226 /** 227 * 删除文件 228 * @param fileName 文件名称 229 * @return 230 */ 231 public static boolean delFile(String fileName){ 232 boolean bool = false; 233 File file = new File(fileName); 234 try { 235 if(file.exists()){ 236 file.delete(); 237 bool = true; 238 } 239 } catch (Exception e) { 240 // TODO: handle exception 241 } 242 return bool; 243 } 244 public static String readFile(String fileName) { 245 File file = new File(fileName); 246 Reader reader = null; 247 String content=new String(); 248 try { 249 // 一次读一个字符 250 reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)); 251 int tempchar; 252 while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) { 253 // 对于windows下,\r\n这两个字符在一起时,表示一个换行。 254 // 但如果这两个字符分开显示时,会换两次行。 255 // 因此,屏蔽掉\r,或者屏蔽\n。否则,将会多出很多空行。 256 if (((char) tempchar) != '\r') { 257 // System.out.print((char) tempchar); 258 content+=((char) tempchar); 259 } 260 } 261 reader.close(); 262 } catch (Exception e) { 263 e.printStackTrace(); 264 } 265 return content; 266 } 267 }
程序完成输出:
邻接矩阵:
-1 6 1 5 -1 -1
6 -1 5 -1 3 -1
1 5 -1 5 6 4
5 -1 5 -1 -1 2
-1 3 6 -1 -1 6
-1 -1 4 2 6 -1
邻接链表:
1:1->2->3->∧
2:0->2->4->∧
3:0->1->3->4->5->∧
4:0->2->5->∧
5:1->2->5->∧
6:2->3->4->∧
最小生成树:
0->2
2->5
5->3
2->1
1->4



