docker 数据挂载的三种方式
前言
我们可以将数据写到容器的可写入层,但是这种写入是有缺点的:
- 当容器停止运行时,写入的数据会丢失。你也很难将这些数据从容器中取出来给另外的应用程序使用。
- 容器的可写入层与宿主机是紧密耦合的。这些写入的数据在可以轻易地被删掉。
- 写入容器的可写入层需要一个存储驱动(
storage driver)来管理文件系统。这个存储驱动通过linux内核提供了一个union filesystem。相比于数据卷(data volume),这种额外的抽象会降低性能。
Docker提供了3种方法将数据从Docker宿主机挂载(mount)到容器:
volumes,bind mountstmpfs mounts。
一般来说,
volumes总是最好的选择。
不管你选择哪种挂载方式,从容器中看都是一样的。数据在容器的文件系统中被展示为一个目录或者一个单独的文件。
一个简单区分volumes,bind mounts和tmpfs mounts不同点的方法是:思考数据在宿主机上是如何存在的。
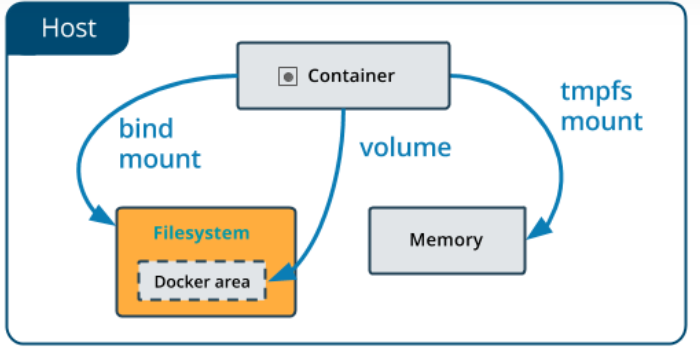
- Volumes由Docker管理,存储在宿主机的某个地方(在linux上是
/var/lib/docker/volumes/)。非Docker应用程序不能改动这一位置的数据。Volumes是Docker最好的数据持久化方法。 - Bind mounts的数据可以存放在宿主机的任何地方。数据甚至可以是重要的系统文件或目录。非Doc
- ker应用程序可以改变这些数据。
- tmpfs mounts的数据只存储在宿主机的内存中,不会写入到宿主机的文件系统。
更详细的Diff
-
Volumes:由Docker创建和管理。你可以通过
docker volume create命令显式地创建volume,Docker也可以在创建容器或服务是自己创建volume。当你创建了一个volume,它会被存放在宿主机的一个目录下。当你将这个volume挂载到某个容器时,这个目录就是挂载到容器的东西。这一点和
bind mounts类似,除了volumes是由Docker创建的,和宿主机的核心(core functionality)隔离。一个volume可以同时被挂载到几个容器中。即使没有正在运行的容器使用这个volume,volume依然存在,不会被自动清除。可以通过
docker volume prune清除不再使用的volumes。volumes也支持
volume driver,可以将数据存放在另外的机器或者云上。 -
Bind mounts:Docker早期就支持这个特性。与volumes相比,
Bind mounts支持的功能有限。使用bind mounts时,宿主机上的一个文件或目录被挂载到容器上。警告:使用
Bind mounts的一个副作用是,容器中运行的程序可以修改宿主机的文件系统,包括创建,修改,删除重要的系统文件或目录。这个功能可能会有安全问题。 -
tmpfs mounts:
tmpfs mounts的数据不会落盘。在容器的生命周期内,它可以被用来存储一些不需要持久化的状态或敏感数据。例如,swarm服务通过tmpfs mounts来将secrets挂载到一个服务的容器中去。
适合Volumes的场景
- 在不同的容器中共享数据。If you don’t explicitly create it, a volume is created the first time it is mounted into a container. When that container stops or is removed, the volume still exists. Multiple containers can mount the same volume simultaneously, either read-write or read-only. Volumes are only removed when you explicitly remove them.
- When the Docker host is not guaranteed to have a given directory or file structure. Volumes help you decouple the configuration of the Docker host from the container runtime.
- When you want to store your container’s data on a remote host or a cloud provider, rather than locally.
- 当你需要备份或迁移数据的时候,When you need to be able to back up, restore, or migrate data from one Docker host to another, volumes are a better choice. You can stop containers using the volume, then back up the volume’s directory (such as /var/lib/docker/volumes/).
适合bind mounts的场景
- 宿主机和容器共享配置文件。Docker提供的DNS解决方案就是如此,将宿主机的
/etc/resolv.conf挂载到每个容器中。 - 开发环境需要在宿主机和容器中共享代码。docker的开发就是如此,毕竟容器中一般是没有编辑器的
- When the file or directory structure of the Docker host is guaranteed to be consistent with the bind mounts the containers require.
适合tmpfs mounts的场景
tmpfs mounts主要用在你既不想在容器内,又不想在宿主机文件系统保存数据的时候。这可能是出于安全原因,也可能是你的应用需要写非常多的非持久化数据,tmpfs mounts这时候可以保证容器性能。
使用
volume(-v)
参数
--volume(或简写为-v)只能创建bind mount。示例:
docker run --name $CONTAINER_NAME -it \ -v /localhost/app:/container/app:rw \ -v /localhost/app:/container/app:ro \
nginx:latest /bin/bash
注释:
- 命令格式:
[宿主机目录:]容器目录[:OPTIONS]]] - 如果指定宿主机目录,则必须是绝对路径,如果路径不存在则会自动创建
- 实例中的
rw为读写,ro为只读
--mount
参数
--mount默认情况下用来挂载volume,但也可以用来创建bind mount和tmpfs。如果不指定type选项,则默认为挂载volume,volume是一种更为灵活的数据管理方式,volume可以通过
docker volume命令集被管理。
示例:
docker run --name $CONTAINER_NAME -it \ --mount type=bind,source=$PWD/$CONTAINER_NAME/app,destination=/app \ --mount source=${CONTAINER_NAME}-data,destination=/data,readonly \ avocado-cloud:latest /bin/bash
注释:
- 挂载volume命令格式:[type=volume,]source=my-volume,destination=/path/in/container[,...]
- 创建bind mount命令格式:type=bind,source=/path/on/host,destination=/path/in/container[,...]
- 如果创建bind mount并指定source则必须是绝对路径,且路径必须已经存在
- 示例中readonly表示只读
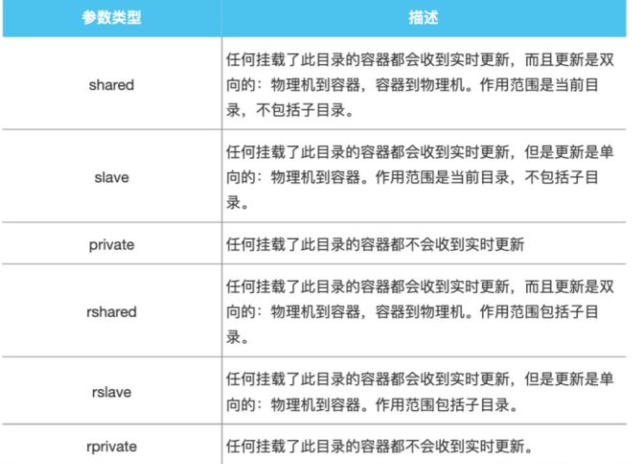
mount 官方文档里面参数有个表格:
原文:
| Propagation setting | Description |
|---|---|
shared |
Sub-mounts of the original mount are exposed to replica mounts, and sub-mounts of replica mounts are also propagated to the original mount. |
slave |
similar to a shared mount, but only in one direction. If the original mount exposes a sub-mount, the replica mount can see it. However, if the replica mount exposes a sub-mount, the original mount cannot see it. |
private |
The mount is private. Sub-mounts within it are not exposed to replica mounts, and sub-mounts of replica mounts are not exposed to the original mount. |
rshared |
The same as shared, but the propagation also extends to and from mount points nested within any of the original or replica mount points. |
rslave |
The same as slave, but the propagation also extends to and from mount points nested within any of the original or replica mount points. |
rprivate |
The default. The same as private, meaning that no mount points anywhere within the original or replica mount points propagate in either direction. |
使用示例:
docker run --name $CONTAINER_NAME -it \ --mount type=bind,source=$PWD/$CONTAINER_NAME/app,destination=/app,bind-Propagation=slave \ avocado-cloud:latest /bin/bash
tmpfs
tmpfs 不在磁盘上持久存储,也不在 Docker 容器里面存储,他存储在 localhost 的内存中,它可以在容器的整个生命周期内被容器所使用。
使用示例:
docker run -d -it -p 80:80 --name tmptest \ --mount type=tmpfs,destination=/usr/share/nginx/html \ nginx:latest
容器对目录所有的读写操作都在内存中。
指定 tmpfs 的权限情况:
docker run -d -it -p 80:80 --name tmptest \ --mount type=tmpfs,destination=/usr/share/nginx/html,tmpfs-mode=1770 \
nginx:latest


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号