1 package com.er;
2
3 import java.math.MathContext;
4 import java.util.Random;
5
6 public class baozhuang {
7
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9
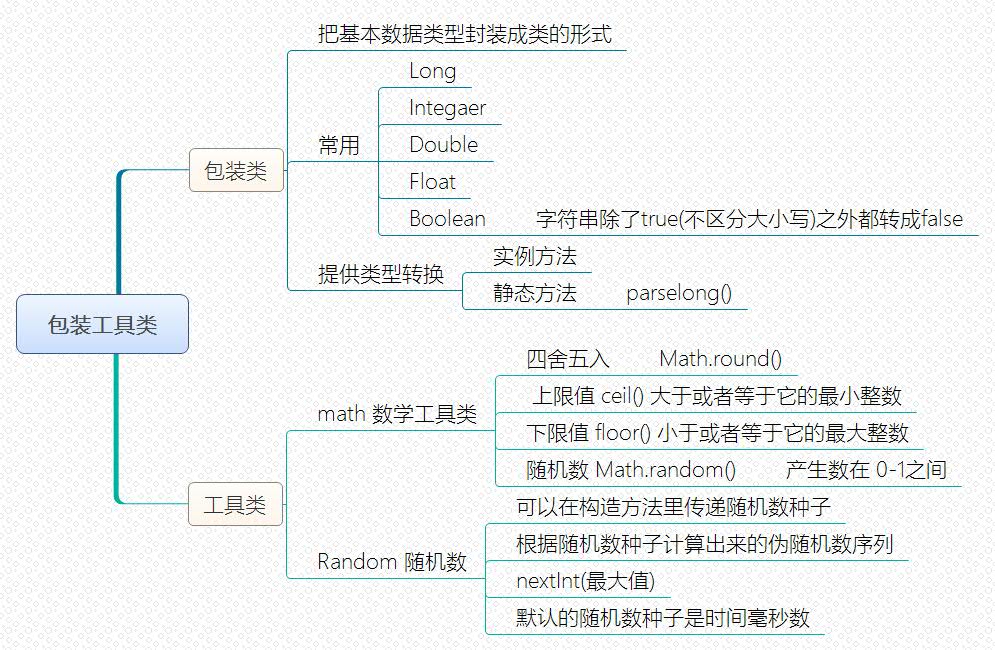
10 //包装类
11 Long l=new Long(100);
12
13 //把字符串转成数值
14 Long l1=new Long("1000");
15
16 String str=1000 + "";
17
18 //包装类转成基本数据类型
19 long l2=l1.longValue();
20
21 System.out.println("12 = "+ 12);
22
23 long l3=Long.parseLong("1200");
24
25 //int
26
27 Integer i=new Integer("1000");
28
29 Integer.parseInt("1000");
30
31 //浮点型
32
33 Float f=new Float("123.456");
34
35 Float.parseFloat("1234.5678");
36
37 Double d=new Double("123456.789");
38
39 Double.parseDouble("123456.789");
40
41 //布尔型
42 Boolean b = new Boolean("TRUE");
43
44 System.out.println(b.booleanValue());
45
46 System.out.println();
47
48 //数学工具类
49
50 System.out.println(Math.PI);
51
52 //四舍五入
53
54 System.out.println(Math.round(1234.46789));
55
56 double de = 1234.5678;
57
58 //保留小数点后两位
59 System.out.println(Math.round(de * 100)/100.0);
60
61 //舍去小数点后数字
62
63 //下限值:小于或等于它的最大整数
64
65 System.out.println(Math.floor(de));
66
67 //上限值:大于或等于它的最小整数
68
69 System.out.println(Math.ceil(de));
70
71 //随机数:0-1之间的数
72
73 System.out.println(Math.random());
74
75 Random r = new Random();
76
77 System.out.println();
78
79 // 随机数种子
80 // 伪随机数
81 // 根据种子计算
82 // 由种子决定随机数的产生系列
83 // 默认使用时间数做种子
84 // r = new Random();
85
86 for (int n = 0;n<10;n++)
87 {
88 System.out.println(r.nextInt(10));
89 }
90
91 92
93
94
95 }
96 }






