0 写在前面
志在顶峰的人,决不会因留恋半山腰的奇花异草而停止攀登的步伐。 ——高尔基
1 基本概念
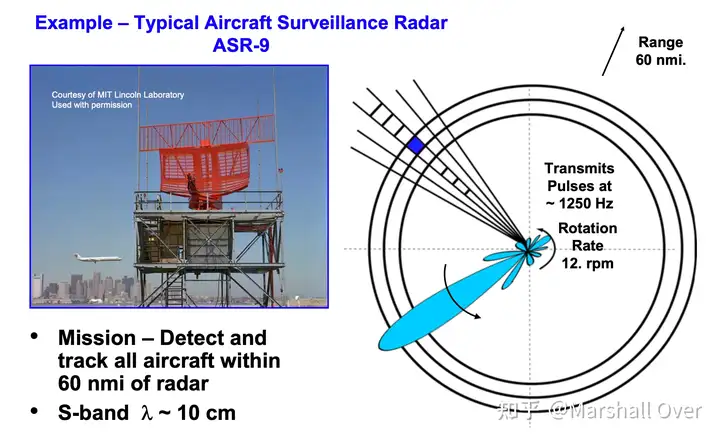
Radar Detection – “The Big Picture”:
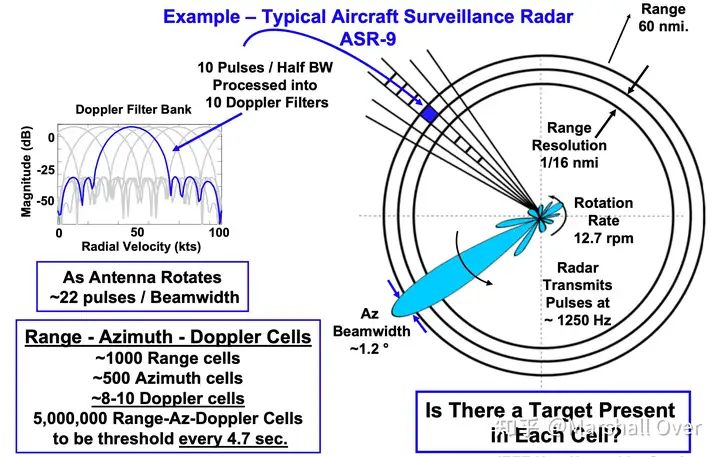
Range-Azimuth-Doppler Cells to Be Thresholded:
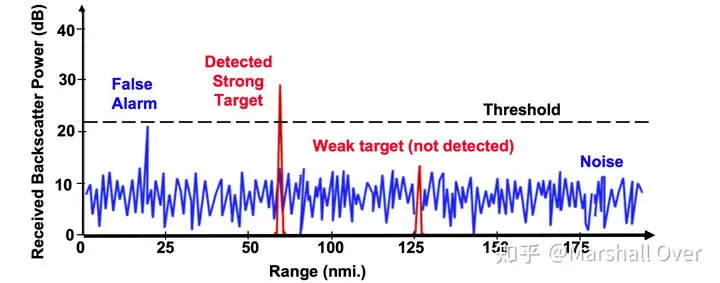
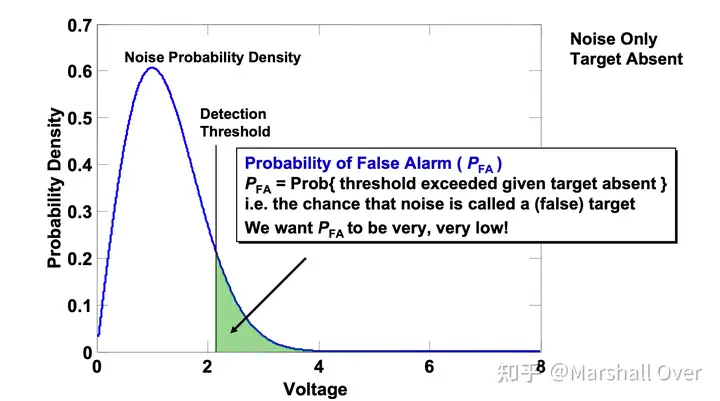
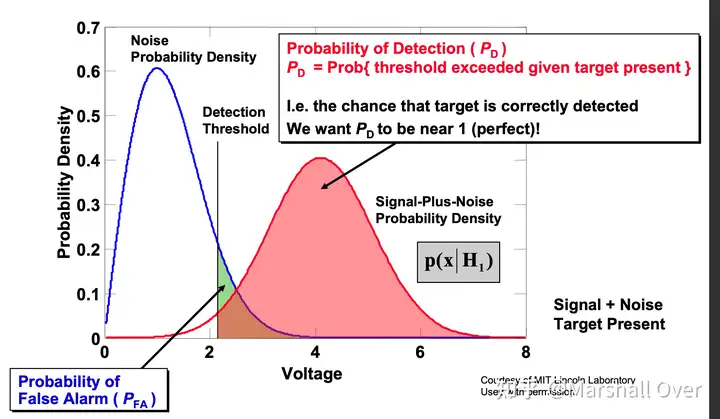
噪声中的目标检测:接收到的背景噪声随机上下波动,目标回波也会波动,两者都是随机变量;为了决定在给定范围内是否存在目标,我们需要设置一个阈值(常数或变量);检测性能(检测概率)取决于目标相对于噪声的强度和阈值设置。
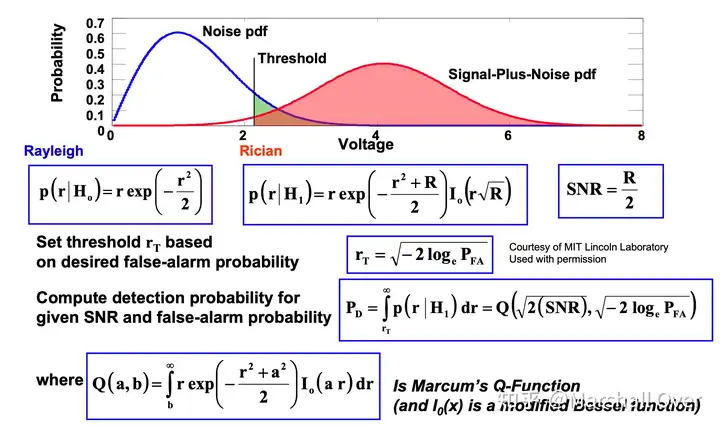
雷达检测问题:
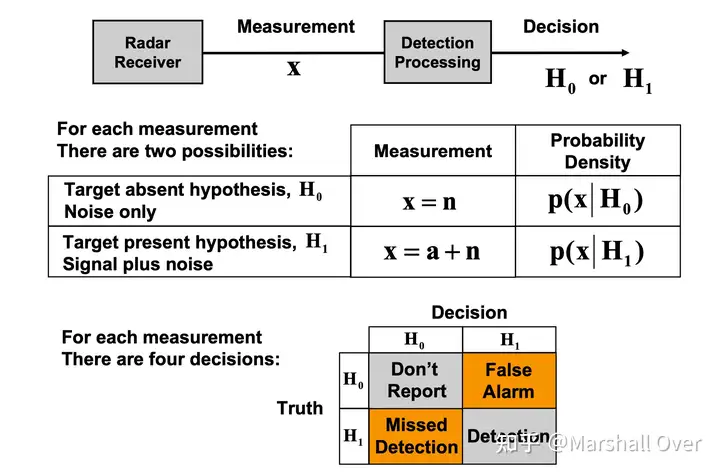
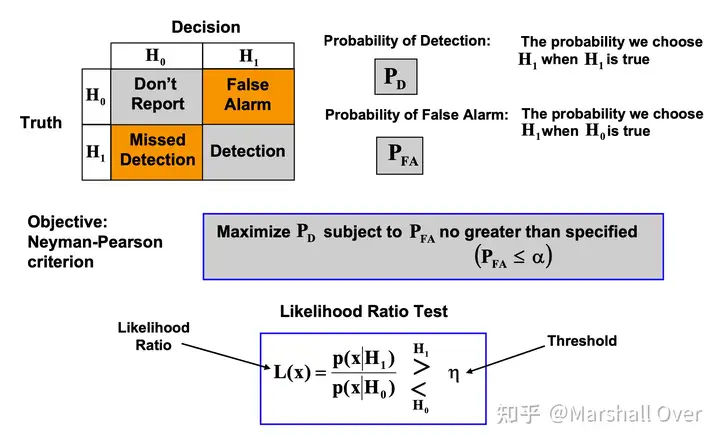
Threshold Test is Optimum:
Basic Target Detection Test:
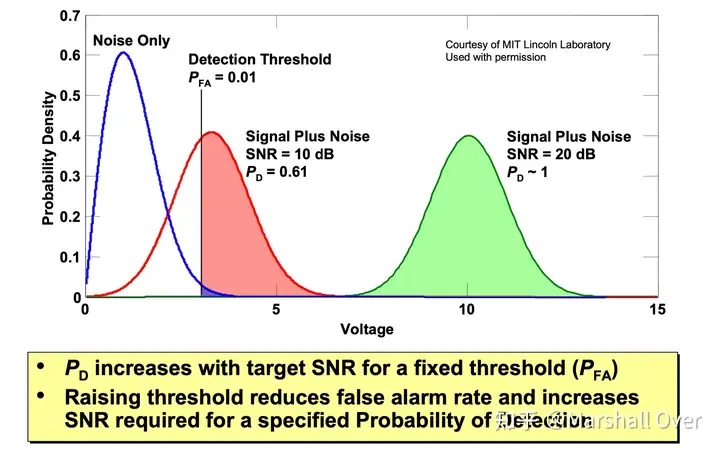
不同SNR的检测示例:
非起伏目标分布:
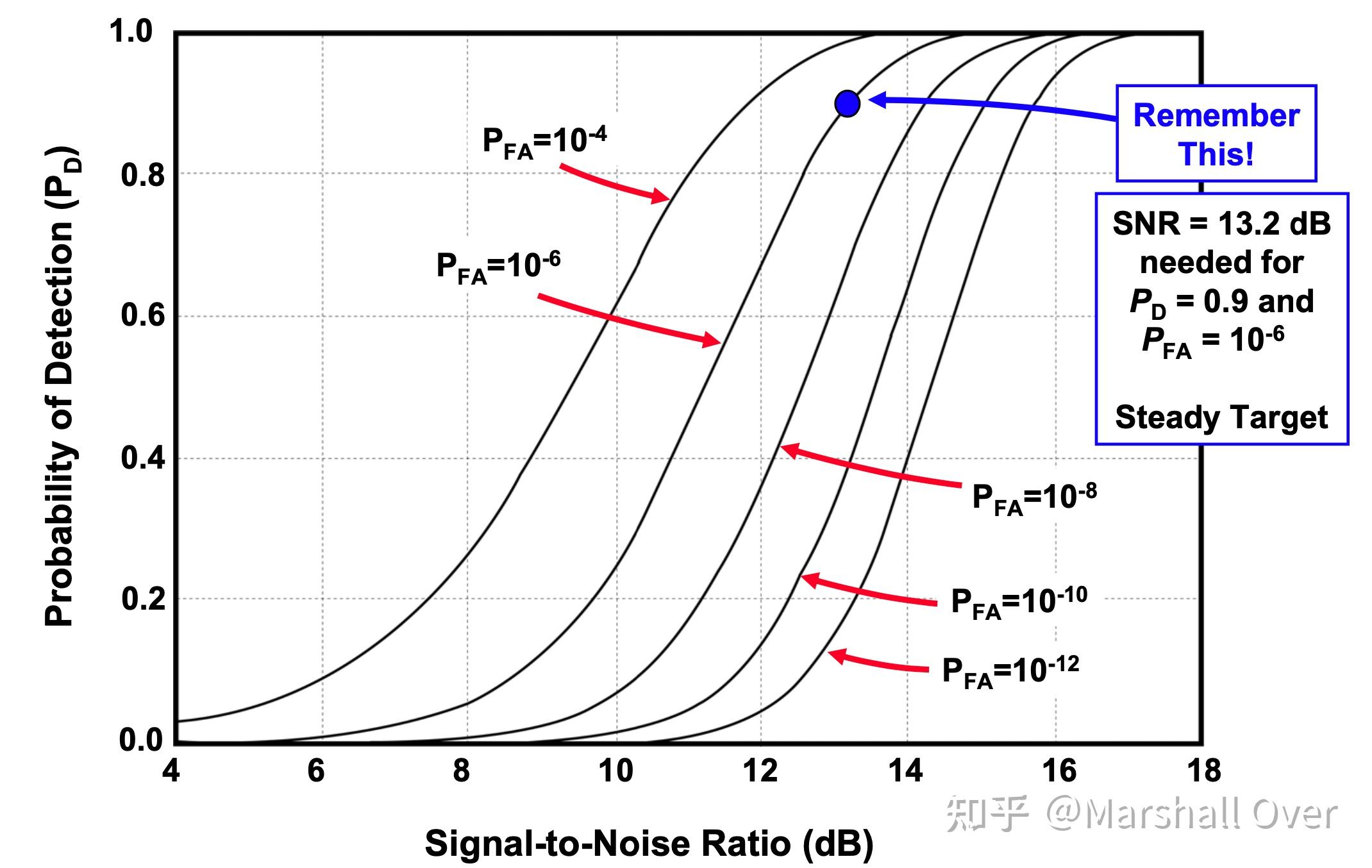
检测概率和信噪比关系:
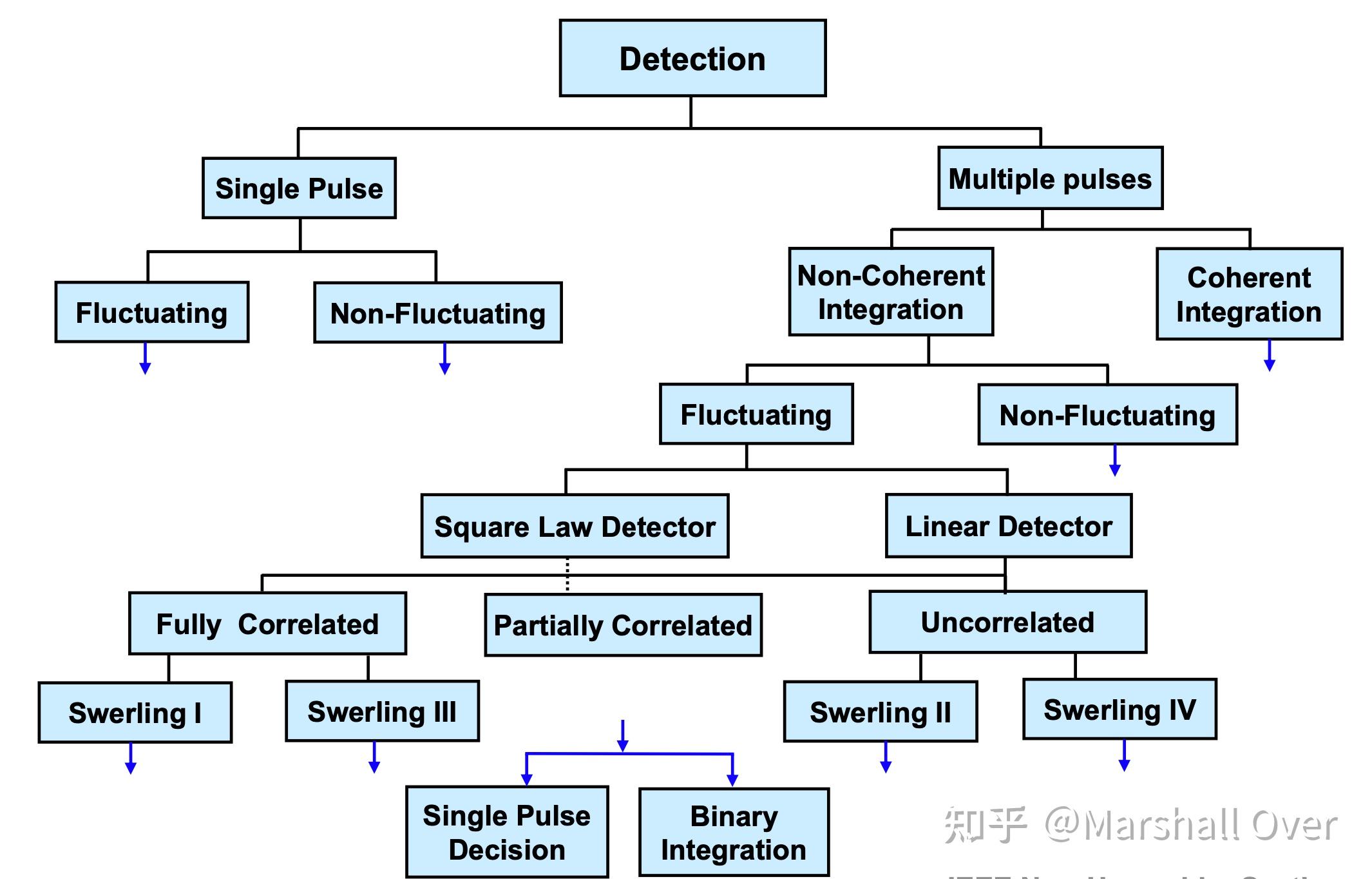
Tree of Detection Issues:
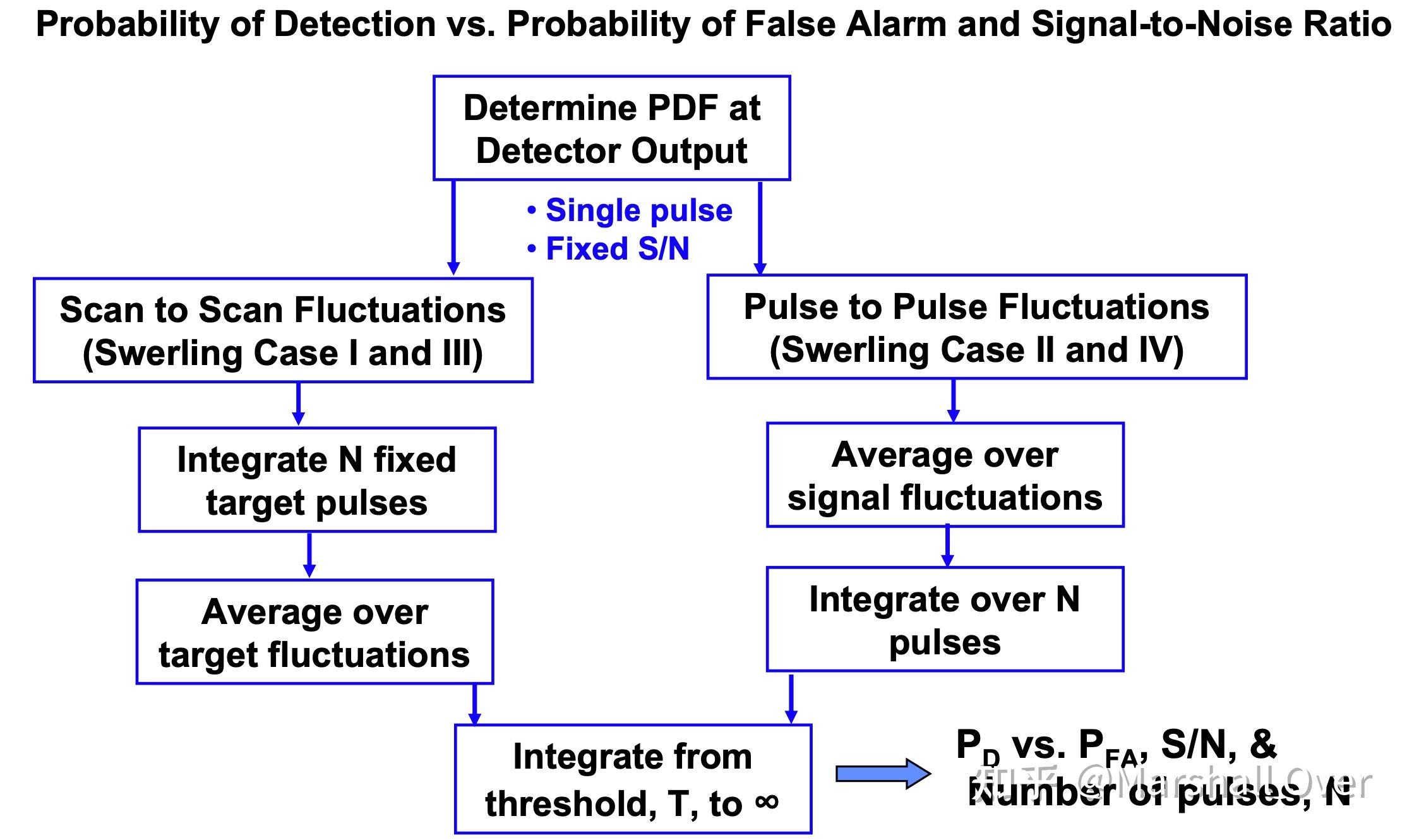
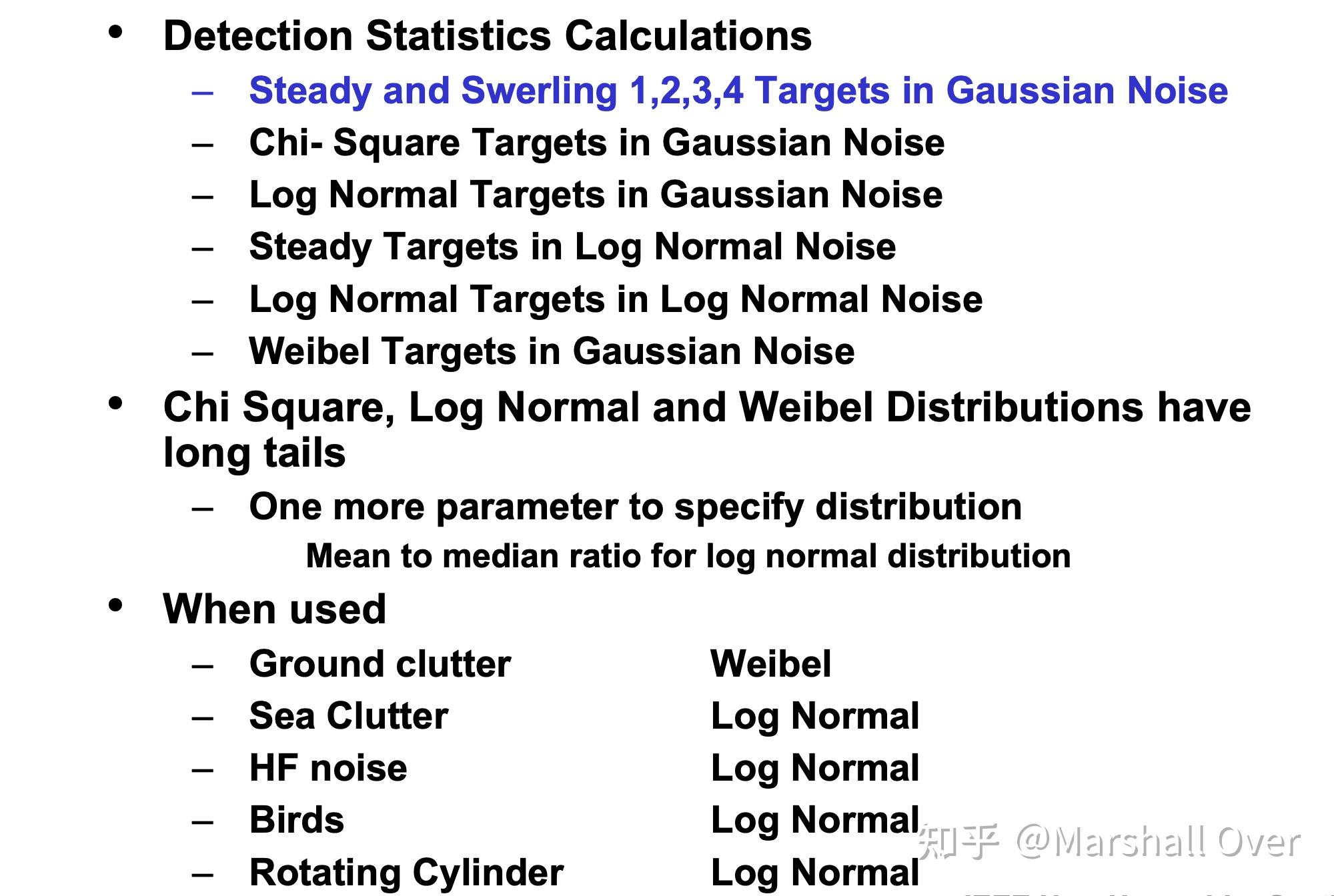
检测计算方法:
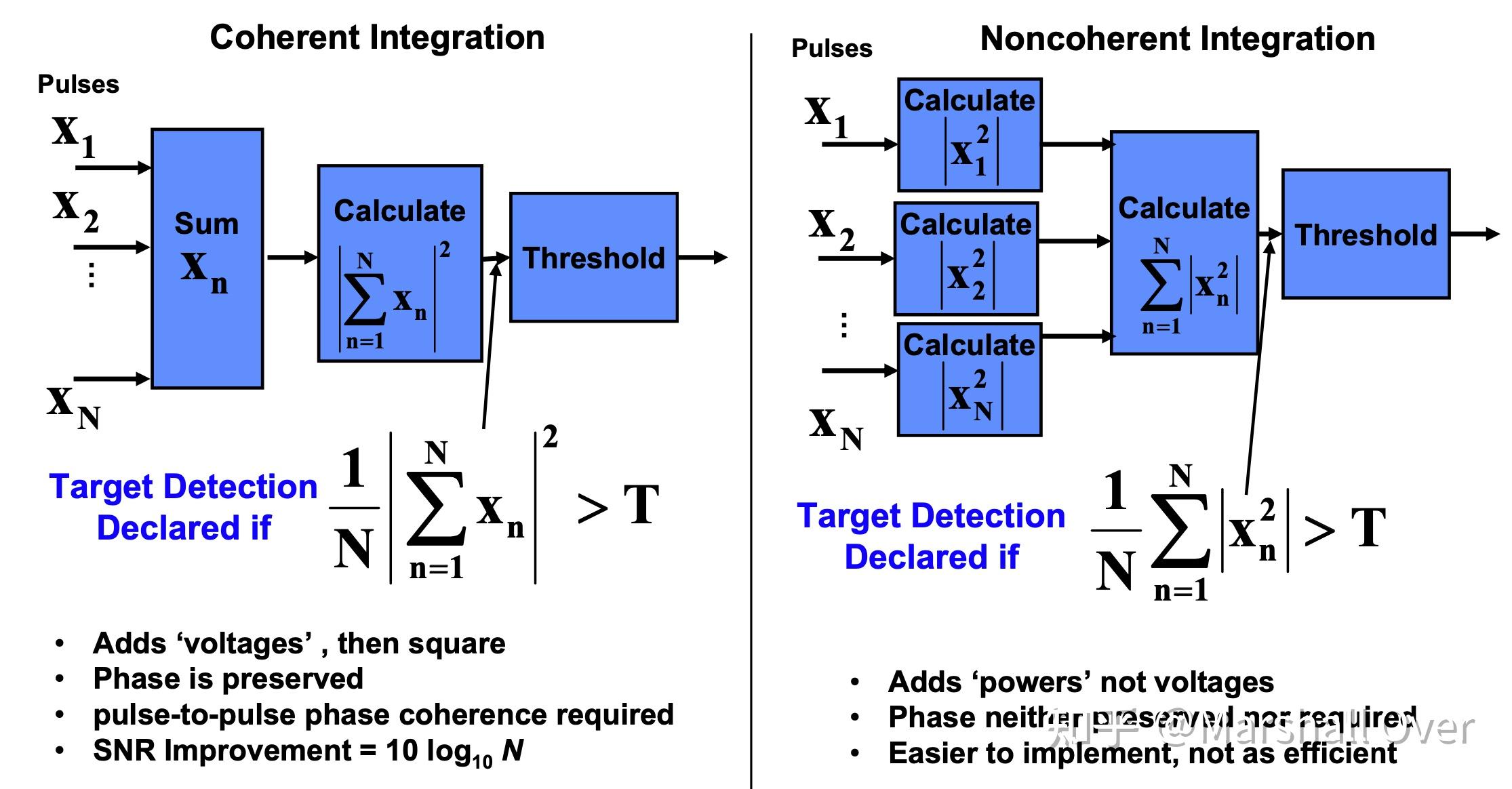
2 脉冲积累
脉冲积累:可以通过对多个脉冲进行积分来提高检测性能。
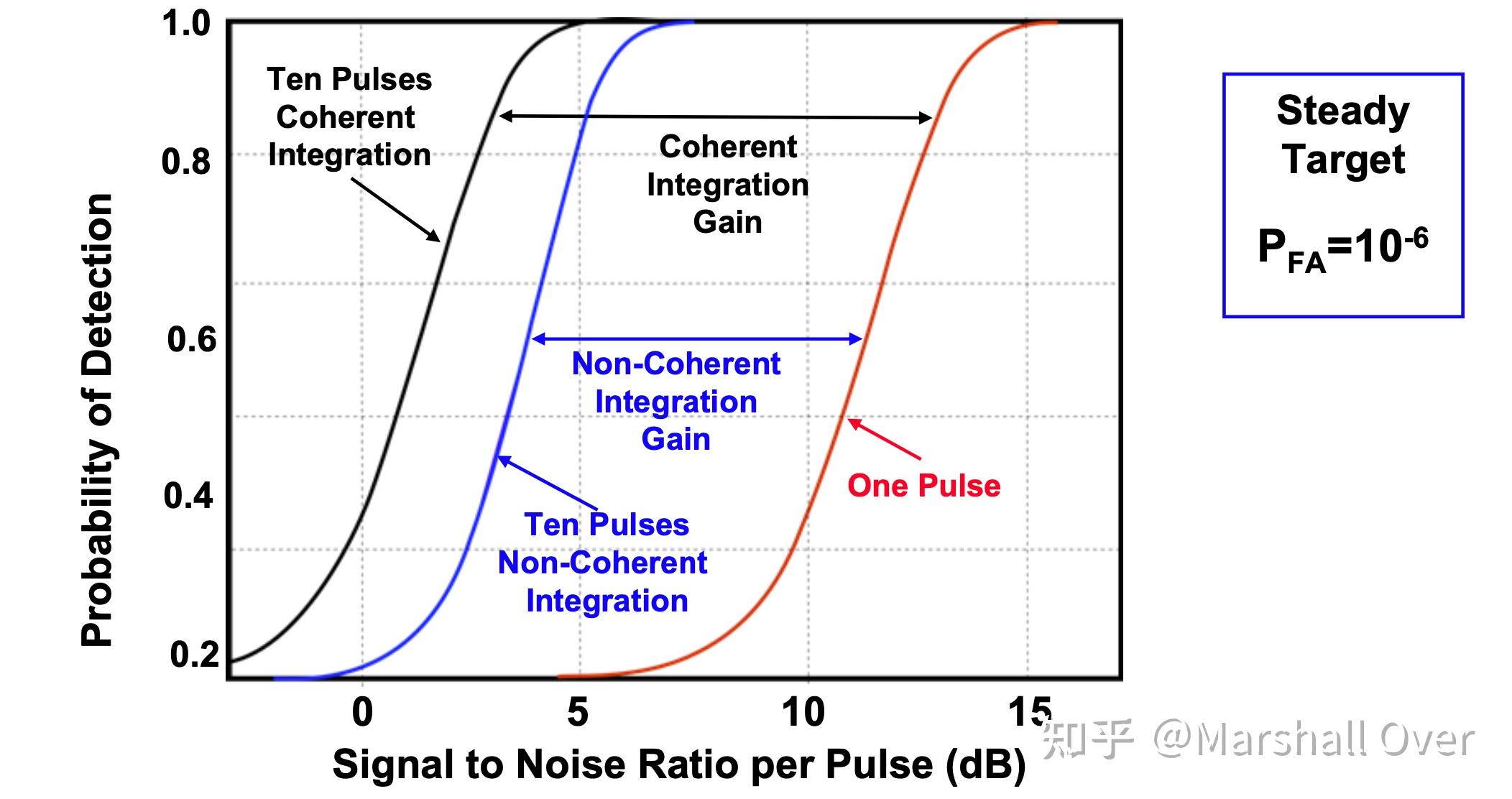
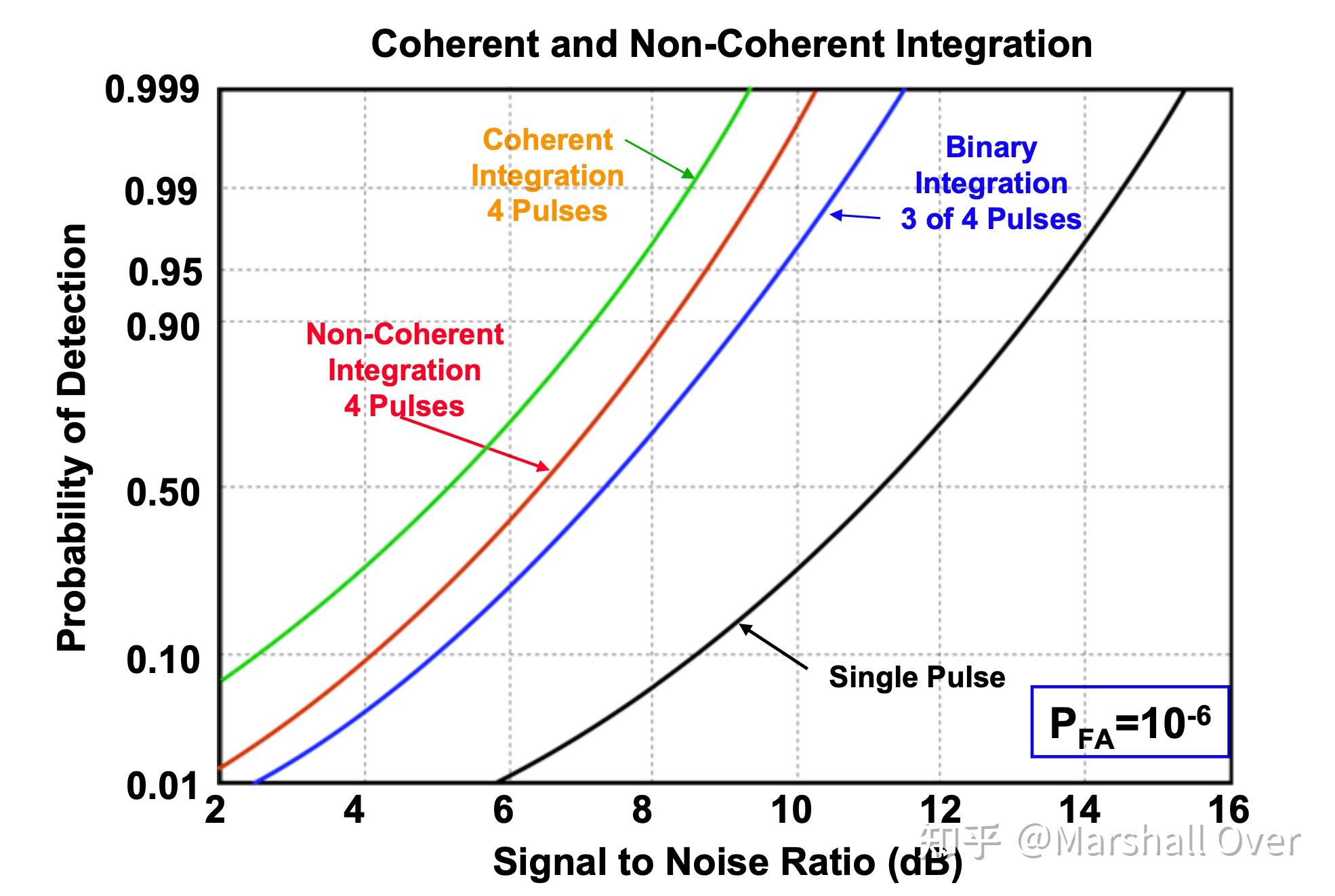
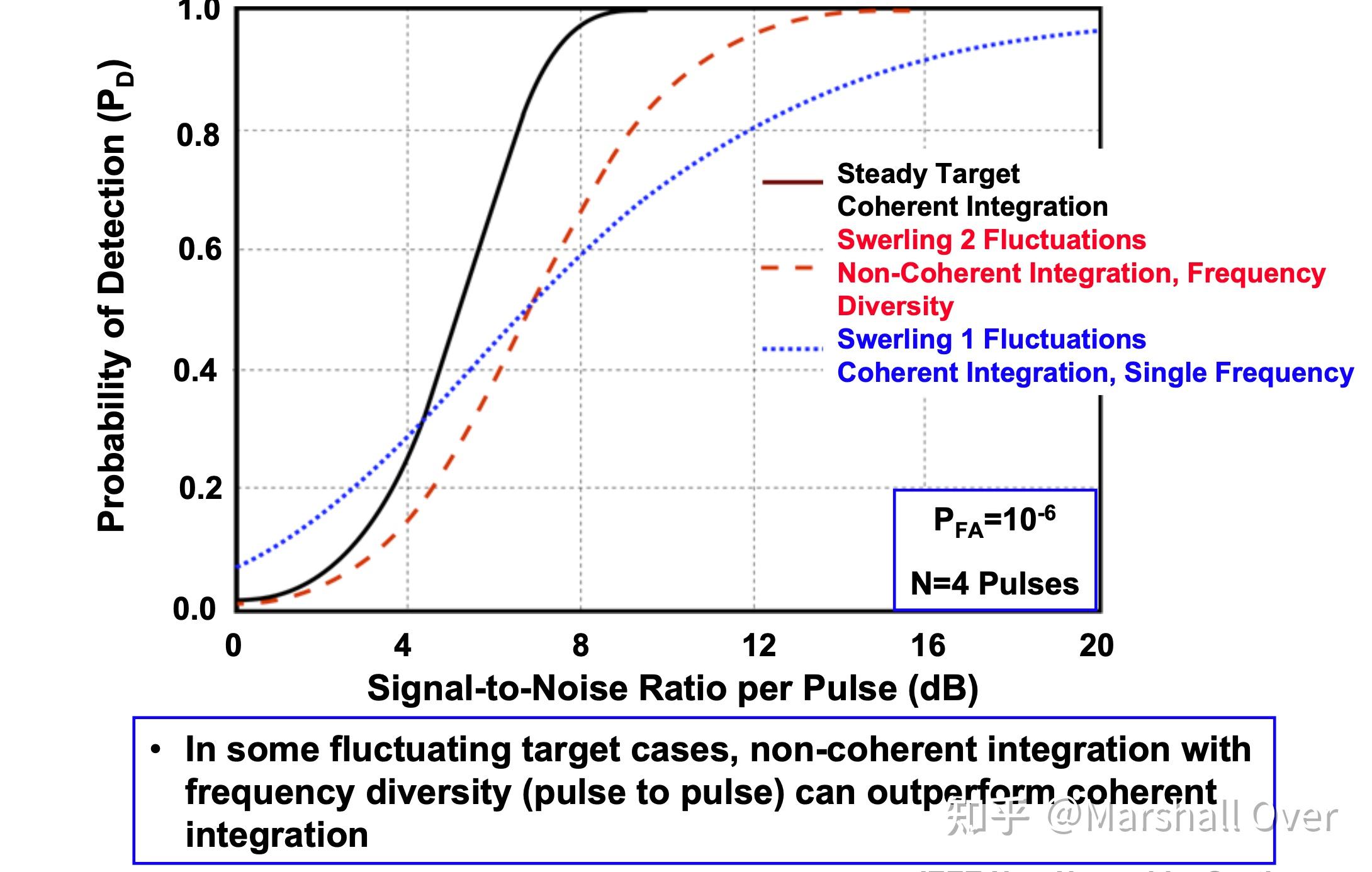
在大多数情况下,相干积累比非相干积累更有效。
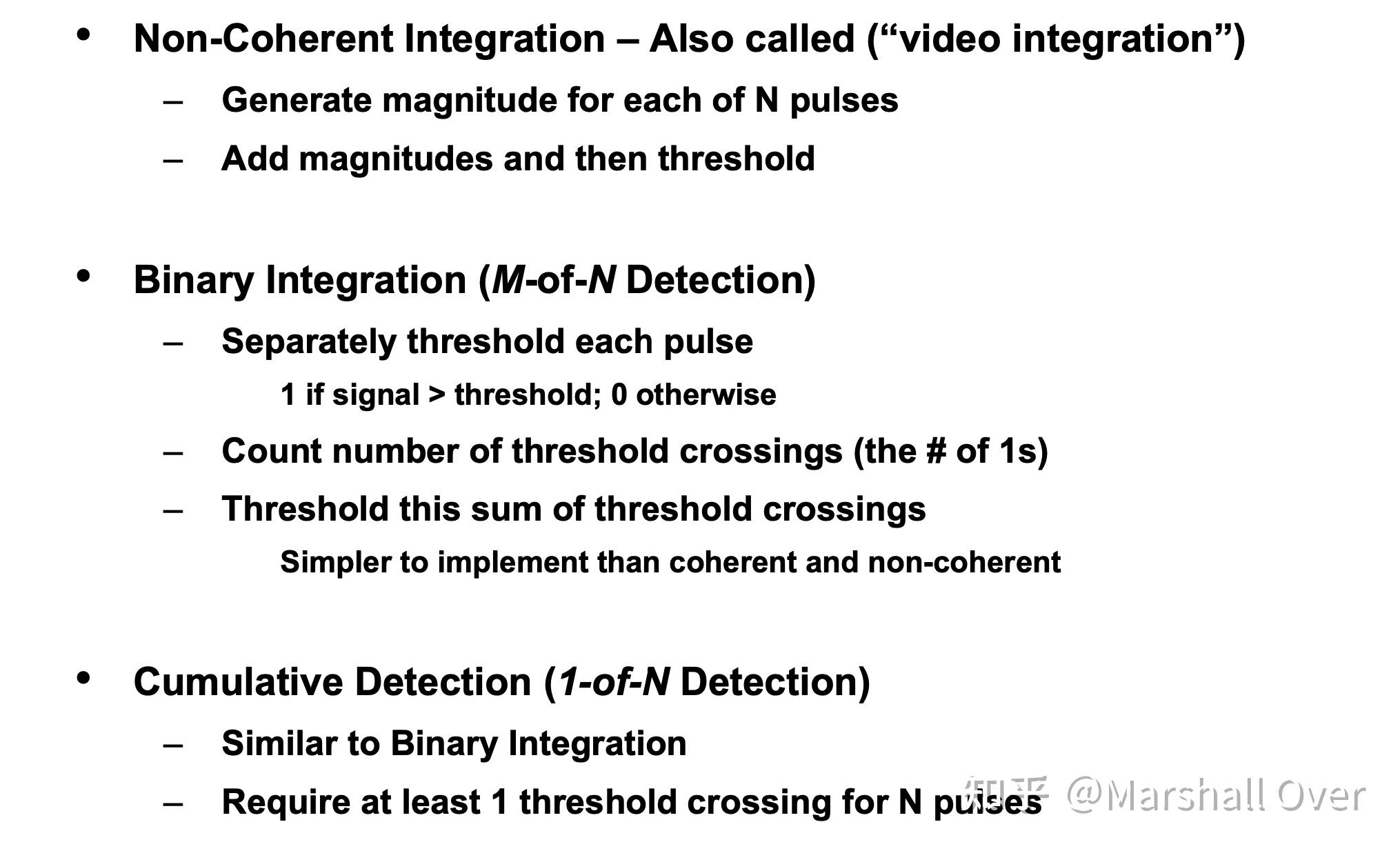
不同类型的非相干积分:
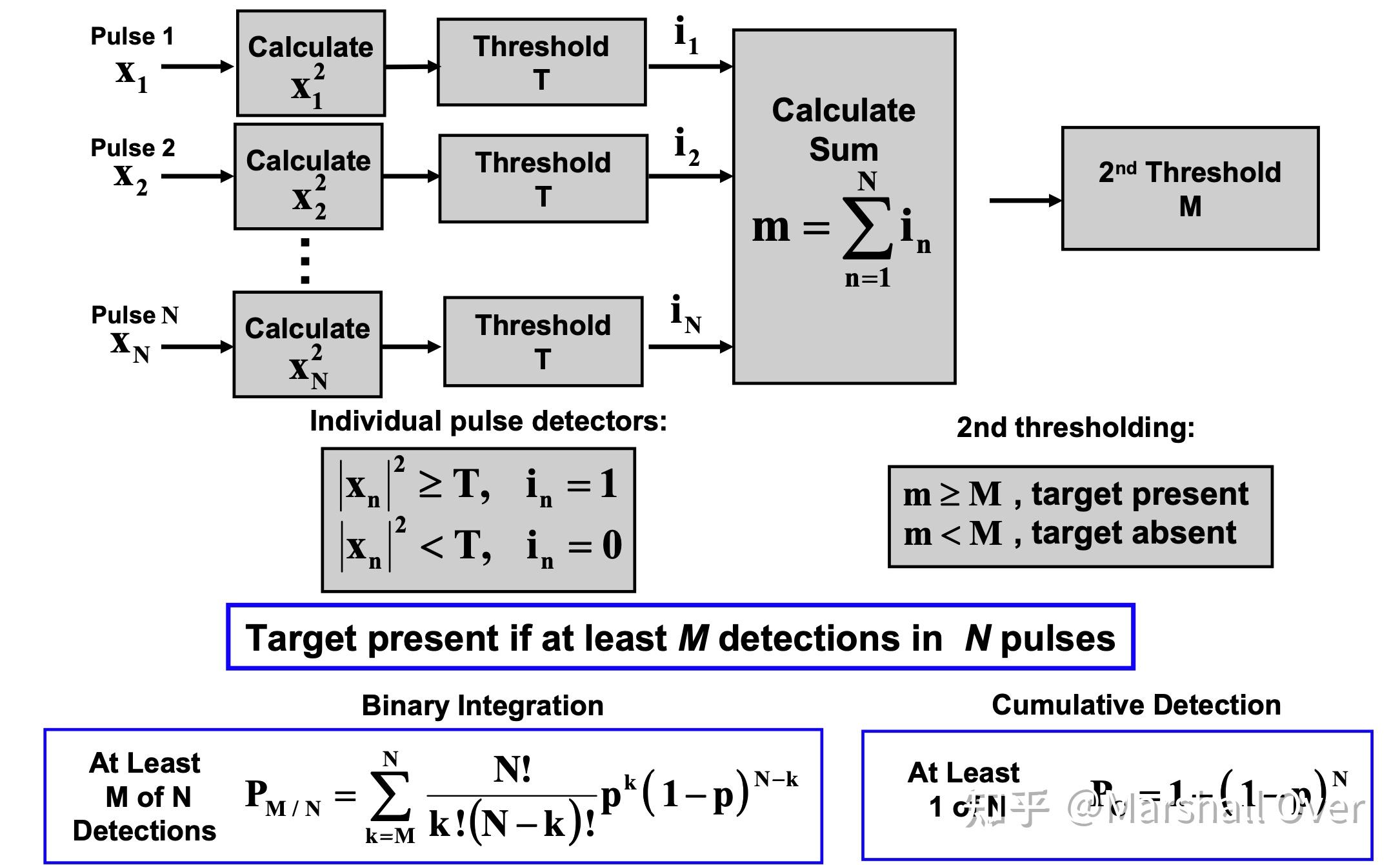
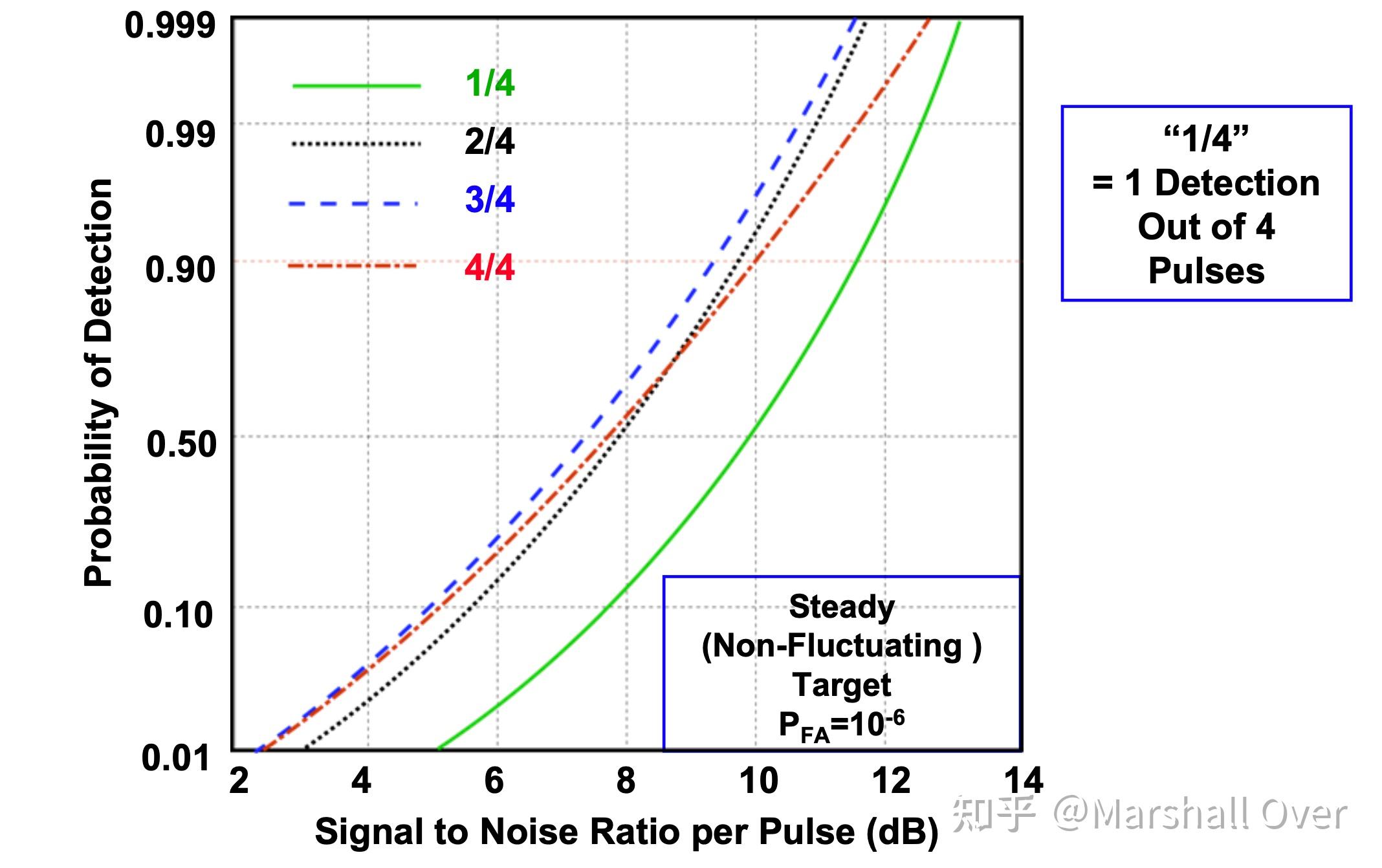
Binary Integration:
二进制积累的检测统计:
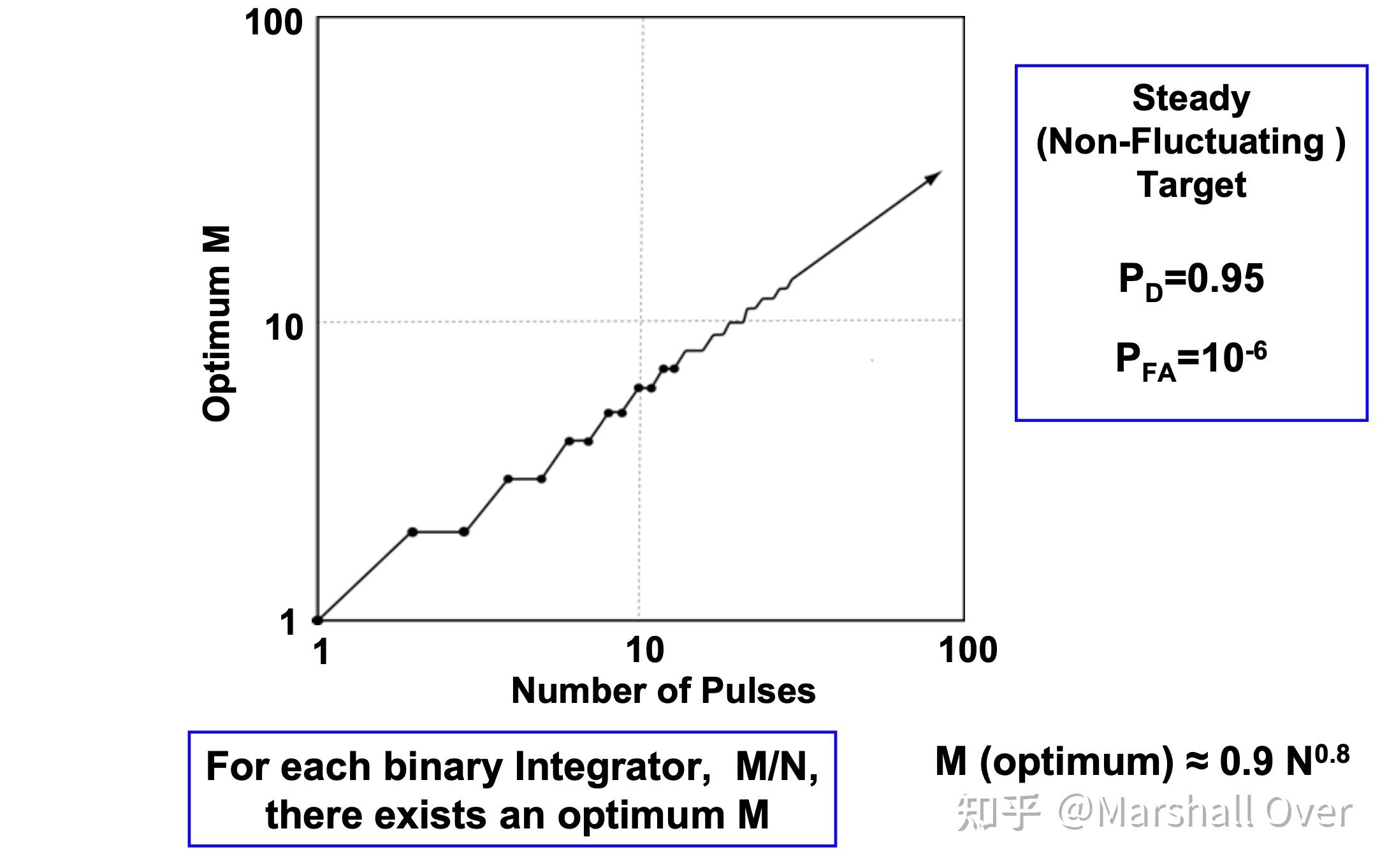
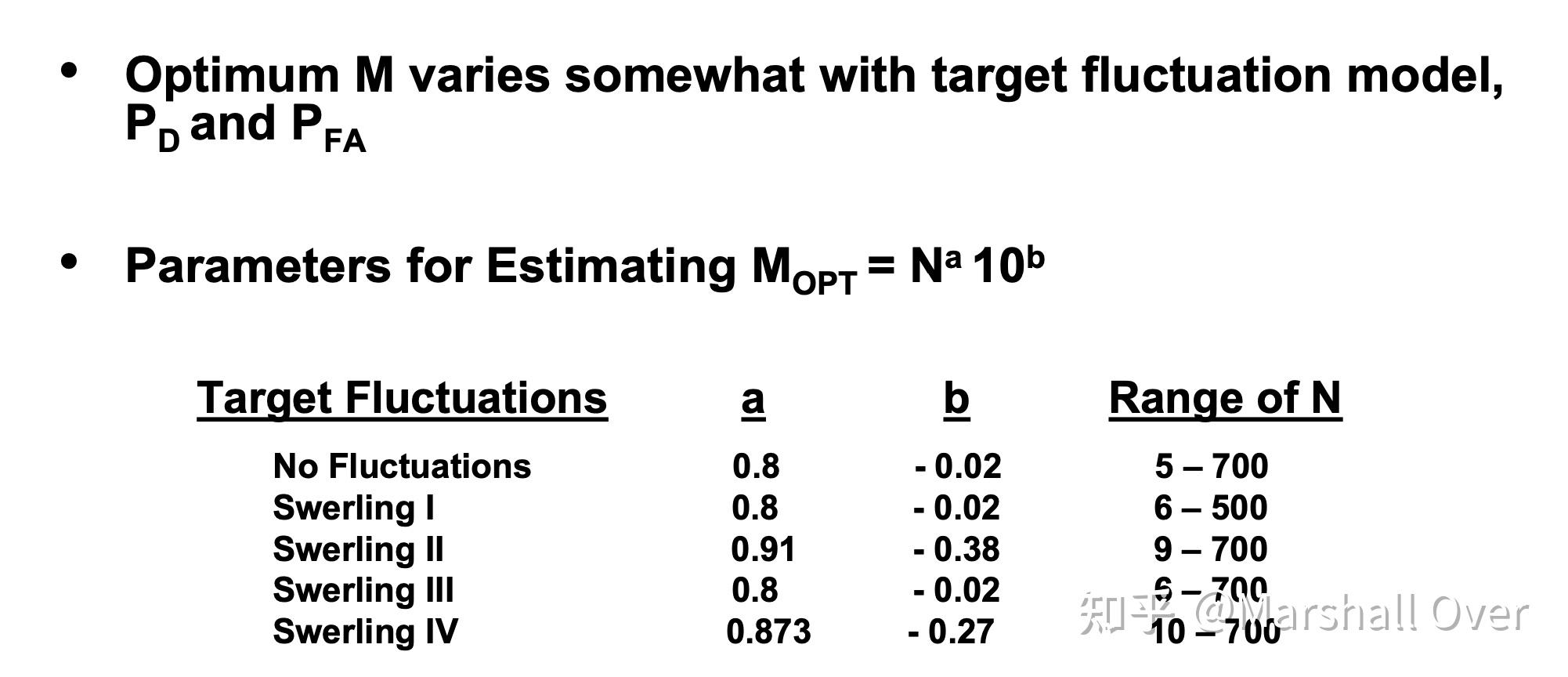
二进制积累的最优M:
不同类型积累的检测统计信息:
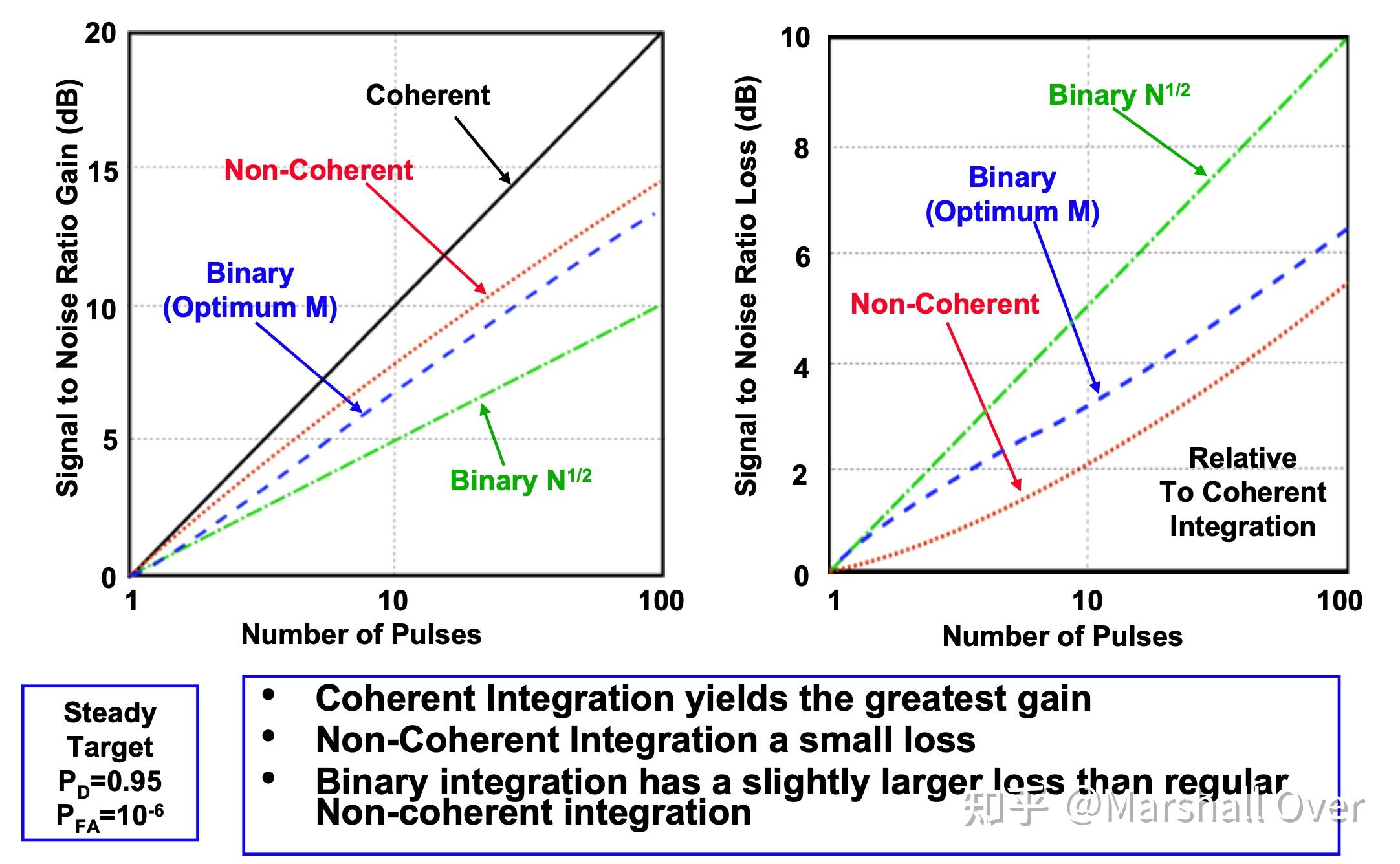
信噪比增益/损耗与脉冲数:
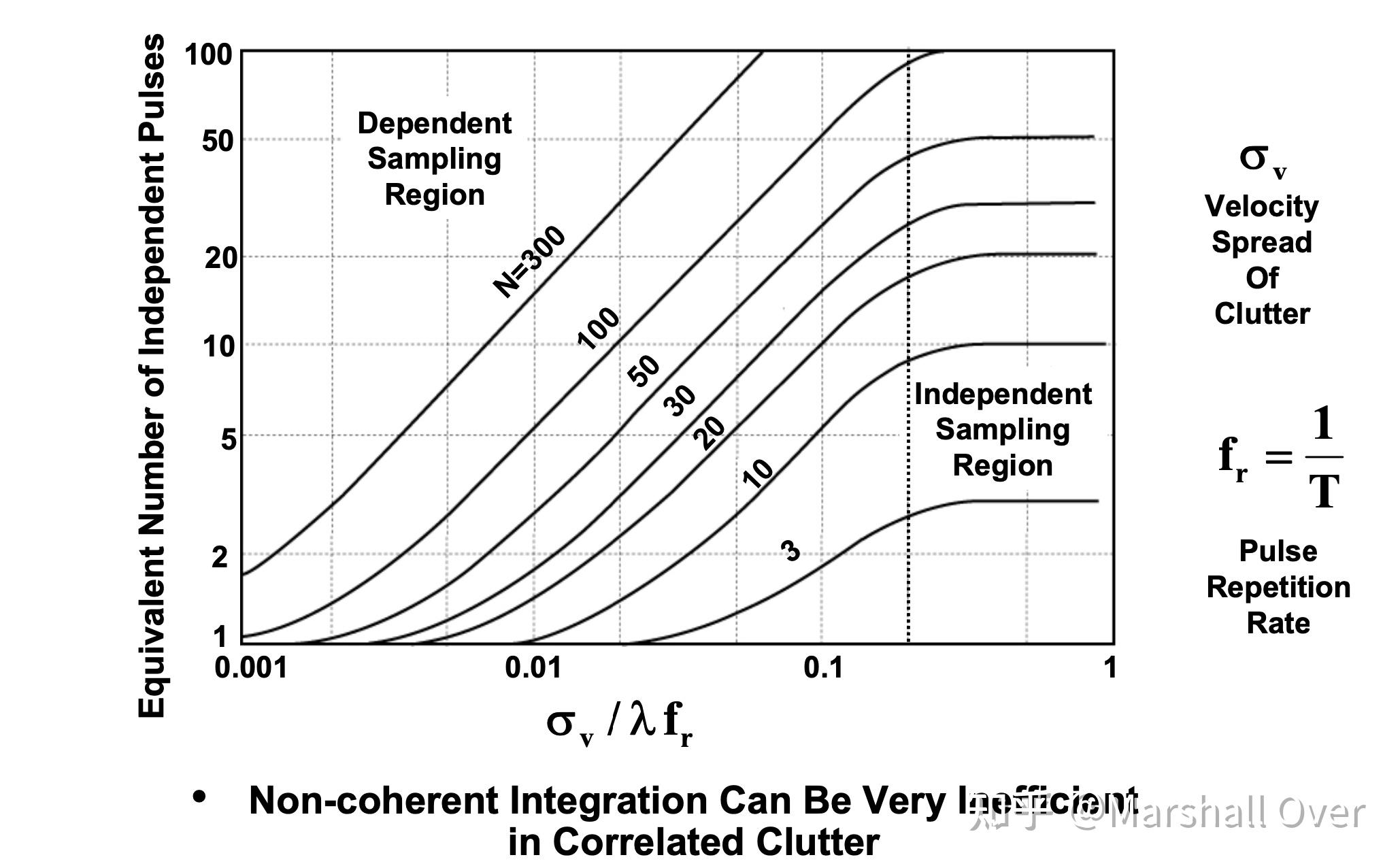
脉冲间相关性对非相干积累增益的影响:
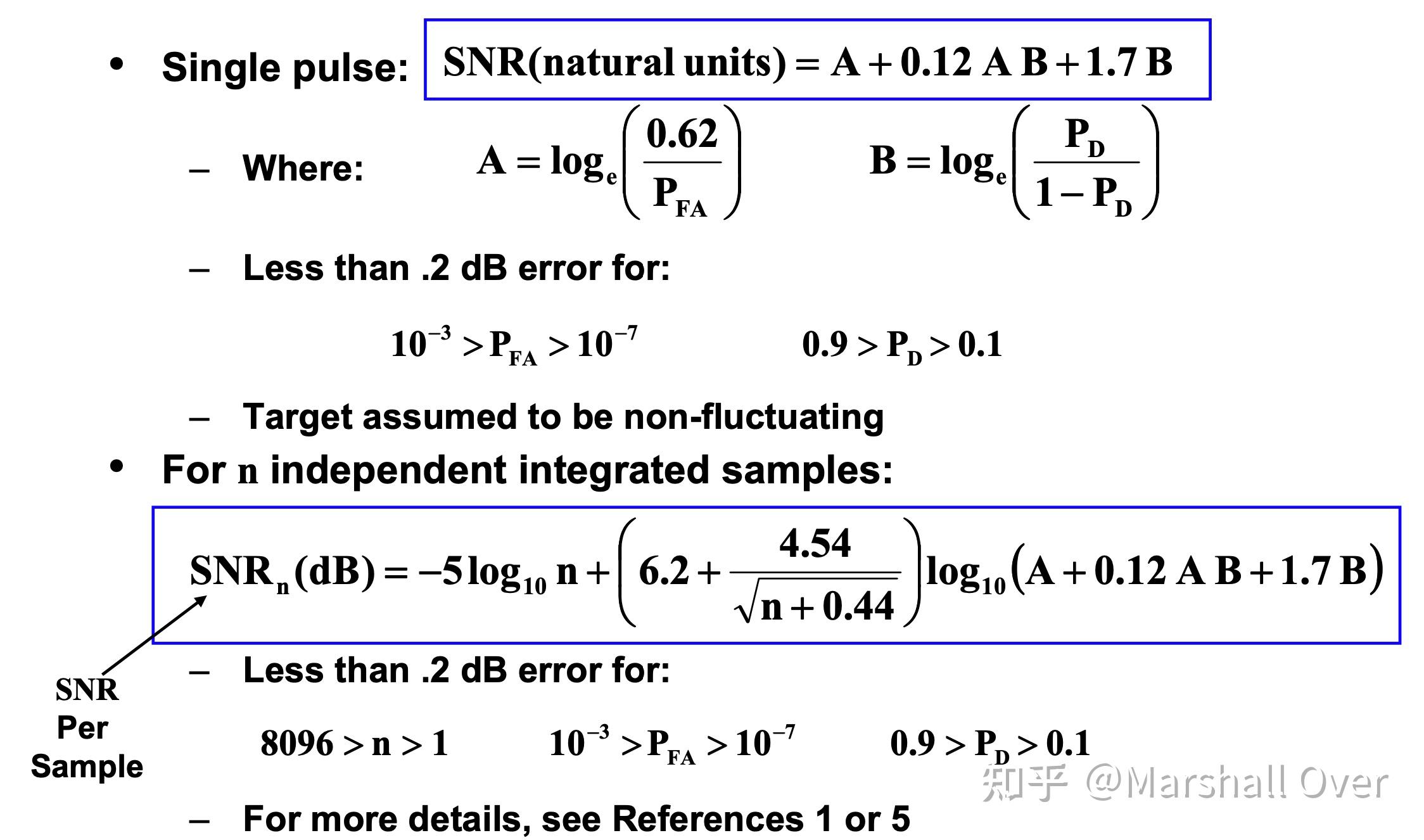
Albersheim Empirical Formula for SNR (Steady Target - Good Method for Approximate Calculations) .
3 目标起伏
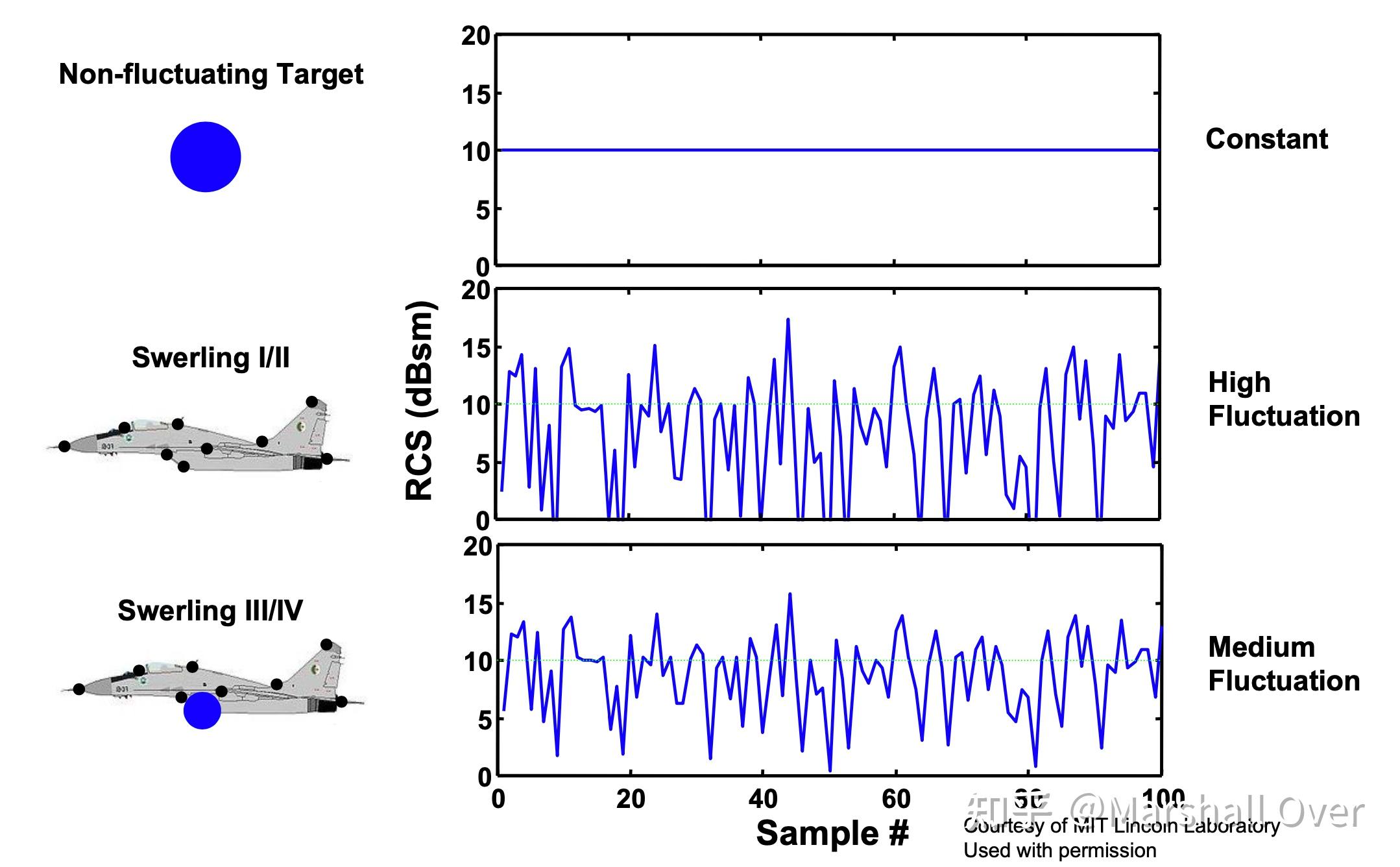
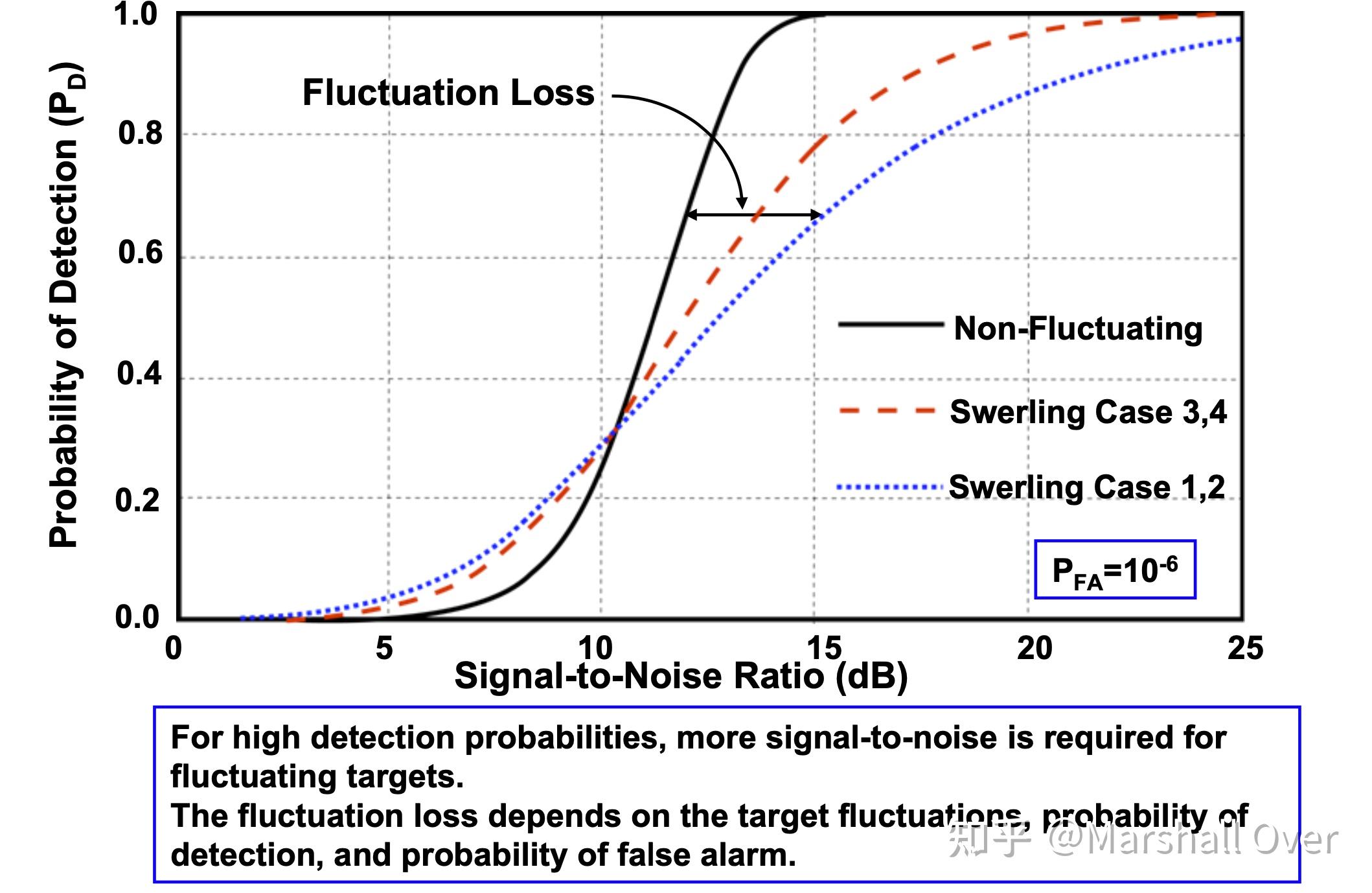
Fluctuating Target Models:
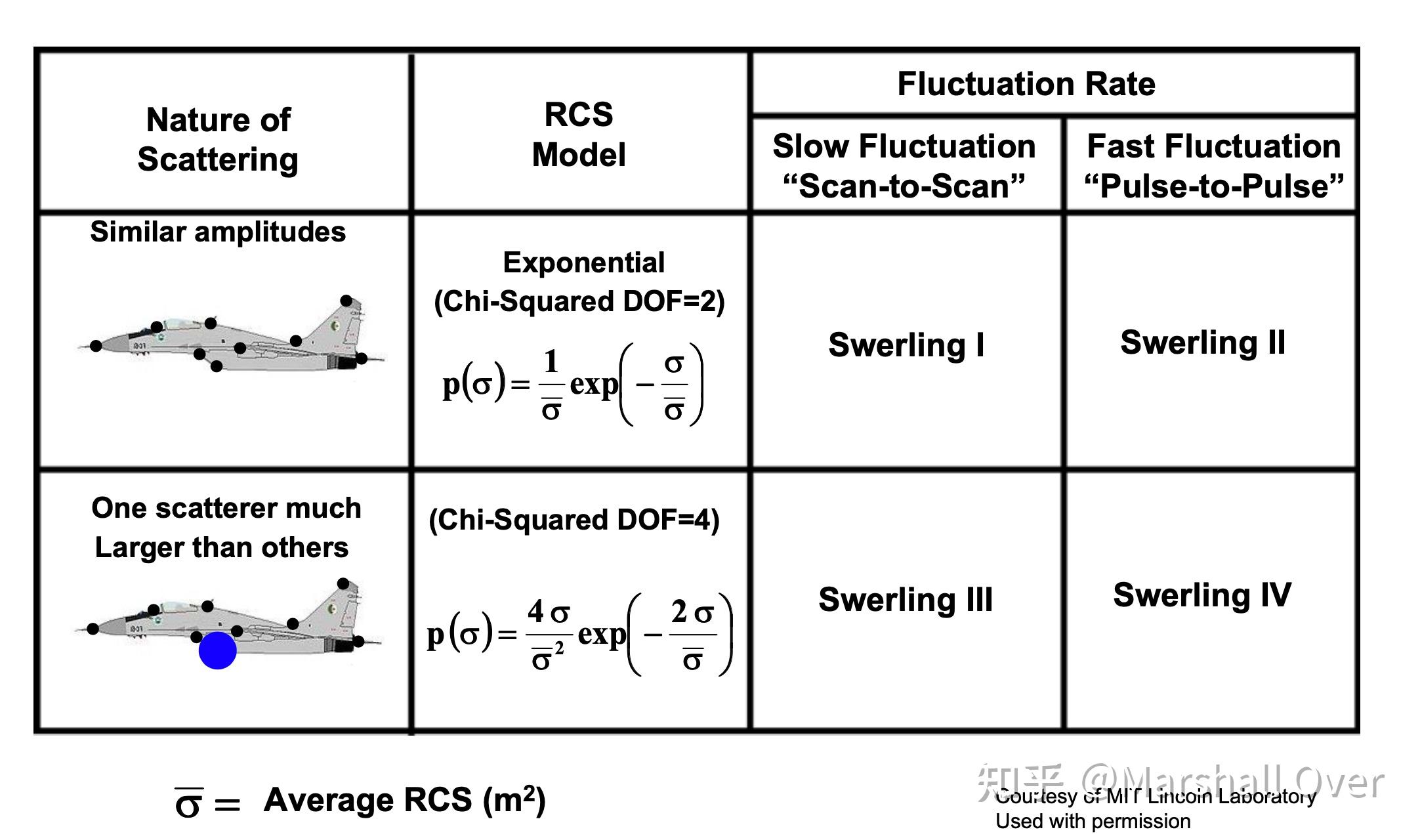
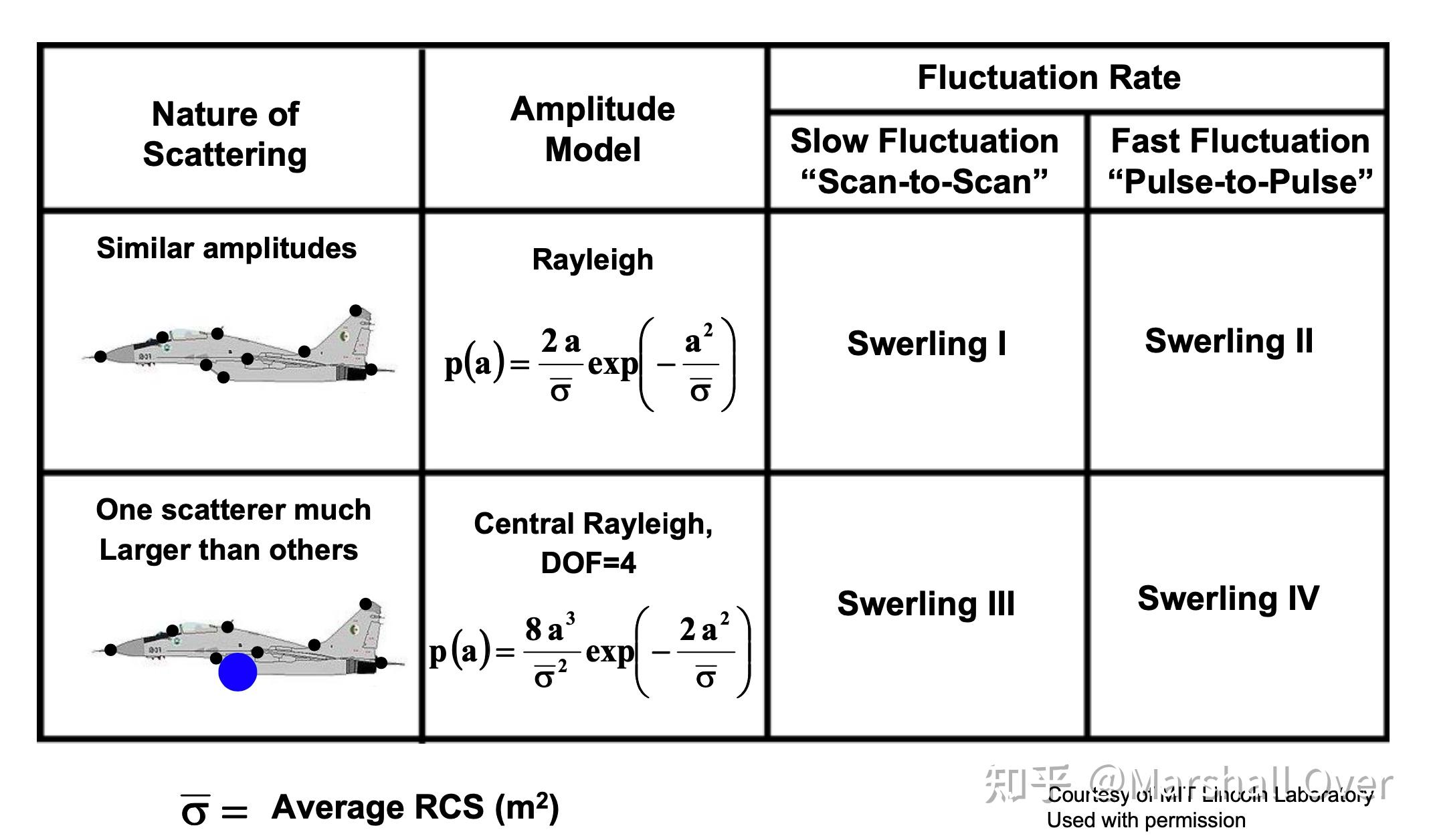
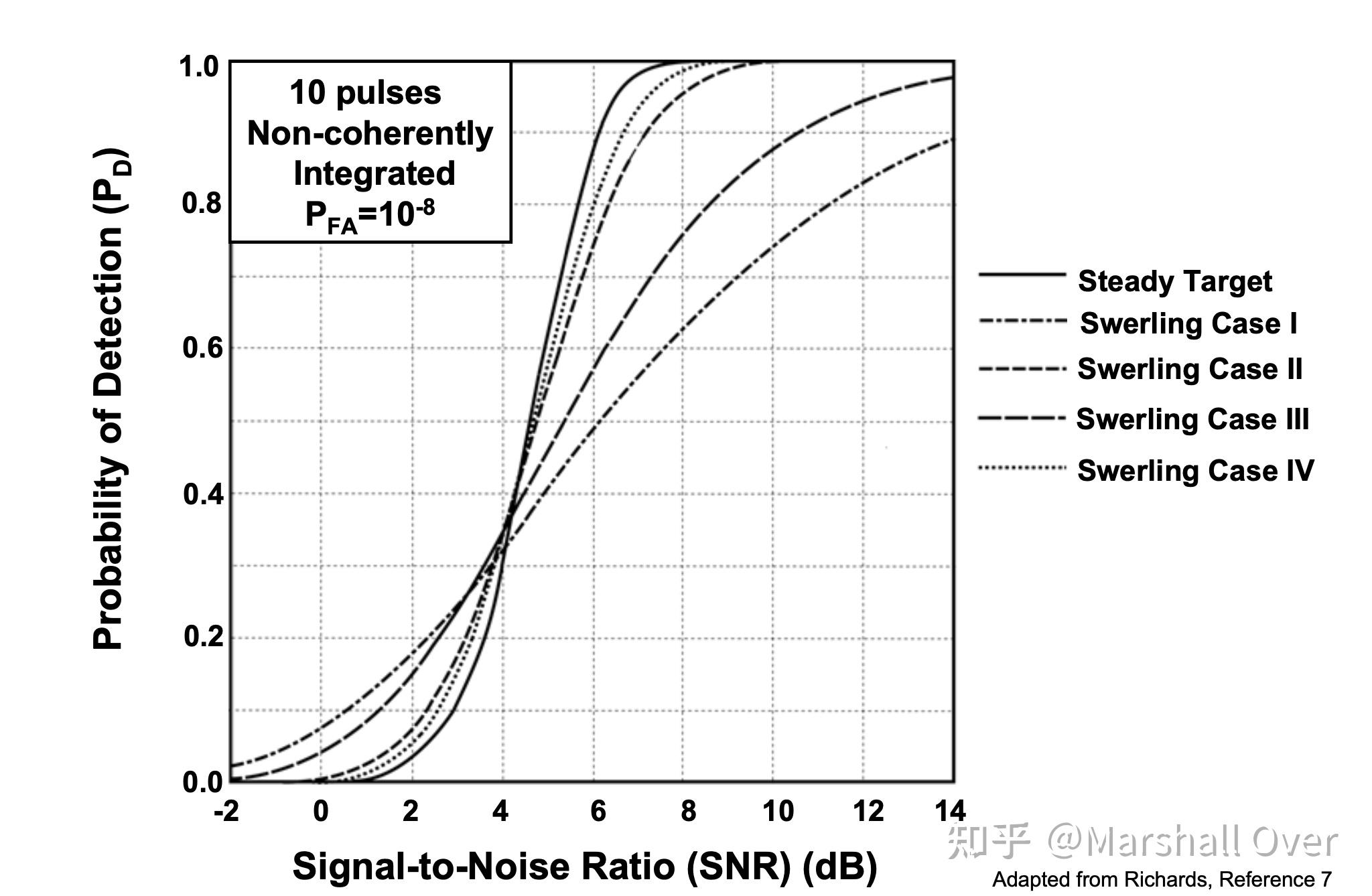
Swerling Target Models:
Other Fluctuation Models:
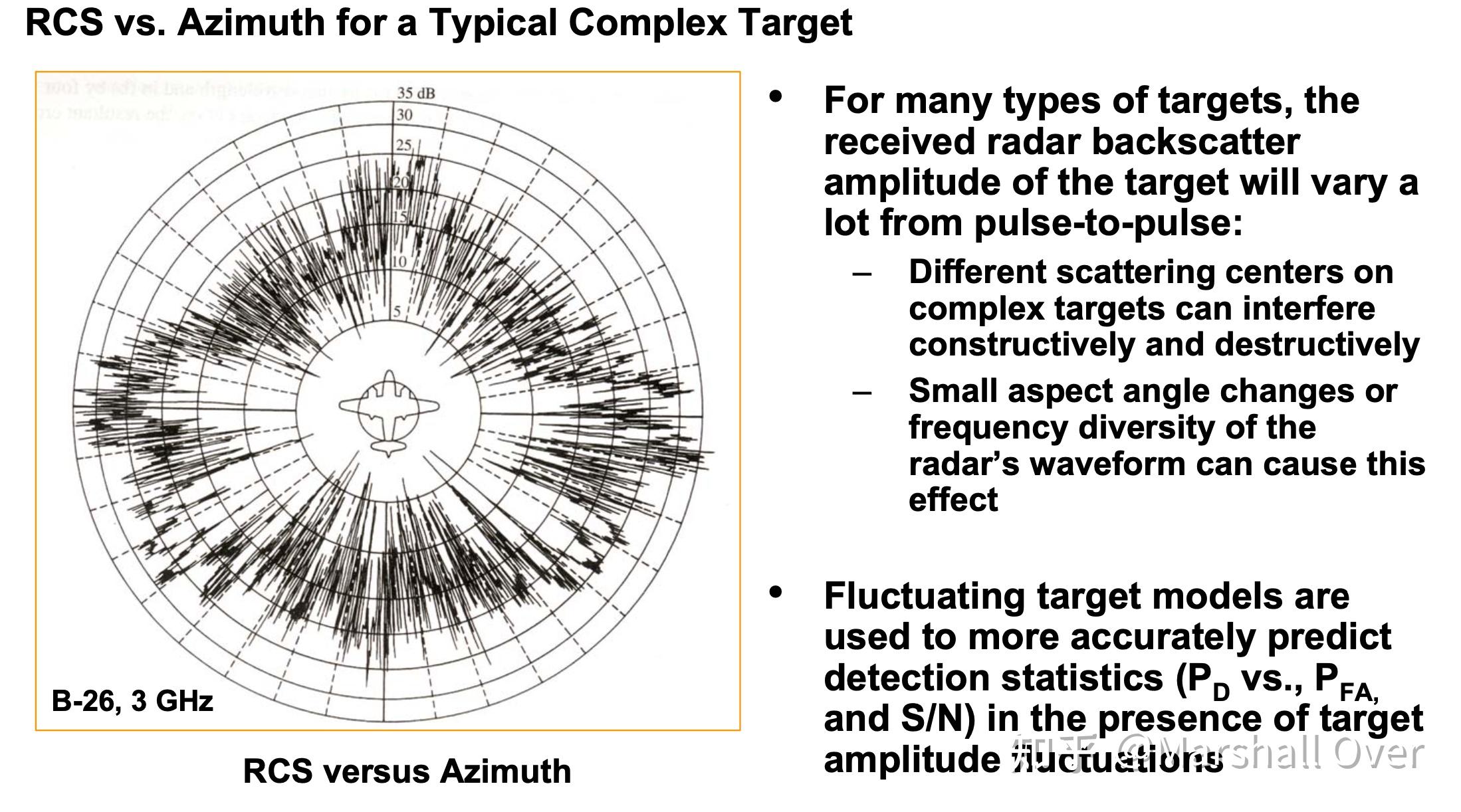
RCS Variability for Different Target Models:
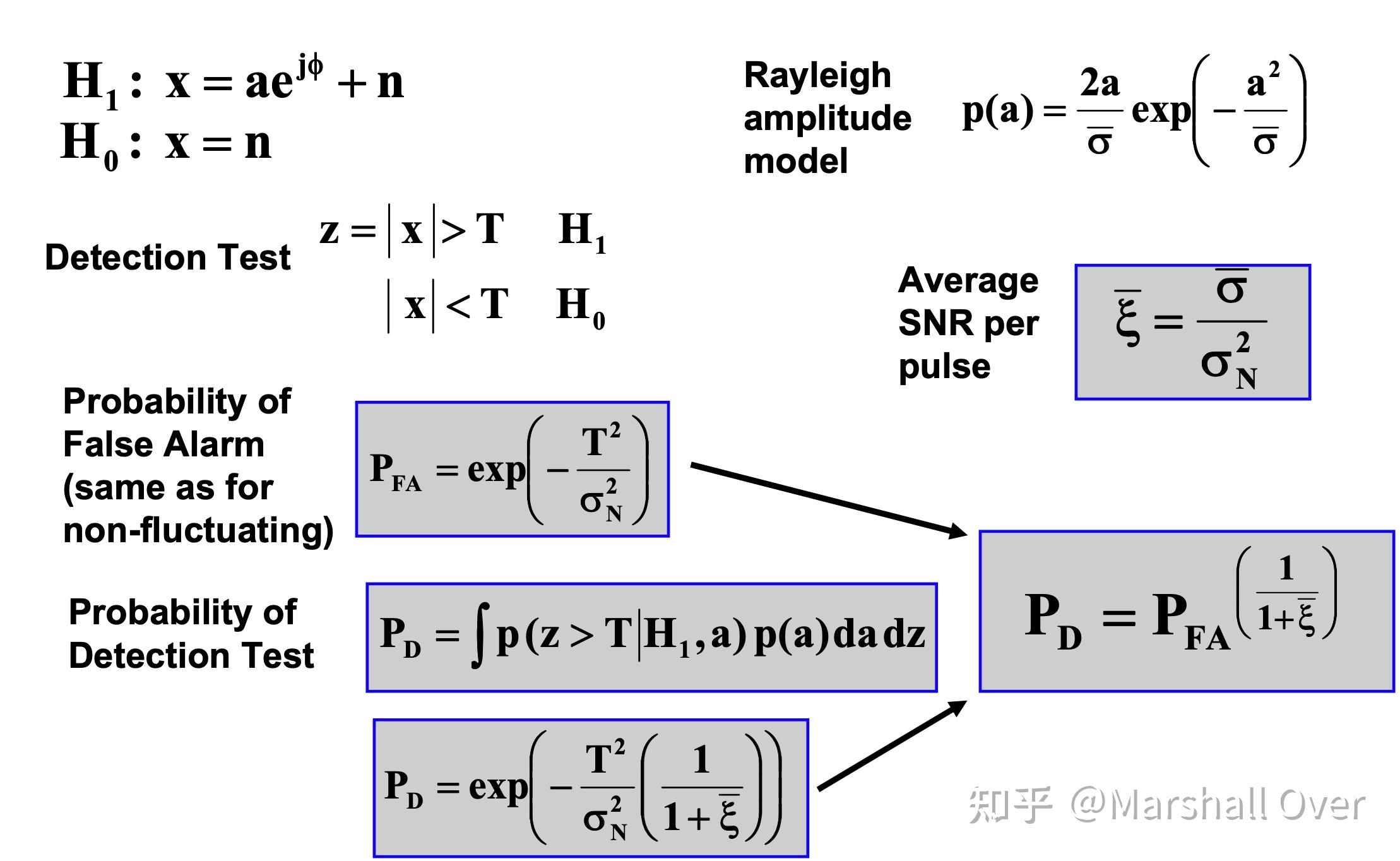
Fluctuating Target Single Pulse Detection : Rayleigh Amplitude:
Fluctuating Target Single Pulse Detection:
Fluctuating Target Multiple Pulse Detection:
Detection Statistics for Different Target Fluctuation Models:
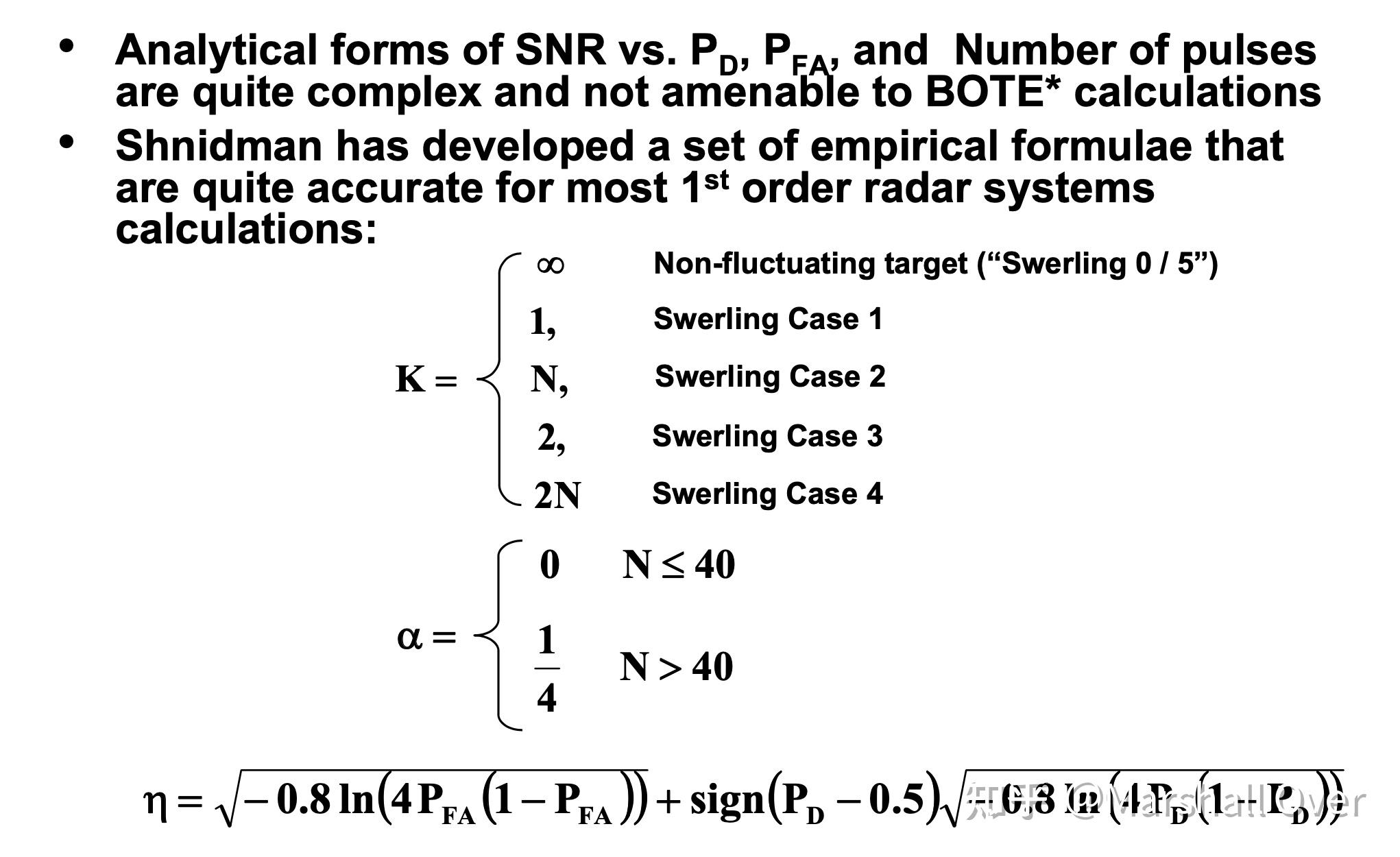
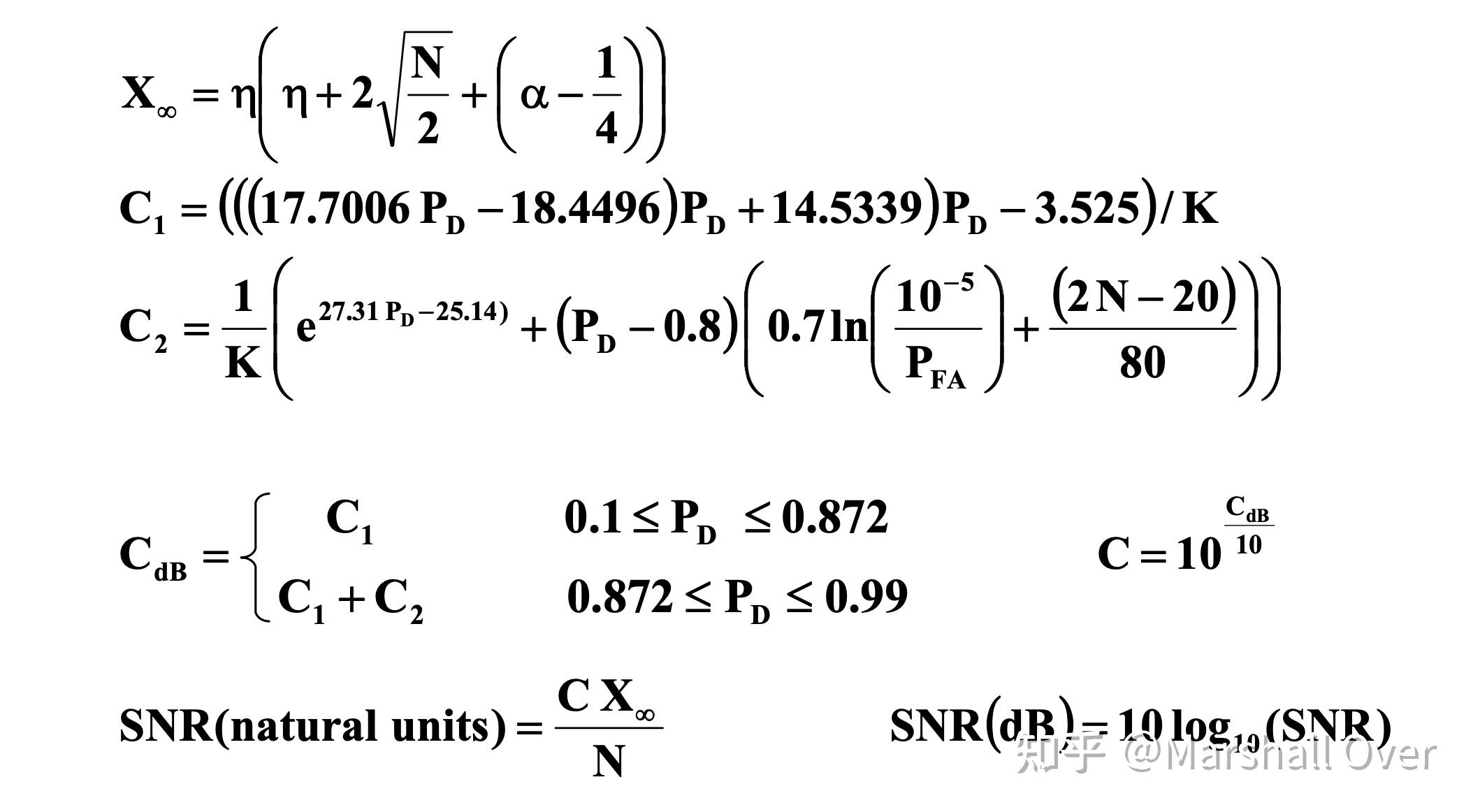
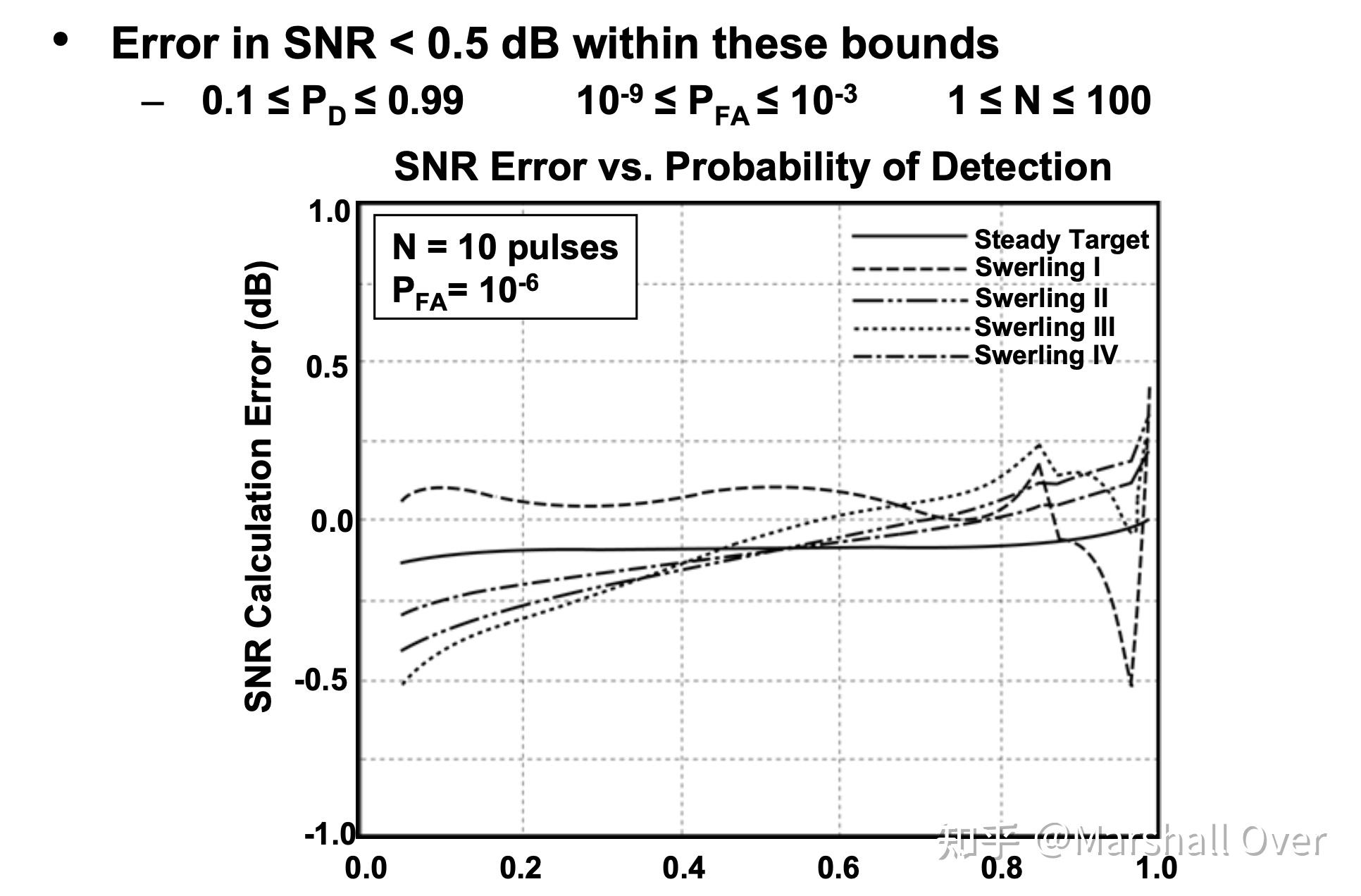
Shnidman Empirical Formulae for SNR:
Shnidman’s Equation:
4 横虚警率检测门限
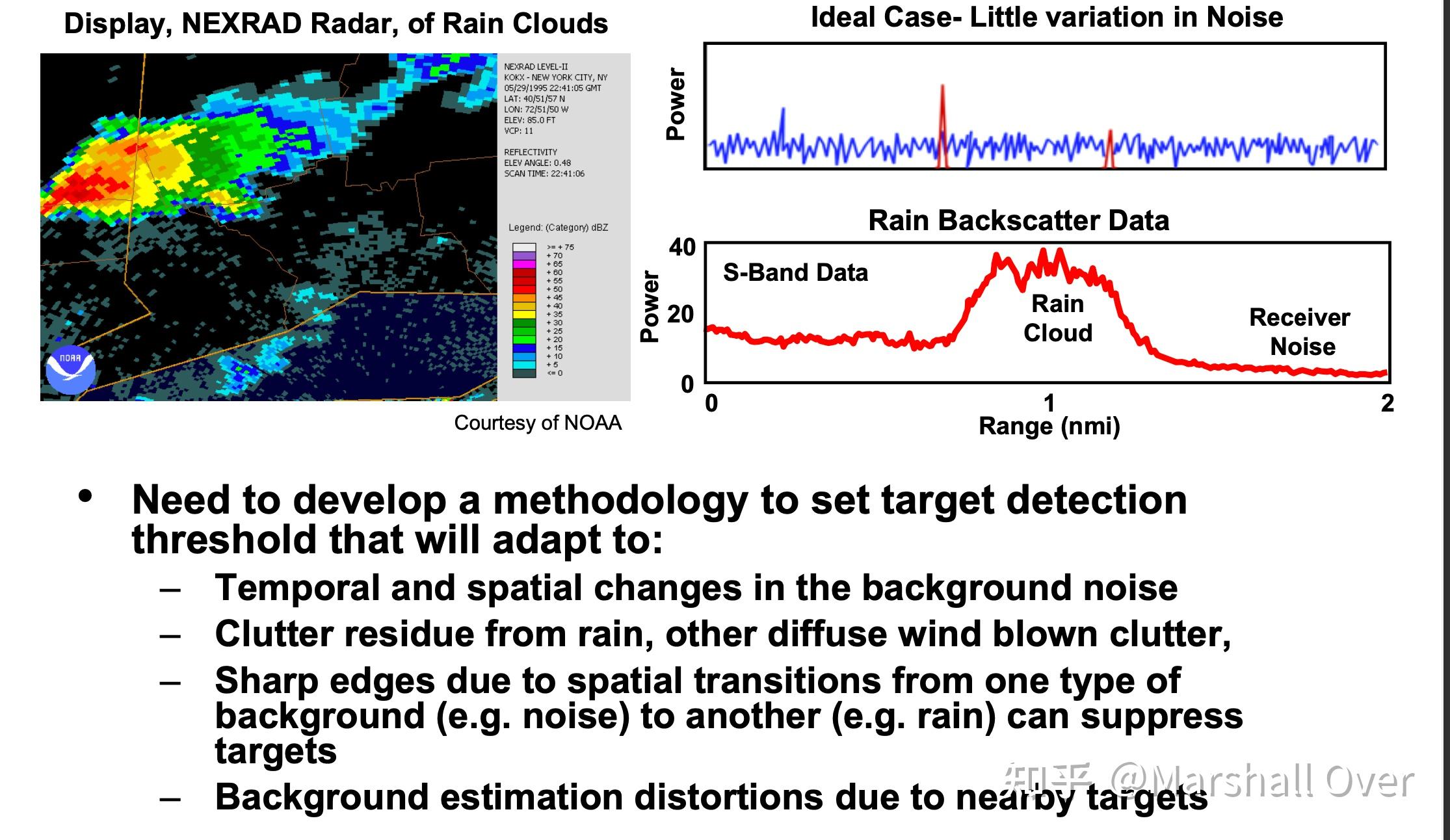
Practical Setting of Thresholds:
恒虚警分类及其对应性能可参考中的自适应门限部分。
5 总结讨论
6 参考文献
[1] 百度翻译
[2] MIT 公开课: Radar Systems Engineering




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号