235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
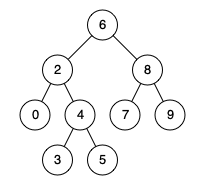
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8 输出: 6 解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4 输出: 2 解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
solution:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { 13 //find 1st element whose val in [p,q],use traversal 14 if(p == nullptr || q== nullptr) 15 return nullptr; 16 if(p == q) 17 return p; 18 //make sure p's val more than q's 19 int max = p->val>q->val?p->val:q->val; 20 int min = p->val>q->val?q->val:p->val; 21 if(root) 22 { 23 queue<TreeNode*> q; 24 q.push(root); 25 while(!q.empty()) 26 { 27 TreeNode* node = q.front(); 28 if(min<=node->val && node->val<=max) 29 { 30 return node; 31 } 32 q.pop(); 33 if(node->left) q.push(node->left); 34 if(node->right)q.push(node->right); 35 } 36 } 37 return nullptr; 38 } 39 };
还是层次遍历思想,既然是二者最近公共祖先,则从根节点往下层次遍历第一个出现在二者之间(含相等)的值就是我们要找的节点。当然边界条件需要提前处理。
此种想法简单,可以试试递归解法。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号