做题记录
8.18
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int n, m, h;
cin >> n >> h >> m;
vector<int> a(n, h);
while(m --) {
int l, r, lim;
cin >> l >> r >> lim;
l --, r --;
while(l <= r) a[l] = min(lim, a[l]), l ++;
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) res += a[i] * a[i];
cout << res << '\n';
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m;
int s[N], t[N], c[N];
int a[N], b[N], p[N], w[N];
int ans = INF;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> s[i] >> t[i] >> c[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> p[i] >> w[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < 1 << m; i ++) {
vector<int> sum(102);
int tmp = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++) {
if(i >> j & 1) {
tmp += w[j];
sum[a[j]] += p[j];
sum[b[j] + 1] -= p[j];
}
}
for(int j = 1; j <= 100; j ++) sum[j] += sum[j - 1];
bool ok = true;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {
for(int k = s[j]; k <= t[j]; k ++) {
if(sum[k] < c[j]) {
ok = false;
break;
}
}
}
if(ok) {
ans = min(ans, tmp);
}
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m, k;
int a[N], b[N];
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
cin >> b[i];
}
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
reverse(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
sort(b + 1, b + 1 + m);
reverse(b + 1, b + 1 + m);
int i = 1, j = 1;
LL res = 0;
while(i <= n && j <= m) {
if(a[i] >= k) res += b[j] + a[i] * 2;
else res += a[i] + b[j] + k;
i ++, j ++;
}
while(i <= n) res += a[i ++];
while(j <= m) res += b[j ++];
cout << res << '\n';
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 4e2 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, k, res;
int g[N][N], sum[N][N];
int solve(int x, int y) {
int ans = 0;
int l = y - k, r = y + k, t = k + 1, cur = x;
while(t && cur) {
ans += sum[cur][min(n, r)] - sum[cur][max(0, l - 1)];
l ++, r --;
t --, cur --;
}
t = k, cur = x + 1;
l = y - k + 1, r = y + k - 1;
while(t && cur <= n) {
ans += sum[cur][min(n, r)] - sum[cur][max(0, l - 1)];
l ++, r --;
cur ++, t --;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {
cin >> g[i][j];
sum[i][j] = sum[i][j - 1] + g[i][j];
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {
res = max(res, solve(i, j));
}
}
cout << res << '\n';
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long long ull;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
int h[N], l[N], timl[N], timh[N];
int n, m, q;
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) h[i] = timh[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= m;i ++) l[i] = timl[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= q;i ++)
{
int op, x, c;
cin >> op >> x >> c;
if(op == 0) h[x] = c, timh[x] = i;
else l[x] = c, timl[x] = i;
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
for(int j = 1;j <= m;j ++)
if(timh[i] >= timl[j]) cout << h[i] << ' ';
else cout << l[j] << ' ';
cout << '\n';
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T --)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
都是sb题,接近1h才调完,还得快。
求解 \(g(x)\) 可以直接快速幂,不放设 \(n = g(x)\)。接下来就是算
\(x_1 + x_2 + x_3 + ...... + x_{k - 1} + x_k = n\) 正整数解的数量。
直接插板法。
出题人没给取模,还得写高精。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 140 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e3;
LL k, x, n;
LL f[1000][100][N];
LL power(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
for(; b; a = a * a % mod, b >>= 1) if(b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
return res;
}
void add(LL *c, LL *a, LL *b) {
for(int i = 0, t = 0; i < N; i ++) {
t += a[i] + b[i];
c[i] = t % 10;
t /= 10;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> k >> x;
n = power(x % 1000, x);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
for(int j = 0; j <= i && j < k; j ++) {
if(!j) f[i][j][0] = 1;
else add(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j], f[i - 1][j - 1]);
}
LL *g = f[n - 1][k - 1];
int cur = N - 1;
while(!g[cur]) cur --;
while(cur >= 0) cout << g[cur --];
return 0;
}
8.19
先考虑在一个 \(n \times m\) 的矩形内放 \(k\) 个的方案 \(f(n, m, k)\)。
答案就是 $ \sum_{i=0}^k f(b, a, i) \times f(d, a +c - i, k - i) $
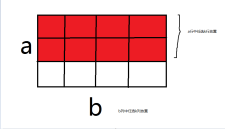
现在 \(a\) 行中任意选出 \(k\) 行来,方案数是 \(C_a^k\),对于每一种方案,第一行有 \(k\) 种选法,第二行有 \(k-1\) 种选法,即 \(A_b^k\)种选法。
得到 \(f(a, b, k) = C_a^k \times A_b^k\)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e3 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e5 + 3;
LL power(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
for(; b; a = a * a % mod, b >>= 1) if(b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
return res;
}
LL fac[N], infac[N];
LL C(int a, int b) {
if(a < b) return 0;
return fac[a] * infac[a - b] % mod * infac[b] % mod;
}
LL A(int a, int b) {
if(a < b) return 0;
return fac[a] * infac[a - b] % mod;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
LL a, b, c, d, k;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d >> k;
fac[0] = 1, infac[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < N; i ++) {
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % mod;
infac[i] = power(fac[i], mod - 2);
}
LL res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i <= k; i ++) {
res = (res + C(b, i) * A(a, i) % mod * C(d, k - i) % mod * A(a + c - i, k - i) % mod) % mod;
}
cout << res << '\n';
return 0;
}
所有的选法减去共线的选法。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
LL n, m;
LL calc(LL a) {
return a * (a - 1) * (a - 2) / 6;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
n ++, m ++;
LL res = calc(n * m) - n * calc(m) - m * calc(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j ++)
res -= 2ll * (__gcd(i, j) - 1) * (n - i) * (m - j);
cout << res << '\n';
return 0;
}
枚举序列长度 \(k\),\(l\) 到 \(r\) 变成 \(r - l\)。
算出 \(x_1 + x_2 + ...... + x_{k-1} + x_k \leq r - l\) 的非负整数解的数量。
令 \(y_i = x_i + 1\)
转变成 \(y_1 + y_2 + ...... + y_{k-1} + y_k \leq r - l + k\) 的正整数解的数量。
依然插板法,\(r-l+k\) 个空插入 \(k\) 个板,方案数为 \(C_{r-l+k}^k\)。
为了方便记 \(m=r-l\)。
答案为 \(\sum\limits_{i=1}^n C_{m+i}^i\)
\(C_{m+1}^1 + C_{m+2}^2 + ...... + C_{m+n - 1}^{n - 1} + C_{m+n}^{n}\)
\(= C_{m+1}^m + C_{m+2}^m + ...... + C_{m+n - 1}^{m} + C_{m+n}^{m}\)
\(= C_{m+1}^{m+1} + C_{m+1}^m + C_{m+2}^m + ...... + C_{m+n - 1}^{m} + C_{m+n}^{m} - C_{m+1}^{m+1}\)
\(= C_{m+2}^{m+1}+ C_{m+2}^m + ...... + C_{m+n - 1}^{m} + C_{m+n}^{m} - C_{m+1}^{m+1}\)
\(= C_{m+3}^{m+1}+ ...... + C_{m+n - 1}^{m} + C_{m+n}^{m} - C_{m+1}^{m+1}\)
\(= C_{m+n+1}^{m+1} - C_{m+1}^{m+1}\)
\(= C_{m+n+1}^{m+1} - 1\)
范围比较大,Lucas定理即可。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e6 + 3;
LL fac[N], infac[N];
LL power(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
for(; b; a = a * a % mod, b >>= 1) if(b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
return res;
}
void init() {
fac[0] = infac[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= mod; i ++) {
fac[i] = fac[i - 1] * i % mod;
infac[i] = power(fac[i], mod - 2);
}
}
LL C(LL a, LL b) {
if(a < b) return 0;
return fac[a] * infac[a - b] % mod * infac[b] % mod;
}
LL Lucas(LL a, LL b) {
if(a < mod && b < mod) return C(a, b);
return Lucas(a / mod, b / mod) * C(a % mod, b % mod) % mod;
}
void solve() {
LL n, l, r;
cin >> n >> l >> r;
cout << (Lucas(r - l + n + 1, r - l + 1) + mod - 1) % mod << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
init();
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
题意:给出一颗 \(n\) 个点的树,把 \(n-1\) 条边每两条分成一组,同一组的两条边必须有公共端点,求分组方法的数量,答案对 998244353 取模。(保证 \(n\) 为奇数)
考虑 \(u\) 的子树,如果 \(u\) 的子树内有偶数条边的话,\(u\) 到父亲的这一条边是不会跟 \(u\) 子树内的边分一组的。
考虑有 \(x\) 条边要配对,任意两条边都能两两配对。
第一条边能配对的边有 \(x - 1\) 种选法,第二条考虑去除前面两条还有 \(x - 3\) 种选法,会发现答案是 \(x ! !\) 的。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 998244353;
int n;
vector<int> e[N];
LL ans = 1;
int siz[N];
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
siz[u] = 1;
int cnt = 0;
for(auto v : e[u])
if(v != fa) {
dfs(v, u);
siz[u] += siz[v];
if(siz[v] & 1) cnt ++;
}
if(cnt & 1) cnt ++;
for(int i = cnt - 1; i >= 1; i -= 2) {
ans = ans * i % mod;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1, 0);
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
sb题,有个sb 10min+才过。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
LL n, T, ans = -1, id;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> T;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
LL v, t;
cin >> v >> t;
int tmp = max(0ll, T - t) * v;
if(ans == -1 || tmp > ans) {
ans = tmp, id = i;
}
}
cout << id << '\n';
return 0;
}
sb题。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m;
string s;
bool st[N];
int now = 1;
vector<int> ans;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> s;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++) {
if(s[i] == 'N') {
if(now > n) {
cout << "No solution\n";
return 0;
}
else {
ans.push_back(now);
st[now] = true;
now ++;
}
}
else {
if(st[1]) {
ans.push_back(1);
}
else {
cout << "No solution\n";
return 0;
}
}
}
for(auto k : ans) cout << k << ' ';
return 0;
}
set模拟。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e5 + 5, base = 1e5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, tot;
multiset<int> s[N];
set<int> se;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
int op, k, b;
cin >> op >> k >> b;
if(op == 1) {
s[k + base].insert(b);
tot ++;
se.insert(k);
}
else if(op == 2) {
cout << tot - s[k + base].size() << '\n';
}
else {
s[k + base].erase(b);
tot = s[k + base].size();
for(auto it = se.begin(); it != se.end(); it ++) {
if(*it == k) continue;
s[*it + base].clear();
}
se.clear();
se.insert(k);
}
}
return 0;
}
一个比较显然的结论是第一问的答案是t有多少个数在s中出现过。
然后拿set暴力模拟。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e6 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m, c1, c2, k;
int s[N];
int cnt[N];
vector<int> t;
set<int> p[N];
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m >> c1 >> c2;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> s[i];
cnt[s[i]] ++;
p[s[i]].insert(i);
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
if(cnt[x]) t.push_back(x);
}
int cur = 0, now = -1;
k = 1;
while(cur < t.size()) {
auto it = p[t[cur]].lower_bound(now + 1);
if(it == p[t[cur]].end()) {
now = -1;
k ++;
continue;
}
cur ++;
now = *it;
}
cout << (int)t.size() * c1 << ' ' << c2 * k << '\n';
return 0;
}
后面会补题解。
8.20
设 \(f_u\) 为到 \(u\) 点时,\(u\) 点上的蝴蝶都已经飞走时能抓到的最大数量, \(g_u\) 为到 \(u\) 这个点, 抓到 \(u\) 上的蝴蝶后又往父亲走时的最大数量,也就是 \(u\) 的儿子节点都没吃到。
得到一个关系式:
\(f\) 的转移有两类。
第一类 :
先走到 \(f_v+a_v\) 最大的子树中,即先走完 \(subtree(v)\) 再回来吃别的子节点。
第二类 :
先走到一个儿子再走上来,再走到另一个儿子的子树中抓,最后上来抓其他子树。
枚举 \(i, j\) 的话复杂度是平方的,显然不行。
令 \(s = \sum\limits_{(v, u) \in G} f_v\)。
那么就有
对于每个 \(i\) 找到最大的 \(j\) 即可,只需要记录 \(a\) 最大的两个就可以了。
Submission #219622614 - Codeforces
二分+并查集乱搞一下。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m;
int p[N];
int a[N], b[N], w[N];
int fa[N];
int find(int x) {
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
fa[find(x)] = find(y);
}
bool check(int x) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) fa[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
if(w[i] >= x) merge(a[i], b[i]);
}
bool ok = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(find(i) != find(p[i])) {
ok = false;
break;
}
}
return ok;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
cin >> p[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> w[i];
}
int l = -1, r = 1e9 + 1, res = -1;
while(l <= r) {
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(check(mid)) l = mid + 1, res = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
if(res == 1e9 + 1) {
res = -1;
}
cout << res << '\n';
return 0;
}
期望 dp。
不是很懂期望。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, m;
int h[N], to[N << 1], val[N << 1], nxt[N << 1], cnt;
int deg[N];
double f[N];
void add(int u, int v, int w) {
to[++ cnt] = v, val[cnt] = w, nxt[cnt] = h[u], h[u] = cnt;
}
double dfs(int u) {
if(f[u] >= 0) return f[u];
f[u] = 0;
for(int i = h[u]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int v = to[i];
f[u] += (val[i] + dfs(v)) / deg[u];
}
return f[u];
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
memset(f, -1, sizeof f);
cin >> n >> m;
while(m --) {
int u, v, w;
cin >> u >> v >> w;
add(u, v, w);
deg[u] ++;
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << dfs(1) << '\n';
return 0;
}
容斥?
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 20 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
LL n, m;
LL f[N];
LL inv = 1;
LL power(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
for(; b; a = a * a % mod, b >>= 1) if(b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
return res;
}
LL calc(LL x) {
if(x < n - 1) return 0;
LL t = 1;
for(LL i = x; i > x - n + 1; i --) {
t = i % mod * t % mod;
}
return t % mod * inv % mod;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> m;
LL res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
cin >> f[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++)
inv = inv * i % mod;
inv = power(inv, mod - 2);
for(int i = 0; i < 1 << n; i ++) {
LL s = 1;
LL x = m + n - 1;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j ++) {
if(i >> j & 1) {
s *= -1;
x -= f[j] + 1;
}
}
res = (res + calc(x) * s) % mod;
}
cout << (res + mod) % mod << '\n';
return 0;
}
额,就猜结论就过了。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
void solve() {
int n;
string s;
cin >> n >> s;
s = " " + s;
vector<int> a(n + 5), f(n + 5, 0), f2(n + 5, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(s[i] == 'T') a[i] = 1, f[i] = f2[i] = 1;
else a[i] = 0;
}
int mx = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(a[i] != a[i + 1] && a[i + 2] != a[i + 3]) {
if(f[i + 1] && f[i + 2]) {
f[i + 3] = 1;
}
}
}
for(int i = n; i - 3>= 1; i --) {
if(a[i] != a[i - 1] && a[i - 2] != a[i - 3]) {
if(f2[i - 1] && f2[i - 2]) {
f2[i - 3] = 1;
}
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if(a[i] == 1) {
int j = i;
while(a[j] == 1) j ++;
mx = max(mx, j - i + f2[j] + f[i - 1]);
i = j;
}
}
cout << mx << '\n';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t --) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
8.21
算出每个点成为好点的概率加起来。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e5 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
int n, k;
vector<int> e[N];
LL ans;
int siz[N];
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
siz[u] = 1;
for(auto v : e[u]) if(v != fa) {
dfs(v, u);
ans += 1ll * siz[u] * siz[v];
ans %= mod;
siz[u] += siz[v];
}
ans += 1ll * siz[u] * (n - siz[u]);
ans %= mod;
}
LL power(LL a, LL b) {
LL res = 1;
for(; b; a = a * a % mod, b >>= 1) if(b & 1) res = res * a % mod;
return res;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cin >> n >> k;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++) {
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
if(k == 1 || k == 3) {
cout << 1 << '\n';
return 0;
}
dfs(1, 0);
cout << ans * power(1ll * n * (n - 1) / 2 % mod, mod - 2) % mod << '\n';
return 0;
}
训练赛考炸了,不想写了md。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号