C++的一般组织结构 学习笔记
5.6.1 C++程序的一般组织结构
• 一个源程序可以划分为多个源文件:
▫ 类声明文件(.h文件)
▫ 类实现文件(.cpp文件)
▫ 类的使用文件(main()所在的.cpp文件)
• 利用工程来组合各个文件。
当代码量很大的时候,可以通过把类写在一个文件中,只需要在main中直接调用就好了
贴下代码
//文件1,类的定义,Point.h class Point { //类的定义 public: //外部接口 Point(int x = 0, int y = 0) : x(x), y(y) { } Point(const Point &p); ~Point() { count--; } int getX() const { return x; } int getY() const { return y; } static void showCount(); //静态函数成员 private: //私有数据成员 int x, y; static int count; //静态数据成员 };
//文件2,类的实现,Point.cpp #include "Point.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; int Point::count = 0; //使用类名初始化静态数据成员 Point::Point(const Point &p) : x(p.x), y(p.y) { //复制构造函数体 count++; } void Point::showCount() { cout << " Object count = " << count << endl; }
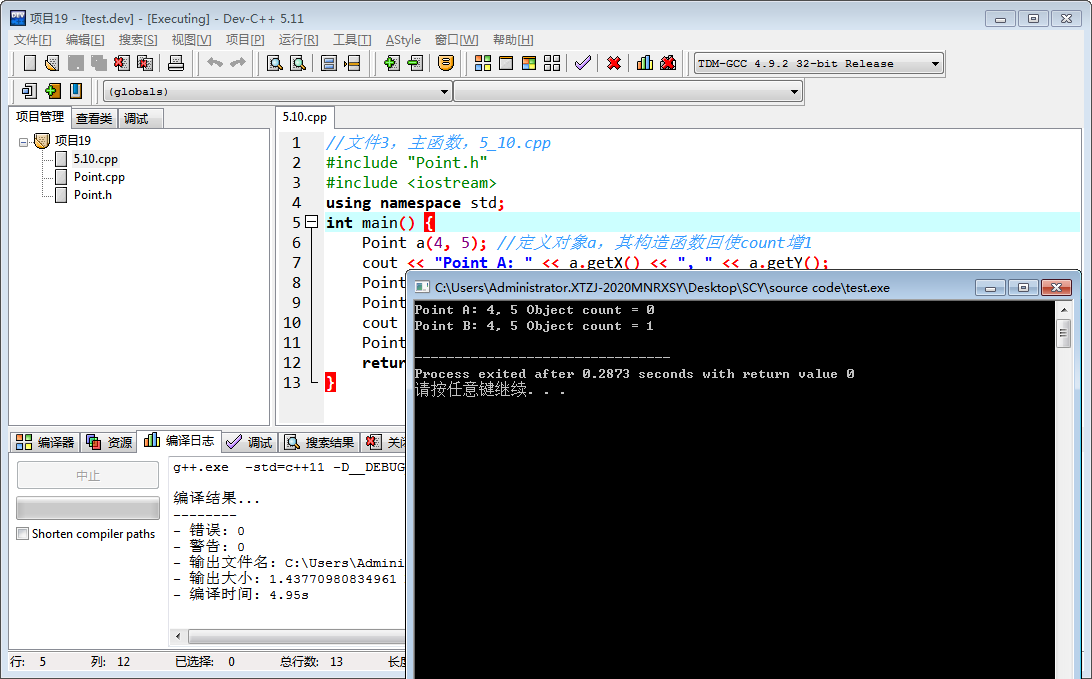
//文件3,主函数,5_10.cpp #include "Point.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { Point a(4, 5); //定义对象a,其构造函数回使count增1 cout << "Point A: " << a.getX() << ", " << a.getY(); Point::showCount(); //输出对象个数 Point b(a); //定义对象b,其构造函数回使count增1 cout << "Point B: " << b.getX() << ", " << b.getY(); Point::showCount(); //输出对象个数 return 0; }
然后当写好这几个文件的时候,运行主函数,显然就报错了,原因是没有放在一个工程下。
解决:
1.新建一个项目
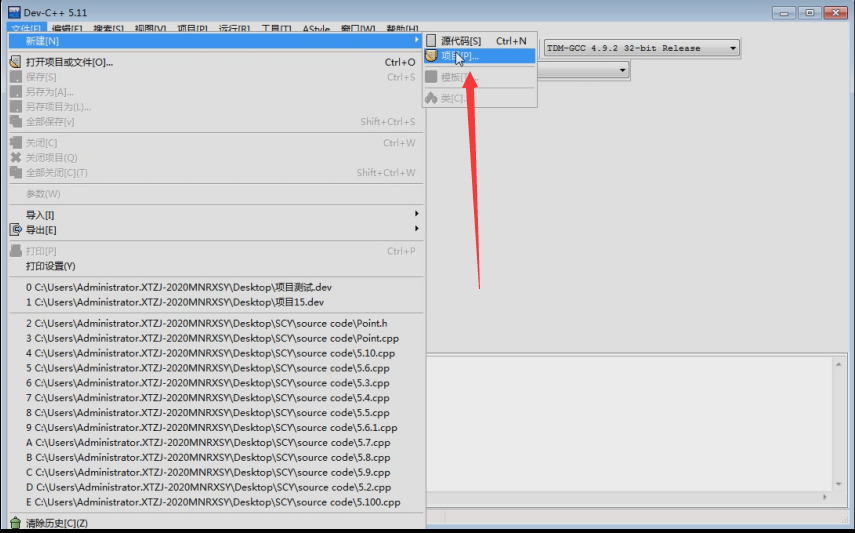
2.选择控制台应用
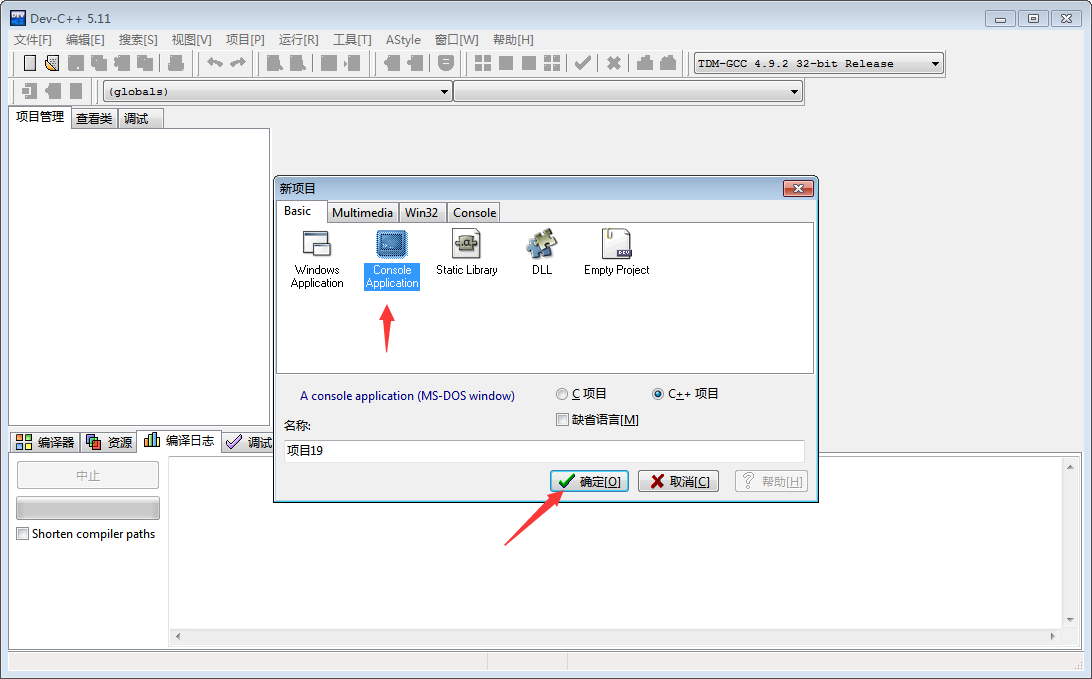
3.就把新的项目整好了
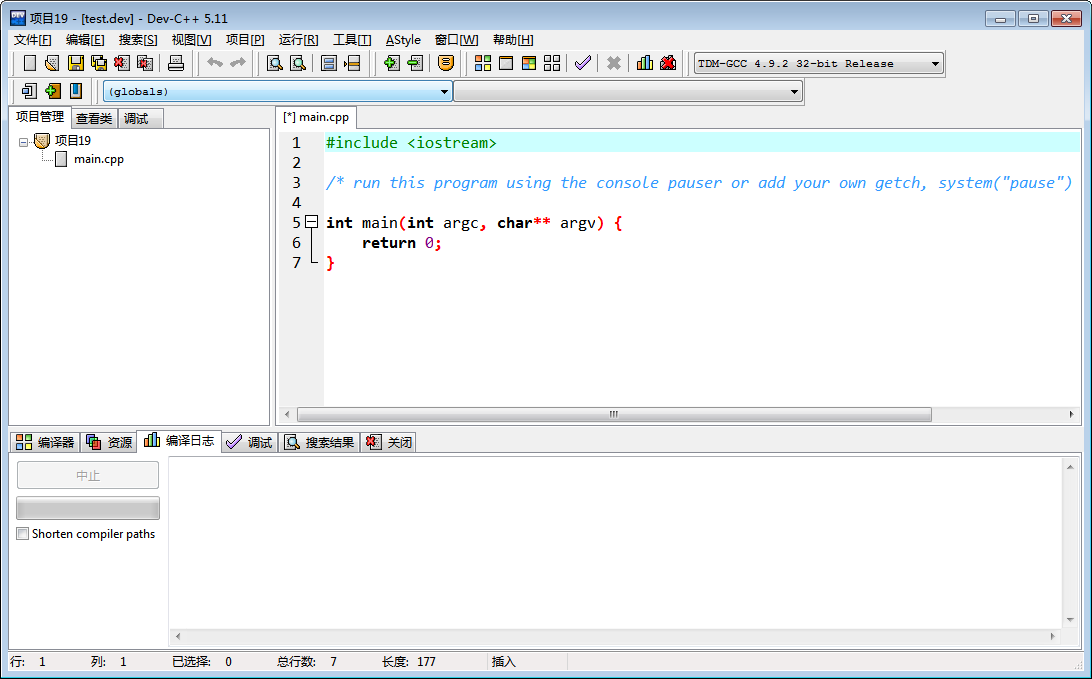
4.可以吧这个main删除掉(右击->移除文件),然后把我们的几个文件添加进来(右击项目名称->添加)
5.最后运行main函数的时候就成功了