牛客小白月赛57
A
思路
问两个矩形重叠的最大面积,显然我们把两个矩形的左下角对齐,形成的重叠部分面积即是最大面积
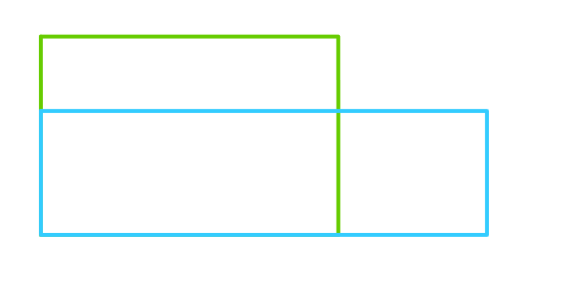
所以答案就是长的最小值*宽的最小值
代码
// ξ†(ᗜ ˰ ᗜ)†ξ
// 去吧,鸭鸭,把希儿和AC都带回来!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int a,b,c,d;
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
cout << min(a,c) * min(b,d) << endl;
return 0;
}
B
思路
简单的思维题,可以发现答案最多不会超过2
分3种情况考虑
- 每一块地都有树 显然这时候我们不需要进行任何操作
- 只有部分地面有树,判断首尾的情况,如果有树,则只用操作一次
- 首尾都没树,这个时候必须要走两次(方向不一样)才能走完
代码
// ξ†(ᗜ ˰ ᗜ)†ξ
// 去吧,鸭鸭,把希儿和AC都带回来!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
string s;
cin >> n;
cin >> s;
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < (int)s.size(); i++){
if(s[i] == '1') p++;
}
if(p == n) cout << 0 << endl;
else if(s[0] == '1' || s[n-1] == '1') cout << 1 << endl;
else cout << 2 << endl;
return 0;
}
C
思路
有点恶心的思维+模拟题,细节有点多
也是分情况讨论
- \(a == b\) 我们不需要做任何操作
- \(a < b\) 那么又会有如下情况
- \(a + k < b\) 我们可以直接从 \(a\) 一步跳到 \(b\)
- \(a - k - 1 > 0\) 如果一步跳不到,我们可以先往下走 \(k+1\) 步,这样一定能跳到
- \(b + k + 1 <= n\) 我们可以直接从 \(a\) 跳到 \(b+k+1\) 再跳到 \(b\)
- \(a + k + 1 <= n\) 我们可以先跳到 \(n\)
如果此时 \(b - k - 1 > 0\) 那我们可以从 \(n\) 跳到 \(b-k-1\) 再跳到 \(b\)
如果不满足就无解
其余情况也无解
- \(a > b\) 从 \(a\) 到 \(b\) 和 从 \(b\) 到 \(a\) 的过程是可逆的,交换一下即可
代码
// ξ†(ᗜ ˰ ᗜ)†ξ
// 去吧,鸭鸭,把希儿和AC都带回来!
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
inline int read()
{
int x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9')
{
if (ch == '-')
f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9')
{
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
inline void print(int x)
{
if (x < 0)
{
putchar('-');
x = -x;
}
if (x > 9)
print(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n, k, a, b;
cin >> n >> k >> a >> b;
if(a > b){
int temp = b;
b = a;
a = temp;
}
if (a == b)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
{
if (a + k < b)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else if (a - k - 1 > 0)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else if (b + k + 1 <= n)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else if(a + k + 1 <= n){
int x = b - k - 1;
if(x > 0) cout << "YES" << endl;
else cout << "NO" << endl;
}
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
D
思路
看到数据范围是 \(10^6\), 暴力的解法是 \(O(n^2)\)
考虑如何去优化
我们可以知道答案一定在 \(10^6\) 以内,关键在于看是否是其因子
如果某个数是它的因子,那必然也是它的倍数
我们可以先把每个数出现的次数存起来,直接 O(logn)的时间枚举看是否是其倍数就行
时间复杂度 \(O(nlogn)\)
代码
// ξ†(ᗜ ˰ ᗜ)†ξ
// 去吧,鸭鸭,把希儿和AC都带回来!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int a[N];
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
int x = 1e6;
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int p;
cin >> p;
a[p]++;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= x; i++){
int ans = 0;
for(int j = 1; j*i <= x; j++){
ans += a[j*i];
if(ans >= 2){
res = i;
break;
}
}
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
E
思路
可以发现输入的数非常大,只能用string储存
但同时也可以知道所有的有效数字不会超过 \(2^{23}\)
所以我们直接枚举即可
代码
// ξ†(ᗜ ˰ ᗜ)†ξ
// 去吧,鸭鸭,把希儿和AC都带回来!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
int c[25];
bool flag = false;
bool check(string s,int p){
int temp = p;
int ws = 0;
int ls = 0;
while(temp) {
ws++;
c[ws] = temp & 1;
if(temp & 1 == 1) ls++;
else ls = 0;
if(ls >= 3) flag = 1;
temp >>= 1;
}
int x = s.size();
if(x > ws) return true;
else if(x == ws){
for(int i = 0; i < x; i++){
int q = s[i] - 48;
if(q < c[ws]) return false;
else if(q > c[ws]) return true;
else ws--;
}
return true;
}
else return false;
}
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
string s;
cin >> s;
int sz = s.size();
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < 1 << sz; i++){
flag = false;
if(check(s,i) && flag) res++;//满足小于s并且至少有3个连续的1
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
F
思路
可以知道每次我们都能直接选择区间 \([1,n]\) 这样之前已经满足的数不会改变,并且不会影响到答案
很容易想到暴力解法 \(O(n\times p)\)
考虑如何优化
举几个例子可以发现答案肯定和差值有关
比如
p = 5
3 3 1 4
2 1 3 2
差值为
4 3 2 3
设差值为 \(y\)
我们只需要找到一个最小的 \(x\) ,使得 $k \times y \equiv x \pmod{p} $
化简一下可知 $k \equiv x \times y ^ {p-2} \pmod{p} $
差值最多只有p种,时间复杂度就简化为 \(O(p \times p)\)
每一次循环找到k的最大值,再求最大值最小
代码
// ξ†(ᗜ ˰ ᗜ)†ξ
// 去吧,鸭鸭,把希儿和AC都带回来!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int a[N];
int b[N];
bool vis[3505];
vector<int> res;
int qmi(int a,int b){
int p1 = b + 2;
int res = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1) res = res * a % p1;
a = a * a % p1;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,p;
cin >> n >> p;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] %= p;
if(b[i] - a[i] >= 0) b[i] = b[i] - a[i];
else b[i] = b[i] - a[i] + p;
if(!vis[b[i]]){
res.push_back(b[i]);
vis[b[i]] = true;
}
}
int sz = res.size();
if(sz == 1 && res[0] == 0){
cout << 0 << endl;
return 0;
}
int k = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = p-1; i >= 1; i--){
int m1 = -1,m2 = 0;
int temp = qmi(i,p-2);
for(int j = 0; j < sz; j++){
int x = res[j];
int x1 = temp;
x1 = x1 * x % p;
if(x1 > m1) {
m1 = x1;
}
}
if(m1 <= k) {
k = m1;
ans = i;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
 拉练一下
拉练一下

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号