算法竞赛模板
背景:放置一些常用的算法模板,方便巩固,会持续更新
快读和快写模板
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
输入空格和回车时的小技巧
cout << a[i] << " \n"[i == n - 1];
因为\n是转义字符,即相当于一个字符
先列举一些出现频率高的,出现频率低的后面补上
前缀和
一维
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int S[N]; //前缀和数组
int a[N]; //样例数组
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
S[i] = a[i] + S[i - 1];
while (m--)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
cout << S[r] - S[l - 1] << endl;
}
二维
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
S[i][j] = S[i][j - 1] + S[i - 1][j] - S[i - 1][j - 1] + a[i][j]; // 求前缀和
}
}
差分
一维
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) dif[i] = a[i] - a[i-1];
while(m--){
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
dif[a] += c;
dif[b+1] -= c;
}
int sum = dif[0];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
sum += dif[i];
cout << sum << " ";
}
二维
cin >> n >> m >> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
{
cin >> Matrix[i][j];
res[i][j] = Matrix[i][j] - Matrix[i - 1][j] - Matrix[i][j - 1] + Matrix[i- 1][j - 1];
}
while (q--)
{
int x1, y1, x2, y2, x;
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> x;
res[x1][y1] += x;
res[x1][y2 + 1] -= x;
res[x2 + 1][y1] -= x;
res[x2 + 1][y2 + 1] += x;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j)
res[i][j] += res[i - 1][j] + res[i][j - 1] - res[i - 1][j - 1];
二分
while(r > l){
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;//这里写法不唯一,只要保证不出现死循环就行
}
二分答案的题一个明显的特点是一般来说可以用答案去检验假设
数学
判定素数
bool isPrime(a) {
if (a < 2) return 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= a / i; ++i)
if (a % i == 0) return 0;
return 1;
}
最大公约数
int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
最小公倍数
a * b / gcd(a,b)
欧拉函数
int euler_phi(int x)
{
int ans = x;
for(int i = 2; i * i <= x; ++i){
if(x % i == 0)
ans = ans / i * (i - 1);
while(x % i == 0) x /= i;
}
if(x > 1) ans = ans / x * (x - 1);
return ans;
}
埃氏筛
const int MAXN = 1000000;
void Prime()
{
for (int i=0; i<MAXN; i++) prime[i]=1; //先把每个数都定义为素数
prime[0]=prime[1]=0;
for (int i=2; i<MAXN; i++)
{
if (!prime[i]) continue;
for (int j=i*2; j<MAXN; j+=i) prime[j] = 0; //将i的倍数标记为合数
}
}
线性筛
for(int i = 2; i <= x; i++)
{
if(!vis[i]) prime[ans++] = i;//判断是否是素数
for(int j = 0; prime[j] <= x / i;++j)
{
vis[prime[j] * i] = true;//最小质因数和最大因子的乘积
if(i % prime[j] == 0) break;//说明不是最小质因数
}
}
筛法求欧拉函数
快速幂
ll quick(ll a,ll b){
ll ans = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1) ans = (ans * a) % mod;
a = (a * a) % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
快速幂 + 逆元求组合数
ll C(ll a,ll b){
if(a < b) return 0;
ll x = ((quick(sp[b],mod-2)) * (quick(sp[a-b],mod-2))) % mod;//sp数组是这个数的阶乘
return (sp[a] * x) % mod;
}
莫队
// ξ†(ᗜ ˰ ᗜ)†ξ
// 去吧,鸭鸭,把希儿和AC都带回来!
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int a[N];
int b[N];
int ans[N];
int temp;
unordered_map<int,int> upp;
struct Q{
int l,r,id;
bool operator < (const Q &p){
return (b[l] ^ b[p.l]) ? b[l] < b[p.l] : (b[l] & 1 ? r < p.r : r > p.r);
}
}Q[N];
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
void add(int x){
if(!upp[a[x]]) temp++;
upp[a[x]]++;
}
void del(int x){
upp[a[x]]--;
if(!upp[a[x]]) temp--;
}
signed main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m;
int len = sqrt(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int l,r;
cin >> l >> r;
Q[i].l = l,Q[i].r = r;
b[i] = (i-1)/len + 1;
Q[i].id = i;
}
sort(Q+1,Q+1+m);
int l = 1,r = 0;//已满足条件的l,r
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int lq = Q[i].l,rq = Q[i].r;
while(l < lq) del(l++);
while(l > lq) add(--l);
while(r < rq) add(++r);
while(r > rq) del(r--);
ans[Q[i].id] = temp;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
cout << ans[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
//题目所考察知识:
//心得体会:
字符串
manacher
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
string s;
cin >> s;
int p = s.size();
vector<char> vec(2*p+5);
vec[0] = '#';
vec[1] = '#';
int y = 2;
for(auto x:s){
vec[y++] = x;
vec[y++] = '#';
}
vector<int> res(2*p+5,0);
auto manacher = [&](){
int mx = 0,mid = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < y; i++){
res[i] = i < mx?min(res[2*mid-i],mx-i):1;//定下限
while(vec[i+res[i]] == vec[i-res[i]]) ++res[i];//时间复杂度是关键
if(i+res[i]>mx){
mx = i + res[i];
mid = i;
}
}
};
manacher();
int maxx = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < y; i++) maxx = max(maxx,res[i]-1);
cout << maxx << endl;
return 0;
}
搜索
当你想用搜素解决问题时,要记住每一层是层层相关联的
有些时候这也许是破题的关键
如果有可以重复搜索的点,要多观察他的状态
dfs
void dfs(int step)
{
判断边界
{
相应操作
}//可以进行剪枝等操作
尝试每一种可能
{
满足check条件
标记
继续下一步dfs(step+1)
恢复初始状态(回溯的时候要用到)
}
}
可行解,回溯,递归,全局变量
尽量减少不必要的递归,因为可能会有爆栈的风险
dfs多参少循环的时间复杂度一般会比较合理
可以采取exit(0)直接结束子进程
记忆化搜索和估值函数都是非常有效的剪枝
bfs
void bfs(int m)
{
queue<pair<int, int> > que;
//初始状态入队
while (!que.empty())
{
pair<int, int> temp = que.front();
//出队
//由初始状态衍生出其他状态并入队
}
}
状态树,队列,最优解
迭代加深搜索(ID)
bool bk;
void dfs(int limit,int x)
{
if(...)
{
bk=true;
return ;
}
if(x==limit)return ;
for(...)dfs(limit,x+1);
}
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++)
{
dfs(i,0);
if(bk==true)return 0;
}
ida* 和 A*
主要是针对估值函数,由估值函数判断剪枝和出队
从而减少不必要的运算
A算法核心:
A 算法的关键在于启发函数,启发函数的优劣直接影响A算法的效率。
f(n)=g(n)+h(n);
这个式子中:f(n)表示从初始状态到目标状态的估测代价。
g(n)表示从初始状态到当前状态的代价(已经确定)。
h(n)表示从当前状态到目标状态的估测代价(预测)。
其中:h(n)的好坏直接影响评估函数的好坏。
一个好的f(n)总能明确指引算法前进的方向,可以迅速的到达目标状态。
f(n)=g(n)+h(n); 我们假设的从初始状态到目标状态的实际最小代价。
这个式子中:f(n)表示从初始状态到目标状态的实际代价。
g(n)表示从初始状态到当前状态的代价(已经确定)g(n)和g(n)是相等的。
h(n)表示从当前状态到目标状态的实际代价。
若h(n)<=h(n),则总能找到最优解。(当h(n)< h*(n)的时候,不可能找到一条从初始状态到达目标状态的路径。在搜索过程中使得h(n)逐渐接近h
数据结构
并查集
int find(int x){
return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find(f[x]);
}
void combin(int x,int y){
f[find(x)] = find(y);
}
单调栈
int st[N],tt;
int main()
{
int n,x;cin>>n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin>>x;
while(tt && st[tt] >= x)
tt--;
if(tt)
cout<<st[tt]<<" ";
else
cout<<-1<<" ";
st[++tt] = x;
}
}
单调队列
void getmin() { // 得到这个队列里的最小值,直接找到最后的就行了
int head = 0, tail = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < k; i++) {
while (head <= tail && a[q[tail]] >= a[i]) tail--;
q[++tail] = i;
}//初始化
for (int i = k; i <= n; i++) {
while (head <= tail && a[q[tail]] >= a[i]) tail--;
q[++tail] = i;
while (q[head] <= i - k) head++;
printf("%d ", a[q[head]]);
}
}
注意单调队列中存的是下标
ST表
int Matrix[200005];
int dp[200000][20];
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,m;
cin >> n ;
fi(1,n)
cin >> Matrix[i];
cin >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
dp[i][0] = Matrix[i];
for(int j = 1; 1 << j <= n;++j)
for(int i = 1;i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n;++i)
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i][j-1],dp[i + (1 << (j -1))][j - 1]);
while(m--)
{
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
int k = log2(b - a + 1);
cout << max(dp[a][k],dp[b - (1 << k) + 1][k]) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
树状数组
int lowbit(int x)
{
return x & (-x);
}
void updata(int i, int k)
{
while (i <= n)
{
c[i] += k;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int i)
{
int res = 0;
while (i > 0)
{
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
线段树
#include<iostream>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define fi(a,b) for(int i = a; i <= b; ++i)
#define fr(a,b) for(int i = a; i >= b; --i)
using pii = pair<int,int>;
const int N = 5e5+5;
#define int long long
int Tree[4 * N];
int sum[4 * N];
int n,m;
int tag[4 * N];
//#define DEBUG
inline int ls(int nod){
return nod << 1;
}
inline int rs(int nod){
return (nod << 1) | 1;
}
inline void build(int l,int r,int nod){
if(l == r)
{
sum[nod] = Tree[l];
return;
}
int mid = l + (r - l >> 1);
build(l,mid,2 * nod);
build(mid+1,r,2 * nod + 1);
sum[nod] = sum[2 * nod] + sum[2 * nod + 1];
}
inline void pushdown(int l, int r,int nod){
int mid = l + (r - l >> 1);
tag[ls(nod)] += tag[nod];
tag[rs(nod)] += tag[nod];
sum[ls(nod)] += tag[nod] * (mid - l + 1);
sum[rs(nod)] += tag[nod] * (r - mid);
tag[nod] = 0;
}
inline void updata(int x,int y, int l,int r,int nod,int data){
if(l >= x && r <= y)
{
sum[nod] += (r - l + 1) * data;
tag[nod] += data;
return;
}
if(tag[nod]) pushdown(l,r,nod);
int mid = l + (r - l >> 1);
if(x <= mid) updata(x,y,l,mid,ls(nod),data);
if(y > mid) updata(x,y,mid + 1,r,rs(nod),data);
sum[nod] = sum[ls(nod)] + sum[rs(nod)];//这里曾经出错过
//这里就代替了上浮的操作
}
inline int summ(int x,int y,int l,int r, int nod){
if(l >= x && r <= y){
return sum[nod];
}
if(tag[nod]) pushdown(l,r,nod);
int mid = l + (r - l >> 1);
int s = 0;
if(x <= mid)
s += summ(x,y,l,mid,ls(nod));
if(y > mid)
s += summ(x,y,mid + 1,r,rs(nod));
return s;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
fi(1,n) cin >> Tree[i];
build(1,n,1);
while(m--){
int op;
cin >> op;
if(op == 2){
int l,r;
cin >> l >> r;
cout << summ(l,r,1,n,1) << endl;
}
else {
int l,r,c;
cin >> l >> r >> c;
updata(l,r,1,n,1,c);
}
}
return 0;
}
异或线段树
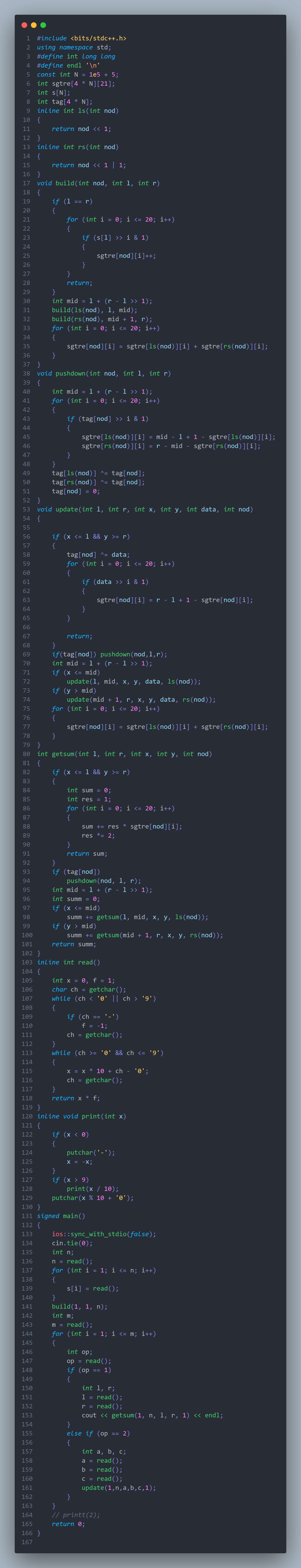
主席树
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int rs[N<<5];
int ls[N<<5];
int sum[N<<5];
int s[N];
int cint[N];
int tot;
int rt[N];
int build(int l,int r){
int root = ++tot;
if(l == r) return root;
int mid = l + (r - l >> 1);
ls[root] = build(l,mid);
rs[root] = build(mid+1,r);
return root;
}
int update(int pre,int l,int r,int k){
int root = ++tot;
sum[root] = sum[pre];
ls[root] = ls[pre],rs[root] = rs[pre];
if(l == r){
sum[root] += 1;
return root;
}
int mid = l + (r - l >> 1);
if(k <= mid) ls[root] = update(ls[pre],l,mid,k);
else rs[root] = update(rs[pre],mid+1,r,k);
sum[root] = sum[ls[root]] + sum[rs[root]];
return root;
}
int query(int u,int v,int k,int l,int r){
int mid = l + (r - l >> 1);
int x = sum[ls[v]] - sum[ls[u]];
if(l == r) return l;
if(k <= x) return query(ls[u],ls[v],k,l,mid);
else return query(rs[u],rs[v],k-x,mid+1,r);
}
inline int read(){
int x=0,f=1;
char ch=getchar();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){
if(ch=='-')
f=-1;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){
x=x*10+ch-'0';
ch=getchar();
}
return x*f;
}
inline void print(int x){
if(x<0){
putchar('-');
x=-x;
}
if(x>9)
print(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
signed main(){
int n,m;
n = read();
m = read();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) s[i] = read(),cint[i] = s[i];
sort(s+1,s+1+n);
int len = unique(s+1,s+1+n) - (s+1);
rt[0] = build(1,len);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int p = lower_bound(s+1,s+len+1,cint[i]) - s;
rt[i] = update(rt[i-1],1,len,p);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
int l,r,k;
l = read(),r = read(),k = read();
int res = query(rt[l-1],rt[r],k,1,len);
print(s[res]),printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
注意:在思考区间问题的时候可以联系前缀和的思想
Dp
dp得关键点在于如何表示所有状态,如何转移状态之间得关系,还有就是要记得优化空间
最关键的一点是要证明是正解,说白了就是数学归纳法
如果一个dp数组只用了上一个状态,那么大概率空间可以优化(利用一个tmp)数组,比如开个f[2][N],以后每次转换就flag^1访问
空间优化有时候也可以是利用bitset
如果一个dp数组需要用到后一个状态,可以尝试利用刷表法或者改变循环的顺序(可能滚动数组也需要改变)
线性dp,区间dp,模数dp,布尔dp,树形dp,期望(概率)dp
# 自顶向下递归的动态规划
def dp(状态1, 状态2, ...):
for 选择 in 所有可能的选择:
# 此时的状态已经因为做了选择而改变
result = 求最值(result, dp(状态1, 状态2, ...))
return result
# 自底向上迭代的动态规划
# 初始化 base case
dp[0][0][...] = base case
# 进行状态转移
for 状态1 in 状态1的所有取值:
for 状态2 in 状态2的所有取值:
for ...
dp[状态1][状态2][...] = 求最值(选择1,选择2...)
线性dp
基本思路就是在一条事件线上进行递推
背包dp
01背包
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++){
int v, w;
cin >> v >> w;
for(int j = V;j >= v;j --)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - v] + w);
}
完全背包
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++){
int v, w;
cin >> v >> w;
for(int j = v;j <= V;j ++)
dp[j] = max(dp[j], dp[j - v] + w);
}
多重背包
while(n--)
{
int w,v,s;
cin >> w >> v >> s;
for(int i = 1; i <= s; ++i)
for(int j = m; j >= w; --j)
dp[j] = max(dp[j],dp[j-w] + v);
}
多重背包二进制优化
分组背包
while(n--){//一共有n组物品
int w;//这组物品有w件
cin >> w;
for(int i = 1; i <= w; i++){
cin >> w[i] >> v[i];
}
for(int i = v; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j = 1; j <= w; j++){
if(i >= w[j])
dp[i] = max(dp[i],dp[i-w[j]] + v[j]);
}
}
}
根据问法的不同解决方法也会有所不一样
如果刚好装满背包,状态数组也是恰好
如果不超过背包的容积,状态数组也应该改为不超过容积
背包问题一般都有明确的上界
二维费用背包+完全背包(求方案数)
dp[0][0] = 1; //初始化数组,避免永远输出0
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
for(int t = a[i]; t <= b; t++) {
dp[j][t] = (dp[j][t] + dp[j - 1][t - a[i]]) % mod; //状态转移
}
}
}
最大连续子段和
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> s[i];
f[n] = s[n];
for(int i = n-1; i >= 1; i--)
f[i] = max(cow[i],f[i+1] + cow[i]);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
maxx = max(maxx,f[i]);
}
cout << maxx << endl;
二分求LIS
f[1] = s[1];
for(int i = 2;i <= n; i++){
int l,r,mid;
if(s[i] > f[len]){
f[++len] = s[i];
}
else{
l = 1,r = len;
while(l < r){
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(s[i] < f[mid]) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
f[l] = s[i];
}
}
//f[i]保存的是长度为i末尾最小的数
更详细的可以参考https://www.cnblogs.com/812-xiao-wen/p/10992613.html
Dilworth 定理(将一个序列剖成若干个单调不升子序列的最小个数等于该序列最长上升子序列的个数)
记忆化搜索
记忆化搜索是一种特殊的dp方式,他保证每种状态最多只访问一次,所以时间复杂度可以降到dp方程的维数相乘
树形dp
int dfs(int x,int fa){
对父节点产生贡献的记忆化搜索
}
dp之四边形优化
学习建议看这篇博客四边形优化
主要是从区间dp引申而来,如果一个递推方程中有i,j,k三个变量也可以纳入考虑
\(dp[l][r]=\min\limits_{l\le k\lt r}(dp[l][k]+dp[k+1][r]) + w(l,r)\)
可以优化一维,需要满足两个条件


最优决策点的每一行,每一列都是单调不减的
一般可以用打表得出结论
dp之单调队列优化
主要优化点在求诸如 \(\max\{f_{i-1,k}\}\)类似的状态时可以利用单调队列O(1)求出
要注意相邻两个状态的左右区间要保持非下降的关系
大多数是从大到小(末状态到初状态)
建议思考dp时先从记忆化搜索入手,这样能提供很多思路
dp表示方法总结
- 以i/dp[i]结尾的方案数/以i开头的方案数/从0到i的方案数
- 表示循环到第i个容量/数量为j的方案数(价值)
- a的前i个和b的前j个相同的方案数/
- 从i开始,区间/长度为j的方案数
- 从i到j的。。。。方案数
1.考虑前面的(完成式)
2.考虑现在的(进行式)
3.考虑之后的(未来式)
图论
最短路
Floyd
for (k = 1; k <= n; k++) {
for (x = 1; x <= n; x++) {
for (y = 1; y <= n; y++) {
f[x][y] = min(f[x][y], f[x][k] + f[k][y]);
}
}
}
Bellman-ford
struct edge {
int v, w;
};
vector<edge> e[maxn];
int dis[maxn];
bool bellmanford(int n, int s) {
memset(dis, 63, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = 0;
bool flag;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
flag = false;
for (int u = 1; u <= n; u++) {
for (auto ed : e[u]) {
int v = ed.v, w = ed.w;
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + w) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + w;
flag = true;
}
}
}
// 没有可以松弛的边时就停止算法
if (!flag) break;
}
// 第 n 轮循环仍然可以松弛时说明 s 点可以抵达一个负环
return flag;
}
spfa
struct edge {
int v, w;
};
vector<edge> e[maxn];
int dis[maxn], cnt[maxn], vis[maxn];
queue<int> q;
bool spfa(int n, int s) {
memset(dis, 63, sizeof(dis));
dis[s] = 0, vis[s] = 1;
q.push(s);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop(), vis[u] = 0;//是否在队列中
for (auto ed : e[u]) {
int v = ed.v, w = ed.w;
if (dis[v] > dis[u] + w) {
dis[v] = dis[u] + w;
cnt[v] = cnt[u] + 1; // 记录最短路经过的边数
if (cnt[v] >= n) return false;
// 在不经过负环的情况下,最短路至多经过 n - 1 条边
// 因此如果经过了多于 n 条边,一定说明经过了负环
if (!vis[v]) q.push(v), vis[v] = 1;
}
}
}
return true;
}
Dijkstra
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
struct edge {
int b,ne,w;
} edge[N];
struct node {
int e,w;
bool operator < (const node p) const {
return w > p.w;
}
};
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m;
vector<int> head(n+5,0);
int cnt = 1;
auto add = [&](int a,int b,int c) {
if(a==b) return;
edge[cnt].b = b;
edge[cnt].w = c;
edge[cnt].ne = head[a];
head[a] = cnt++;
};
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a,b,c);
}
vector<int> dis(n+5,INF);
vector<bool> vis(n+5,false);
dis[1] = 0;
auto djsktra = [&]() {
priority_queue<node> pri;
pri.push({1,0});
while(!pri.empty()) {
node temp = pri.top();
pri.pop();
int e = temp.e;
int w1 = temp.w;
if(vis[e]) continue;//每个点只会放缩一次
vis[e] = true;
for(int i = head[e]; i != 0; i = edge[i].ne) {
int q = edge[i].w;
int b = edge[i].b;
if(dis[b] > dis[e] + q) {
dis[b] = dis[e] + q;
pri.push({b,dis[b]});
}
}
}
if(dis[n] == INF) return (int)-1;
else return dis[n];
};
cout << djsktra() << endl;
}
最小生成树
Kruscal
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
vector<int> f(N+5);
int find(int x) {
return x == f[x]?x:f[x]=find(f[x]);
}
void combin(int x,int y) {
f[find(x)] = f[find(y)];
}
struct edge {
int a,b,w;
bool operator < (const edge p) const {
return w < p.w;
}
} edge[N];
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n,m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
edge[i].a = a;
edge[i].b = b;
edge[i].w = c;
}
sort(edge+1,edge+1+m);
int ans = 0;
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) f[i] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int a = edge[i].a;
int b = edge[i].b;
int c = edge[i].w;
if(find(a) != find(b)) {
combin(a,b);
ans += c;
cnt++;
}
}
if(cnt != n-1) cout << "impossible" << endl;
else cout << ans << endl;
}
堆排序
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
public class heap{
public static void swap(int[] arr,int x,int y){
int temp = arr[x];
arr[x] = arr[y];
arr[y] = temp;
}
public static void heapsort(int[] arr){
int n = arr.length;
for(int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) heapify(arr,n,i);
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){
swap(arr,0,i);
heapify(arr,i,0);
}
}
public static void heapify(int[] arr,int n,int i){
int largest = i;
int left = i*2+1;
int right = i*2+2;
if(left < n && arr[left] > arr[largest]) largest = left;
if(right < n && arr[right] > arr[largest]) largest = right;
if(largest != i) {
swap(arr,largest,i);
heapify(arr,n,largest);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
String[] ss = br.readLine().split(" ");
int[] res = new int[ss.length];
for(int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) res[i] = Integer.parseInt(ss[i]);
heapsort(res);
for(int i = 0; i < res.length; i++) out.printf("%d ",res[i]);
out.printf("\n");
out.flush();
out.close();
br.close();
}
}
拓扑排序(bfs版)
class Solution {
public class edge{
int b;
int ne;
}
public int cnt;
public void add(int a,int b,edge[] edg,int[] head){
edg[cnt] = new edge();
edg[cnt].b = b;
edg[cnt].ne = head[a];
head[a] = cnt++;
}
public boolean bfs(int[] rb,edge[] edg,int[] head){
Deque<Integer> que = new ArrayDeque<>();
for(int i = 0; i < rb.length;i++){
if(rb[i] == 0) que.addLast(i);
}
while(que.size() != 0){
int x = que.getFirst();
que.removeFirst();
for(int i = head[x];i != 0;i = edg[i].ne){
int b = edg[i].b;
rb[b]--;
if(rb[b] == 0) que.addLast(b);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < rb.length; i++){
if(rb[i] != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
cnt = 1;
edge[] edg = new edge[prerequisites.length+5];
int[] head = new int[numCourses+5];
int[] rb = new int[numCourses+5];
for(int i = 0; i < prerequisites.length; i++) {
add(prerequisites[i][1],prerequisites[i][0],edg,head);
rb[prerequisites[i][0]]++;
}
return bfs(rb,edg,head);
}
}
最近公共祖先
#include <iostream>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 5;
/* run this program using the console pauser or add your own getch, system("pause") or input loop */
int head[N];
int cnt = 1;
int f[N][25];
int deep[N];
struct edg {
int b, w, ne;
}edg[2*N];
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
edg[cnt].b = b;
edg[cnt].w = c;
edg[cnt].ne = head[a];
head[a] = cnt++;
}
void dfs(int x, int fa) {
deep[x] = deep[fa] + 1;
f[x][0] = fa;
for (int i = 1; i <= 19; i++) f[x][i] = f[f[x][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (int i = head[x]; i != 0; i = edg[i].ne) {
int b = edg[i].b;
if (b == fa) continue;
dfs(b, x);
}
}
int lca(int a, int b) {
if (deep[a] < deep[b]) swap(a, b);
int p = deep[a] - deep[b];
for (int i = 0; i <= 19; i++) {
if (p >> i & 1) a = f[a][i];
}
// cout << p << endl;
// cout << a << " " << b <<endl;
if (a == b) return a;
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--) {
if (f[a][i] != f[b][i]) {
a = f[a][i];
b = f[b][i];
}
}
return f[a][0];
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n, m, s;
cin >> n >> m >> s;
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
add(a, b, 0);
add(b, a, 0);
}
dfs(s, 0);
// for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << f[5][i] << " ";
// cout << endl;
while (m--) {
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int q = lca(a, b);
cout << q << endl;
}
return 0;
}
贪心
基本思路是由子最优结构得到父最优结构,从而得到最终的值
关键还要看每个部分对父结构的贡献
计算几何
多边形
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAXN 1000
#define offset 10000
#define eps 1e-8
#define zero(x) (((x)>0?(x):-(x))<eps)
#define _sign(x) ((x)>eps?1:((x)<-eps?2:0))
struct point{double x,y;};
struct line{point a,b;};
double xmult(point p1,point p2,point p0){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
//判定凸多边形,顶点按顺时针或逆时针给出,允许相邻边共线
int is_convex(int n,point* p){
int i,s[3]={1,1,1};
for (i=0;i<n&&s[1]|s[2];i++)
s[_sign(xmult(p[(i+1)%n],p[(i+2)%n],p[i]))]=0;
return s[1]|s[2];
}
//判定凸多边形,顶点按顺时针或逆时针给出,不允许相邻边共线
int is_convex_v2(int n,point* p){
int i,s[3]={1,1,1};
for (i=0;i<n&&s[0]&&s[1]|s[2];i++)
s[_sign(xmult(p[(i+1)%n],p[(i+2)%n],p[i]))]=0;
return s[0]&&s[1]|s[2];
}
//判点在凸多边形内或多边形边上,顶点按顺时针或逆时针给出
int inside_convex(point q,int n,point* p){
int i,s[3]={1,1,1};
for (i=0;i<n&&s[1]|s[2];i++)
s[_sign(xmult(p[(i+1)%n],q,p[i]))]=0;
return s[1]|s[2];
}
//判点在凸多边形内,顶点按顺时针或逆时针给出,在多边形边上返回0
int inside_convex_v2(point q,int n,point* p){
int i,s[3]={1,1,1};
for (i=0;i<n&&s[0]&&s[1]|s[2];i++)
s[_sign(xmult(p[(i+1)%n],q,p[i]))]=0;
return s[0]&&s[1]|s[2];
}
//判点在任意多边形内,顶点按顺时针或逆时针给出
//on_edge表示点在多边形边上时的返回值,offset为多边形坐标上限
int inside_polygon(point q,int n,point* p,int on_edge=1){
point q2;
int i=0,count;
while (i<n)
for (count=i=0,q2.x=rand()+offset,q2.y=rand()+offset;i<n;i++)
if (zero(xmult(q,p[i],p[(i+1)%n]))&&(p[i].x-q.x)*(p[(i+1)%n].x-q.x)<eps&&(p[i].y-q.y)*(p[(i+1)%n].y-q.y)<eps)
return on_edge;
else if (zero(xmult(q,q2,p[i])))
break;
else if (xmult(q,p[i],q2)*xmult(q,p[(i+1)%n],q2)<-eps&&xmult(p[i],q,p[(i+1)%n])*xmult(p[i],q2,p[(i+1)%n])<-eps)
count++;
return count&1;
}
inline int opposite_side(point p1,point p2,point l1,point l2){
return xmult(l1,p1,l2)*xmult(l1,p2,l2)<-eps;
}
inline int dot_online_in(point p,point l1,point l2){
return zero(xmult(p,l1,l2))&&(l1.x-p.x)*(l2.x-p.x)<eps&&(l1.y-p.y)*(l2.y-p.y)<eps;
}
//判线段在任意多边形内,顶点按顺时针或逆时针给出,与边界相交返回1
int inside_polygon(point l1,point l2,int n,point* p){
point t[MAXN],tt;
int i,j,k=0;
if (!inside_polygon(l1,n,p)||!inside_polygon(l2,n,p))
return 0;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
if (opposite_side(l1,l2,p[i],p[(i+1)%n])&&opposite_side(p[i],p[(i+1)%n],l1,l2))
return 0;
else if (dot_online_in(l1,p[i],p[(i+1)%n]))
t[k++]=l1;
else if (dot_online_in(l2,p[i],p[(i+1)%n]))
t[k++]=l2;
else if (dot_online_in(p[i],l1,l2))
t[k++]=p[i];
for (i=0;i<k;i++)
for (j=i+1;j<k;j++){
tt.x=(t[i].x+t[j].x)/2;
tt.y=(t[i].y+t[j].y)/2;
if (!inside_polygon(tt,n,p))
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
point intersection(line u,line v){
point ret=u.a;
double t=((u.a.x-v.a.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-v.a.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x))
/((u.a.x-u.b.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-u.b.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x));
ret.x+=(u.b.x-u.a.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u.b.y-u.a.y)*t;
return ret;
}
point barycenter(point a,point b,point c){
line u,v;
u.a.x=(a.x+b.x)/2;
u.a.y=(a.y+b.y)/2;
u.b=c;
v.a.x=(a.x+c.x)/2;
v.a.y=(a.y+c.y)/2;
v.b=b;
return intersection(u,v);
}
//多边形重心
point barycenter(int n,point* p){
point ret,t;
double t1=0,t2;
int i;
ret.x=ret.y=0;
for (i=1;i<n-1;i++)
if (fabs(t2=xmult(p[0],p[i],p[i+1]))>eps){
t=barycenter(p[0],p[i],p[i+1]);
ret.x+=t.x*t2;
ret.y+=t.y*t2;
t1+=t2;
}
if (fabs(t1)>eps)
ret.x/=t1,ret.y/=t1;
return ret;
}
几何位置关系
//浮点几何函数库
#include <math.h>
#define eps 1e-8
#define zero(x) (((x)>0?(x):-(x))<eps)
struct point{double x,y;};
struct line{point a,b;};
//计算cross product (P1-P0)x(P2-P0)
double xmult(point p1,point p2,point p0){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
double xmult(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x0,double y0){
return (x1-x0)*(y2-y0)-(x2-x0)*(y1-y0);
}
//计算dot product (P1-P0).(P2-P0)
double dmult(point p1,point p2,point p0){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.x-p0.x)+(p1.y-p0.y)*(p2.y-p0.y);
}
double dmult(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x0,double y0){
return (x1-x0)*(x2-x0)+(y1-y0)*(y2-y0);
}
//两点距离
double distance(point p1,point p2){
return sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
}
double distance(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){
return sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
}
//判三点共线
int dots_inline(point p1,point p2,point p3){
return zero(xmult(p1,p2,p3));
}
int dots_inline(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3){
return zero(xmult(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3));
}
//判点是否在线段上,包括端点
int dot_online_in(point p,line l){
return zero(xmult(p,l.a,l.b))&&(l.a.x-p.x)*(l.b.x-p.x)<eps&&(l.a.y-p.y)*(l.b.y-p.y)<eps;
}
int dot_online_in(point p,point l1,point l2){
return zero(xmult(p,l1,l2))&&(l1.x-p.x)*(l2.x-p.x)<eps&&(l1.y-p.y)*(l2.y-p.y)<eps;
}
int dot_online_in(double x,double y,double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){
return zero(xmult(x,y,x1,y1,x2,y2))&&(x1-x)*(x2-x)<eps&&(y1-y)*(y2-y)<eps;
}
//判点是否在线段上,不包括端点
int dot_online_ex(point p,line l){
return dot_online_in(p,l)&&(!zero(p.x-l.a.x)||!zero(p.y-l.a.y))&&(!zero(p.x-l.b.x)||!zero(p.y-l.b.y));
}
int dot_online_ex(point p,point l1,point l2){
return dot_online_in(p,l1,l2)&&(!zero(p.x-l1.x)||!zero(p.y-l1.y))&&(!zero(p.x-l2.x)||!zero(p.y-l2.y));
}
int dot_online_ex(double x,double y,double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){
return dot_online_in(x,y,x1,y1,x2,y2)&&(!zero(x-x1)||!zero(y-y1))&&(!zero(x-x2)||!zero(y-y2));
}
//判两点在线段同侧,点在线段上返回0
int same_side(point p1,point p2,line l){
return xmult(l.a,p1,l.b)*xmult(l.a,p2,l.b)>eps;
}
int same_side(point p1,point p2,point l1,point l2){
return xmult(l1,p1,l2)*xmult(l1,p2,l2)>eps;
}
//判两点在线段异侧,点在线段上返回0
int opposite_side(point p1,point p2,line l){
return xmult(l.a,p1,l.b)*xmult(l.a,p2,l.b)<-eps;
}
int opposite_side(point p1,point p2,point l1,point l2){
return xmult(l1,p1,l2)*xmult(l1,p2,l2)<-eps;
}
//判两直线平行
int parallel(line u,line v){
return zero((u.a.x-u.b.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(v.a.x-v.b.x)*(u.a.y-u.b.y));
}
int parallel(point u1,point u2,point v1,point v2){
return zero((u1.x-u2.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(v1.x-v2.x)*(u1.y-u2.y));
}
//判两直线垂直
int perpendicular(line u,line v){
return zero((u.a.x-u.b.x)*(v.a.x-v.b.x)+(u.a.y-u.b.y)*(v.a.y-v.b.y));
}
int perpendicular(point u1,point u2,point v1,point v2){
return zero((u1.x-u2.x)*(v1.x-v2.x)+(u1.y-u2.y)*(v1.y-v2.y));
}
//判两线段相交,包括端点和部分重合
int intersect_in(line u,line v){
if (!dots_inline(u.a,u.b,v.a)||!dots_inline(u.a,u.b,v.b))
return !same_side(u.a,u.b,v)&&!same_side(v.a,v.b,u);
return dot_online_in(u.a,v)||dot_online_in(u.b,v)||dot_online_in(v.a,u)||dot_online_in(v.b,u);
}
int intersect_in(point u1,point u2,point v1,point v2){
if (!dots_inline(u1,u2,v1)||!dots_inline(u1,u2,v2))
return !same_side(u1,u2,v1,v2)&&!same_side(v1,v2,u1,u2);
return dot_online_in(u1,v1,v2)||dot_online_in(u2,v1,v2)||dot_online_in(v1,u1,u2)||dot_online_in(v2,u1,u2);
}
//判两线段相交,不包括端点和部分重合
int intersect_ex(line u,line v){
return opposite_side(u.a,u.b,v)&&opposite_side(v.a,v.b,u);
}
int intersect_ex(point u1,point u2,point v1,point v2){
return opposite_side(u1,u2,v1,v2)&&opposite_side(v1,v2,u1,u2);
}
//计算两直线交点,注意事先判断直线是否平行!
//线段交点请另外判线段相交(同时还是要判断是否平行!)
point intersection(line u,line v){
point ret=u.a;
double t=((u.a.x-v.a.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-v.a.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x))
/((u.a.x-u.b.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-u.b.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x));
ret.x+=(u.b.x-u.a.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u.b.y-u.a.y)*t;
return ret;
}
point intersection(point u1,point u2,point v1,point v2){
point ret=u1;
double t=((u1.x-v1.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-v1.y)*(v1.x-v2.x))
/((u1.x-u2.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-u2.y)*(v1.x-v2.x));
ret.x+=(u2.x-u1.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u2.y-u1.y)*t;
return ret;
}
//点到直线上的最近点
point ptoline(point p,line l){
point t=p;
t.x+=l.a.y-l.b.y,t.y+=l.b.x-l.a.x;
return intersection(p,t,l.a,l.b);
}
point ptoline(point p,point l1,point l2){
point t=p;
t.x+=l1.y-l2.y,t.y+=l2.x-l1.x;
return intersection(p,t,l1,l2);
}
//点到直线距离
double disptoline(point p,line l){
return fabs(xmult(p,l.a,l.b))/distance(l.a,l.b);
}
double disptoline(point p,point l1,point l2){
return fabs(xmult(p,l1,l2))/distance(l1,l2);
}
double disptoline(double x,double y,double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){
return fabs(xmult(x,y,x1,y1,x2,y2))/distance(x1,y1,x2,y2);
}
//点到线段上的最近点
point ptoseg(point p,line l){
point t=p;
t.x+=l.a.y-l.b.y,t.y+=l.b.x-l.a.x;
if (xmult(l.a,t,p)*xmult(l.b,t,p)>eps)
return distance(p,l.a)<distance(p,l.b)?l.a:l.b;
return intersection(p,t,l.a,l.b);
}
point ptoseg(point p,point l1,point l2){
point t=p;
t.x+=l1.y-l2.y,t.y+=l2.x-l1.x;
if (xmult(l1,t,p)*xmult(l2,t,p)>eps)
return distance(p,l1)<distance(p,l2)?l1:l2;
return intersection(p,t,l1,l2);
}
//点到线段距离
double disptoseg(point p,line l){
point t=p;
t.x+=l.a.y-l.b.y,t.y+=l.b.x-l.a.x;
if (xmult(l.a,t,p)*xmult(l.b,t,p)>eps)
return distance(p,l.a)<distance(p,l.b)?distance(p,l.a):distance(p,l.b);
return fabs(xmult(p,l.a,l.b))/distance(l.a,l.b);
}
double disptoseg(point p,point l1,point l2){
point t=p;
t.x+=l1.y-l2.y,t.y+=l2.x-l1.x;
if (xmult(l1,t,p)*xmult(l2,t,p)>eps)
return distance(p,l1)<distance(p,l2)?distance(p,l1):distance(p,l2);
return fabs(xmult(p,l1,l2))/distance(l1,l2);
}
//矢量V以P为顶点逆时针旋转angle并放大scale倍
point rotate(point v,point p,double angle,double scale){
point ret=p;
v.x-=p.x,v.y-=p.y;
p.x=scale*cos(angle);
p.y=scale*sin(angle);
ret.x+=v.x*p.x-v.y*p.y;
ret.y+=v.x*p.y+v.y*p.x;
return ret;
}
//p点关于直线L的对称点
ponit symmetricalPointofLine(point p, line L)
{
point p2;
double d;
d = L.a * L.a + L.b * L.b;
p2.x = (L.b * L.b * p.x - L.a * L.a * p.x -
2 * L.a * L.b * p.y - 2 * L.a * L.c) / d;
p2.y = (L.a * L.a * p.y - L.b * L.b * p.y -
2 * L.a * L.b * p.x - 2 * L.b * L.c) / d;
return p2;
}
//求两点的平分线
struct line { double a, b, c; point st, end;
void set(point& u, point& v) {a = v.y - u.y; b = u.x - v.x; c = a*u.x + b*u.y; st = u; end = v; }
};
line bisector(point& a, point& b) {
line ab, ans; ab.set(a, b);
double midx = (a.x + b.x)/2.0, midy = (a.y + b.y)/2.0;
ans.a = -ab.b, ans.b = -ab.a, ans.c = -ab.b * midx + ab.a * midy;
return ans;
}
// 已知入射线、镜面,求反射线。
// a1,b1,c1为镜面直线方程(a1 x + b1 y + c1 = 0 ,下同)系数;
a2,b2,c2为入射光直线方程系数;
a,b,c为反射光直线方程系数.
// 光是有方向的,使用时注意:入射光向量:<-b2,a2>;反射光向量:<b,-a>.
// 不要忘记结果中可能会有"negative zeros"
void reflect(double a1,double b1,double c1,
double a2,double b2,double c2,
double &a,double &b,double &c)
{
double n,m;
double tpb,tpa;
tpb=b1*b2+a1*a2;
tpa=a2*b1-a1*b2;
m=(tpb*b1+tpa*a1)/(b1*b1+a1*a1);
n=(tpa*b1-tpb*a1)/(b1*b1+a1*a1);
if(fabs(a1*b2-a2*b1)<1e-20)
{
a=a2;b=b2;c=c2;
return;
}
double xx,yy; //(xx,yy)是入射线与镜面的交点。
xx=(b1*c2-b2*c1)/(a1*b2-a2*b1);
yy=(a2*c1-a1*c2)/(a1*b2-a2*b1);
a=n;
b=-m;
c=m*yy-xx*n;
}
面积
#include <math.h>
struct point{double x,y;};
//计算cross product (P1-P0)x(P2-P0)
double xmult(point p1,point p2,point p0){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
double xmult(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x0,double y0){
return (x1-x0)*(y2-y0)-(x2-x0)*(y1-y0);
}
//计算三角形面积,输入三顶点
double area_triangle(point p1,point p2,point p3){
return fabs(xmult(p1,p2,p3))/2;
}
double area_triangle(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3){
return fabs(xmult(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3))/2;
}
//计算三角形面积,输入三边长
double area_triangle(double a,double b,double c){
double s=(a+b+c)/2;
return sqrt(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c));
}
//计算多边形面积,顶点按顺时针或逆时针给出
double area_polygon(int n,point* p){
double s1=0,s2=0;
int i;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
s1+=p[(i+1)%n].y*p[i].x,s2+=p[(i+1)%n].y*p[(i+2)%n].x;
return fabs(s1-s2)/2;
}
球面
#include <math.h>
const double pi=acos(-1);
//计算圆心角lat表示纬度,-90<=w<=90,lng表示经度
//返回两点所在大圆劣弧对应圆心角,0<=angle<=pi
double angle(double lng1,double lat1,double lng2,double lat2){
double dlng=fabs(lng1-lng2)*pi/180;
while (dlng>=pi+pi)
dlng-=pi+pi;
if (dlng>pi)
dlng=pi+pi-dlng;
lat1*=pi/180,lat2*=pi/180;
return acos(cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(dlng)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2));
}
//计算距离,r为球半径
double line_dist(double r,double lng1,double lat1,double lng2,double lat2){
double dlng=fabs(lng1-lng2)*pi/180;
while (dlng>=pi+pi)
dlng-=pi+pi;
if (dlng>pi)
dlng=pi+pi-dlng;
lat1*=pi/180,lat2*=pi/180;
return r*sqrt(2-2*(cos(lat1)*cos(lat2)*cos(dlng)+sin(lat1)*sin(lat2)));
}
//计算球面距离,r为球半径
inline double sphere_dist(double r,double lng1,double lat1,double lng2,double lat2){
return r*angle(lng1,lat1,lng2,lat2);
}
//球面反射
//SGU110
// http://acm.sgu.ru/problem.php?contest=0&problem=110
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
const int size = 555;
const double eps = 1e-9;
struct point {double x, y, z;} centre = {0, 0, 0};
struct circle {point o; double r;} cir[size];
struct ray {point s, dir;} l;
int n;
int dcmp (double x){return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps;}
double sqr (double x){return x*x;}
double dot (point a, point b){return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y + a.z * b.z;}
double dis2 (point a, point b){return sqr(a.x-b.x) + sqr(a.y-b.y) + sqr(a.z-b.z);}
double disToLine2 (point a, ray l){ /**** 点到直线L的距离的平方 **/
point tmp;
tmp.x = l.dir.y * (a.z - l.s.z) - l.dir.z * (a.y - l.s.y);
tmp.y = -l.dir.x * (a.z - l.s.z) + l.dir.z * (a.x - l.s.x);
tmp.z = l.dir.x * (a.y - l.s.y) - l.dir.y * (a.x - l.s.x);
return dis2 (tmp, centre) / dis2 (l.dir, centre);
}
/** 用解方程(点到圆心的距离为r)法求交点 (下面有向量法求交点, 两者取其一, 都OK)*/
/* 是向量分量表示发的系数, 必须在射线上,故K必须为正, t是交点***/
/*
bool find (circle p, ray l, double &k, point &t)
{
double x = l.s.x - p.o.x, y = l.s.y - p.o.y, z = l.s.z - p.o.z;
double a = sqr(l.dir.x) + sqr(l.dir.y) + sqr(l.dir.z);
double b = 2 * (x*l.dir.x + y*l.dir.y + z*l.dir.z);
double c = x*x + y*y + z*z - p.r*p.r;
double det = b*b - 4*a*c;
// printf ("a = %lf, b = %lf, c = %lf", a, b, c);
// printf ("det = %lf\n", det);
if (dcmp(det) == -1) return false;
k = (-b - sqrt(det)) / a / 2;
if (dcmp(k) != 1) return false;
t.x = l.s.x + k * l.dir.x;
t.y = l.s.y + k * l.dir.y;
t.z = l.s.z + k * l.dir.z;
return true;
}
*/
/**** 用向量法求交点 ***/
bool find (circle p, ray l, double &k, point &t)
{
double h2 = disToLine2 (p.o, l);
// printf ("h2 = %lf\n", h2);
if (dcmp(p.r*p.r - h2) < 0) return false;
point tmp;
tmp.x = p.o.x - l.s.x;
tmp.y = p.o.y - l.s.y;
tmp.z = p.o.z - l.s.z;
if (dcmp(dot(tmp, l.dir)) <= 0) return false;
k = sqrt(dis2(p.o, l.s) - h2) - sqrt(p.r*p.r - h2);
double k1 = k / sqrt(dis2(l.dir, centre));
t.x = l.s.x + k1 * l.dir.x;
t.y = l.s.y + k1 * l.dir.y;
t.z = l.s.z + k1 * l.dir.z;
return true;
}
/*计算新射线的起点和方向 */
void newRay (ray &l, ray l1, point inter)
{
double k = - 2 * dot(l.dir, l1.dir);
l.dir.x += l1.dir.x * k;
l.dir.y += l1.dir.y * k;
l.dir.z += l1.dir.z * k;
l.s = inter;
}
/* 返回的是最先相交的球的编号,均不相交,返回-1 */
int update ()
{
int sign = -1, i;
double k = 1e100, tmp;
point inter, t;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++){ //找到最先相交的球
if (!find (cir[i], l, tmp, t)) continue;
if (dcmp (tmp - k) < 0) k = tmp, inter = t, sign = i;
}
//ray 变向
if (sign == -1) return sign;
ray l1;
l1.s = cir[sign].o;
l1.dir.x = (inter.x - l1.s.x) / cir[sign].r;
l1.dir.y = (inter.y - l1.s.y) / cir[sign].r;
l1.dir.z = (inter.z - l1.s.z) / cir[sign].r;
newRay (l, l1, inter);
return sign;
}
int main ()
{
// freopen ("in", "r", stdin);
int i;
scanf ("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) //输入空间的球位置
scanf ("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &cir[i].o.x, &cir[i].o.y, &cir[i].o.z, &cir[i].r);
scanf ("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &l.s.x, &l.s.y, &l.s.z, &l.dir.x, &l.dir.y, &l.dir.z);
for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++){ //最多输出十次相交的球的编号
int sign = update ();
if (sign == -1) break;
if (i == 0) printf ("%d", sign);
else if (i < 10) printf (" %d", sign);
else printf (" etc.");
}
puts ("");
}
三角形
#include <math.h>
struct point{double x,y;};
struct line{point a,b;};
double distance(point p1,point p2){
return sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
}
point intersection(line u,line v){
point ret=u.a;
double t=((u.a.x-v.a.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-v.a.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x))
/((u.a.x-u.b.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-u.b.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x));
ret.x+=(u.b.x-u.a.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u.b.y-u.a.y)*t;
return ret;
}
//外心
point circumcenter(point a,point b,point c){
line u,v;
u.a.x=(a.x+b.x)/2;
u.a.y=(a.y+b.y)/2;
u.b.x=u.a.x-a.y+b.y;
u.b.y=u.a.y+a.x-b.x;
v.a.x=(a.x+c.x)/2;
v.a.y=(a.y+c.y)/2;
v.b.x=v.a.x-a.y+c.y;
v.b.y=v.a.y+a.x-c.x;
return intersection(u,v);
}
//内心
point incenter(point a,point b,point c){
line u,v;
double m,n;
u.a=a;
m=atan2(b.y-a.y,b.x-a.x);
n=atan2(c.y-a.y,c.x-a.x);
u.b.x=u.a.x+cos((m+n)/2);
u.b.y=u.a.y+sin((m+n)/2);
v.a=b;
m=atan2(a.y-b.y,a.x-b.x);
n=atan2(c.y-b.y,c.x-b.x);
v.b.x=v.a.x+cos((m+n)/2);
v.b.y=v.a.y+sin((m+n)/2);
return intersection(u,v);
}
//垂心
point perpencenter(point a,point b,point c){
line u,v;
u.a=c;
u.b.x=u.a.x-a.y+b.y;
u.b.y=u.a.y+a.x-b.x;
v.a=b;
v.b.x=v.a.x-a.y+c.y;
v.b.y=v.a.y+a.x-c.x;
return intersection(u,v);
}
//重心
//到三角形三顶点距离的平方和最小的点
//三角形内到三边距离之积最大的点
point barycenter(point a,point b,point c){
line u,v;
u.a.x=(a.x+b.x)/2;
u.a.y=(a.y+b.y)/2;
u.b=c;
v.a.x=(a.x+c.x)/2;
v.a.y=(a.y+c.y)/2;
v.b=b;
return intersection(u,v);
}
//费马点
//到三角形三顶点距离之和最小的点
point fermentpoint(point a,point b,point c){
point u,v;
double step=fabs(a.x)+fabs(a.y)+fabs(b.x)+fabs(b.y)+fabs(c.x)+fabs(c.y);
int i,j,k;
u.x=(a.x+b.x+c.x)/3;
u.y=(a.y+b.y+c.y)/3;
while (step>1e-10)
for (k=0;k<10;step/=2,k++)
for (i=-1;i<=1;i++)
for (j=-1;j<=1;j++){
v.x=u.x+step*i;
v.y=u.y+step*j;
if (distance(u,a)+distance(u,b)+distance(u,c)>distance(v,a)+distance(v,b)+distance(v,c))
u=v;
}
return u;
}
//求曲率半径 三角形内最大可围成面积
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
const double pi=3.14159265358979;
int main()
{
double a,b,c,d,p,s,r,ans,R,x,l; int T=0;
while(cin>>a>>b>>c>>d&&a+b+c+d)
{
T++;
l=a+b+c;
p=l/2;
s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
R= s /p;
if (d >= l) ans = s;
else if(2*pi*R>=d) ans=d*d/(4*pi);
else
{
r = (l-d)/((l/R)-(2*pi));
x = r*r*s/(R*R);
ans = s - x + pi * r * r;
}
printf("Case %d: %.2lf\n",T,ans);
}
return 0;
}
三维几何
//三维几何函数库
#include <math.h>
#define eps 1e-8
#define zero(x) (((x)>0?(x):-(x))<eps)
struct point3{double x,y,z;};
struct line3{point3 a,b;};
struct plane3{point3 a,b,c;};
//计算cross product U x V
point3 xmult(point3 u,point3 v){
point3 ret;
ret.x=u.y*v.z-v.y*u.z;
ret.y=u.z*v.x-u.x*v.z;
ret.z=u.x*v.y-u.y*v.x;
return ret;
}
//计算dot product U . V
double dmult(point3 u,point3 v){
return u.x*v.x+u.y*v.y+u.z*v.z;
}
//矢量差 U - V
point3 subt(point3 u,point3 v){
point3 ret;
ret.x=u.x-v.x;
ret.y=u.y-v.y;
ret.z=u.z-v.z;
return ret;
}
//取平面法向量
point3 pvec(plane3 s){
return xmult(subt(s.a,s.b),subt(s.b,s.c));
}
point3 pvec(point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return xmult(subt(s1,s2),subt(s2,s3));
}
//两点距离,单参数取向量大小
double distance(point3 p1,point3 p2){
return sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y)+(p1.z-p2.z)*(p1.z-p2.z));
}
//向量大小
double vlen(point3 p){
return sqrt(p.x*p.x+p.y*p.y+p.z*p.z);
}
//判三点共线
int dots_inline(point3 p1,point3 p2,point3 p3){
return vlen(xmult(subt(p1,p2),subt(p2,p3)))<eps;
}
//判四点共面
int dots_onplane(point3 a,point3 b,point3 c,point3 d){
return zero(dmult(pvec(a,b,c),subt(d,a)));
}
//判点是否在线段上,包括端点和共线
int dot_online_in(point3 p,line3 l){
return zero(vlen(xmult(subt(p,l.a),subt(p,l.b))))&&(l.a.x-p.x)*(l.b.x-p.x)<eps&&
(l.a.y-p.y)*(l.b.y-p.y)<eps&&(l.a.z-p.z)*(l.b.z-p.z)<eps;
}
int dot_online_in(point3 p,point3 l1,point3 l2){
return zero(vlen(xmult(subt(p,l1),subt(p,l2))))&&(l1.x-p.x)*(l2.x-p.x)<eps&&
(l1.y-p.y)*(l2.y-p.y)<eps&&(l1.z-p.z)*(l2.z-p.z)<eps;
}
//判点是否在线段上,不包括端点
int dot_online_ex(point3 p,line3 l){
return dot_online_in(p,l)&&(!zero(p.x-l.a.x)||!zero(p.y-l.a.y)||!zero(p.z-l.a.z))&&
(!zero(p.x-l.b.x)||!zero(p.y-l.b.y)||!zero(p.z-l.b.z));
}
int dot_online_ex(point3 p,point3 l1,point3 l2){
return dot_online_in(p,l1,l2)&&(!zero(p.x-l1.x)||!zero(p.y-l1.y)||!zero(p.z-l1.z))&&
(!zero(p.x-l2.x)||!zero(p.y-l2.y)||!zero(p.z-l2.z));
}
//判点是否在空间三角形上,包括边界,三点共线无意义
int dot_inplane_in(point3 p,plane3 s){
return zero(vlen(xmult(subt(s.a,s.b),subt(s.a,s.c)))-vlen(xmult(subt(p,s.a),subt(p,s.b)))-
vlen(xmult(subt(p,s.b),subt(p,s.c)))-vlen(xmult(subt(p,s.c),subt(p,s.a))));
}
int dot_inplane_in(point3 p,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return zero(vlen(xmult(subt(s1,s2),subt(s1,s3)))-vlen(xmult(subt(p,s1),subt(p,s2)))-
vlen(xmult(subt(p,s2),subt(p,s3)))-vlen(xmult(subt(p,s3),subt(p,s1))));
}
//判点是否在空间三角形上,不包括边界,三点共线无意义
int dot_inplane_ex(point3 p,plane3 s){
return dot_inplane_in(p,s)&&vlen(xmult(subt(p,s.a),subt(p,s.b)))>eps&&
vlen(xmult(subt(p,s.b),subt(p,s.c)))>eps&&vlen(xmult(subt(p,s.c),subt(p,s.a)))>eps;
}
int dot_inplane_ex(point3 p,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return dot_inplane_in(p,s1,s2,s3)&&vlen(xmult(subt(p,s1),subt(p,s2)))>eps&&
vlen(xmult(subt(p,s2),subt(p,s3)))>eps&&vlen(xmult(subt(p,s3),subt(p,s1)))>eps;
}
//判两点在线段同侧,点在线段上返回0,不共面无意义
int same_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,line3 l){
return dmult(xmult(subt(l.a,l.b),subt(p1,l.b)),xmult(subt(l.a,l.b),subt(p2,l.b)))>eps;
}
int same_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,point3 l1,point3 l2){
return dmult(xmult(subt(l1,l2),subt(p1,l2)),xmult(subt(l1,l2),subt(p2,l2)))>eps;
}
//判两点在线段异侧,点在线段上返回0,不共面无意义
int opposite_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,line3 l){
return dmult(xmult(subt(l.a,l.b),subt(p1,l.b)),xmult(subt(l.a,l.b),subt(p2,l.b)))<-eps;
}
int opposite_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,point3 l1,point3 l2){
return dmult(xmult(subt(l1,l2),subt(p1,l2)),xmult(subt(l1,l2),subt(p2,l2)))<-eps;
}
//判两点在平面同侧,点在平面上返回0
int same_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,plane3 s){
return dmult(pvec(s),subt(p1,s.a))*dmult(pvec(s),subt(p2,s.a))>eps;
}
int same_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return dmult(pvec(s1,s2,s3),subt(p1,s1))*dmult(pvec(s1,s2,s3),subt(p2,s1))>eps;
}
//判两点在平面异侧,点在平面上返回0
int opposite_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,plane3 s){
return dmult(pvec(s),subt(p1,s.a))*dmult(pvec(s),subt(p2,s.a))<-eps;
}
int opposite_side(point3 p1,point3 p2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return dmult(pvec(s1,s2,s3),subt(p1,s1))*dmult(pvec(s1,s2,s3),subt(p2,s1))<-eps;
}
//判两直线平行
int parallel(line3 u,line3 v){
return vlen(xmult(subt(u.a,u.b),subt(v.a,v.b)))<eps;
}
int parallel(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 v1,point3 v2){
return vlen(xmult(subt(u1,u2),subt(v1,v2)))<eps;
}
//判两平面平行
int parallel(plane3 u,plane3 v){
return vlen(xmult(pvec(u),pvec(v)))<eps;
}
int parallel(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 u3,point3 v1,point3 v2,point3 v3){
return vlen(xmult(pvec(u1,u2,u3),pvec(v1,v2,v3)))<eps;
}
//判直线与平面平行
int parallel(line3 l,plane3 s){
return zero(dmult(subt(l.a,l.b),pvec(s)));
}
int parallel(point3 l1,point3 l2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return zero(dmult(subt(l1,l2),pvec(s1,s2,s3)));
}
//判两直线垂直
int perpendicular(line3 u,line3 v){
return zero(dmult(subt(u.a,u.b),subt(v.a,v.b)));
}
int perpendicular(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 v1,point3 v2){
return zero(dmult(subt(u1,u2),subt(v1,v2)));
}
//判两平面垂直
int perpendicular(plane3 u,plane3 v){
return zero(dmult(pvec(u),pvec(v)));
}
int perpendicular(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 u3,point3 v1,point3 v2,point3 v3){
return zero(dmult(pvec(u1,u2,u3),pvec(v1,v2,v3)));
}
//判直线与平面平行
int perpendicular(line3 l,plane3 s){
return vlen(xmult(subt(l.a,l.b),pvec(s)))<eps;
}
int perpendicular(point3 l1,point3 l2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return vlen(xmult(subt(l1,l2),pvec(s1,s2,s3)))<eps;
}
//判两线段相交,包括端点和部分重合
int intersect_in(line3 u,line3 v){
if (!dots_onplane(u.a,u.b,v.a,v.b))
return 0;
if (!dots_inline(u.a,u.b,v.a)||!dots_inline(u.a,u.b,v.b))
return !same_side(u.a,u.b,v)&&!same_side(v.a,v.b,u);
return dot_online_in(u.a,v)||dot_online_in(u.b,v)||dot_online_in(v.a,u)||dot_online_in(v.b,u);
}
int intersect_in(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 v1,point3 v2){
if (!dots_onplane(u1,u2,v1,v2))
return 0;
if (!dots_inline(u1,u2,v1)||!dots_inline(u1,u2,v2))
return !same_side(u1,u2,v1,v2)&&!same_side(v1,v2,u1,u2);
return dot_online_in(u1,v1,v2)||dot_online_in(u2,v1,v2)||dot_online_in(v1,u1,u2)||dot_online_in(v2,u1,u2);
}
//判两线段相交,不包括端点和部分重合
int intersect_ex(line3 u,line3 v){
return dots_onplane(u.a,u.b,v.a,v.b)&&opposite_side(u.a,u.b,v)&&opposite_side(v.a,v.b,u);
}
int intersect_ex(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 v1,point3 v2){
return dots_onplane(u1,u2,v1,v2)&&opposite_side(u1,u2,v1,v2)&&opposite_side(v1,v2,u1,u2);
}
//判线段与空间三角形相交,包括交于边界和(部分)包含
int intersect_in(line3 l,plane3 s){
return !same_side(l.a,l.b,s)&&!same_side(s.a,s.b,l.a,l.b,s.c)&&
!same_side(s.b,s.c,l.a,l.b,s.a)&&!same_side(s.c,s.a,l.a,l.b,s.b);
}
int intersect_in(point3 l1,point3 l2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return !same_side(l1,l2,s1,s2,s3)&&!same_side(s1,s2,l1,l2,s3)&&
!same_side(s2,s3,l1,l2,s1)&&!same_side(s3,s1,l1,l2,s2);
}
//判线段与空间三角形相交,不包括交于边界和(部分)包含
int intersect_ex(line3 l,plane3 s){
return opposite_side(l.a,l.b,s)&&opposite_side(s.a,s.b,l.a,l.b,s.c)&&
opposite_side(s.b,s.c,l.a,l.b,s.a)&&opposite_side(s.c,s.a,l.a,l.b,s.b);
}
int intersect_ex(point3 l1,point3 l2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return opposite_side(l1,l2,s1,s2,s3)&&opposite_side(s1,s2,l1,l2,s3)&&
opposite_side(s2,s3,l1,l2,s1)&&opposite_side(s3,s1,l1,l2,s2);
}
//计算两直线交点,注意事先判断直线是否共面和平行!
//线段交点请另外判线段相交(同时还是要判断是否平行!)
point3 intersection(line3 u,line3 v){
point3 ret=u.a;
double t=((u.a.x-v.a.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-v.a.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x))
/((u.a.x-u.b.x)*(v.a.y-v.b.y)-(u.a.y-u.b.y)*(v.a.x-v.b.x));
ret.x+=(u.b.x-u.a.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u.b.y-u.a.y)*t;
ret.z+=(u.b.z-u.a.z)*t;
return ret;
}
point3 intersection(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 v1,point3 v2){
point3 ret=u1;
double t=((u1.x-v1.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-v1.y)*(v1.x-v2.x))
/((u1.x-u2.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-u2.y)*(v1.x-v2.x));
ret.x+=(u2.x-u1.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u2.y-u1.y)*t;
ret.z+=(u2.z-u1.z)*t;
return ret;
}
//计算直线与平面交点,注意事先判断是否平行,并保证三点不共线!
//线段和空间三角形交点请另外判断
point3 intersection(line3 l,plane3 s){
point3 ret=pvec(s);
double t=(ret.x*(s.a.x-l.a.x)+ret.y*(s.a.y-l.a.y)+ret.z*(s.a.z-l.a.z))/
(ret.x*(l.b.x-l.a.x)+ret.y*(l.b.y-l.a.y)+ret.z*(l.b.z-l.a.z));
ret.x=l.a.x+(l.b.x-l.a.x)*t;
ret.y=l.a.y+(l.b.y-l.a.y)*t;
ret.z=l.a.z+(l.b.z-l.a.z)*t;
return ret;
}
point3 intersection(point3 l1,point3 l2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
point3 ret=pvec(s1,s2,s3);
double t=(ret.x*(s1.x-l1.x)+ret.y*(s1.y-l1.y)+ret.z*(s1.z-l1.z))/
(ret.x*(l2.x-l1.x)+ret.y*(l2.y-l1.y)+ret.z*(l2.z-l1.z));
ret.x=l1.x+(l2.x-l1.x)*t;
ret.y=l1.y+(l2.y-l1.y)*t;
ret.z=l1.z+(l2.z-l1.z)*t;
return ret;
}
//计算两平面交线,注意事先判断是否平行,并保证三点不共线!
line3 intersection(plane3 u,plane3 v){
line3 ret;
ret.a=parallel(v.a,v.b,u.a,u.b,u.c)?intersection(v.b,v.c,u.a,u.b,u.c):intersection(v.a,v.b,u.a,u.b,u.c);
ret.b=parallel(v.c,v.a,u.a,u.b,u.c)?intersection(v.b,v.c,u.a,u.b,u.c):intersection(v.c,v.a,u.a,u.b,u.c);
return ret;
}
line3 intersection(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 u3,point3 v1,point3 v2,point3 v3){
line3 ret;
ret.a=parallel(v1,v2,u1,u2,u3)?intersection(v2,v3,u1,u2,u3):intersection(v1,v2,u1,u2,u3);
ret.b=parallel(v3,v1,u1,u2,u3)?intersection(v2,v3,u1,u2,u3):intersection(v3,v1,u1,u2,u3);
return ret;
}
//点到直线距离
double ptoline(point3 p,line3 l){
return vlen(xmult(subt(p,l.a),subt(l.b,l.a)))/distance(l.a,l.b);
}
double ptoline(point3 p,point3 l1,point3 l2){
return vlen(xmult(subt(p,l1),subt(l2,l1)))/distance(l1,l2);
}
//点到平面距离
double ptoplane(point3 p,plane3 s){
return fabs(dmult(pvec(s),subt(p,s.a)))/vlen(pvec(s));
}
double ptoplane(point3 p,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return fabs(dmult(pvec(s1,s2,s3),subt(p,s1)))/vlen(pvec(s1,s2,s3));
}
//直线到直线距离
double linetoline(line3 u,line3 v){
point3 n=xmult(subt(u.a,u.b),subt(v.a,v.b));
return fabs(dmult(subt(u.a,v.a),n))/vlen(n);
}
double linetoline(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 v1,point3 v2){
point3 n=xmult(subt(u1,u2),subt(v1,v2));
return fabs(dmult(subt(u1,v1),n))/vlen(n);
}
//两直线夹角cos值
double angle_cos(line3 u,line3 v){
return dmult(subt(u.a,u.b),subt(v.a,v.b))/vlen(subt(u.a,u.b))/vlen(subt(v.a,v.b));
}
double angle_cos(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 v1,point3 v2){
return dmult(subt(u1,u2),subt(v1,v2))/vlen(subt(u1,u2))/vlen(subt(v1,v2));
}
//两平面夹角cos值
double angle_cos(plane3 u,plane3 v){
return dmult(pvec(u),pvec(v))/vlen(pvec(u))/vlen(pvec(v));
}
double angle_cos(point3 u1,point3 u2,point3 u3,point3 v1,point3 v2,point3 v3){
return dmult(pvec(u1,u2,u3),pvec(v1,v2,v3))/vlen(pvec(u1,u2,u3))/vlen(pvec(v1,v2,v3));
}
//直线平面夹角sin值
double angle_sin(line3 l,plane3 s){
return dmult(subt(l.a,l.b),pvec(s))/vlen(subt(l.a,l.b))/vlen(pvec(s));
}
double angle_sin(point3 l1,point3 l2,point3 s1,point3 s2,point3 s3){
return dmult(subt(l1,l2),pvec(s1,s2,s3))/vlen(subt(l1,l2))/vlen(pvec(s1,s2,s3));
}
凸包
//水平序
#define maxn 100005
struct point
{double x,y;}p[maxn],s[maxn];
bool operator < (point a,point b)
{return a.x<b.x || a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y;}
int n,f;
double cp(point a,point b,point c)
{return (c.y-a.y)*(b.x-a.x)-(b.y-a.y)*(c.x-a.x);}
void Convex(point *p,int &n)
{
sort(p,p+n);
int i,j,r,top,m;
s[0] = p[0];s[1] = p[1];top = 1;
for(i=2;i<n;i++)
{
while( top>0 && cp(p[i],s[top],s[top-1])>=0 ) top--;
top++;s[top] = p[i];
}
m = top;
top++;s[top] = p[n-2];
for(i=n-3;i>=0;i--)
{
while( top>m && cp(p[i],s[top],s[top-1])>=0 ) top--;
top++;s[top] = p[i];
}
top--;
n = top+1;
}
极角序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 100005
int N;
struct A
{
int x,y;
int v,l;
}P[maxn];
int xmult(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3)
{
return (y2-y1)*(x3-x1)-(y3-y1)*(x2-x1);
}
void swap(A &a,A &b)
{
A t = a;a = b,b = t;
}
bool operator < (A a,A b)
{
int k = xmult(P[0].x,P[0].y,a.x,a.y,b.x,b.y);
if( k<0 )
return 1;
else if( k==0 )
{
if( abs(P[0].x-a.x)<abs(P[0].x-b.x) )
return 1;
if( abs(P[0].y-a.y)<abs(P[0].y-b.y) )
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
void Grem_scan(int n)
{
int i,j,k,l;
k = 0x7fffffff;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
if( P[i].x<k || P[i].x==k && P[i].y<P[l].y )
k = P[i].x,l = i;
swap(P[l],P[0]);
sort(P+1,P+n);
l = 3;
for(i=3;i<n;i++)
{
while( xmult(P[l-2].x,P[l-2].y,P[l-1].x,P[l-1].y,P[i].x,P[i].y)>0 )
l--;
P[l++] = P[i];
}
}
main()
{
int i,j,k,l;
N = 0;
while( scanf("%d%d",&P[N].x,&P[N].y)!=EOF )
N++;
Grem_scan(N);
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
if( P[i].x==0 && P[i].y==0 )
break;
k = i++;
printf("(0,0)\n");
while( i!=k )
printf("(%d,%d)\n",P[i].x,P[i].y),i = (i+1)%N;
}
//卷包裹法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 55
struct A
{
int x,y;
}P[maxn];
int T,N;
bool B[maxn];
int as[maxn],L;
int xmult(A a,A b,A c)
{
return (b.x-a.x)*(c.y-a.y)-(b.y-a.y)*(c.x-a.x);
}
main()
{
int i,j,k,l;
scanf("%d",&T);
while( T-- )
{
scanf("%d",&N);
k = 0x7ffffff;
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&j,&P[i].x,&P[i].y);
if( P[i].y<k )
k = P[i].y,l = i;
}
memset(B,0,sizeof(B));
B[l] = 1;
as[0] = l;
L = 1;
while( 1 )
{
A a,b;
if( L==1 )
a.x = 0,a.y = P[as[0]].y;
else
a = P[as[L-2]];
b = P[as[L-1]];
k = -1;
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
if( B[i] )
continue;
if( xmult(a,b,P[i])<0 )
continue;
if( k==-1 || xmult(P[as[L-1]],P[k],P[i])<0 || xmult(P[as[L-1]],P[k],P[i])==0 && P[i].y<P[k].y )
k = i;
}
if( k==-1 )
break;
B[k] = 1;
as[L++] = k;
}
printf("%d ",L);
for(i=0;i<L;i++)
printf("%d ",as[i]+1);
printf("\n");
}
}
}
圆
#include <math.h>
#define eps 1e-8
struct point{double x,y;};
double xmult(point p1,point p2,point p0){
return (p1.x-p0.x)*(p2.y-p0.y)-(p2.x-p0.x)*(p1.y-p0.y);
}
double distance(point p1,point p2){
return sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
}
double disptoline(point p,point l1,point l2){
return fabs(xmult(p,l1,l2))/distance(l1,l2);
}
point intersection(point u1,point u2,point v1,point v2){
point ret=u1;
double t=((u1.x-v1.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-v1.y)*(v1.x-v2.x))
/((u1.x-u2.x)*(v1.y-v2.y)-(u1.y-u2.y)*(v1.x-v2.x));
ret.x+=(u2.x-u1.x)*t;
ret.y+=(u2.y-u1.y)*t;
return ret;
}
//判直线和圆相交,包括相切
int intersect_line_circle(point c,double r,point l1,point l2){
return disptoline(c,l1,l2)<r+eps;
}
//判线段和圆相交,包括端点和相切
int intersect_seg_circle(point c,double r,point l1,point l2){
double t1=distance(c,l1)-r,t2=distance(c,l2)-r;
point t=c;
if (t1<eps||t2<eps)
return t1>-eps||t2>-eps;
t.x+=l1.y-l2.y;
t.y+=l2.x-l1.x;
return xmult(l1,c,t)*xmult(l2,c,t)<eps&&disptoline(c,l1,l2)-r<eps;
}
//判圆和圆相交,包括相切
int intersect_circle_circle(point c1,double r1,point c2,double r2){
return distance(c1,c2)<r1+r2+eps&&distance(c1,c2)>fabs(r1-r2)-eps;
}
//计算圆上到点p最近点,如p与圆心重合,返回p本身
point dot_to_circle(point c,double r,point p){
point u,v;
if (distance(p,c)<eps)
return p;
u.x=c.x+r*fabs(c.x-p.x)/distance(c,p);
u.y=c.y+r*fabs(c.y-p.y)/distance(c,p)*((c.x-p.x)*(c.y-p.y)<0?-1:1);
v.x=c.x-r*fabs(c.x-p.x)/distance(c,p);
v.y=c.y-r*fabs(c.y-p.y)/distance(c,p)*((c.x-p.x)*(c.y-p.y)<0?-1:1);
return distance(u,p)<distance(v,p)?u:v;
}
//计算直线与圆的交点,保证直线与圆有交点
//计算线段与圆的交点可用这个函数后判点是否在线段上
void intersection_line_circle(point c,double r,point l1,point l2,point& p1,point& p2){
point p=c;
double t;
p.x+=l1.y-l2.y;
p.y+=l2.x-l1.x;
p=intersection(p,c,l1,l2);
t=sqrt(r*r-distance(p,c)*distance(p,c))/distance(l1,l2);
p1.x=p.x+(l2.x-l1.x)*t;
p1.y=p.y+(l2.y-l1.y)*t;
p2.x=p.x-(l2.x-l1.x)*t;
p2.y=p.y-(l2.y-l1.y)*t;
}
//计算圆与圆的交点,保证圆与圆有交点,圆心不重合
void intersection_circle_circle(point c1,double r1,point c2,double r2,point& p1,point& p2){
point u,v;
double t;
t=(1+(r1*r1-r2*r2)/distance(c1,c2)/distance(c1,c2))/2;
u.x=c1.x+(c2.x-c1.x)*t;
u.y=c1.y+(c2.y-c1.y)*t;
v.x=u.x+c1.y-c2.y;
v.y=u.y-c1.x+c2.x;
intersection_line_circle(c1,r1,u,v,p1,p2);
}
//将向量p逆时针旋转angle角度
Point Rotate(Point p,double angle) {
Point res;
res.x=p.x*cos(angle)-p.y*sin(angle);
res.y=p.x*sin(angle)+p.y*cos(angle);
return res;
}
//求圆外一点对圆(o,r)的两个切点result1和result2
void TangentPoint_PC(Point poi,Point o,double r,Point &result1,Point &result2) {
double line=sqrt((poi.x-o.x)*(poi.x-o.x)+(poi.y-o.y)*(poi.y-o.y));
double angle=acos(r/line);
Point unitvector,lin;
lin.x=poi.x-o.x;
lin.y=poi.y-o.y;
unitvector.x=lin.x/sqrt(lin.x*lin.x+lin.y*lin.y)*r;
unitvector.y=lin.y/sqrt(lin.x*lin.x+lin.y*lin.y)*r;
result1=Rotate(unitvector,-angle);
result2=Rotate(unitvector,angle);
result1.x+=o.x;
result1.y+=o.y;
result2.x+=o.x;
result2.y+=o.y;
return;
}
矢量运算求几何位置模板
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define MAX_N 100
using namespace std;
///
//常量区
const double INF = 1e10; // 无穷大
const double EPS = 1e-15; // 计算精度
const int LEFT = 0; // 点在直线左边
const int RIGHT = 1; // 点在直线右边
const int ONLINE = 2; // 点在直线上
const int CROSS = 0; // 两直线相交
const int COLINE = 1; // 两直线共线
const int PARALLEL = 2; // 两直线平行
const int NOTCOPLANAR = 3; // 两直线不共面
const int INSIDE = 1; // 点在图形内部
const int OUTSIDE = 2; // 点在图形外部
const int BORDER = 3; // 点在图形边界
const int BAOHAN = 1; // 大圆包含小圆
const int NEIQIE = 2; // 内切
const int XIANJIAO = 3; // 相交
const int WAIQIE = 4; // 外切
const int XIANLI = 5; // 相离
const double pi = acos(-1.0) //圆周率
///
///
//类型定义区
struct Point { // 二维点或矢量
double x, y;
double angle, dis;
Point() {}
Point(double x0, double y0): x(x0), y(y0) {}
};
struct Point3D { //三维点或矢量
double x, y, z;
Point3D() {}
Point3D(double x0, double y0, double z0): x(x0), y(y0), z(z0) {}
};
struct Line { // 二维的直线或线段
Point p1, p2;
Line() {}
Line(Point p10, Point p20): p1(p10), p2(p20) {}
};
struct Line3D { // 三维的直线或线段
Point3D p1, p2;
Line3D() {}
Line3D(Point3D p10, Point3D p20): p1(p10), p2(p20) {}
};
struct Rect { // 用长宽表示矩形的方法 w, h分别表示宽度和高度
double w, h;
Rect() {}
Rect(double _w,double _h) : w(_w),h(_h) {}
};
struct Rect_2 { // 表示矩形,左下角坐标是(xl, yl),右上角坐标是(xh, yh)
double xl, yl, xh, yh;
Rect_2() {}
Rect_2(double _xl,double _yl,double _xh,double _yh) : xl(_xl),yl(_yl),xh(_xh),yh(_yh) {}
};
struct Circle { //圆
Point c;
double r;
Circle() {}
Circle(Point _c,double _r) :c(_c),r(_r) {}
};
typedef vector<Point> Polygon; // 二维多边形
typedef vector<Point> Points; // 二维点集
typedef vector<Point3D> Points3D; // 三维点集
///
///
//基本函数区
inline double max(double x,double y)
{
return x > y ? x : y;
}
inline double min(double x, double y)
{
return x > y ? y : x;
}
inline bool ZERO(double x) // x == 0
{
return (fabs(x) < EPS);
}
inline bool ZERO(Point p) // p == 0
{
return (ZERO(p.x) && ZERO(p.y));
}
inline bool ZERO(Point3D p) // p == 0
{
return (ZERO(p.x) && ZERO(p.y) && ZERO(p.z));
}
inline bool EQ(double x, double y) // eqaul, x == y
{
return (fabs(x - y) < EPS);
}
inline bool NEQ(double x, double y) // not equal, x != y
{
return (fabs(x - y) >= EPS);
}
inline bool LT(double x, double y) // less than, x < y
{
return ( NEQ(x, y) && (x < y) );
}
inline bool GT(double x, double y) // greater than, x > y
{
return ( NEQ(x, y) && (x > y) );
}
inline bool LEQ(double x, double y) // less equal, x <= y
{
return ( EQ(x, y) || (x < y) );
}
inline bool GEQ(double x, double y) // greater equal, x >= y
{
return ( EQ(x, y) || (x > y) );
}
// 注意!!!
// 如果是一个很小的负的浮点数
// 保留有效位数输出的时候会出现-0.000这样的形式,
// 前面多了一个负号
// 这就会导致错误!!!!!!
// 因此在输出浮点数之前,一定要调用次函数进行修正!
inline double FIX(double x)
{
return (fabs(x) < EPS) ? 0 : x;
}
//
/
//二维矢量运算
bool operator==(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return ( EQ(p1.x, p2.x) && EQ(p1.y, p2.y) );
}
bool operator!=(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return ( NEQ(p1.x, p2.x) || NEQ(p1.y, p2.y) );
}
bool operator<(Point p1, Point p2)
{
if (NEQ(p1.x, p2.x)) {
return (p1.x < p2.x);
} else {
return (p1.y < p2.y);
}
}
Point operator+(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return Point(p1.x + p2.x, p1.y + p2.y);
}
Point operator-(Point p1, Point p2)
{
return Point(p1.x - p2.x, p1.y - p2.y);
}
double operator*(Point p1, Point p2) // 计算叉乘 p1 × p2
{
return (p1.x * p2.y - p2.x * p1.y);
}
double operator&(Point p1, Point p2) { // 计算点积 p1·p2
return (p1.x * p2.x + p1.y * p2.y);
}
double Norm(Point p) // 计算矢量p的模
{
return sqrt(p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y);
}
// 把矢量p旋转角度angle (弧度表示)
// angle > 0表示逆时针旋转
// angle < 0表示顺时针旋转
Point Rotate(Point p, double angle)
{
Point result;
result.x = p.x * cos(angle) - p.y * sin(angle);
result.y = p.x * sin(angle) + p.y * cos(angle);
return result;
}
//
//
//三维矢量运算
bool operator==(Point3D p1, Point3D p2)
{
return ( EQ(p1.x, p2.x) && EQ(p1.y, p2.y) && EQ(p1.z, p2.z) );
}
bool operator<(Point3D p1, Point3D p2)
{
if (NEQ(p1.x, p2.x)) {
return (p1.x < p2.x);
} else if (NEQ(p1.y, p2.y)) {
return (p1.y < p2.y);
} else {
return (p1.z < p2.z);
}
}
Point3D operator+(Point3D p1, Point3D p2)
{
return Point3D(p1.x + p2.x, p1.y + p2.y, p1.z + p2.z);
}
Point3D operator-(Point3D p1, Point3D p2)
{
return Point3D(p1.x - p2.x, p1.y - p2.y, p1.z - p2.z);
}
Point3D operator*(Point3D p1, Point3D p2) // 计算叉乘 p1 x p2
{
return Point3D(p1.y * p2.z - p1.z * p2.y,
p1.z * p2.x - p1.x * p2.z,
p1.x * p2.y - p1.y * p2.x );
}
double operator&(Point3D p1, Point3D p2) { // 计算点积 p1·p2
return (p1.x * p2.x + p1.y * p2.y + p1.z * p2.z);
}
double Norm(Point3D p) // 计算矢量p的模
{
return sqrt(p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y + p.z * p.z);
}
//
/
//点.线段.直线问题
//
double Distance(Point p1, Point p2) //2点间的距离
{
return sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y));
}
double Distance(Point3D p1, Point3D p2) //2点间的距离,三维
{
return sqrt((p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x)+(p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y)+(p1.z-p2.z)*(p1.z-p2.z));
}
double Distance(Point p, Line L) // 求二维平面上点到直线的距离
{
return ( fabs((p - L.p1) * (L.p2 - L.p1)) / Norm(L.p2 - L.p1) );
}
double Distance(Point3D p, Line3D L)// 求三维空间中点到直线的距离
{
return ( Norm((p - L.p1) * (L.p2 - L.p1)) / Norm(L.p2 - L.p1) );
}
bool OnLine(Point p, Line L) // 判断二维平面上点p是否在直线L上
{
return ZERO( (p - L.p1) * (L.p2 - L.p1) );
}
bool OnLine(Point3D p, Line3D L) // 判断三维空间中点p是否在直线L上
{
return ZERO( (p - L.p1) * (L.p2 - L.p1) );
}
int Relation(Point p, Line L) // 计算点p与直线L的相对关系 ,返回ONLINE,LEFT,RIGHT
{
double res = (L.p2 - L.p1) * (p - L.p1);
if (EQ(res, 0)) {
return ONLINE;
} else if (res > 0) {
return LEFT;
} else {
return RIGHT;
}
}
bool SameSide(Point p1, Point p2, Line L) // 判断点p1, p2是否在直线L的同侧
{
double m1 = (p1 - L.p1) * (L.p2 - L.p1);
double m2 = (p2 - L.p1) * (L.p2 - L.p1);
return GT(m1 * m2, 0);
}
bool OnLineSeg(Point p, Line L) // 判断二维平面上点p是否在线段l上
{
return ( ZERO( (L.p1 - p) * (L.p2 - p) ) &&
LEQ((p.x - L.p1.x)*(p.x - L.p2.x), 0) &&
LEQ((p.y - L.p1.y)*(p.y - L.p2.y), 0) );
}
bool OnLineSeg(Point3D p, Line3D L) // 判断三维空间中点p是否在线段l上
{
return ( ZERO((L.p1 - p) * (L.p2 - p)) &&
EQ( Norm(p - L.p1) + Norm(p - L.p2), Norm(L.p2 - L.p1)) );
}
Point SymPoint(Point p, Line L) // 求二维平面上点p关于直线L的对称点
{
Point result;
double a = L.p2.x - L.p1.x;
double b = L.p2.y - L.p1.y;
double t = ( (p.x - L.p1.x) * a + (p.y - L.p1.y) * b ) / (a*a + b*b);
result.x = 2 * L.p1.x + 2 * a * t - p.x;
result.y = 2 * L.p1.y + 2 * b * t - p.y;
return result;
}
bool Coplanar(Points3D points) // 判断一个点集中的点是否全部共面
{
int i;
Point3D p;
if (points.size() < 4) return true;
p = (points[2] - points[0]) * (points[1] - points[0]);
for (i = 3; i < points.size(); i++) {
if (! ZERO(p & points[i]) ) return false;
}
return true;
}
bool LineIntersect(Line L1, Line L2) // 判断二维的两直线是否相交
{
return (! ZERO((L1.p1 - L1.p2)*(L2.p1 - L2.p2)) ); // 是否平行
}
bool LineIntersect(Line3D L1, Line3D L2) // 判断三维的两直线是否相交
{
Point3D p1 = L1.p1 - L1.p2;
Point3D p2 = L2.p1 - L2.p2;
Point3D p = p1 * p2;
if (ZERO(p)) return false; // 是否平行
p = (L2.p1 - L1.p2) * (L1.p1 - L1.p2);
return ZERO(p & L2.p2); // 是否共面
}
bool LineSegIntersect(Line L1, Line L2) // 判断二维的两条线段是否相交
{
return ( GEQ( max(L1.p1.x, L1.p2.x), min(L2.p1.x, L2.p2.x) ) &&
GEQ( max(L2.p1.x, L2.p2.x), min(L1.p1.x, L1.p2.x) ) &&
GEQ( max(L1.p1.y, L1.p2.y), min(L2.p1.y, L2.p2.y) ) &&
GEQ( max(L2.p1.y, L2.p2.y), min(L1.p1.y, L1.p2.y) ) &&
LEQ( ((L2.p1 - L1.p1) * (L1.p2 - L1.p1)) * ((L2.p2 - L1.p1) * (L1.p2 - L1.p1)), 0 ) &&
LEQ( ((L1.p1 - L2.p1) * (L2.p2 - L2.p1)) * ((L1.p2 - L2.p1) * (L2.p2 - L2.p1)), 0 ) );
}
bool LineSegIntersect(Line3D L1, Line3D L2) // 判断三维的两条线段是否相交
{
// todo
return true;
}
// 计算两条二维直线的交点,结果在参数P中返回
// 返回值说明了两条直线的位置关系: COLINE -- 共线 PARALLEL -- 平行 CROSS -- 相交
int CalCrossPoint(Line L1, Line L2, Point& P)
{
double A1, B1, C1, A2, B2, C2;
A1 = L1.p2.y - L1.p1.y;
B1 = L1.p1.x - L1.p2.x;
C1 = L1.p2.x * L1.p1.y - L1.p1.x * L1.p2.y;
A2 = L2.p2.y - L2.p1.y;
B2 = L2.p1.x - L2.p2.x;
C2 = L2.p2.x * L2.p1.y - L2.p1.x * L2.p2.y;
if (EQ(A1 * B2, B1 * A2)) {
if (EQ( (A1 + B1) * C2, (A2 + B2) * C1 )) {
return COLINE;
} else {
return PARALLEL;
}
} else {
P.x = (B2 * C1 - B1 * C2) / (A2 * B1 - A1 * B2);
P.y = (A1 * C2 - A2 * C1) / (A2 * B1 - A1 * B2);
return CROSS;
}
}
// 计算两条三维直线的交点,结果在参数P中返回
// 返回值说明了两条直线的位置关系 COLINE -- 共线 PARALLEL -- 平行 CROSS -- 相交 NONCOPLANAR -- 不公面
int CalCrossPoint(Line3D L1, Line3D L2, Point3D& P)
{
// todo
return 0;
}
// 计算点P到直线L的最近点
Point NearestPointToLine(Point P, Line L)
{
Point result;
double a, b, t;
a = L.p2.x - L.p1.x;
b = L.p2.y - L.p1.y;
t = ( (P.x - L.p1.x) * a + (P.y - L.p1.y) * b ) / (a * a + b * b);
result.x = L.p1.x + a * t;
result.y = L.p1.y + b * t;
return result;
}
// 计算点P到线段L的最近点
Point NearestPointToLineSeg(Point P, Line L)
{
Point result;
double a, b, t;
a = L.p2.x - L.p1.x;
b = L.p2.y - L.p1.y;
t = ( (P.x - L.p1.x) * a + (P.y - L.p1.y) * b ) / (a * a + b * b);
if ( GEQ(t, 0) && LEQ(t, 1) ) {
result.x = L.p1.x + a * t;
result.y = L.p1.y + b * t;
} else {
if ( Norm(P - L.p1) < Norm(P - L.p2) ) {
result = L.p1;
} else {
result = L.p2;
}
}
return result;
}
// 计算险段L1到线段L2的最短距离
double MinDistance(Line L1, Line L2)
{
double d1, d2, d3, d4;
if (LineSegIntersect(L1, L2)) {
return 0;
} else {
d1 = Norm( NearestPointToLineSeg(L1.p1, L2) - L1.p1 );
d2 = Norm( NearestPointToLineSeg(L1.p2, L2) - L1.p2 );
d3 = Norm( NearestPointToLineSeg(L2.p1, L1) - L2.p1 );
d4 = Norm( NearestPointToLineSeg(L2.p2, L1) - L2.p2 );
return min( min(d1, d2), min(d3, d4) );
}
}
// 求二维两直线的夹角,
// 返回值是0~Pi之间的弧度
double Inclination(Line L1, Line L2)
{
Point u = L1.p2 - L1.p1;
Point v = L2.p2 - L2.p1;
return acos( (u & v) / (Norm(u)*Norm(v)) );
}
// 求三维两直线的夹角,
// 返回值是0~Pi之间的弧度
double Inclination(Line3D L1, Line3D L2)
{
Point3D u = L1.p2 - L1.p1;
Point3D v = L2.p2 - L2.p1;
return acos( (u & v) / (Norm(u)*Norm(v)) );
}
/
/
// 判断两个矩形是否相交
// 如果相邻不算相交
bool Intersect(Rect_2 r1, Rect_2 r2)
{
return ( max(r1.xl, r2.xl) < min(r1.xh, r2.xh) &&
max(r1.yl, r2.yl) < min(r1.yh, r2.yh) );
}
// 判断矩形r2是否可以放置在矩形r1内
// r2可以任意地旋转
//发现原来的给出的方法过不了OJ上的无归之室这题,
//所以用了自己的代码
bool IsContain(Rect r1, Rect r2) //矩形的w>h
{
if(r1.w >r2.w && r1.h > r2.h) return true;
else
{
double r = sqrt(r2.w*r2.w + r2.h*r2.h) / 2.0;
double alpha = atan2(r2.h,r2.w);
double sita = asin((r1.h/2.0)/r);
double x = r * cos(sita - 2*alpha);
double y = r * sin(sita - 2*alpha);
if(x < r1.w/2.0 && y < r1.h/2.0 && x > 0 && y > -r1.h/2.0) return true;
else return false;
}
}
//圆
Point Center(const Circle & C) //圆心
{
return C.c;
}
double Area(const Circle &C)
{
return pi*C.r*C.r;
}
double CommonArea(const Circle & A, const Circle & B) //两个圆的公共面积
{
double area = 0.0;
const Circle & M = (A.r > B.r) ? A : B;
const Circle & N = (A.r > B.r) ? B : A;
double D = Distance(Center(M), Center(N));
if ((D < M.r + N.r) && (D > M.r - N.r))
{
double cosM = (M.r * M.r + D * D - N.r * N.r) / (2.0 * M.r * D);
double cosN = (N.r * N.r + D * D - M.r * M.r) / (2.0 * N.r * D);
double alpha = 2.0 * acos(cosM);
double beta = 2.0 * acos(cosN);
double TM = 0.5 * M.r * M.r * sin(alpha);
double TN = 0.5 * N.r * N.r * sin(beta);
double FM = (alpha / (2*pi)) * Area(M);
double FN = (beta / (2*pi)) * Area(N);
area = FM + FN - TM - TN;
}
else if (D <= M.r - N.r)
{
area = Area(N);
}
return area;
}
bool IsInCircle(const Circle & C, const Rect_2 & rect)//判断圆是否在矩形内(不允许相切)
{
return (GT(C.c.x - C.r, rect.xl)
&& LT(C.c.x + C.r, rect.xh)
&& GT(C.c.y - C.r, rect.yl)
&& LT(C.c.y + C.r, rect.yh));
}
//判断2圆的位置关系
//返回:
//BAOHAN = 1; // 大圆包含小圆
//NEIQIE = 2; // 内切
//XIANJIAO = 3; // 相交
//WAIQIE = 4; // 外切
//XIANLI = 5; // 相离
int CirCir(const Circle &c1, const Circle &c2)//判断2圆的位置关系
{
double dis = Distance(c1.c,c2.c);
if(LT(dis,fabs(c1.r-c2.r))) return BAOHAN;
if(EQ(dis,fabs(c1.r-c2.r))) return NEIQIE;
if(LT(dis,c1.r+c2.r) && GT(dis,fabs(c1.r-c2.r))) return XIANJIAO;
if(EQ(dis,c1.r+c2.r)) return WAIQIE;
return XIANLI;
}
int main()
{
return 0;
}
扇形重心
//Xc = 2*R*sinA/3/A
//A为圆心角的一半
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double r, angle;
while(scanf("%lf%lf", &r, &angle) != EOF){
angle /= 2;
printf("%.6lf\n", 2 * r * sin(angle) / 3 / angle);
}
return 0;
}
n个点中三个点组成的三角形面积最大
//Rotating Calipers algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MaxNode 50005
int stack[MaxNode];
int top;
double max;
typedef struct TPoint
{
int x;
int y;
}TPoint;
TPoint point[MaxNode];
void swap(TPoint point[], int i, int j)
{
TPoint tmp;
tmp = point[i];
point[i] = point[j];
point[j] = tmp;
}
double multi(TPoint p1, TPoint p2, TPoint p0)
{
return (p1.x - p0.x) * (p2.y - p0.y) - (p2.x - p0.x) * (p1.y - p0.y);
}
double distance(TPoint p1, TPoint p2)
{
return (p1.x - p2.x) * (p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y) * (p1.y - p2.y);
}
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{
TPoint *c = (TPoint *)a;
TPoint *d = (TPoint *)b;
double k = multi(*c, *d, point[0]);
if(k< 0) return 1;
else if(k == 0 && distance(*c, point[0]) >= distance(*d, point[0]))
return 1;
else return -1;
}
void grahamScan(int n)
{
//Graham扫描求凸包
int i, u;
//将最左下的点调整到p[0]的位置
u = 0;
for(i = 1;i <= n - 1;i++){
if((point[i].y < point[u].y) ||
(point[i].y == point[u].y && point[i].x < point[u].x))
u = i;
}
swap(point, 0, u);
//将平p[1]到p[n - 1]按按极角排序,可采用快速排序
qsort(point + 1, n - 1, sizeof(point[0]), cmp);
for(i = 0;i <= 2;i++) stack[i] = i;
top = 2;
for(i = 3;i <= n - 1;i++){
while(multi(point[i], point[stack[top]], point[stack[top - 1]]) >= 0){
top--;
if(top == 0) break;
}
top++;
stack[top] = i;
}
}
int main()
{
double triangleArea(int i, int j, int k);
void PloygonTriangle();
int i, n;
while(scanf("%d", &n) && n != -1){
for(i = 0;i < n;i++)
scanf("%d%d", &point[i].x, &point[i].y);
if(n <= 2){
printf("0.00\n");
continue;
}
if(n == 3){
printf("%.2lf\n", triangleArea(0, 1, 2));
continue;
}
grahamScan(n);
PloygonTriangle();
printf("%.2lf\n", max);
}
return 0;
}
void PloygonTriangle()
{
double triangleArea(int i, int j, int k);
int i, j , k;
double area, area1;
max = -1;
for(i = 0;i <= top - 2;i++){
k = -1;
for(j = i + 1; j <= top - 1;j++){
if(k <= j) k= j + 1;
area = triangleArea(stack[i], stack[j], stack[k]);
if(area > max) max = area;
while(k + 1 <= top){
area1= triangleArea(stack[i], stack[j], stack[k + 1]);
if(area1 < area) break;
if(area1 > max) max = area1;
area = area1;
k++;
}
}
}
}
double triangleArea(int i, int j, int k)
{
//已知三角形三个顶点的坐标,求三角形的面积
double l = fabs(point[i].x * point[j].y + point[j].x * point[k].y
+ point[k].x * point[i].y - point[j].x * point[i].y
- point[k].x * point[j].y - point[i].x * point[k].y) / 2;
return l;
}
单位圆覆盖最多的点
/*
平面上N个点,用一个半径R的圆去覆盖,最多能覆盖多少个点?
比较经典的题目。
对每个点以R为半径画圆,对N个圆两两求交。这一步O(N^2)。问题转化为求被覆盖次数最多的弧。
对每一个圆,求其上的每段弧重叠次数。假如A圆与B圆相交。A上[PI/3, PI/2]的区间被B覆盖(PI为圆周率)。那么对于A圆,我们在PI/3处做一个+1标记,在PI/2处做一个-1标记。
对于[PI*5/3, PI*7/3]这样横跨0点的区间只要在0点处拆成两段即可。
将一个圆上的所有标记排序,从头开始扫描。初始ans = 0,碰到+1标记给ans++,碰到-1标记ans--。扫描过程中ans的最大值就是圆上被覆盖最多的弧。求所有圆的ans的最大值就是答案。
总复杂度O(N^2 * logN)
*/#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#define eps 1e-6
struct point
{
double x, y;
};
double dis(point p1, point p2)
{
point p3;
p3.x = p2.x - p1.x;
p3.y = p2.y - p1.y;
return p3.x * p3.x + p3.y * p3.y;
}
point find_centre(point p1, point p2)
{
point p3, mid, centre;
double b, c, ang;
p3.x = p2.x - p1.x;
p3.y = p2.y - p1.y;
mid.x = (p1.x + p2.x) / 2;
mid.y = (p1.y + p2.y) / 2;
b = dis(p1, mid);
c = sqrt(1 - b);
if(fabs(p3.y) < eps)//垂线的斜角90度
{
centre.x = mid.x;
centre.y = mid.y + c;
}
else
{
ang = atan(-p3.x / p3.y);
centre.x = mid.x + c * cos(ang);
centre.y = mid.y + c * sin(ang);
}
return centre;
}
int main()
{
int n, ans, tmpans, i, j, k;
point p[305], centre;
double tmp;
while(scanf("%d", &n) && n)
{
for(i = 0;i < n;i++)
scanf("%lf%lf", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
ans = 1;
for(i = 0;i < n;i++)
for(j = i + 1;j < n;j++)
{
if(dis(p[i], p[j]) > 4) continue;
tmpans = 0;
centre = find_centre(p[i], p[j]);
for(k = 0;k < n;k++)
{
//if(tmpans + n - k <= ans) break;
tmp = dis(centre, p[k]);
//if(tmp < 1.0 || fabs(tmp - 1.0) < eps) tmpans++;
if(tmp <= 1.000001) tmpans++;
}
if(ans < tmpans) ans = tmpans;
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
return 0;
}
 算法竞赛常用模板
算法竞赛常用模板

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号