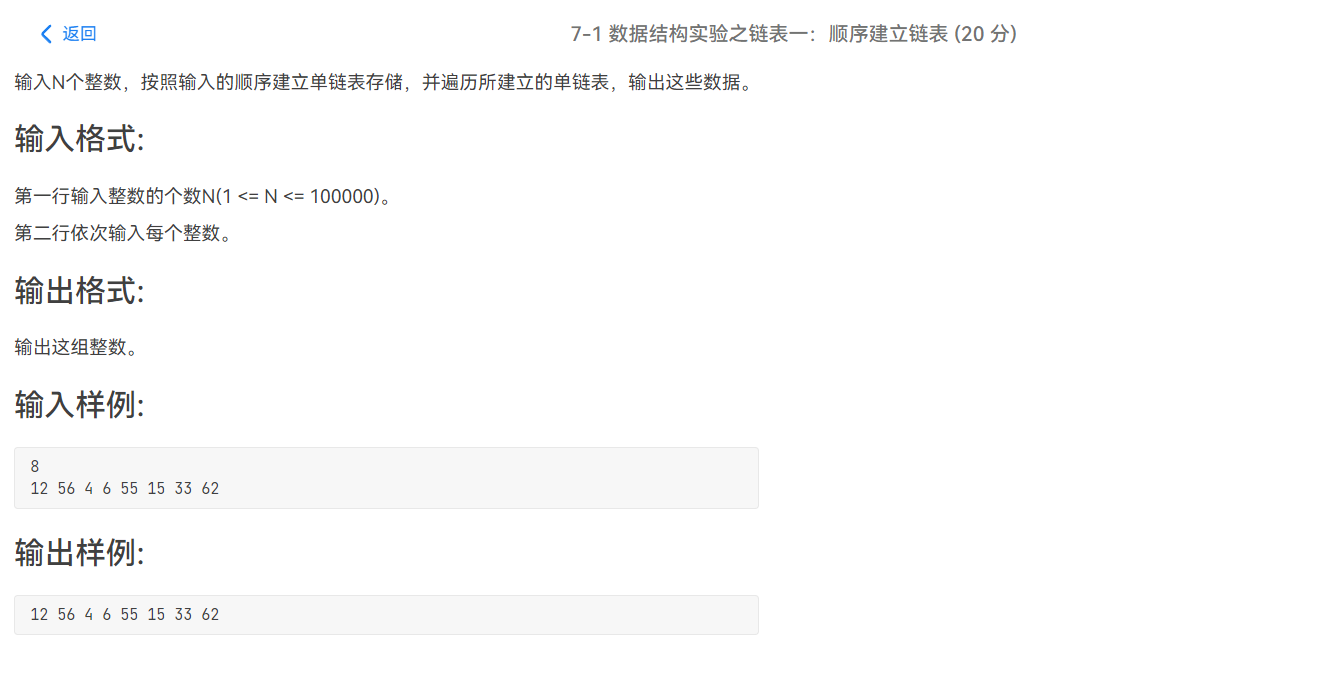
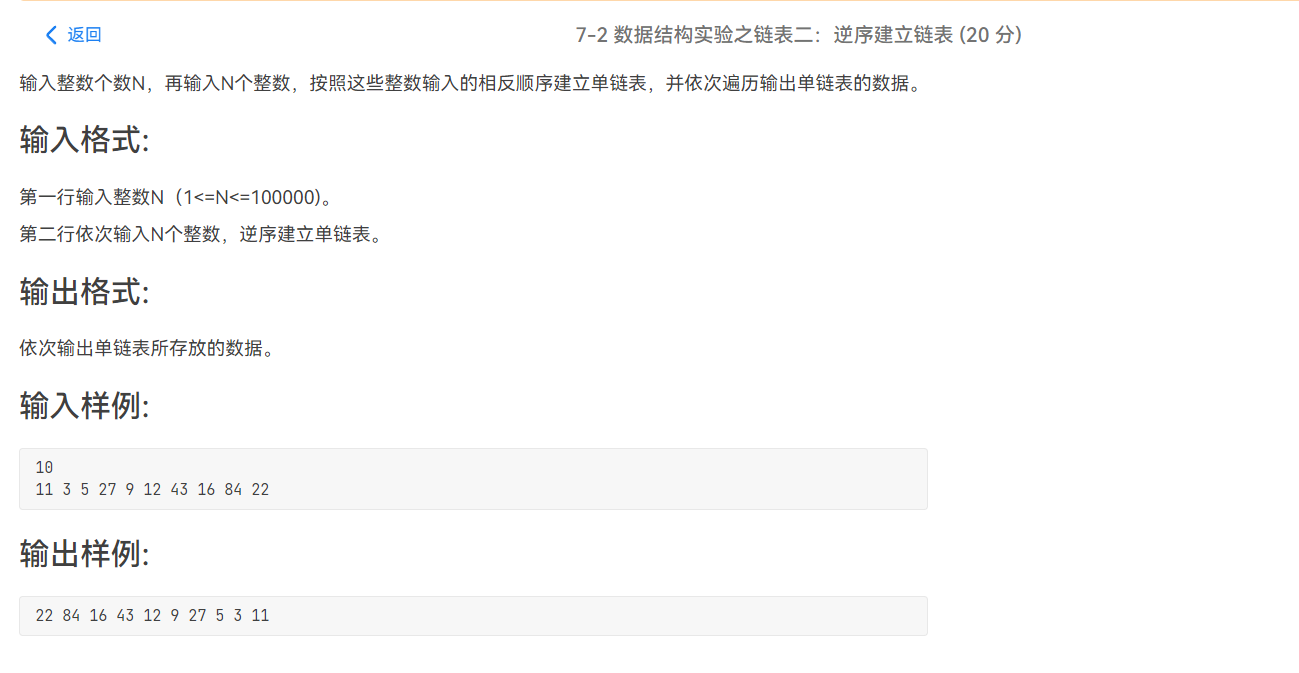
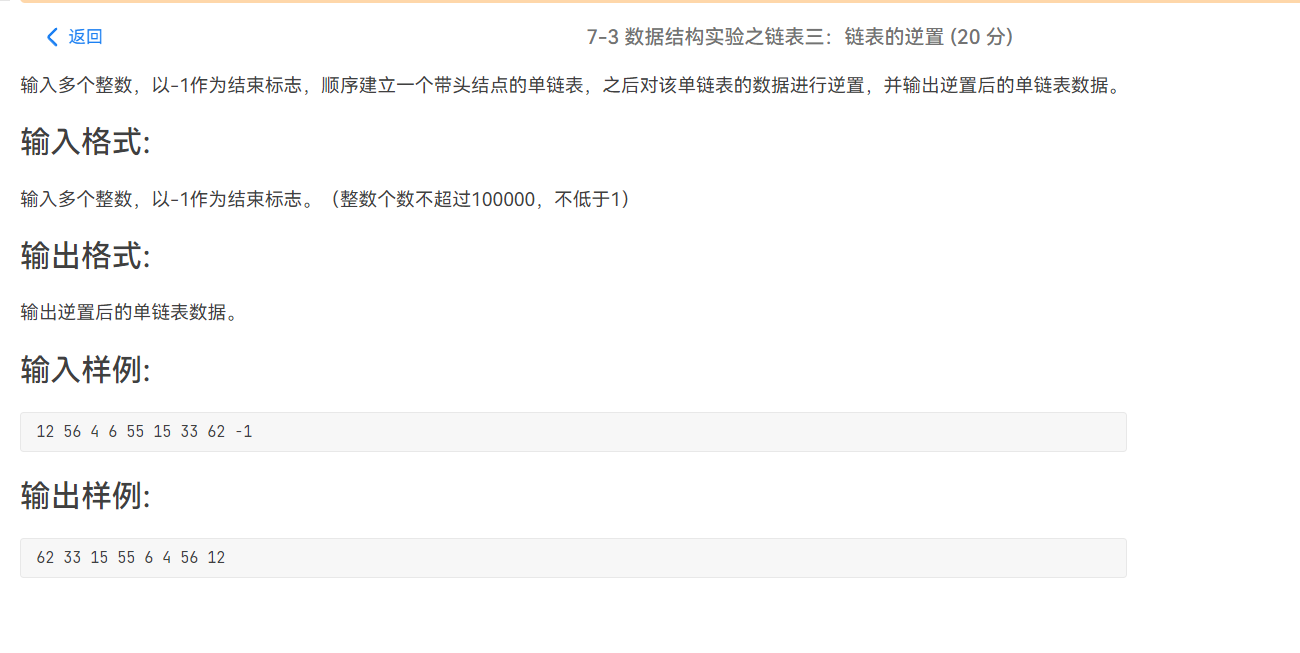
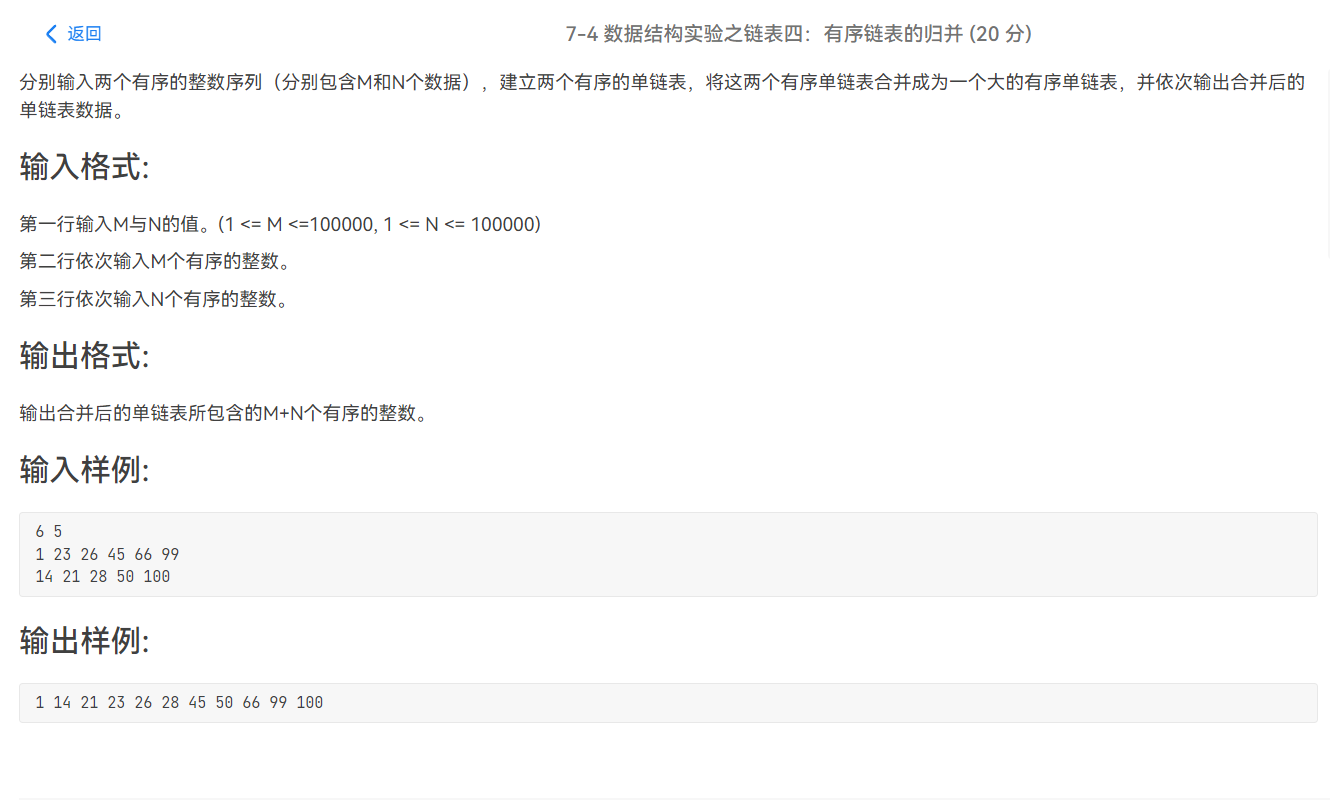
PTA——链表——相关习题(程设二)
今天又是整理代码的一天呐
( 。_ 。) ✎ _

(逃!)
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 }node; 9 10 node *creat(int n) //尾插法建立链表 11 { 12 13 node *head,*p,*tail; //创建新节点并置空 14 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 15 16 head->next=NULL; 17 tail=head; //此时只有链表中只有一个节点 18 19 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 20 { 21 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); //开辟新节点 22 scanf("%d",&p->data); 23 24 p->next=NULL; 25 tail->next=p; 26 tail=p; //将tail更新为p,相当于尾部多了一个节点,此时tail仍然指的是尾部 27 } 28 return head; //返回头节点 29 30 } 31 32 void pri(node *p) 33 { 34 while(p)//遍历链表 35 { 36 if(p->next==NULL) 37 printf("%d",p->data); 38 else printf("%d ",p->data); 39 p=p->next; 40 } 41 } 42 43 void solve() 44 { 45 46 int n; 47 scanf("%d", &n); 48 49 node *head; 50 head=creat(n); //建立链表 51 52 pri(head->next); //遍历输出链表的值 53 54 } 55 56 int main() 57 { 58 59 int T=1; 60 //scanf("%d",&T); 61 while(T--) 62 solve(); 63 64 return 0; 65 }
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 }node; 9 10 node *creat(int n) //头插法建立链表 11 { 12 13 node *head,*p; //创建新节点并置空 14 15 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 16 head->next=NULL; 17 18 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 19 { 20 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 21 scanf("%d",&p->data); 22 23 p->next=head->next; //p现在指向head的下一位 24 head->next=p; //再让head指向p相当于p完成了插入操作,插到了head和head->next的中间部分 25 } 26 27 return head; //返回头节点 28 29 } 30 31 void pri(node *p) 32 { 33 while(p)//遍历链表 34 { 35 if(p->next==NULL) 36 printf("%d",p->data); 37 else printf("%d ",p->data); 38 p=p->next; 39 } 40 } 41 42 void solve() 43 { 44 45 int n; 46 scanf("%d", &n); 47 48 node *head; 49 head=creat(n); //建立链表 50 51 pri(head->next); //遍历输出链表的值 52 53 } 54 55 int main() 56 { 57 58 int T=1; 59 //scanf("%d",&T); 60 while(T--) 61 solve(); 62 63 return 0; 64 }
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 }node; 9 10 node *creat() //头插法建立链表 11 { 12 13 int k; 14 node *head,*p,*tail; 15 16 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 17 head-> next = NULL; 18 tail=head; 19 20 while(~scanf("%d",&k) && k!=-1) 21 { 22 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 23 p->data=k; 24 p->next=NULL; 25 tail->next=p; 26 tail=p; 27 } 28 29 return head; 30 31 } 32 33 void reserve(node *head)//倒置 34 { 35 node *p,*s; //定义两个指针 36 37 p=head->next; 38 head->next=NULL; 39 40 while(p) 41 { 42 s=p; 43 p=p->next; //p和s是两个相邻的指针(p在s后面一位) 44 s->next=head->next; //s->next第一次置空,第二次指向第一个数,遍历(参考下一行) 45 head->next=s; //head指向的位置越来越靠后 46 } 47 } 48 49 void pri(node *p) 50 { 51 while(p)//遍历链表 52 { 53 if(p->next==NULL) 54 printf("%d\n",p->data); 55 else printf("%d ",p->data); 56 p=p->next; 57 } 58 } 59 60 void solve() 61 { 62 node *head; 63 64 head=creat(); //建立链表 65 66 reserve(head); 67 68 pri(head->next); 69 70 } 71 72 int main() 73 { 74 75 int T=1; 76 //scanf("%d",&T); 77 while(T--) 78 solve(); 79 80 return 0; 81 }
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 }node; 9 10 node *creat(int n) //尾插法建立链表 11 { 12 13 node *head,*p,*tail; //创建新节点并置空 14 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 15 16 head->next=NULL; 17 tail=head; //此时只有链表中只有一个节点 18 19 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 20 { 21 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); //开辟新节点 22 scanf("%d",&p->data); 23 24 p->next=NULL; 25 tail->next=p; 26 tail=p; //将tail更新为p,相当于尾部多了一个节点,此时tail仍然指的是尾部 27 } 28 return head; //返回头节点 29 30 } 31 32 node *Merge(node *head1,node *head2) //归并算法 典中典了属于是 33 { 34 35 node *p1,*p2,*tail; 36 37 p1=head1->next; 38 p2=head2->next; 39 tail=head1; 40 41 while(p1 && p2) 42 { 43 if(p1->data<=p2->data) //比较两个data的值看指针指向哪一个 44 { 45 tail->next=p1; 46 tail=p1; 47 p1=p1->next; 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 tail->next=p2; 52 tail=p2; 53 p2=p2->next; 54 } 55 } 56 if(p1) //跳出循环是因为有一方数据输入完毕,判断哪个链表还有剩余,接上尾巴即可 57 tail->next=p1; 58 else 59 tail->next=p2; 60 61 return head1; 62 63 } 64 65 void pri(node *p) 66 { 67 while(p)//遍历链表 68 { 69 if(p->next==NULL) 70 printf("%d",p->data); 71 else printf("%d ",p->data); 72 p=p->next; 73 } 74 } 75 76 void solve() 77 { 78 79 int n,m; 80 scanf("%d %d", &n,&m); 81 82 node *head1,*head2; 83 84 head1=creat(n); 85 head2=creat(m); //建立链表 86 87 head1=Merge(head1,head2); 88 89 pri(head1->next); //遍历输出链表的值 90 91 } 92 93 int main() 94 { 95 96 int T=1; 97 //scanf("%d",&T); 98 while(T--) 99 solve(); 100 101 return 0; 102 }
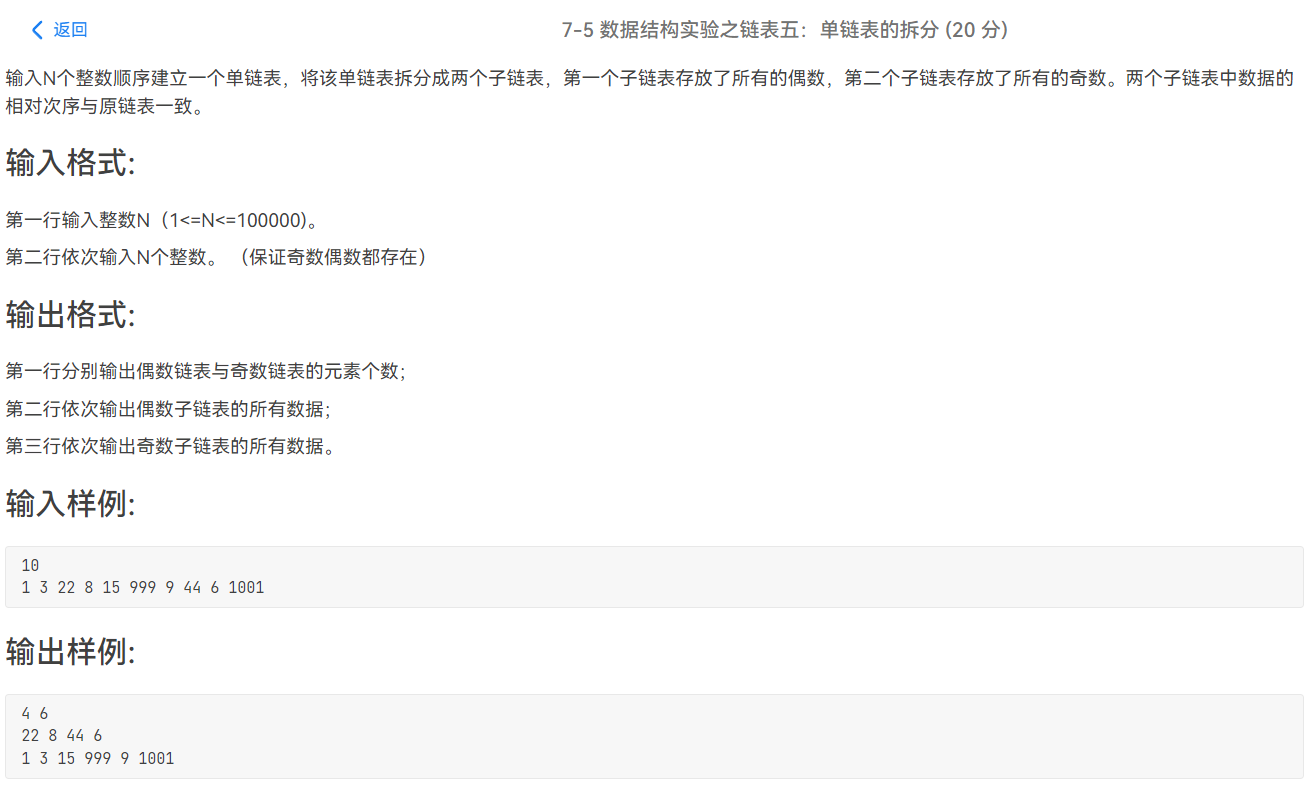
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 }node; 9 10 int n; 11 int len1,len2; 12 13 node *creat(int n) //尾插法建立链表 14 { 15 16 node *head,*p; //创建新节点并置空 17 18 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 19 head->next=NULL; 20 21 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 22 { 23 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 24 scanf("%d",&p->data); 25 26 p->next=head->next; //p现在指向head的下一位 27 head->next=p; //再让head指向p相当于p完成了插入操作,插到了head和head->next的中间部分 28 } 29 30 return head; //返回头节点 31 32 } 33 34 node *Divide(node *head1) 35 { 36 node *head2,*p,*s; 37 head2=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 38 39 head2->next=NULL; 40 p=head1->next; 41 s=p->next; 42 head1->next=NULL; 43 44 while(p) 45 { 46 if(p->data%2==0) 47 { 48 len1++; 49 p->next=head1->next; 50 head1->next=p; 51 } 52 else 53 { 54 len2++; 55 p->next=head2->next; 56 head2->next=p; 57 } 58 p=s; 59 if(s) 60 s=s->next; 61 } 62 return head2; 63 } 64 65 void pri(node *p) 66 { 67 while(p)//遍历链表 68 { 69 if(p->next==NULL) 70 printf("%d\n",p->data); 71 else printf("%d ",p->data); 72 p=p->next; 73 } 74 } 75 76 void solve() 77 { 78 79 scanf("%d",&n); 80 81 node *head1,*head2; 82 83 head1=creat(n); 84 head2=Divide(head1); 85 86 printf("%d %d\n",len1,len2); 87 88 pri(head1->next); 89 pri(head2->next); 90 91 } 92 93 int main() 94 { 95 96 int T=1; 97 //scanf("%d",&T); 98 while(T--) 99 solve(); 100 101 return 0; 102 }
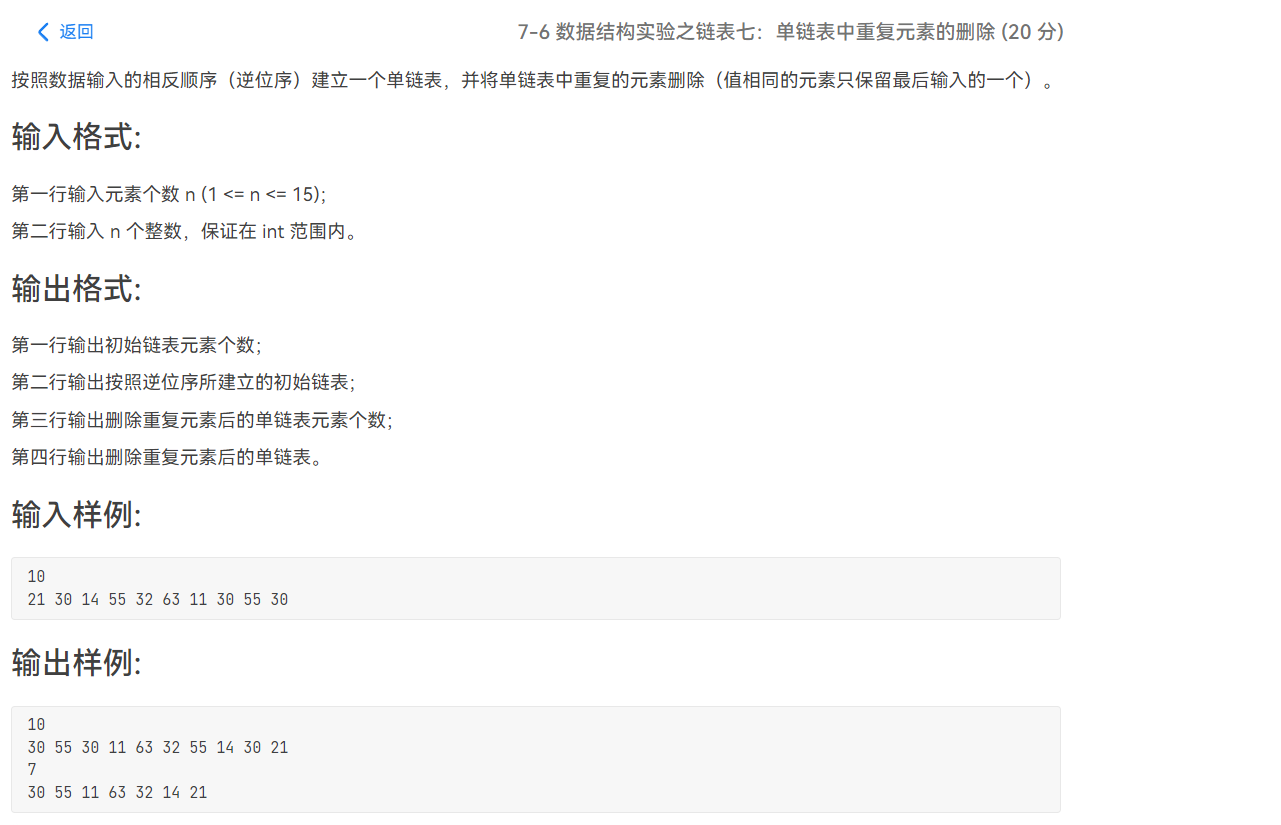
相关代码

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 }node; 9 int n; 10 node *creat(int n) //尾插法建立链表 11 { 12 13 node *head,*p; //创建新节点并置空 14 15 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 16 head->next=NULL; 17 18 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 19 { 20 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 21 scanf("%d",&p->data); 22 23 p->next=head->next; //p现在指向head的下一位 24 head->next=p; //再让head指向p相当于p完成了插入操作,插到了head和head->next的中间部分 25 } 26 27 return head; //返回头节点 28 29 } 30 31 void pri(node *p) 32 { 33 while(p)//遍历链表 34 { 35 if(p->next==NULL) 36 printf("%d\n",p->data); 37 else printf("%d ",p->data); 38 p=p->next; 39 } 40 } 41 42 void solve() 43 { 44 45 scanf("%d", &n); 46 47 node *head,*p; 48 head=creat(n); //建立链表 49 50 printf("%d\n",n); 51 pri(head->next); //遍历输出链表的值 52 53 node *q,*k; 54 p=head->next; 55 q=head; 56 while(p) //可以看作暴力对比 57 { 58 int flag=1; 59 k=head->next; 60 while(k!=p) 61 { 62 if(k->data==p->data) 63 { 64 flag=0; 65 n--; 66 q->next=p->next; 67 p=p->next; 68 break; 69 } 70 k=k->next; 71 } 72 if(flag) 73 { 74 p=p->next; 75 q=q->next; 76 } 77 } 78 printf("%d\n",n); 79 pri(head->next); 80 } 81 82 int main() 83 { 84 85 int T=1; 86 //scanf("%d",&T); 87 while(T--) 88 solve(); 89 90 return 0; 91 }
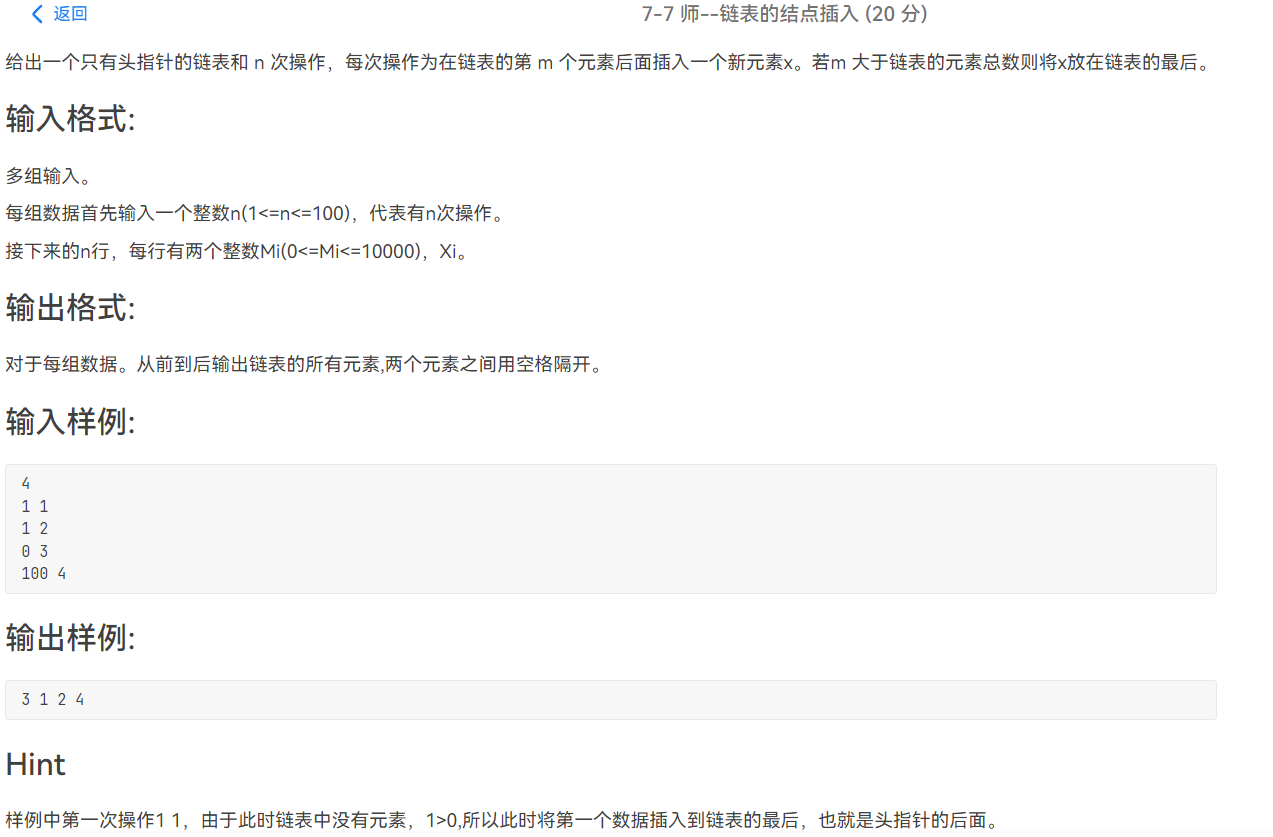
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 }node; 9 10 void Insert(node *head,int m,int k) 11 { 12 node *q=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); //q相当于应该插入的节点 13 node *p=head; 14 q->data=k; 15 for(int i=0;i<m && p->next!=NULL;i++) 16 p=p->next; //找到q插入的位置 17 q->next=p->next; //用头节点插入的方法插入q节点 18 p->next=q; 19 } 20 21 void pri(node *p) 22 { 23 while(p)//遍历链表 24 { 25 if(p->next==NULL) 26 printf("%d",p->data); 27 else printf("%d ",p->data); 28 p=p->next; 29 } 30 } 31 32 void solve() 33 { 34 35 int n; 36 while(~scanf("%d",&n)) 37 { 38 node *head,*p; 39 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 40 head->next=NULL; 41 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 42 { 43 int m,k; 44 scanf("%d%d",&m,&k); 45 46 Insert(head,m,k); 47 } 48 pri(head->next); 49 puts(""); 50 } 51 52 } 53 54 int main() 55 { 56 57 int T=1; 58 //scanf("%d",&T); 59 while(T--) 60 solve(); 61 62 return 0; 63 }
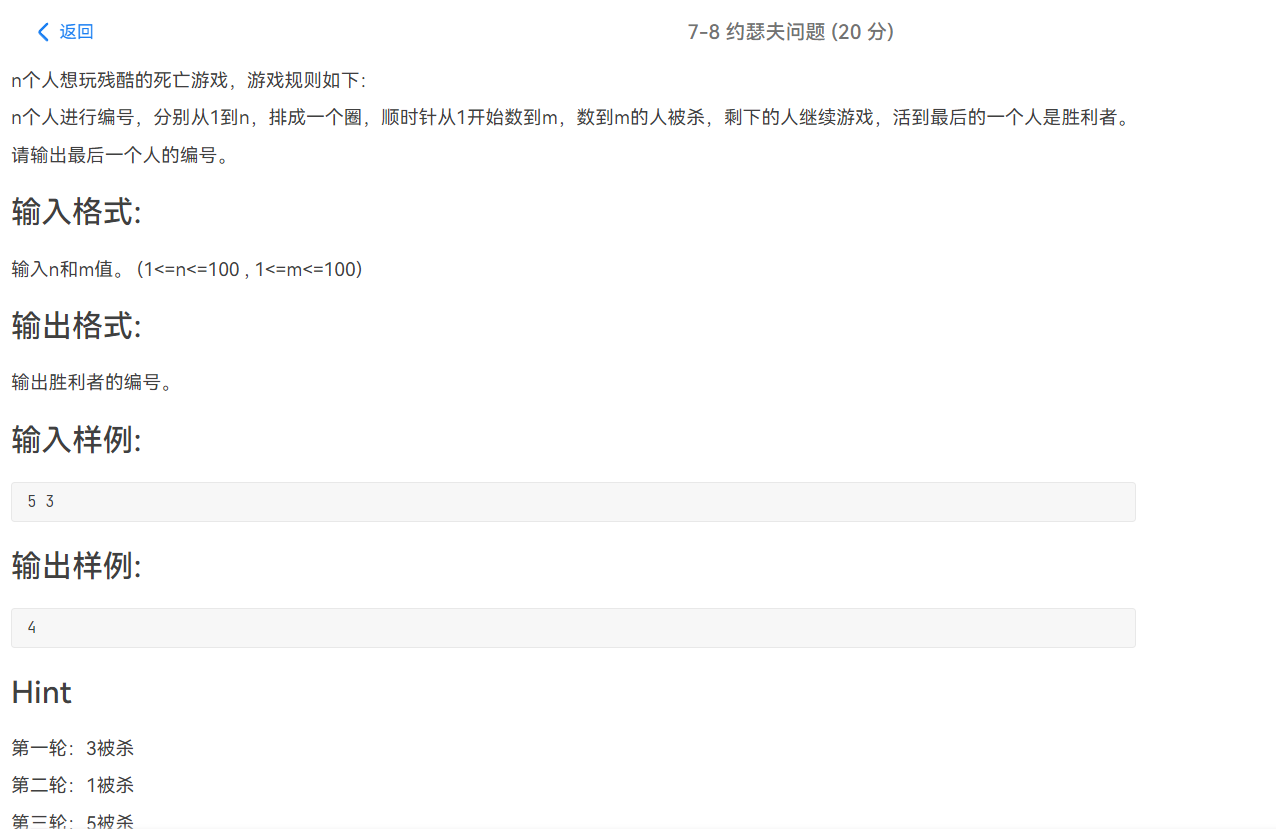
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <malloc.h> 4 5 typedef struct Node 6 { 7 int data; 8 struct Node *next; 9 }node; 10 11 node *creat(int n) 12 { 13 node *head,*p,*tail; 14 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 15 16 p->data=1; 17 p->next=NULL; 18 head=p; 19 tail=p; 20 21 for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) //现在head=tail=p=1,从2开始正向建立链表(尾插法) 22 { 23 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 24 25 p->data=i; 26 p->next=NULL; 27 tail->next=p; 28 tail=p; 29 } 30 tail->next=head; //首尾相连 31 32 return head; 33 } 34 35 void solve() 36 { 37 38 int n,m; 39 int cnt=0; 40 41 scanf("%d %d",&n,&m); 42 node *head,*p,*s; 43 44 head=creat(n); 45 s=head; 46 47 while(s->next!=head) //s表示为队尾的元素 48 s=s->next; 49 50 while(s->next!=s) //当链表中直剩下一个元素时跳出 51 { 52 p=s->next; //第一轮第一个数是链表中第一个元素,所以起始应该是队尾的元素(p在s前面) 53 cnt++;//每次喊数字 54 if(cnt==m) 55 { 56 s->next=p->next; 57 free(p); //释放节点p,并将cnt归零重新计数 58 cnt=0; 59 } 60 else 61 s=p; 62 } 63 printf("%d",s->data); 64 65 66 67 } 68 69 int main() 70 { 71 72 int T=1; 73 //scanf("%d",&T); 74 while(T--) 75 solve(); 76 77 return 0; 78 }

代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef struct Node 5 { 6 int data; 7 struct Node *next; 8 struct Node *front; 9 }node; 10 11 node *creat(int n) //尾插法建立链表 12 { 13 14 node *head,*p,*tail; //创建新节点并置空 15 head=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 16 17 head->next=NULL; 18 head->front=NULL; 19 tail=head; //此时只有链表中只有一个节点 20 21 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 22 { 23 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); //开辟新节点 24 scanf("%d",&p->data); 25 26 p->next=NULL; 27 tail->next=p; 28 p->front=tail; //多了一个前节点 29 tail=p; //将tail更新为p,相当于尾部多了一个节点,此时tail仍然指的是尾部 30 } 31 return head; //返回头节点 32 33 } 34 35 void solve() 36 { 37 38 int n,m; 39 scanf("%d %d", &n, &m); 40 41 node *head; 42 head=creat(n); //建立链表 43 44 while(m--) 45 { 46 int k; 47 scanf("%d",&k); 48 49 node *p=head->next; 50 while(p->data!=k) 51 p=p->next; 52 if(p->front==head) 53 printf("%d\n",p->next->data); 54 else if(p->next==NULL) 55 printf("%d\n",p->front->data); 56 else 57 printf("%d %d\n",p->front->data,p->next->data); 58 } 59 60 } 61 62 int main() 63 { 64 65 int T=1; 66 //scanf("%d",&T); 67 while(T--) 68 solve(); 69 70 return 0; 71 }
代码链接

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <malloc.h> 4 5 typedef struct Node 6 { 7 int data; 8 struct Node *next; 9 }node; 10 11 node *creat(int n) 12 { 13 node *head,*p,*tail; 14 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 15 16 p->data=1; 17 p->next=NULL; 18 head=tail=p; 19 20 for(int i=2; i<=n; i++) //现在head=tail=p=1,从2开始正向建立链表(尾插法) 21 { 22 p=(node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); 23 24 p->data=i; 25 p->next=NULL; 26 tail->next=p; 27 tail=p; 28 } 29 tail->next=head; //首尾相连 30 31 return head; 32 } 33 34 void solve() 35 { 36 37 int n; 38 while(~scanf("%d",&n) && n) 39 { 40 node *head,*p,*s; 41 int cnt=0,ans=0; 42 43 head=creat(n); 44 s=head; 45 46 while(s->next!=head) 47 s=s->next; 48 49 while(s->next!=s) 50 { 51 p=s->next; 52 cnt++; 53 if(cnt==5) 54 { 55 ans++; 56 if(p->data==1) 57 break; 58 s->next=p->next; 59 free(p); 60 cnt=0; 61 } 62 else 63 s=p; 64 } 65 if(s->data==1) //最后一次循环提前结束,如果最后剩下一号的话需要单独判断 66 printf("%d\n",ans+1); 67 else 68 printf("%d\n",ans); 69 } 70 71 72 73 } 74 75 int main() 76 { 77 78 int T=1; 79 //scanf("%d",&T); 80 while(T--) 81 solve(); 82 83 return 0; 84 }
小结
链表的代码较长若不充分李姐(理解)的情况下暴力背诵一般不会有什么好结果QAQ
重点是理解,懂得建表过程
salute!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号