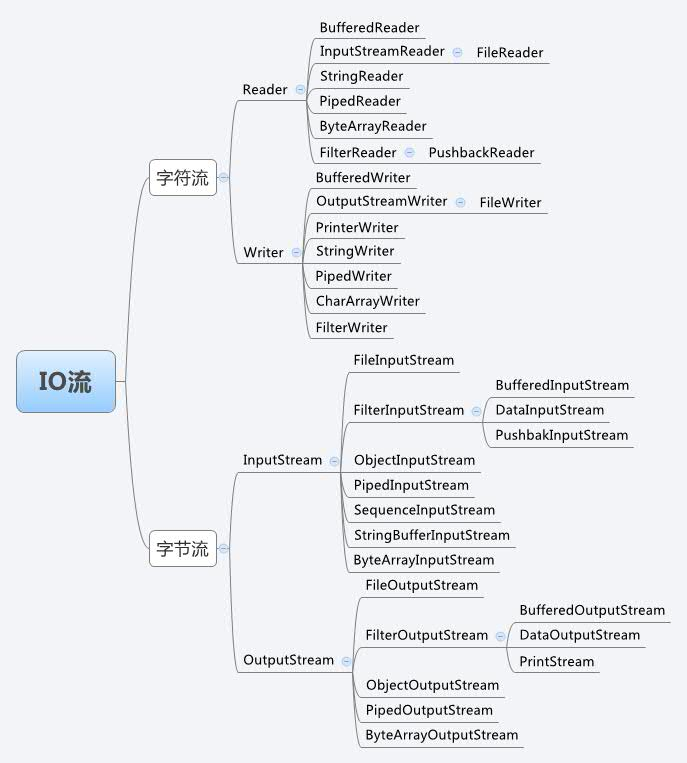
IO流
问题1:IO流一定要关闭么?
问题2:字符流和字节流使用上有什么区别?
问题3:IO流分哪几种?
一、思维导图
前言:IO流都为对文件操作,所以IO流都需要使用File类
String filePath="/Users/text.txt"; File file = new File(filePath);
file.isDirectory();//判断是否为文件夹
File files[] = file.listFiles();//获取路径下的所有文件&文件夹
一、缓冲流--最常用
1、字符缓冲流(BufferedReader&BufferedWriter)
String filePath = "/Users/haoc/course/code/cakes-course/0.notes/day01.md";
File file = new File(filePath);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));//不一样的地方
String res;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((res = reader.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(res).append("\n");
}
String val = sb.toString();
System.out.println("val = " + val);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("这个文件不存在呀," + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件读取失败了," + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (null != reader) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2、字节缓冲流(BufferedInputStream&BufferedOutputStream)
二、字符流(FileReader&FileWriter)
public static void normalReader1() {
String filePath = "/Users/haoc/course/code/cakes-course/0.notes/day01.md";
File file = new File(filePath);
Reader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader(file);
int len;
char[] buf = new char[256];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((len = reader.read(buf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(buf, 0, len);
sb.append(str);
}
String val = sb.toString();
System.out.println("val = " + val);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("这个文件不存在呀," + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件读取失败了," + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (null != reader) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//FileWrite
public void FileWrite(){
File file =new File("");
FileWriter fileWriter=null;
byte[] result =new byte[256];
try {
fileWriter=new FileWriter(file);
fileWriter.write(result.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fileWriter !=null){
}
}
}
三、字节流(InputSream&OutputStream)
public static void normalRead1() {
String filePath = "/Users/haoc/course/code/cakes-course/0.notes/day01.md";
InputStream ins = null;
try {
File file = new File(filePath);
ins = new FileInputStream(file);
int len;
byte[] buf = new byte[256];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((len = ins.read(buf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(buf, 0, len);
sb.append(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) { // if e == FileNotFoundException
System.out.println("这个文件不存在呀," + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("文件读取失败了," + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (null != ins) {
try {
ins.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("流关闭失败了," + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public static void testWriteFile1() throws Exception {
String filePath = "/Users/haoc/course/temp/xxxx.md";
File file = new File(filePath);
OutputStream ous = new FileOutputStream(file);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
String str = "hello java io" + i + "\n";
ous.write(str.getBytes());
}
ous.flush();
}



