数模--2022华中杯A题(Java实现)
一.赛题
1.订单分批
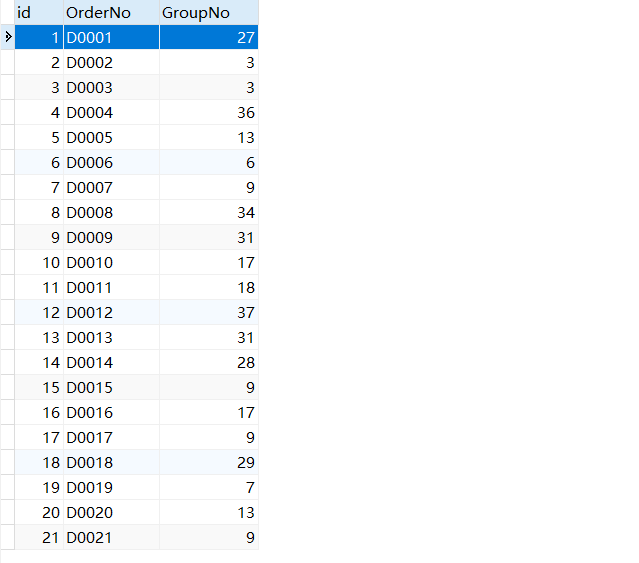
将当日订单分为多个批次。要求每个批次的订单所含货品种类数均不超过 ,且批次越少越好(相应转运次数也越少,效率越高)。针对附件 1 中的订单信息,应用你们的算法,计算当货架数量 时最少的批次数,给出每批订单数量、货品种类数、分批方案等结果,并将完整原始分批方案按指定格式输出到文件result1.csv 中,格式要求见附件 2。
2.商品摆放
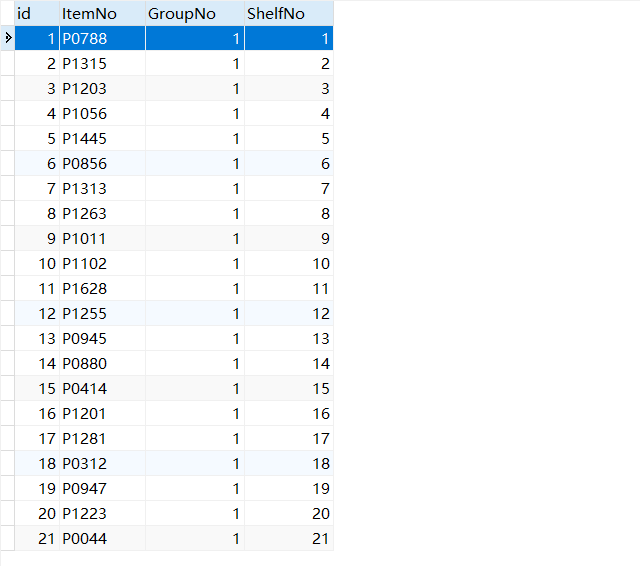
确定每一种货品放置在哪一个货架。分拣工拣选货品时,同一订单所含货品的位置越集中,移动距离越短,拣选效率越高。某一订单 的拣选距离定义为该订单中货品所在货架序号的最大值与最小值之差。对于给定的某一批分拣任务,请设计货品摆放算法,使得该批分拣任务所有订单的拣选距离总和尽量小。并针对附件 1 的数据,在第 1 问得到的分批结果基础上,考虑拣选距离,设计各批次中每一种货品的摆放位置,给出各批分拣任务的拣选距离总和,以及所有批次全部订单的拣选距离总和,并将完整原始货品摆放方案按指定格式输出到文件 result2.csv 中,格式要求见附件 3。
二.思路
1.订单分批
计算订单相似度,即订单中商品的重复度,重复度越高将这两个订单放在一起的效率就越高
2.商品摆放
遗传算法不断优化最短拣选距离
三.Java代码
1.订单分批
---batchService
package org.manage.batch; import cn.fabrice.jfinal.service.BaseService; import com.jfinal.kit.Kv; import com.jfinal.plugin.activerecord.Db; import com.jfinal.plugin.activerecord.Record; import com.jfinal.plugin.activerecord.SqlPara; import org.manage.common.module.Order; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.PrintStream; import java.util.*; import static java.lang.Math.max; import static java.lang.Math.min; /** * @author Administrator */ public class BatchService extends BaseService<Order>{ public BatchService() { super("batch.", Order.class, "batch"); } /** * 将商品处理为数组坐标的形式用于求商品之间的相似度 * @return 所有商品的数组坐标 */ public int[][] getAllAddress(){ //大约1000条订单,2000种商品,对每种订单,找出其存在的商品 int[][] a = new int[1000][2000]; for(int i=1;i<1000;i++){ for(int j=1;j<2000;j++){ a[i][j]=0; } } for(int i=1;i<=923;i++){ Kv cond=Kv.by("order_id",i); SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getOrderById", cond); List<Record> orderList=Db.find(sqlPara); for(Record order:orderList){ a[i][order.getInt("item_id")]+=1; } } try { PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\数模\\getAddress.txt"); System.setOut(ps); for(int i=1;i<=923;i++){ for(int j=1;j<2000;j++){ System.out.print(a[i][j]); } System.out.println("第"+i+"条"); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return a; } /** * 获取某一个具体订单的数组坐标 * @param orderId 订单编号 * @return 返回数组坐标 */ public double[] getAddress(int orderId){ double[] a = new double[2000]; for(int j=1;j<2000;j++){ a[j]=0; } Kv cond=Kv.by("order_id",orderId); SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getOrderById", cond); List<Record> orderList=Db.find(sqlPara); for(Record order:orderList){ a[order.getInt("item_id")]+=1; } return a; } /** * 获取两个数组的相似度 * @param place1 原有数组 * @param place2 放入数据 * @return 返回相似度 */ public double getCoincide(double[] place1,double[] place2){ //遍历近2000种商品,得到预放入的orderId和批次的商品重合度 int sum1=0,sum2=0; for(int i=1;i<2000;i++){ if(place1[i]==1&&place2[i]==1){ sum1++; } } for(int i=1;i<2000;i++){ if(place2[i]==1){ sum2++; } } return (double) sum1/sum2; } /** * 找出某一个坐标到其他所有符合条件(先判断种类和<=200)的未使用订单的最大相似度,返回对应订单编号 * @param place 坐标 * @param orderId 符合条件的订单id * @return 最相似的订单编号 */ public int getMaxCoincide(double[] place,int[] orderId){ int sum=0; for(int i=1;i<2000;i++){ if(orderId[i]>0){ sum++; } } //说明此时不存在符合条件的orderId,该批次结束 if(sum==0){ return 0; } int maxOrderId=0; double coincide,maxCoincide=0; for(int i=1;i<=sum;i++){ coincide=getCoincide(place,getAddress(orderId[i])); if(coincide>maxCoincide){ maxCoincide=coincide; maxOrderId=orderId[i]; } } return maxOrderId; } /** * 查找当前要处理的批次,批次中包含一系列订单,找到该批次存在的商品情况(同时传递当前批次,存在core[0]) * @return 返回商品存在情况 */ public double[] getCore(){ SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getNowBatch"); List<Record> nowBatchList=Db.find(sqlPara); int nowBatch=nowBatchList.get(0).getInt("batch"),sum=0; double[] core = new double[2000]; for(int j=1;j<2000;j++){ core[j]=0; } for(Record record:nowBatchList){ core[record.getInt("item_id")]=1; } core[0]=nowBatch; return core; } public int getNowSum(){ //统计当前批次的种类和 SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getNowBatch"); List<Record> recordList0=Db.find(sqlPara); int[] nowSum=new int[2000]; for(int i=1;i<2000;i++){ nowSum[i]=0; } for(Record record:recordList0){ nowSum[record.getInt("item_id")]++; } //统计当前商品种类 int now=0; for(int i=1;i<2000;i++){ if(nowSum[i]!=0){ now++; } } return now; } /** * 分批算法 */ public void getBatch(){ int now=0; while(now<200){ //查找所有未放入某个批次的订单,将订单id存入unUsed数组中 int[] unUsed=new int[1000]; for(int j=1;j<1000;j++){ unUsed[j]=0; } SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getUnUsed"); List<Record> recordList=Db.find(sqlPara); for(Record record:recordList){ unUsed[record.getInt("order_id")]++; } //获取聚类批次商品情况 double[] core=getCore(); //从unUsed中筛选,如果加上符合种类和不超过200的订单id,存入orderId int[] orderId=new int[2000]; for(int i=0;i<2000;i++){ orderId[i]=0; } int accord=1; for(int i=1;i<1000;i++){ //不等于0表示此订单存在,下标表示订单id if(unUsed[i]!=0){ double[] unUsedItem=getAddress(i); //此时得到的unUsedItem就是种类和 for(int j=1;j<2000;j++){ unUsedItem[j]+=core[j]; } //统计当前商品种类 int sum=0; for(int j=1;j<2000;j++){ if(unUsedItem[j]!=0){ sum++; } } //将符合条件的orderId存入数组中,数组的值表示订单id if(sum<=200){ orderId[accord]=i; accord++; } } } //获取符合条件的订单中,与当前类商品最相似的订单,无法找到相似且满足条件的订单,该批次结束 int newOrderId=getMaxCoincide(core,orderId); int nowBatch= (int) core[0]; if(newOrderId==0){ //结束当前订单 Kv cond=Kv.by("batch",nowBatch); sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.updateIsFinished",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); //开启下个订单 nowBatch++; addFirst(nowBatch); } else{ //将该订单放入该批次(放入前不需要测试--已经满足种类和<=200的条件) Kv cond=Kv.by("order_id",newOrderId).set("batch",nowBatch); sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.updateIsUsedBatch",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); } now=getNowSum(); } double[] core=getCore(); int nowBatch= (int) core[0]; //结束当前订单 Kv cond=Kv.by("batch",nowBatch); SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.updateIsFinished",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); //开启下个订单 nowBatch++; addFirst(nowBatch); } /** * 在每批结束后,从所有未处理的订单中选择长度最大的订单作为新的批次的第一个订单 * @param batch 表示想要新增的批次 */ public void addFirst(int batch){ SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getFirst"); Record maxLine=Db.findFirst(sqlPara); Kv cond =Kv.by("order_id",maxLine.getInt("order_id")).set("batch",batch); sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.updateFirst",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); } public void getAllBatch(){ SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getIsUsed"); List<Record> records=Db.find(sqlPara); if(records.isEmpty()){ addFirst(1); } sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getUnUsed"); records=Db.find(sqlPara); //当所有订单都处理完后,循环结束 while (!records.isEmpty()){ getBatch(); records=Db.find(sqlPara); } } public void addD(){ SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getResult"); List<Record> list=Db.find(sqlPara); for(Record record:list){ String oldOrderNo=record.getStr("OrderNo"); String newOrderNo="D"+oldOrderNo; Kv cond=Kv.by("id",record.getLong("id")).set("newOrderNo",newOrderNo); sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.updateResult",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); } } }
---batchService
package org.manage.batch; import com.jfinal.aop.Inject; import com.jfinal.core.Controller; import com.jfinal.core.Path; /** * @author Administrator */ @Path("/batch") public class BatchController extends Controller { @Inject BatchService batchService; public void getAllBatch(){ batchService.getAllBatch(); } public void addD(){ batchService.addD(); } }
2.商品摆放
---putService
package org.manage.put; import cn.fabrice.jfinal.service.BaseService; import com.alibaba.druid.sql.ast.expr.SQLCaseExpr; import com.jfinal.kit.Kv; import com.jfinal.plugin.activerecord.Db; import com.jfinal.plugin.activerecord.Record; import com.jfinal.plugin.activerecord.SqlPara; import org.manage.common.module.Order; import java.util.*; import static java.lang.Math.max; import static java.lang.Math.min; /** * @author Administrator */ public class PutService extends BaseService<Order>{ public PutService() { super("batch.", Order.class, "batch");} /** * 根据批次号,获取该批次的商品信息 * @param batch 批次号 * @return 返回商品信息,值表示商品号 */ public int[] getBatchGood(int batch){ Kv cond=Kv.by("batch",batch); SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getBatchGood",cond); List<Record> recordList=Db.find(sqlPara); int[] good=new int[2000]; //可用于存商品的位数1~200共200位,首位0存商品种类数,末尾空置便于染色体存储拣选距离 int[] result=new int[202]; for(Record record:recordList){ good[record.getInt("item_id")]++; } //统计商品种类 int sum=1; for(int i=1;i<2000;i++){ if(good[i]!=0){ result[sum]=i; sum++; } } //result首位存放商品种类数 result[0]=sum-1; return result; } /** * 根据批次号,获取该批次的商品具体信息 * @param batch 批次号 * @return 返回商品信息,行表示订单编号,列表示商品编号,值表示商品是否存在 */ public int[][] getGood(int batch){ Kv cond=Kv.by("batch",batch); SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getBatchGood",cond); List<Record> recordList=Db.find(sqlPara); int[][] good=new int[1000][2000]; for(Record record:recordList){ good[record.getInt("order_id")][record.getInt("item_id")]=1; } return good; } /** * 生成染色体,即某个批次所有种类商品在货架上的排列方案 * @param batch 传入批次号 * @return 返回商品的排列方案,下标表示货架号,值表示商品号,首位0存商品种类数,末尾201存商品拣选距离 */ public int[] createChromosome(int batch){ int[] a=getBatchGood(batch); int[] chromosome=new int[202]; Random random=new Random(); for(int i=a[0];i>=1;i--){ //random.nextInt得到从1到i+1(不包含i+1)的一系列整数中的随机一个 int place2=random.nextInt(i)%(i) + 1; int t=a[i]; a[i]=a[place2]; a[place2]=t; } for(int i=0;i<=200;i++){ chromosome[i]=a[i]; } return chromosome; } /** * 根据批次,生成包含一定数量染色体(即货品放置方案)的种群 * @param num 种群中希望的染色体数量 * @param batch 批次 * @return 返回种群,1~num每行首位0存商品种类数 */ public int[][] createPopulation(int batch,int num){ int[][] population=new int[num+1][202]; for(int i=1;i<=num;i++){ population[i]=createChromosome(batch); } //在population[0]行存储一些种群相关信息,便于取用 population[0][0]=num; return population; } /** * 计算某一个订单在相应货架摆放方案上的拣选距离 * @param chromosome 染色体(摆放方案)--下标表示货架号,值表示商品编号 * @param good 订单商品情况--下标表示商品编号,值01表示商品是否存在 * @return 返回拣选距离 */ public int getDistance(int[] chromosome,int[] good){ int[] place=new int[201]; int j=1; //遍历货架,判断该货架号对应的商品编号是否在该订单中存在,得到该订单的商品放置位置place for(int i=1;i<=200;i++){ if(good[chromosome[i]]!=0){ //说明该订单在货架i上存在商品 place[j]=i; j++; } } //j-1表示订单商品一共放在了多少个货架上,place[j-1]表示最后一个货架号 return place[j-1]-place[1]; } /** * 计算某一个批次中所有订单在相应货架摆放方案上的拣选距离总和 * @param chromosome 染色体(摆放方案)--下标表示货架号,值表示商品编号 * @param good 订单商品情况--行表示订单编号,列表示商品编号,值01表示商品是否存在 * @return 返回拣选距离 */ public int getAllDistance(int[] chromosome,int[][] good){ int distance=0; for(int i=1;i<1000;i++){ distance+=getDistance(chromosome,good[i]); } return distance; } /** * 在种群中添加子代:用子代代替父代中distance最大的 * @param father 父代种群 * @param son 子代 * @param good 某一个批次订单信息 * @return 返回替换后的父代种群 */ public int[][] addSon(int[][] father,int[] son,int[][] good){ int sonDistance=getAllDistance(son,good); son[201]=sonDistance; if(father[father[0][0]][201]>sonDistance){ //把最后一个距离最大的父代换掉 father[father[0][0]]=son; } return father; } /** * 选择算子 * * 从种群中选择一定数量作为父代进行遗传(择优,拣选距离较短) * @param good 该批订单商品信息 * @param population 种群 * @param percent 选择的百分比 * @return 返回父代结果,1~father行首位0存商品种类数,末尾201存总距离,第0行第0位存father(即种群中染色体个数) */ public int[][] chooseGenetics(int[][] good,int[][] population,double percent){ int num=population[0][0]; int father= (int) (num*percent); class Dis{ int i; int distance; } ArrayList<Dis> list=new ArrayList<Dis>(population.length); //得到该批次订单到每种放置方案的距离,选择其中较短的距离对应的染色体作为父代 for(int i=1;i<=num;i++){ Dis d=new Dis(); d.i=i; d.distance=getAllDistance(population[i],good); list.add(d); } //距离从小到大进行排序 list.sort((Comparator<Object>) (a, b) -> { Dis distance1 = (Dis) a; Dis distance2 = (Dis) b; return distance1.distance-distance2.distance; }); //从排序完的list中取出前father个对应的chromosome作为父代(list的序号是从0开始的) int[][] populationFather=new int[population.length][202]; for(int i=1;i<=father;i++){ populationFather[i]=population[list.get(i-1).i]; populationFather[i][201]=list.get(i-1).distance; } populationFather[0][0]=father; return populationFather; } /** * 交叉算子 * * 根据两个父代,基因交叉后得到子代 * @param father 父代种群 * @param f1 父代1 * @param f2 父代2 * @param good 批次订单 * @return 返回经过交叉遗传后的种群 */ public int[][] crossGenetics(int[][] father,int[] f1,int[] f2,int[][] good){ //随机产生交叉互换位置 int size = f1[0]; Random random=new Random(); int a = random.nextInt(f1[0])+1; int b = random.nextInt(f1[0])+1; int min = Math.min(a, b); int max = Math.max(a, b); while(min==max){ a = random.nextInt(f1[0])+1; b = random.nextInt(f1[0])+1; min = Math.min(a, b); max = Math.max(a, b); } int[] son=new int[202]; List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>(); //首先将f1的begin到end的染色体复制到son for (int i = min; i <= max; i++) { son[i]=f1[i]; } son[0]=f1[0]; //其次将f2中除了son中已有的基因外的其他基因复制到son for (int i=1;i<=f2[0];i++) { t.add(f2[i]); } for (int k=min;k<=max;k++) { for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++) { if (son[k]==t.get(i)) { t.remove(i); break; } } } int j=0; for(int i=1;i<min;i++){ son[i]=t.get(j); j++; } for(int i=max+1;i<=son[0];i++){ son[i]=t.get(j); j++; } father=addSon(father,son,good); return father; } /** * 变异算子 * * 染色体上的基因随机交换位置 * @param a 需要进行变异的染色体 * @return 返回变异后的种群 */ public int[][] variantGenetics(int[][] father,int[] a,int[][] good){ int[] t=new int[202]; for(int i=1;i<=a[0];i++){ t[i]=a[i]; } Random random=new Random(); int chromosomeLength=a[0]; int d1=random.nextInt(chromosomeLength)+1; int d2=random.nextInt(chromosomeLength)+1; int temp=t[d1]; t[d1]=t[d2]; t[d2]=temp; father=addSon(father,a,good); return father; } /** * 种群经过选择,交叉,变异交配得到新的种群 * @param population 原种群 * @param good 商品(对于每一个批次求最优是保持不变的) * @param percent1 选择算子百分比 * @param percent2 交叉算子百分比 * @param percent3 变异算子百分比 * @return 新种群 */ public int[][] populationMating(int[][] good,int[][] population,double percent1,double percent2,double percent3){ //从原种群中筛选得到父代 int[][] populationFather= chooseGenetics(good,population,percent1); //对于父代,根据交叉遗传百分比得到用于交叉的父代 int limit= (int) (100*percent2); Random random=new Random(); for (int i=1;i<populationFather[0][0];i++){ for(int j=i+1;j<=populationFather[0][0];j++){ //两层循环使所有的父代都有两两交叉的可能性 int number=random.nextInt(100)+1; //得到1~100的随机数<limit,即交叉概率,此时将i,j父代交叉得到新的染色体 if(number<limit){ populationFather=crossGenetics(populationFather,populationFather[i],populationFather[j],good); } } } //对于此时的种群,根据变异遗传百分比得到变异后的种群 limit=(int)(100*percent3); for(int i=1;i<=populationFather[0][0];i++){ int number=random.nextInt(100)+1; if(number<limit){ populationFather=variantGenetics(populationFather,populationFather[i],good); } } return populationFather; } /** * 对于某一个批次,得到它的最优染色体,即商品摆放方案 * @param batch 批次 * @param populationNum 初始种群中染色体数量 * @param percent1 择优率 * @param percent2 交叉率 * @param percent3 变异率 * @param time 循环次数 */ public void getBest(int batch,int populationNum,double percent1,double percent2,double percent3,int time){ int[][] good=getGood(batch); int[][] population=createPopulation(batch,populationNum); while(time>0){ System.out.println("第"+batch+"批第"+(101-time)+"次"); population=populationMating(good,population,percent1,percent2,percent3); System.out.println("当前最优摆放"+Arrays.toString(population[1])); System.out.println("当前最优距离"+population[1][201]); if(population[0][0]==1){ System.out.println("第"+(101-time)+"次"); System.out.println("最优摆放:"+Arrays.toString(population[1])); //将最终结果存入数据库 for(int i=1;i<=population[1][0];i++){ Kv cond=Kv.by("ItemNo",population[1][i]).set("GroupNo",batch).set("ShelfNo",i); SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.putShelf",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); } break; } time--; } if(population[0][0]>1) { System.out.println("较优摆放:"+Arrays.toString(population[1])); for(int i=1;i<=population[1][0];i++){ Kv cond=Kv.by("ItemNo",population[1][i]).set("GroupNo",batch).set("ShelfNo",i); SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.putShelf",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); } } } public void addP(){ SqlPara sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.getPut"); List<Record> list=Db.find(sqlPara); for(Record record:list){ String oldItemNo=record.getStr("ItemNo"); String newOrderNo="P"+oldItemNo; Kv cond=Kv.by("id",record.getLong("id")).set("newItemNo",newOrderNo); sqlPara=Db.getSqlPara("batch.updatePut",cond); Db.update(sqlPara); } } }
---putController
package org.manage.put; import cn.fabrice.common.pojo.BaseResult; import com.jfinal.aop.Inject; import com.jfinal.core.Controller; import com.jfinal.core.Path; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @author Administrator */ @Path("/put") public class PutController extends Controller { @Inject PutService putService; public void test(){ for(int i=1;i<=40;i++){ putService.getBest(i, 500, 0.8,0.6,0.05,100); } renderJson(BaseResult.ok()); } public void addP(){ putService.addP(); } }
3.SQL语句
#sql("getOrderById") select * from order_item where order_id = #para(order_id) #end #sql("updateIsUsedBatch") update order_item set is_used=1,batch=#para(batch) where order_id = #para(order_id) #end #sql("getUnUsed") select * from order_item where is_used = 0 #end #sql("getIsUsed") select * from order_item where is_used = 1 #end #sql("getNowBatch") select * from order_item where is_used=1 and is_finished=0 #end #sql("updateIsFinished") update order_item set is_finished=1 where batch = #para(batch) #end #sql("getFirst") select count(order_id) as a,order_id from order_item where is_used=0 group by order_id order by a desc #end /*update中的set多列要用逗号连接而不是and*/ #sql("updateFirst") update order_item set is_used=1,batch=#para(batch) where order_id=#para(order_id) #end #sql("getResult") select * from result #end #sql("updateResult") update result set OrderNo=#para(newOrderNo) where id=#para(id) #end #sql("getBatchGood") select * from order_item where batch=#para(batch) #end #sql("putShelf") insert into put value(#para(ItemNo),#para(GroupNo),#para(ShelfNo)) #end #sql("getPut") select * from put #end #sql("updatePut") update put set ItemNo=#para(newItemNo) where id=#para(id) #end
四.结果
1.分批
2.摆放



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号