YBTOJ 4.1堆的应用
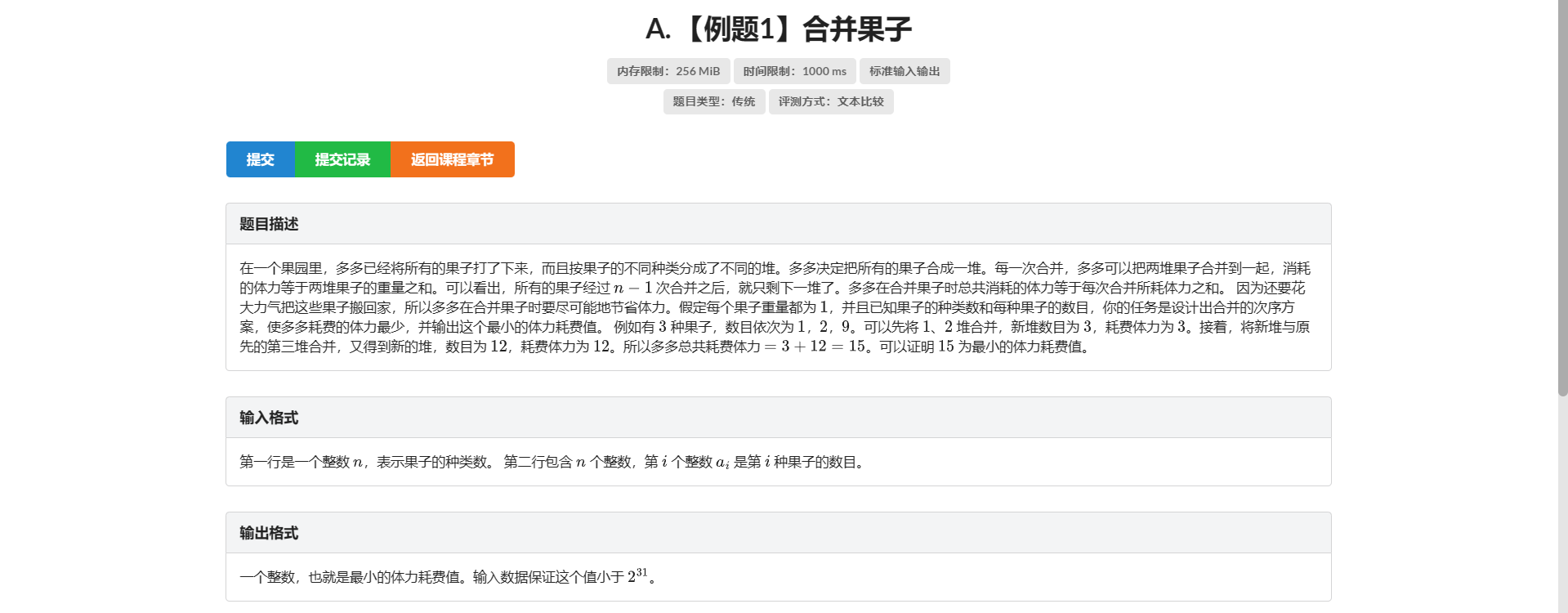
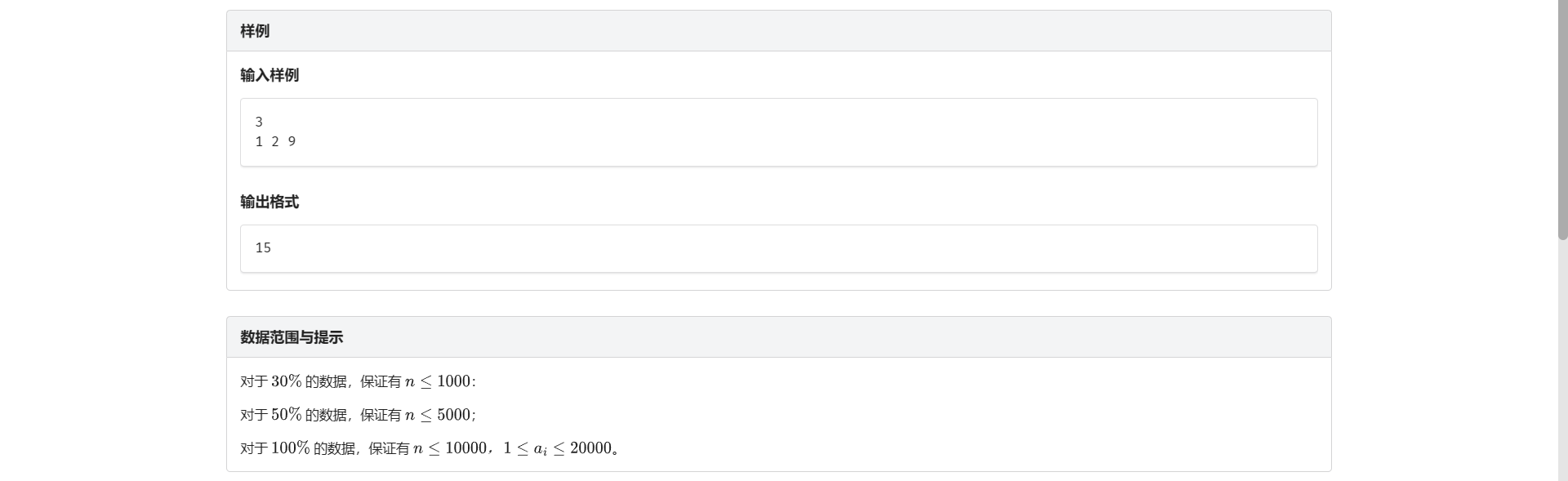
A.合并果子
很容易想到 先合并的果子 对答案的贡献明显更多
所以我们每次合并都取最小的两堆进行合并
因为每次变动的元素数量很少 选择堆排
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll ans;
int n;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > q;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
q.push(x);
}
while (q.size() > 1) {
int x1 = q.top();
q.pop();
int x2 = q.top();
q.pop();
ans += (ll)x1 + (ll)x2;
q.push(x1 + x2);
}
printf("%lld", ans);
return 0;
}
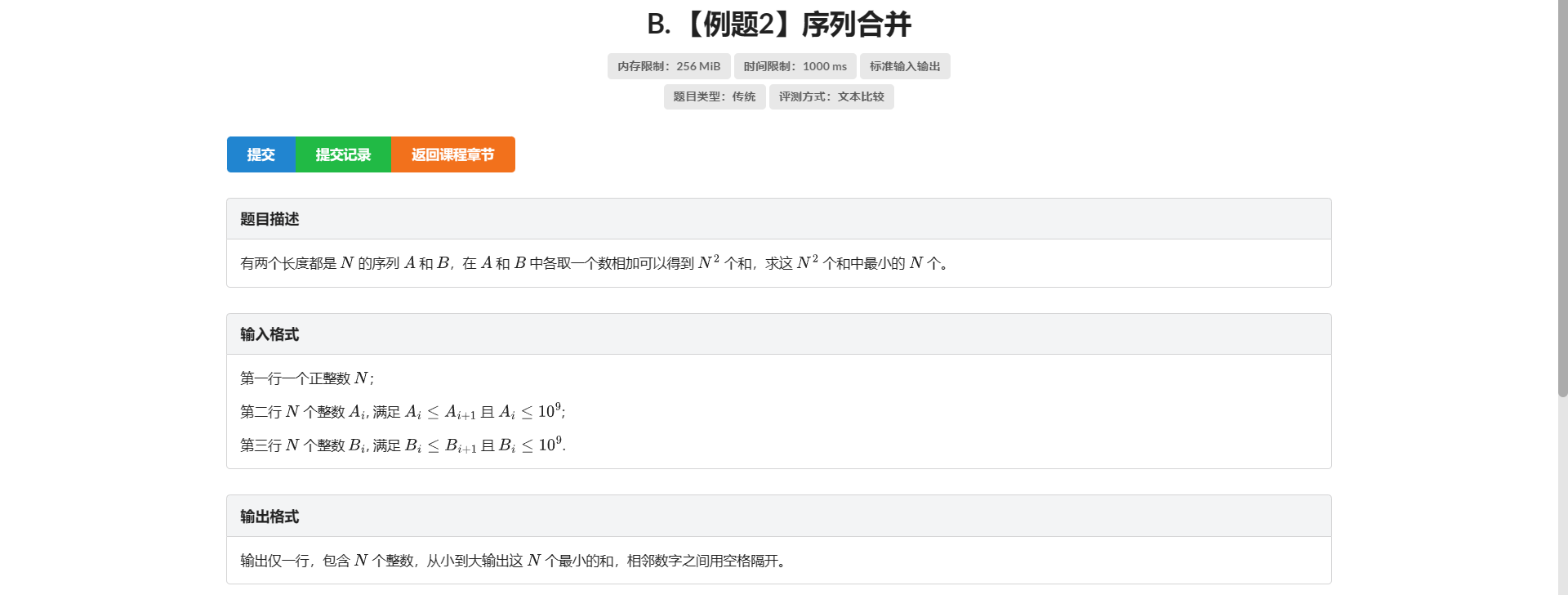
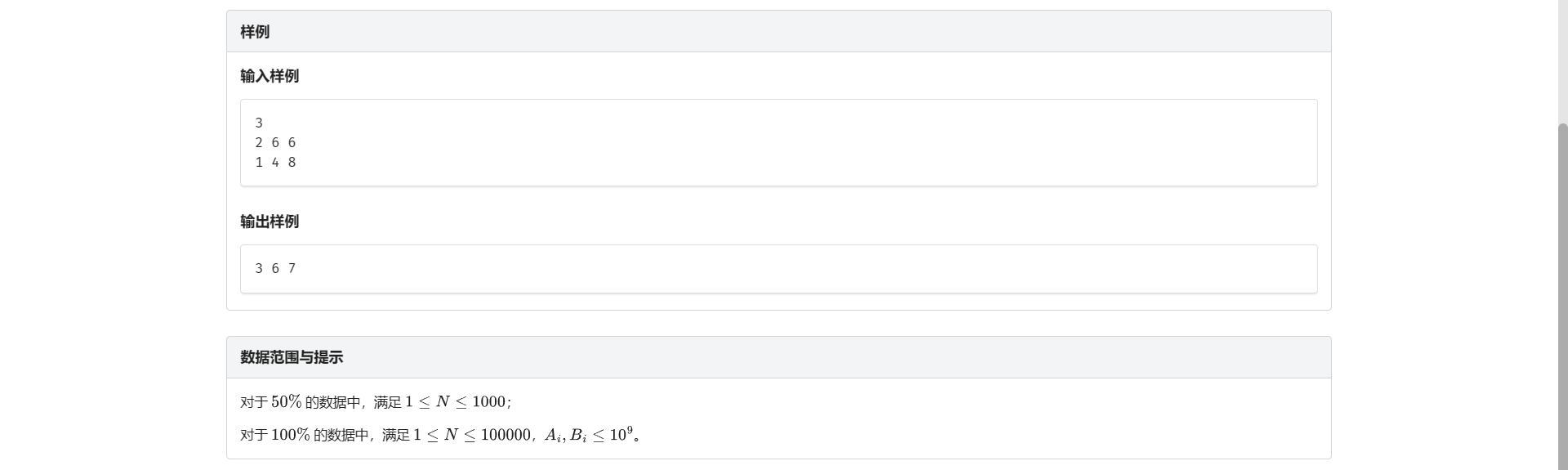
B.序列合并
暴力枚举是 \(O(n^2)\) 考虑优化
思考一下我们枚举的各种和
结合题干所给的特殊性质
不难发现 \(A[1] + B[1] < A[2] + B[1] < A[3] + B[1] < ···\)
那么我们有 \(n\) 个这样的关系式
在这样的式子里 只有头才有可能成为当前最小的对数和
那么我们就可以开一个大小为 \(n\) 的堆 里面存队头元素
每次取出最小的元素 然后把它所在那行的下一个元素入队
重复 \(n\) 次
又因为每次排序对原序列影响不大 选择优先队列
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct node {
ll val, id1, id2;
friend bool operator<(node a, node b) { return a.val > b.val; }
};
priority_queue<node> q;
const int N = 1e5 + 0721;
ll a1[N], a2[N];
int n;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", &a1[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", &a2[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) q.push((node){ a1[i] + a2[1], i, 1 });
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
node now = q.top();
q.pop();
printf("%lld ", now.val);
q.push((node){ a1[now.id1] + a2[now.id2 + 1], now.id1, now.id2 + 1 });
}
return 0;
}
C.龙珠游戏
字典序最大 就非常的贪心
我们也贪心地选取序列里最大的数 然后把它的下一个取出来即可
这题本意似乎是让手写堆排的 但是用双向链表就能逃课
虽然我感觉这个债迟早要还
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 0721;
int a[N], vis[N], nxt[N], lst[N];
int ans[N], top;
int n;
struct node {
int id, val;
friend bool operator<(node a, node b) { return a.val < b.val; }
};
priority_queue<node> q;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
if (i != n)
q.push((node){ i, a[i] });
nxt[i] = i + 1;
lst[i] = i - 1;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
node now = q.top();
q.pop();
if (vis[now.id] || nxt[now.id] == n + 1)
continue;
int nid = now.id;
vis[nid] = vis[nxt[nid]] = 1;
nxt[lst[nid]] = nxt[nxt[nid]];
lst[nxt[nxt[nid]]] = lst[nid];
ans[++top] = a[nid];
ans[++top] = a[nxt[nid]];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) printf("%d ", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
D.工作安排
经典反悔贪心
我们按时间排序 然后考虑
如果对于这个物品 它之前的天数没卖满 就把它卖掉
如果满了 查询之前卖的物品 如果有比它便宜的 就反悔 把那个丢弃把它卖掉
然后用一个小根堆维护就行
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 0721;
struct node {
int val, t;
friend bool operator < (node x, node y) {
return x.t < y.t;
}
}a[N];
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> >q;
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d%d",&a[i].t,&a[i].val);
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (a[i].t > q.size())
q.push(a[i].val);
else if (a[i].t == q.size()) {
int now = q.top();
q.pop();
q.push(max(now, a[i].val));
}
}
ll ans = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
ans += (ll)q.top();
q.pop();
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}
E.家庭作业
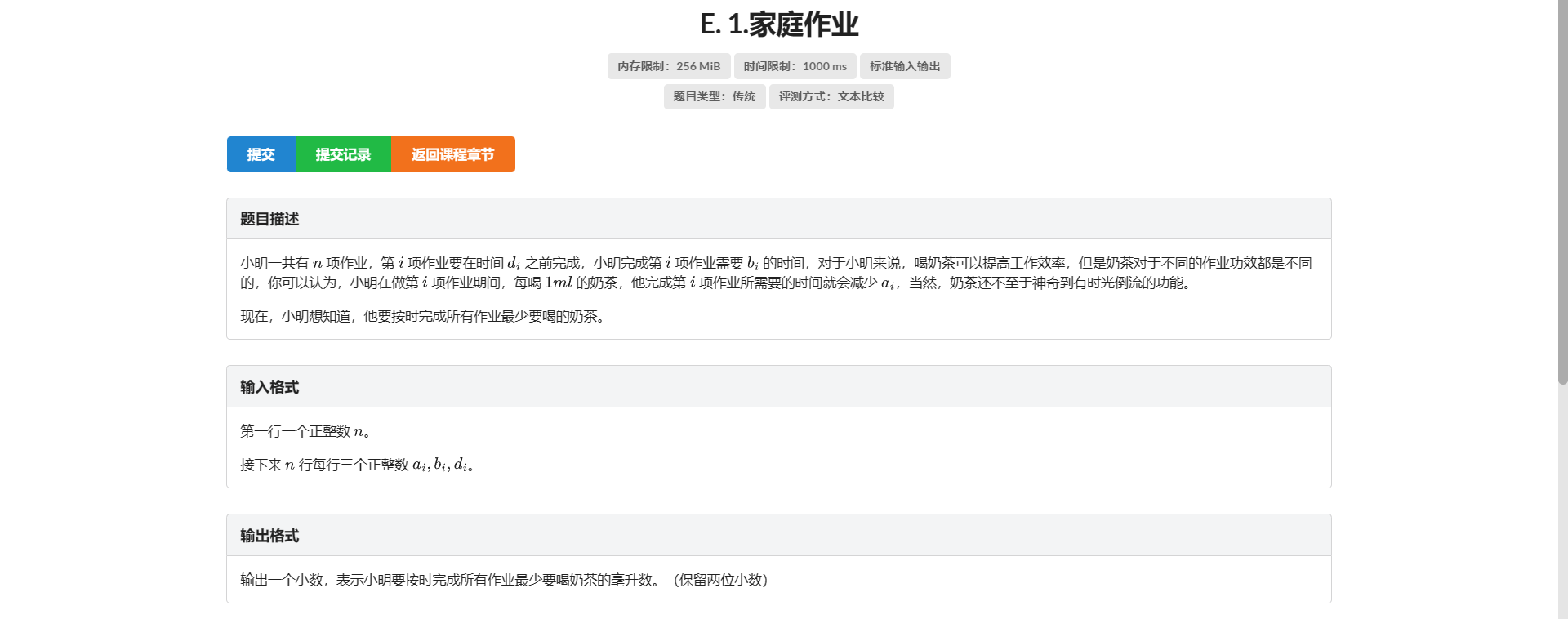
考虑反悔贪心
首先把所有任务按完成时间排序 然后挨个加入
如果超时 就把已完成任务中喝奶茶收益最大的 (即 \(a_i\) 最大的)拿出来考虑缩短它的时间
如果差值大于这个时间 那么直接把它减到 0 然后重复此过程
否则 把这个时间减掉这个差值 然后把它塞回去
这个过程就可以使用优先队列来实现
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 2e5 + 0721;
int n;
ll sum;
double ans;
struct node {
int a, b, d;
friend bool operator<(node x, node y) {
if (x.a != y.a) return x.a < y.a;
else return x.b < y.b; //优先队列反着重载运算符
}
} a[N];
priority_queue<node> q;
inline int read() {
int xr = 0, F = 1;
char cr;
while (cr = getchar(), cr < '0' || cr > '9') if (cr == '-') F = -1;
while (cr >= '0' && cr <= '9')
xr = (xr << 3) + (xr << 1) + (cr ^ 48), cr = getchar();
return xr * F;
}
inline bool cmp(node x, node y) {
return x.d < y.d;
}
void main() {
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) a[i].a = read(), a[i].b = read(), a[i].d = read();
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n, cmp);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
q.push((node){a[i].a, a[i].b, a[i].d});
sum += a[i].b;
if (sum > a[i].d) {
while (1) {
node now = q.top();
q.pop();
if (now.b >= sum - a[i].d) {
int delta = sum - a[i].d;
now.b -= delta;
sum = a[i].d;
ans += 1.0 * delta / now.a;
if (now.b) q.push(now);
break;
} else {
sum -= now.b;
ans += 1.0 * now.b / now.a;
}
}
}
}
printf("%.2lf", ans);
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
2
20 50 100
10 100 50
*/
F.选数游戏
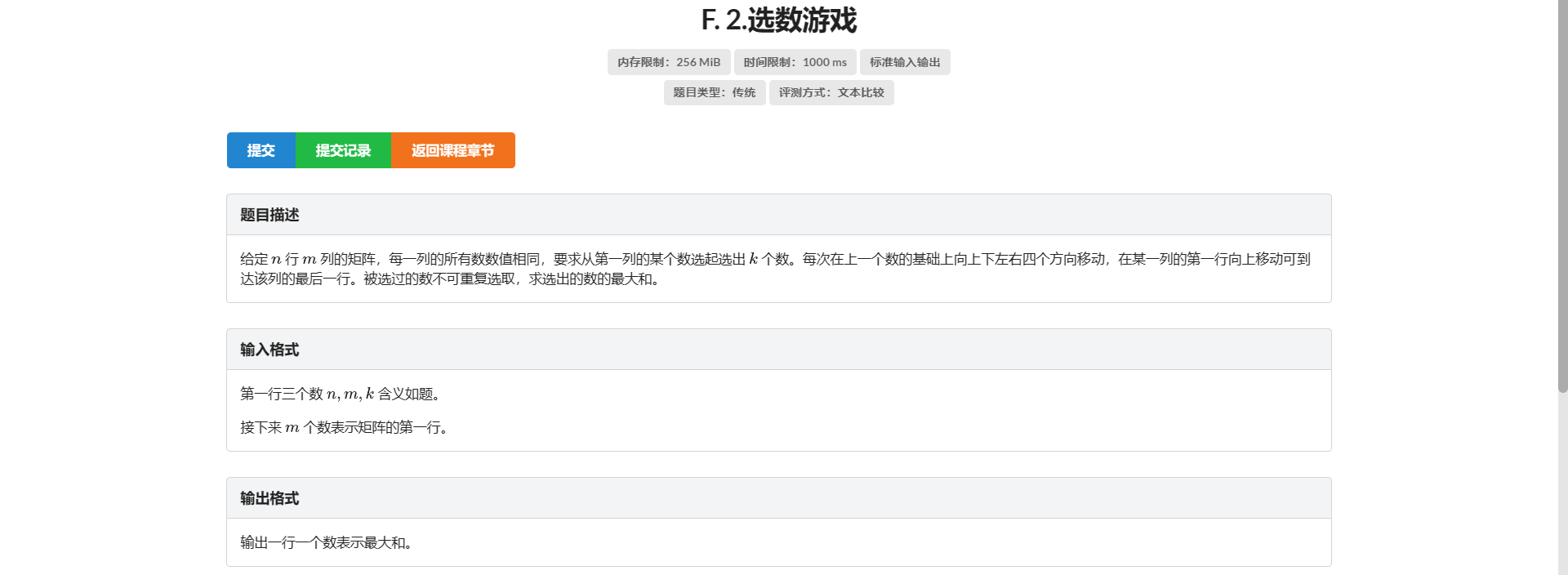
很神秘的一道题 不难 但是没做出来:(
最开始的想法是首先延伸出最长 每个数只选一个 到头了就从最大的数继续选
然后考虑回退一格是否会更优 但是发现这个东西不好用堆维护
结果这题正着做就行
考虑每次走到新的一列 就把这一列所有的点都加进去
如果当前选择的点数超过 \(k\) 我们就不断地选走过的选了 \(n\) 个的最小点
把它丢掉 \(n - 1\) 个
重复上述过程直到 \(siz < k\)
这时我们记录一下最后一次被丢掉的点是什么
然后加上 \(k - siz\) 个即可
这个东西显然可以用堆来维护
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 1e6 + 0721;
ll a[N];
ll n, m, k, ans;
priority_queue<ll, vector<ll>, greater<ll> > q;
void main() {
scanf("%lld%lld%lld", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) scanf("%lld", &a[i]);
ll siz = 0, sum = 0;
ll maxn = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= min(m, k); ++i) {
q.push(a[i]);
siz += n;
sum += n * a[i];
while (siz > k && !q.empty()) {
ll now = q.top();
q.pop();
siz -= n - 1;
sum -= (n - 1) * now;
maxn = now;
}
ans = max(ans, sum + (k - siz) * maxn);
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
1 5 3
1 2 3 4 5
*/
G.内存管理
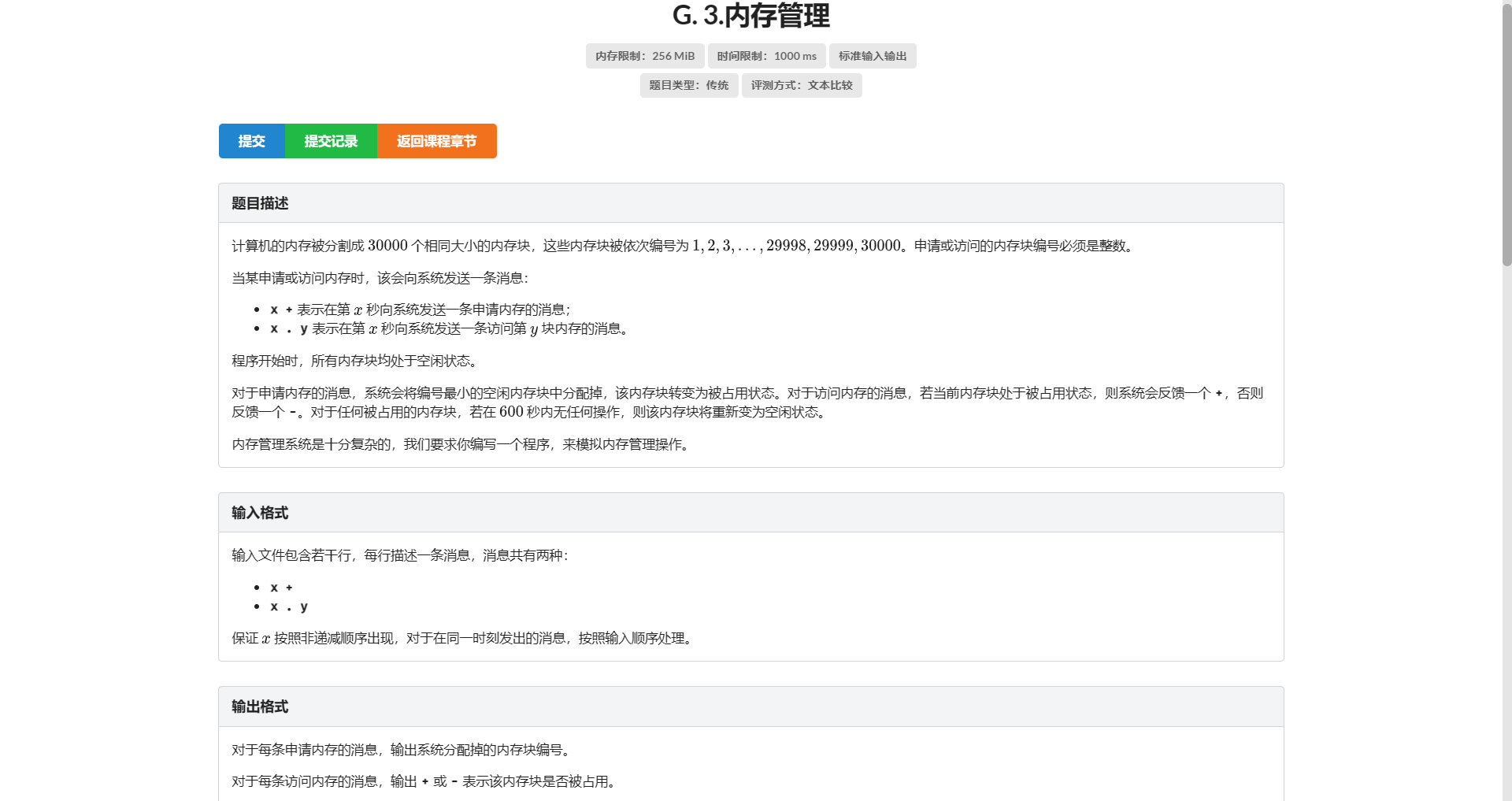
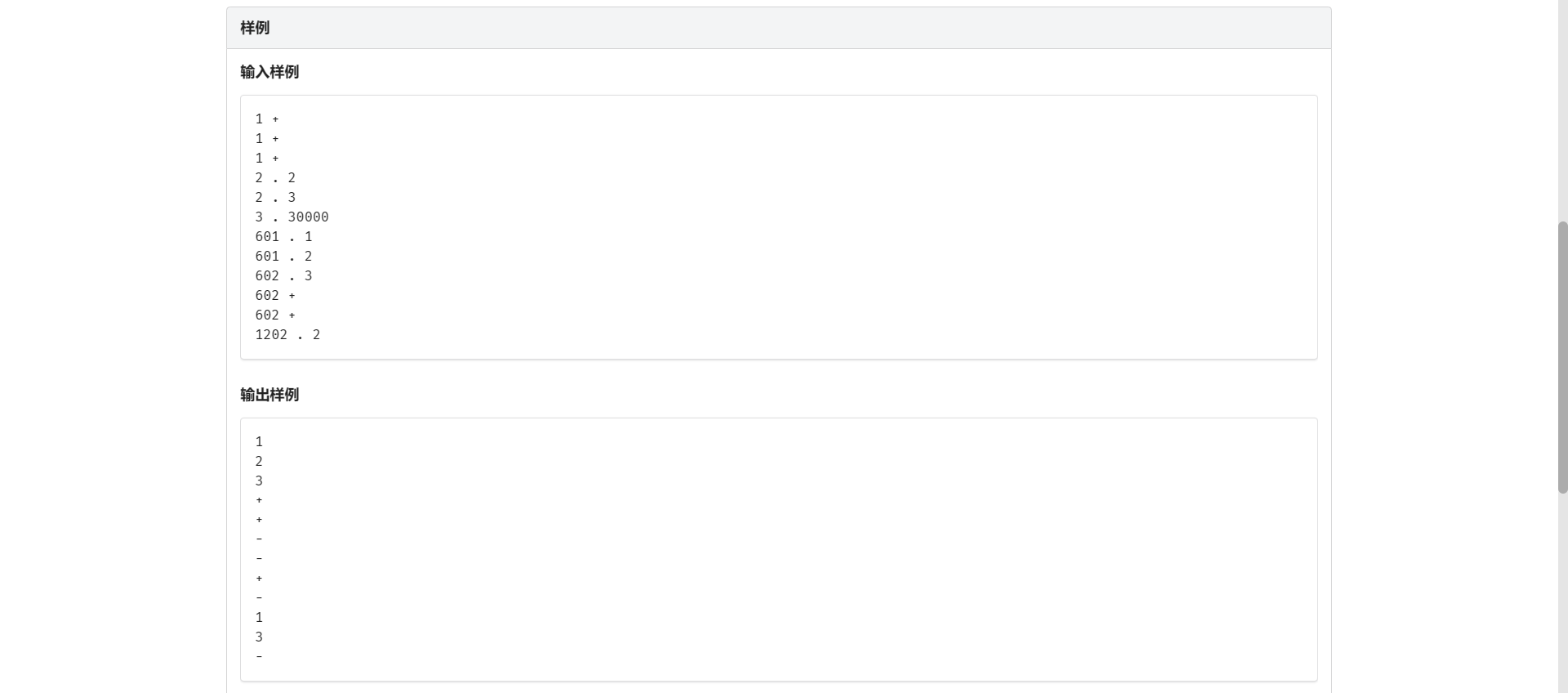
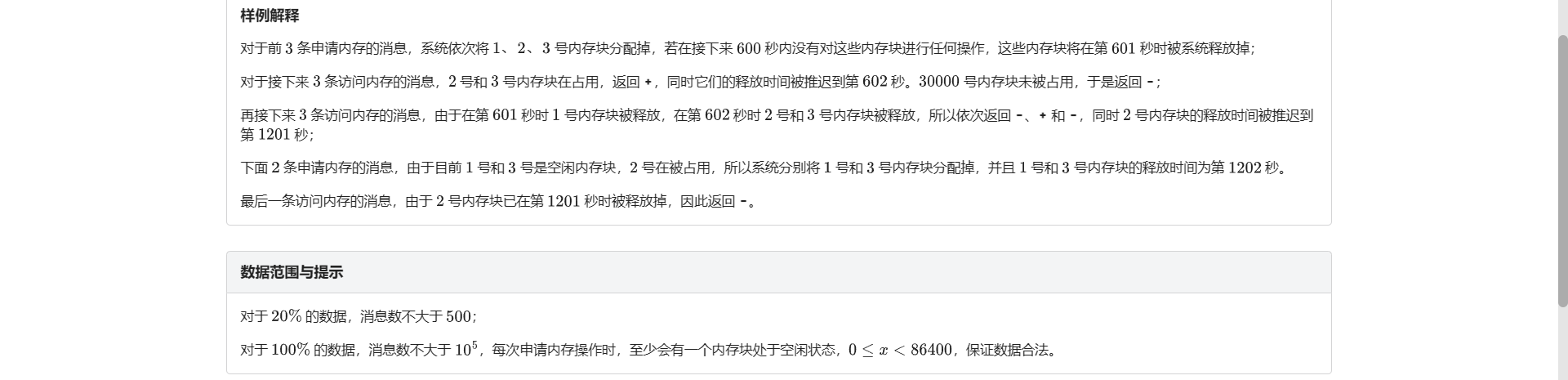
我的想法:
维护lstvis表示释放时间
vis表示是否正在被访问
每次询问开始前 弹出与该询问时间距离大于等于600s的内存 并判断与其lstvis是否吻合 如果吻合更新vis并放入空闲堆
每次申请新的时 从空闲堆中取出编号最小 vis改为1 更新lstvis 插入堆
每次询问 直接查询vis并更新lstvis 并且把新的插入堆
然后喜获 90pts
因为如果有两个在同一时间询问对象相同的询问 就会寄掉
正确的做法是维护每个内存被询问的次数
并且维护访问中的内存用双端队列就行
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 1e5 + 0721;
int n;
int vis[N];
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > emp;
struct node {
int id, t;
friend bool operator<(node x, node y) {
return x.t > y.t;
}
};
priority_queue<node> work;
void main() {
// freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
int x, y;
for (int i = 1; i <= 30000; ++i) emp.push(i);
while (scanf("%d", &x) != EOF) {
char opt;
scanf(" %c", &opt);
while (!work.empty() && work.top().t + 600 <= x) {
int now = work.top().id;
work.pop();
--vis[now];
if (!vis[now]) {
vis[now] = 0;
emp.push(now);
}
}
// cout << opt << "\n";
if (opt == '+') {
int now = emp.top();
emp.pop();
vis[now] = 1;
work.push((node){now, x});
printf("%d\n", now);
} else {
scanf("%d", &y);
if (!vis[y]) printf("-\n");
else {
++vis[y];
work.push((node){y, x});
printf("+\n");
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
1 +
1 +
1 +
2 . 2
2 . 3
3 . 30000
601 . 1
601 . 2
602 . 3
602 +
602 +
1202 . 2
*/
H.火车载客
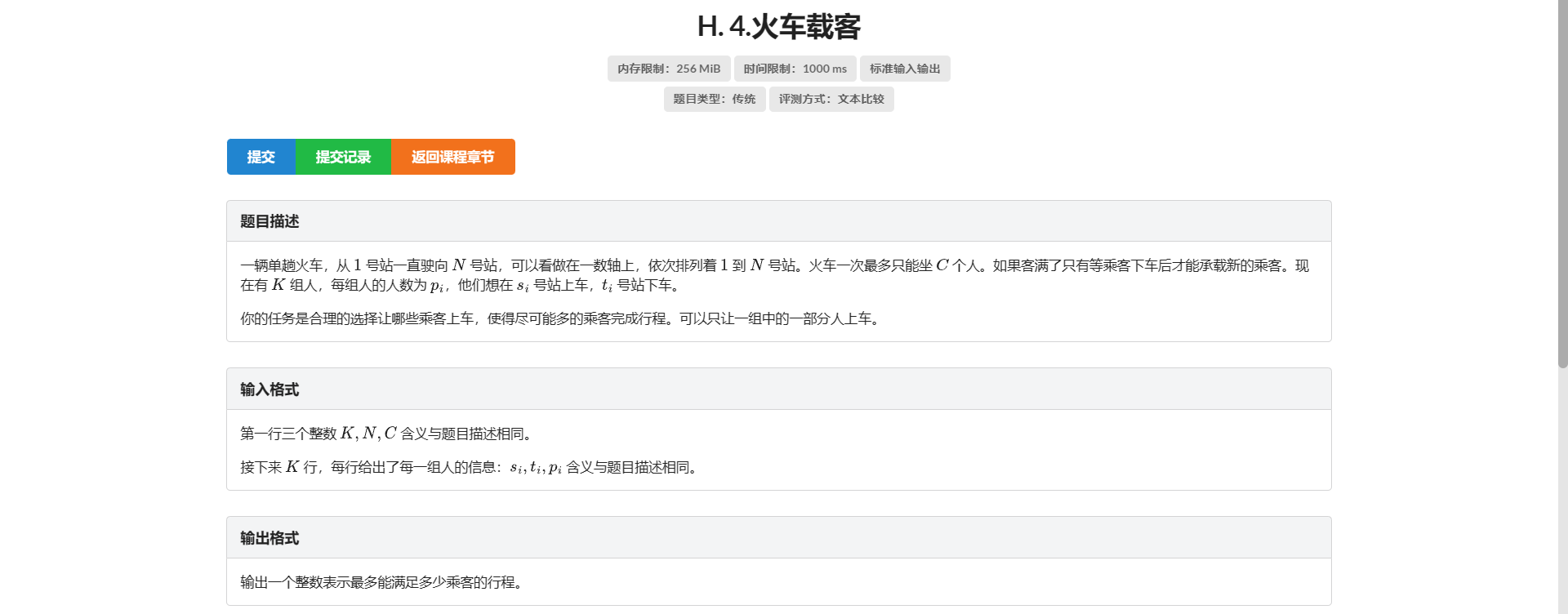
考虑这样一个反悔贪心:到一个站先下车 每次有新的乘客上车时 比较它们的右端点 把右端点远的踢出去
然后我们开个 in 数组记录对于每组乘客 还有多少人在堆里面
然后我们可以借鉴 F 题的优秀经验 先全塞进去然后全弹出来最后记录最后一个弹出来的多弹出了多少给它补回去
注意要判有东西最后一个弹出来 即代码中的 \(lst \ne 0\)
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 3e5 + 0721;
vector<int> arr[N];
vector<int> st[N];
int k, n, c;
int p[N], in[N];
struct node {
int l, r, id;
friend bool operator<(node x, node y) {
return x.r < y.r;
}
} a[N];
priority_queue<node> q;
void main() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &k, &n, &c);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &a[i].l, &a[i].r, &p[i]);
st[a[i].l].push_back(i);
arr[a[i].r].push_back(i);
a[i].id = i;
}
int cnt = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j : arr[i]) { //先下车
cnt -= in[j];
in[j] = 0;
}
for (int j : st[i]) { //后上车
in[j] = p[j];
q.push((node){a[j].l, a[j].r, j});
ans += in[j];
cnt += in[j];
int lst = 0;
while (!q.empty() && cnt > c) {
lst = q.top().id;
q.pop();
cnt -= in[lst];
ans -= in[lst];
in[lst] = 0;
}
if (cnt < c && lst) {
in[lst] = c - cnt;
ans += in[lst];
cnt = c;
q.push((node){a[lst].l, a[lst].r, lst});
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
8 15 3
1 5 2
13 14 1
5 8 3
8 14 2
14 15 1
9 12 1
12 15 2
4 6 1
*/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号