YBTOJ 3.1并查集
A.并查集
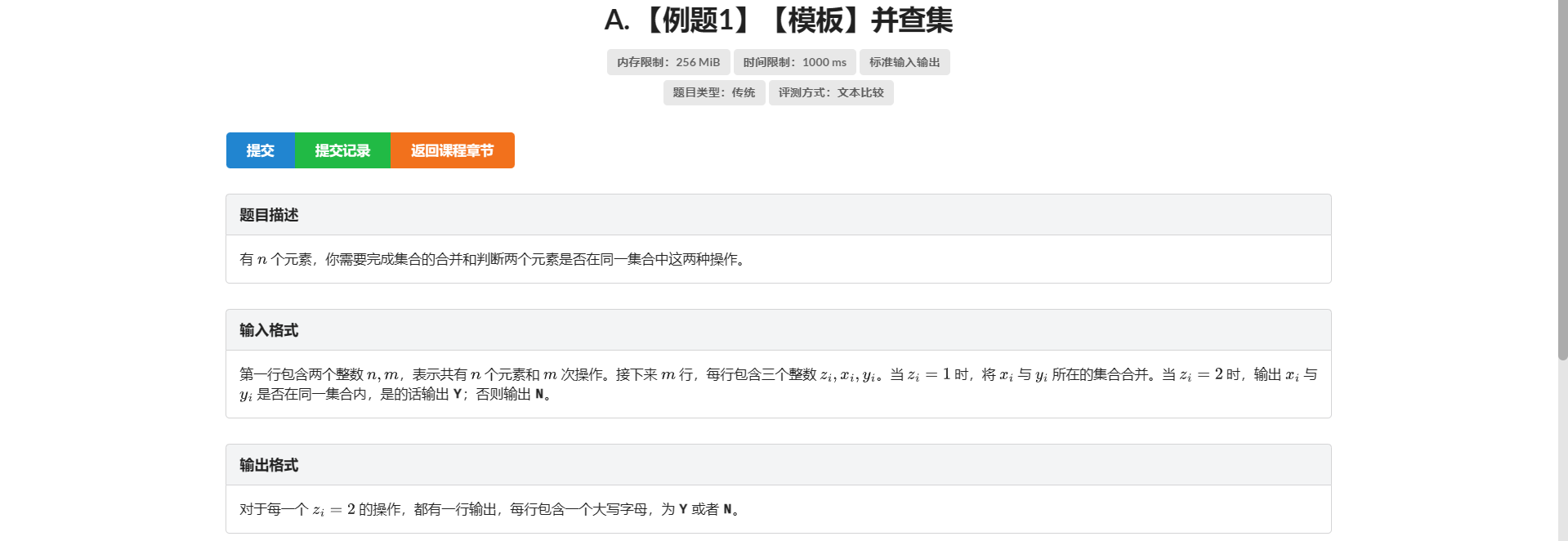
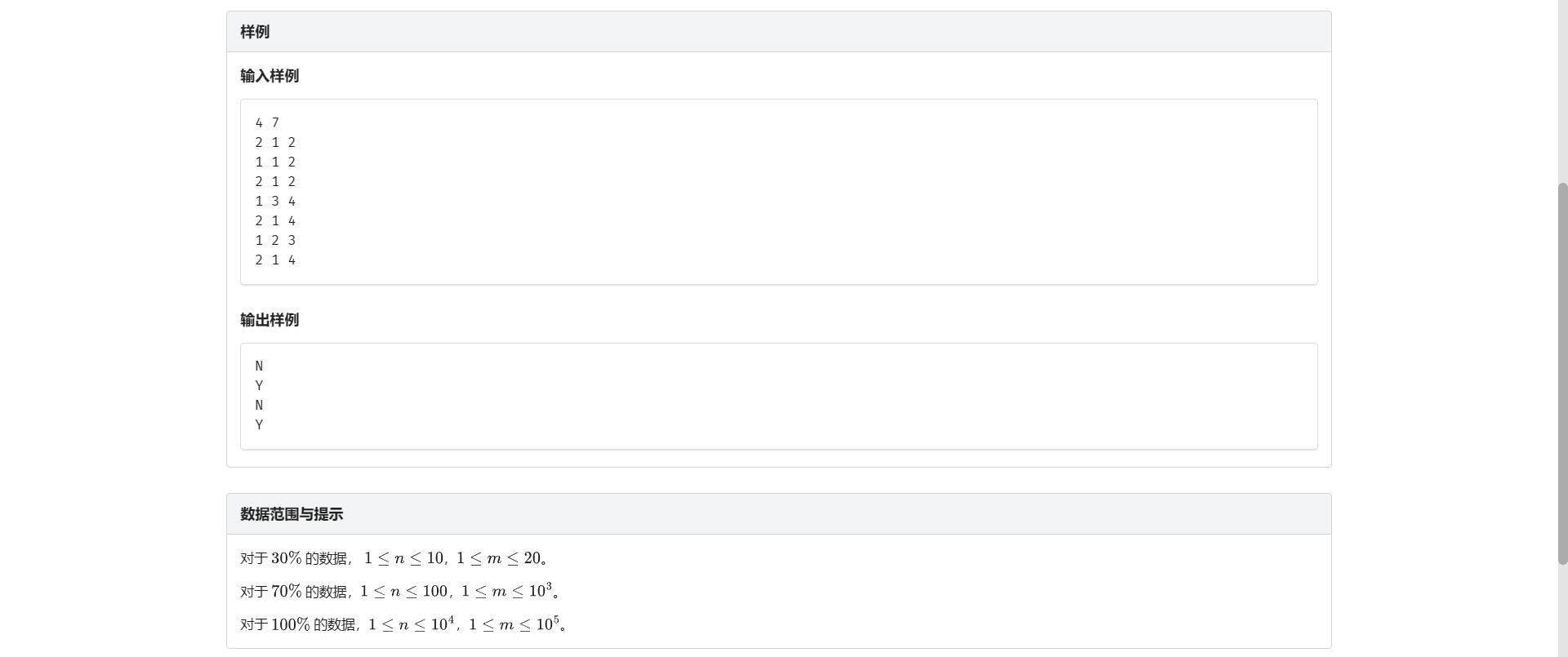
他都说模板了!!!
那就是板子
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 0721;
int fa[N];
int n, m;
int find(int x) {
if (x == fa[x])
return fa[x];
else
return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
fa[i] = i;
while (m--) {
int num, x, y;
scanf("%d%d%d", &num, &x, &y);
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if (num == 1)
fa[fx] = fy;
else {
if (fx == fy)
printf("Y\n");
else
printf("N\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
B.银河英雄传说
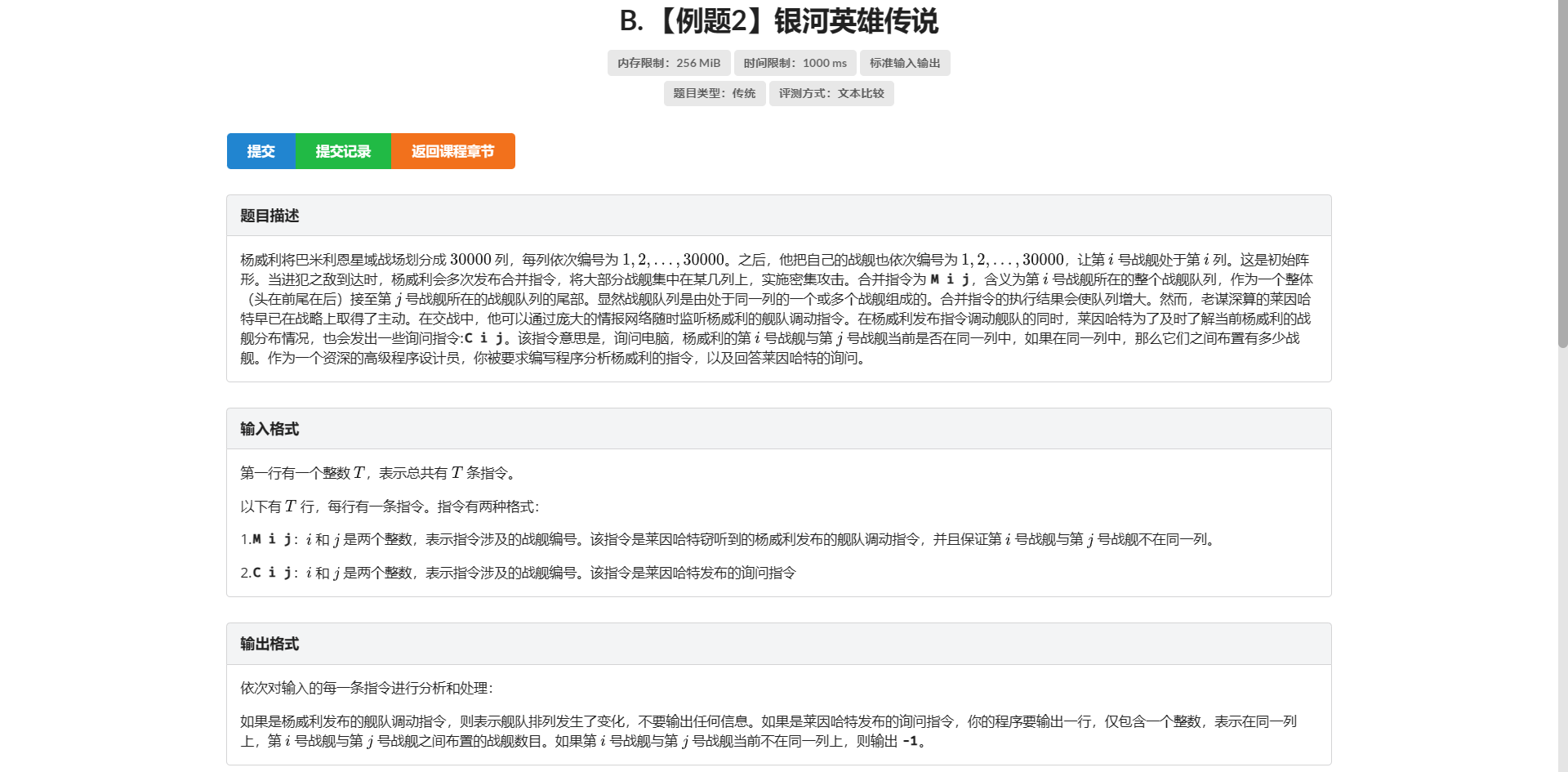
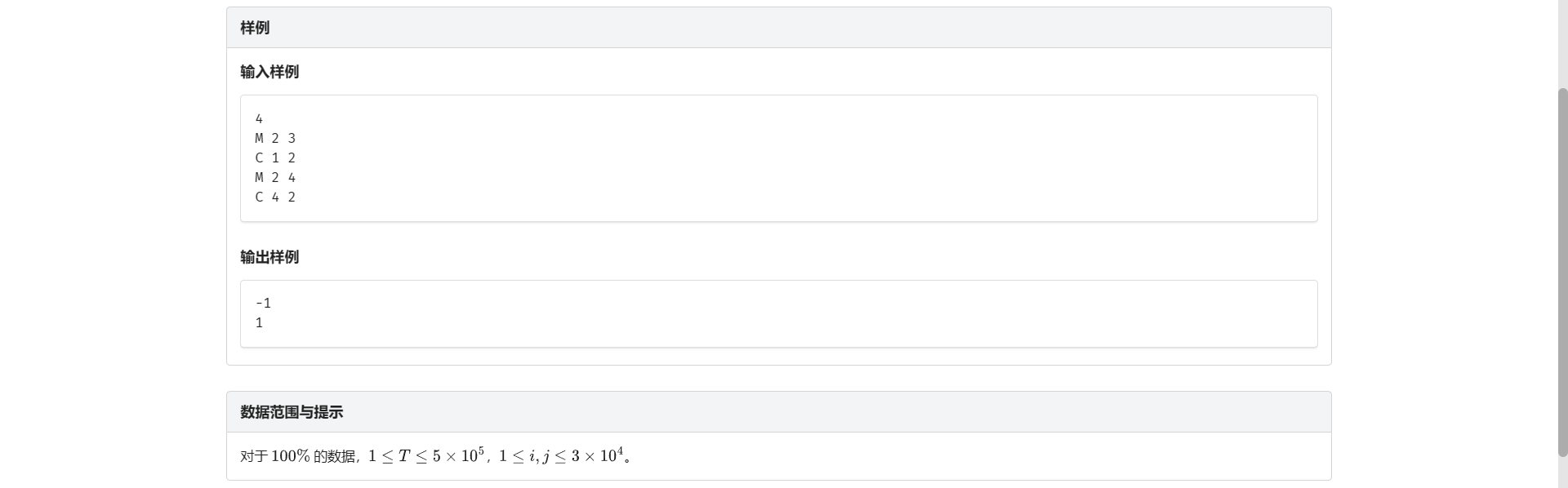
首先战舰只有合并 还要查在不在一列
长得就很像并查集
但是要维护距离 很谔谔
但我们还是得考虑一下怎么维护
因为是查询 \(i\) 和 \(j\) 之间的距离 想到维护它们各自到根节点的距离然后作差
那我们思考一下路径压缩的时候怎么维护到根节点的距离
因为我们压缩的时候是把这个节点连到它父亲的父亲
原来它到根节点距离是它和父亲的距离
现在它的距离是它到父亲的距离加上父亲到根节点的距离
所以有 \(cnt[x] += cnt[fa[x]]\)
然后还有一个操作需要维护 就是那个 \(fa[fx] = fy\)
因为是把 \(fx\) 连接到 \(fy\) 所在队的末尾
所以 \(cnt[fx]\) 显然增加的数量就是 \(fy\) 这个集合的大小
然后就没啥了
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 30721;
int fa[N], cnt[N], tot[N];
int n;
int find(int x) {
if (x == fa[x])
return x;
int fx = find(fa[x]);
cnt[x] += cnt[fa[x]];
return fa[x] = fx;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= 30000; ++i) fa[i] = i, tot[i] = 1;
while (n--) {
char c;
int x, y;
cin >> c;
scanf("%d%d", &x, &y);
if (c == 'M') {
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
cnt[fx] += tot[fy];
fa[fx] = fy;
tot[fy] += tot[fx], tot[fx] = 0;
} else {
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if (fx != fy)
printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d\n", abs(cnt[x] - cnt[y]) - 1);
}
}
return 0;
}
C.食物链
看到总共有三种动物 有一个比较显然的思路
就是拿一个代表元素维护一类动物 然后查询的时候直接查询代表元素即可
但是发现有可能会出现 \(A\) 吃 \(B\) 但是 \(A\) 和 \(B\) 都尚未归入哪一类的情况 然后就麻烦了
那我们可不可以考虑这样一个问题 \(A\) 吃 \(B\) 是不是就代表 \(A\) 和 \(B\) 不在一个集合中 也是一种关系 我们是否可以维护这种的信息呢
进一步思考 我们能不能造出这样一个和 \(A\) 有关联的元素 \(x\) 然后让 \(x\) 和 \(B\) 合并到一个集合中 这样我们查询 \(A\) 与 \(B\) 是否不在一个集合中 就查询 \(x\) 和 \(B\) 是否在一个集合中就行了
当然这个 \(x\) 最好不在这 \(n\) 和元素里面
那我们如果让 \(x = A + n\) 呢
那么显然就解决了
我们基于这个思路继续考虑 如何维护 \(A\) 吃 \(B\) 这样一个信息
假如我们设 \(A + n\) 表示 \(A\) 吃的元素集合
那 \(B + n\) 怎么办呢
根据题干 我们有 \(B\) 吃的东西肯定是吃 \(A\) 的东西
那假如说我们再弄一个 \(a + 2n\) 表示吃 \(A\) 的元素集合
那么就全解决了对吧
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200721;
int fa[N];
int n, tot, num, x, y, k;
int find(int x) {
if (fa[x] == x)
return fa[x];
else
return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= n * 3; ++i) fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &num, &x, &y);
if (num == 1) {
if (x > n || y > n) {
tot++;
continue;
}
if (x == y)
continue;
int fa1 = find(x);
int fa2 = find(x + n);
int fa3 = find(x + n * 2);
int fa4 = find(y);
int fa5 = find(y + n);
int fa6 = find(y + n * 2);
if (fa4 == fa2 || fa4 == fa3) {
tot++;
continue;
} else {
fa[fa4] = fa1;
fa[fa5] = fa2;
fa[fa6] = fa3;
}
} else {
if (x > n || y > n) {
tot++;
continue;
}
if (x == y) {
tot++;
continue;
}
int fa1 = find(x);
int fa2 = find(x + n);
int fa3 = find(x + n * 2);
int fa4 = find(y);
int fa5 = find(y + n);
int fa6 = find(y + n * 2);
if (fa4 == fa1 || fa4 == fa2) {
tot++;
continue;
} else {
fa[fa4] = fa3;
fa[fa5] = fa1;
fa[fa6] = fa2;
}
}
}
printf("%d", tot);
return 0;
}
D.超市购物
非常典的反悔贪心题
我们想到这样一种思路:把所有商品按价值从大到小排序
然后让它尽可能晚的卖出去
那么我们就查每个商品最晚能卖出去的时间就行
如果暴力往前一个一个找的话会T
然后看起来用一个双向链表维护就行
但是显然只是看起来 比如你要查这天以前最早没有商品售卖的日期
但这天已经有商品售卖了
那么在这个双向链表里它就跳不到任何地方
这时候怎么办呢 我们思考暴力跳的过程
一定是经过了一坨有商品售卖的日期
那我们是否可以考虑路径压缩呢 显然可以
所以就这么维护就行
代码我写的反悔贪心就不贴了
E.逐个击破
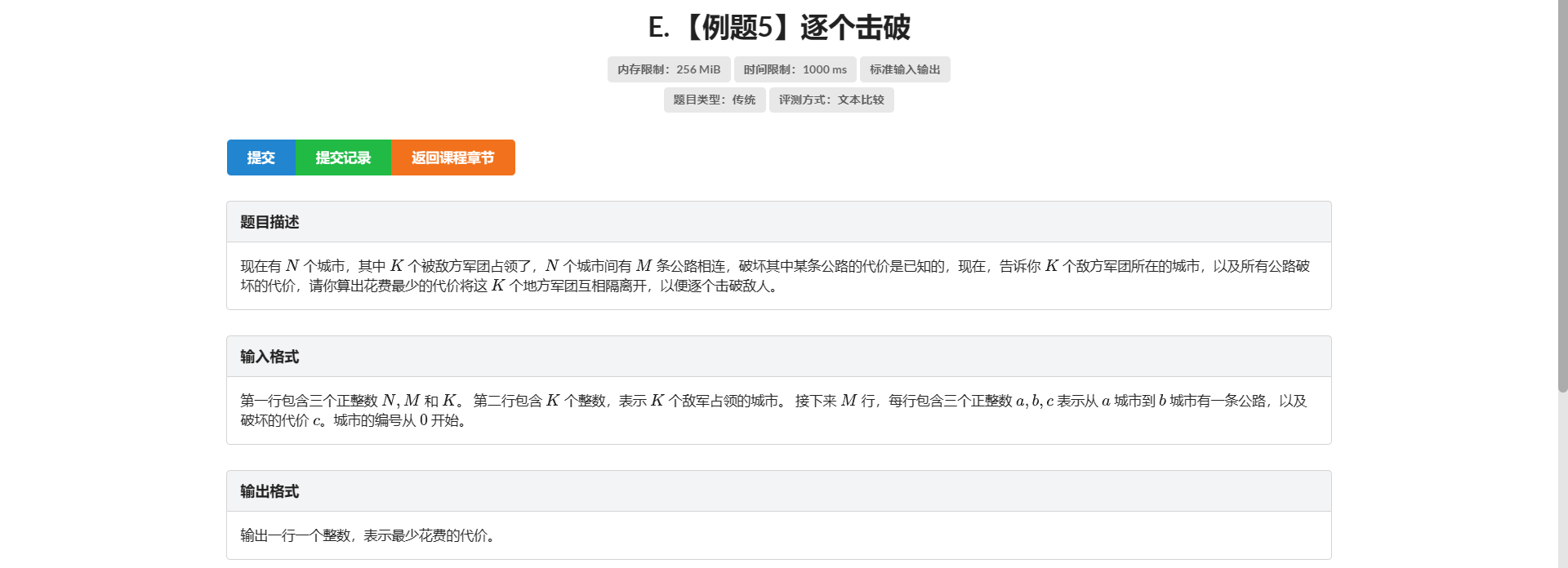
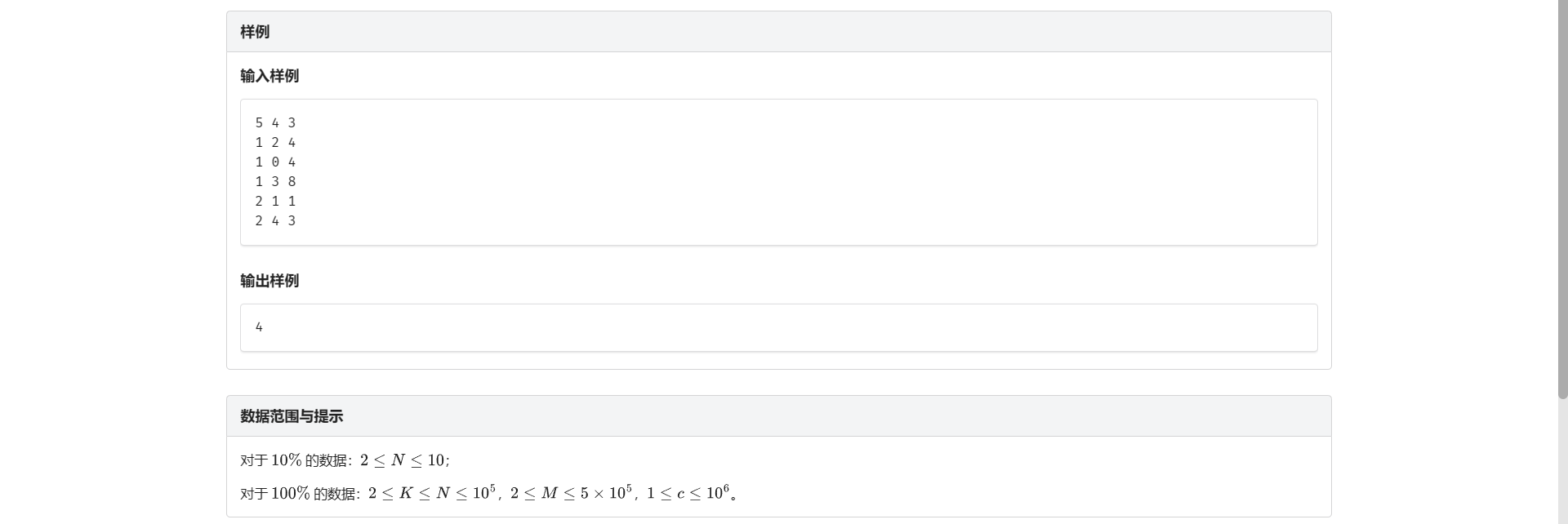
如果有可支持删除操作的并查集有多好!
那不能删我倒过来做总行了吧
那么我们就转化为要连上价值尽可能大的边 并且这两个连通块不是都有敌人的
然后就没啥了
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 0721;
int fa[N];
int n, m, k;
bool ene[N];
ll ans;
struct node {
int fr, to, val;
friend bool operator<(node x, node y) { return x.val > y.val; }
} a[N];
int find(int x) {
if (x == fa[x])
return fa[x];
else
return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) {
int x;
scanf("%d", &x);
ene[x] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) scanf("%d%d%d", &a[i].fr, &a[i].to, &a[i].val);
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int fx = find(a[i].fr), fy = find(a[i].to);
if (fx == fy)
continue;
else if (ene[fx] == 1 && ene[fy] == 1)
ans += (ll)a[i].val;
else if (ene[fx] == 1 && ene[fy] == 0) {
fa[fy] = fx;
} else
fa[fx] = fy;
}
printf("%lld", ans);
return 0;
}
F.躲避拥挤
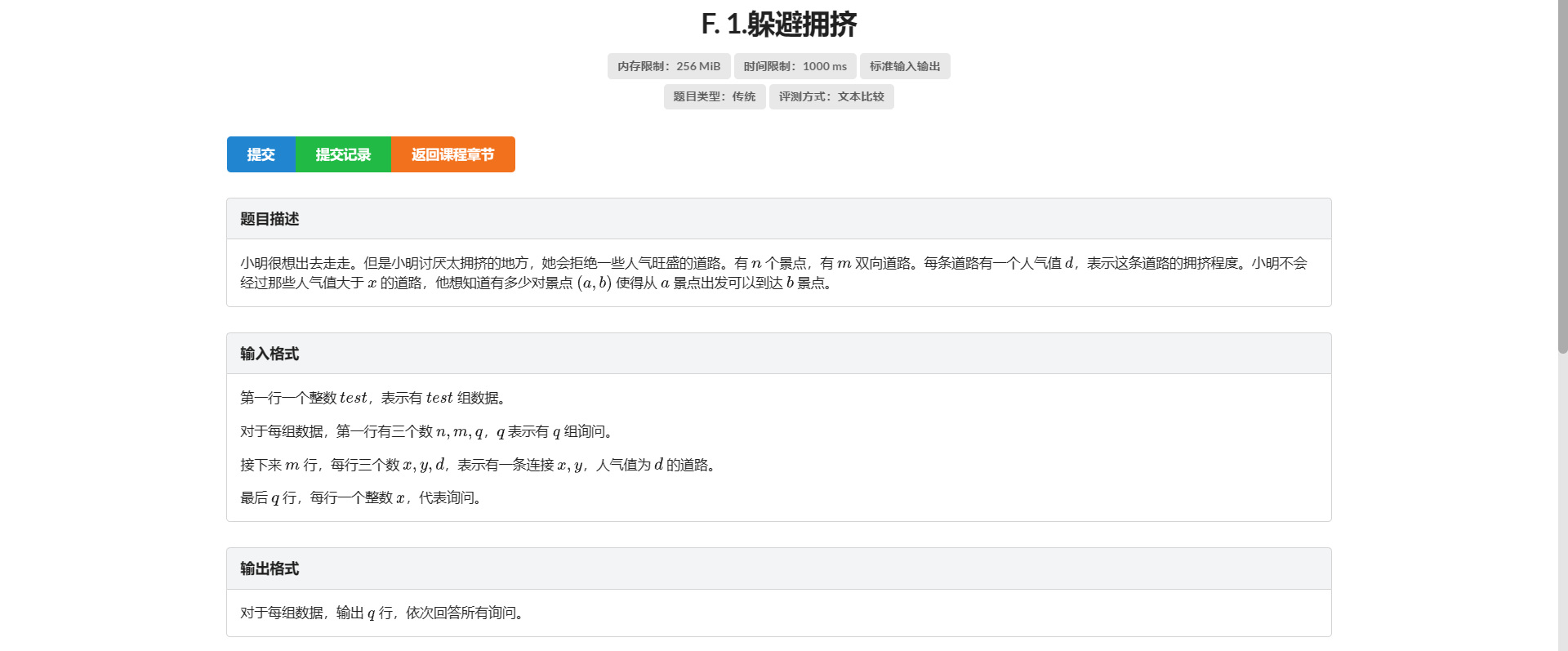
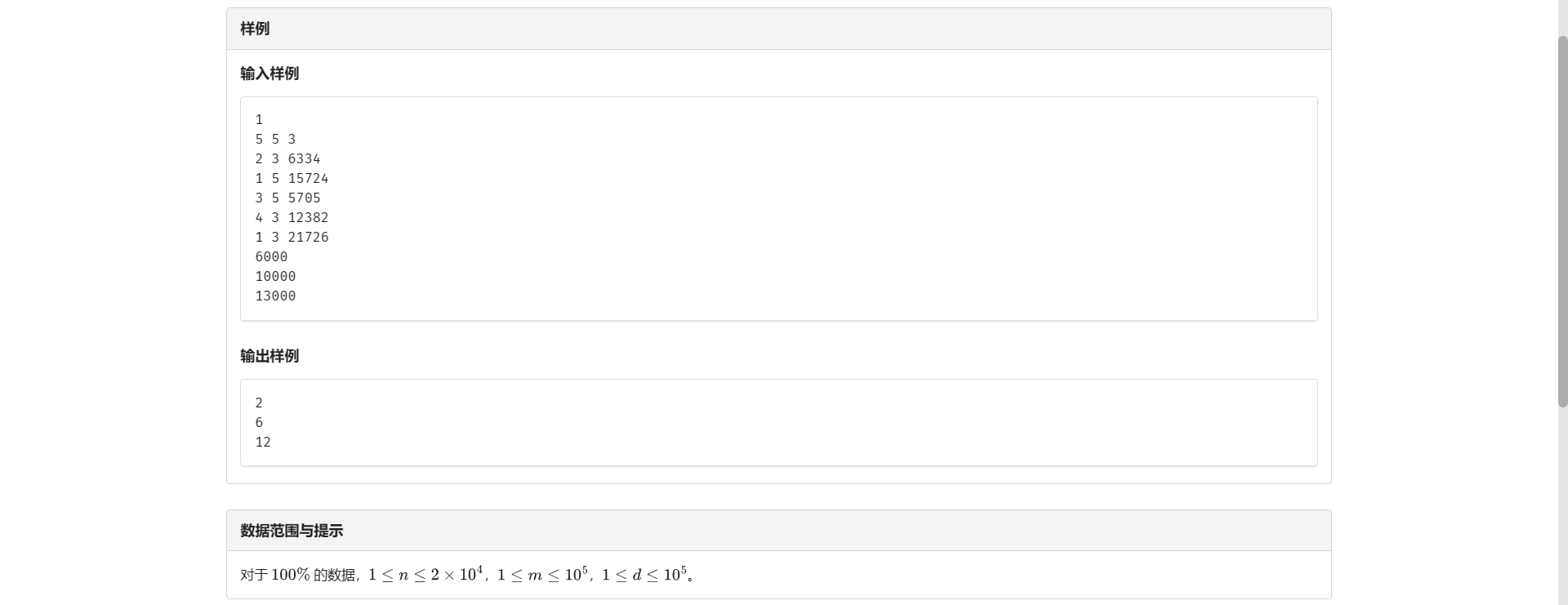
秒了(
考虑最小生成树
对于所有大于最大边的询问 直接就是 \((n - 1) \times n\)
否则 删去比该询问大的边 然后各个联通块内互相可以到达
进而发现只有询问 可以离线
另外考虑每次合并对当前答案的影响就做完了
注意多测清空
另外这题不给 q 的范围 十分之可恶
复杂度 \(\text{O}(m \log m + q)\)
一次 AC 很舒服
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 2e4 + 0721;
const int M = 1e5 + 0721;
const int Q = 5e5 + 0721;
int fa[N], siz[N];
ll ans[M];
ll nowans;
int T, n, m, q;
struct node {
int u, v, w;
friend bool operator<(node x, node y) {
return x.w < y.w;
}
} edge[M];
struct ques {
int id, val;
friend bool operator<(ques x, ques y) {
return x.val < y.val;
}
} qu[Q];
inline int read() {
int xr = 0, F = 1;
char cr;
while (cr = getchar(), cr < '0' || cr > '9') if (cr == '-') F = -1;
while (cr >= '0' && cr <= '9')
xr = (xr << 3) + (xr << 1) + (cr ^ 48), cr = getchar();
return xr * F;
}
void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
fa[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
nowans = 0;
}
int find(int x) {
return x == fa[x] ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
nowans -= siz[x] * (siz[x] - 1);
nowans -= siz[y] * (siz[y] - 1); //撤销原先两个联通块对答案的贡献
fa[y] = x;
siz[x] += siz[y];
nowans += siz[x] * (siz[x] - 1); //加上合并之后对答案的贡献
}
void kruskal() {
int prs = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int u = edge[i].u, v = edge[i].v, w = edge[i].w;
int fu = find(u), fv = find(v);
if (fu == fv) continue;
while (qu[prs].val < w && prs <= q) ans[qu[prs].id] = nowans, ++prs;
siz[fu] >= siz[fv] ? merge(fu, fv) : merge(fv, fu); //记录了siz就顺便启发式合并一下((
}
for (int i = prs; i <= q; ++i) ans[qu[i].id] = nowans;
}
void main() {
T = read();
while (T--) {
n = read(), m = read(), q = read();
init();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) edge[i].u = read(), edge[i].v = read(), edge[i].w = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= q; ++i) qu[i].val = read(), qu[i].id = i;
sort(qu + 1, qu + 1 + q);
sort(edge + 1, edge + 1 + m);
kruskal();
for (int i = 1; i <= q; ++i) printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
}
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
1
5 5 3
2 3 6334
1 5 15724
3 5 5705
4 3 12382
1 3 21726
6000
10000
13000
*/
G.约束条件

第一眼:这不扩展域并查集裸题???直接秒了
离散化复杂度可能有点大 但是没啥别的办法了
一交 90pts
后来发现 因为 \(x_1 \ne x_2\) 与 \(x_2 \ne x_3\) 是不冲突的 假了
改成首先先合并然后判是否在一个联通块内就过了
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 2e6 + 0721;
int fa[N];
int a[N];
int T, n, m, tot;
struct node {
int i, j, e;
friend bool operator<(node x, node y) {
return x.e > y.e;
}
} ques[N];
inline int read() {
int xr = 0, F = 1;
char cr;
while (cr = getchar(), cr < '0' || cr > '9') if (cr == '-') F = -1;
while (cr >= '0' && cr <= '9')
xr = (xr << 3) + (xr << 1) + (cr ^ 48), cr = getchar();
return xr * F;
}
void init() {
for (int i = 1; i <= (m << 1); ++i) fa[i] = i;
}
int find(int x) {
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void discretization() {
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + tot);
m = unique(a + 1, a + 1 + tot) - a - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ques[i].i = lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + m, ques[i].i) - a;
ques[i].j = lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + m, ques[i].j) - a;
}
}
void main() {
T = read();
while (T--) {
n = read();
tot = 0;
bool flag = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
ques[i].i = read(), ques[i].j = read(), ques[i].e = read();
a[++tot] = ques[i].i;
a[++tot] = ques[i].j;
}
discretization();
init();
sort(ques + 1, ques + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
int x = ques[i].i, y = ques[i].j;
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
int fmx = find(x + m), fmy = find(y + m);
if (ques[i].e) {
if (fx == fy) continue;
fa[fx] = fy;
} else {
if (fx == fy) {
flag = 0;
printf("NO\n");
break;
}
}
}
if (flag) printf("YES\n");
}
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
2
3
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 1 1
4
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 4 1
1 4 0
*/
H.染色操作
我会线段树!
考虑删除操作 就是一个类似链表的东西
那么对于一个询问删除的两个端点:
- 若它还没被删 那么就从它开始删
- 若它已经被删 那就查询它右边第一个没被删的元素开始删
我们发现这个操作显然是可以用并查集维护的
删除的时候跳链表保证复杂度
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 1e6 + 0721;
int lst[N], nxt[N];
bool vis[N];
int n, m, ans;
int read() {
int xr = 0, F = 1;
char cr;
while (cr = getchar(), cr < '0' || cr > '9') if (cr == '-') F = -1;
while (cr >= '0' && cr <= '9')
xr = (xr << 3) + (xr << 1) + (cr ^ 48), cr = getchar();
return xr * F;
}
struct union_find_set {
int fa[N];
void init() {
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; ++i) fa[i] = i;
}
int find(int x) {
return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
void merge(int x, int y) {
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
fa[fx] = fy;
}
} z, y;
void main() {
n = read(), m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
lst[i] = i - 1;
nxt[i] = i + 1;
}
z.init();
y.init();
ans = n;
while (m--) {
int l, r;
l = read(), r = read();
int dl = y.find(l), dr = z.find(r);
int cl = z.find(l), cr = z.find(r);
if (!vis[l]) cl = lst[l];
if (!vis[r]) cr = nxt[r];
if (dl > dr) {
printf("%d\n", ans);
continue;
}
for (int i = dl; i <= dr; i = nxt[i]) {
if (!vis[i]) --ans;
vis[i] = 1;
z.fa[i] = cl;
y.fa[i] = cr;
}
nxt[cl] = cr;
lst[cr] = cl;
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
10 3
3 3
5 7
2 8
*/
I.数列询问
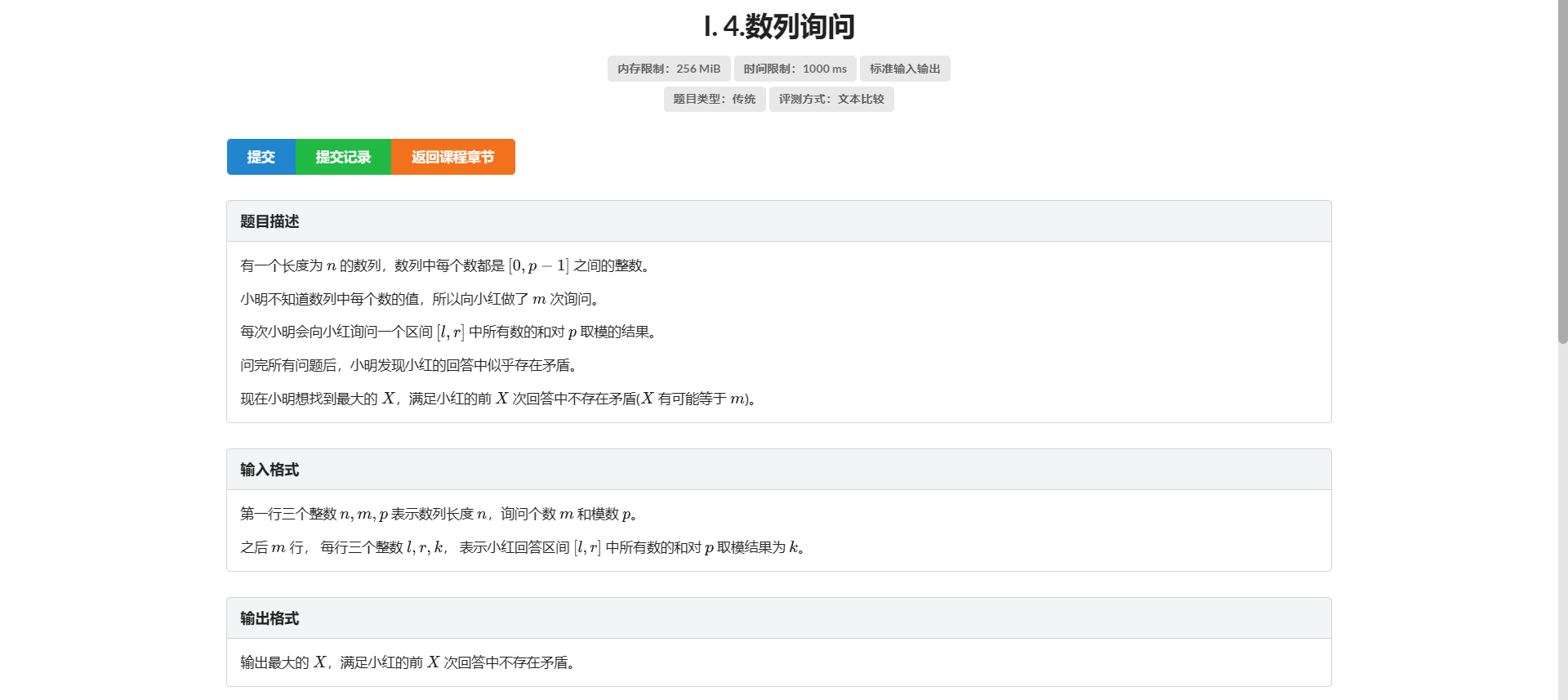
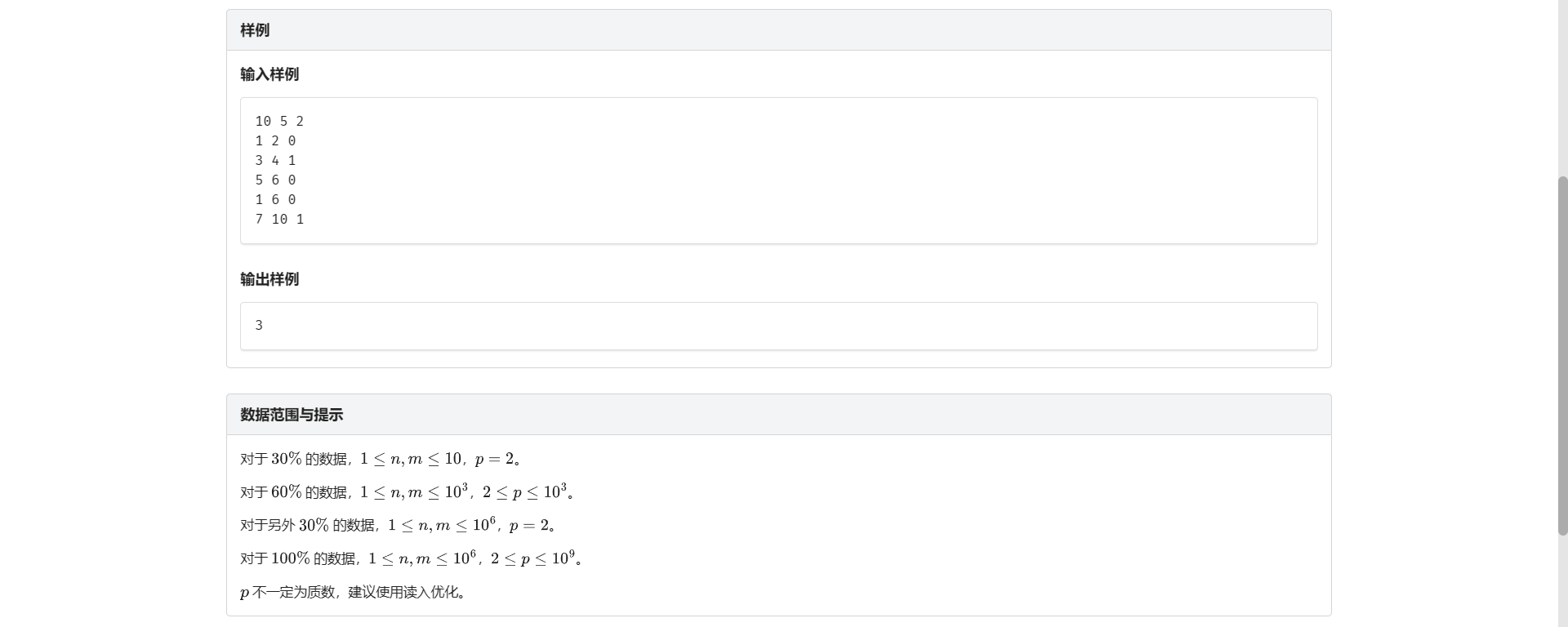
想偏了。
实际考虑这样一个东西:
已知 \(\left[x, y\right]\) 和 \(\left[y, z\right]\) 两段区间的信息 则就可以得到 \(\left[x, z\right]\) 这段区间的信息
因此我们就可以用并查集维护这个关系
但是有这样一个问题 对于一个 \(x\) 本身它和它自己就在一个集合中
所以如果 \(x\) 和自己在一个集合中并不能表示 \(\left[x, x\right]\) 这段区间已知
所以我们用 \(\left[x - 1, x\right]\) 表示 \(\left[x, x\right]\) 的区间已知
那么对于一段 \(\left[l, r\right]\) 我们就把 \(l - 1\) 和 \(r\) 连起来
还有另一个问题:如何维护信息
考虑我们用它到集合代表元素的距离表示这段的区间和
那么对于在同一个集合中的 \(x, y\) 我们分别查询它们到代表元素的区间和然后相减就是它们的区间和了
那么这就要求我们合并的时候要有一定的方向 注意一下即可
细节见代码
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
namespace steven24 {
const int N = 1e6 + 0721;
int fa[N], cnt[N];
int n, m, p;
inline int read() {
int xr = 0, F = 1;
char cr;
while (cr = getchar(), cr < '0' || cr > '9') if (cr == '-') F = -1;
while (cr >= '0' && cr <= '9')
xr = (xr << 3) + (xr << 1) + (cr ^ 48), cr = getchar();
return xr * F;
}
int find(int x) {
if (fa[x] == x) return x;
int f = find(fa[x]);
cnt[x] = (cnt[fa[x]] + cnt[x]) % p;
fa[x] = f;
return f;
}
void merge(int x, int y, int z) { //把x合并到y上
int fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if (fx == fy) return;
fa[fx] = fy;
//考虑因为每次是把l-1合并到r上 即把小的合到大的上
//那么此时x-y的距离为z fy-y的距离为cnt[y]
//那么fy-x的距离就为cnt[y]-z
//fx-x的距离为cnt[x]
//所以fx-fy的距离为cnt[y]-z-cnt[x]
cnt[fx] = ((cnt[y] - z - cnt[x]) % p + p) % p;
return;
}
void main() {
n = read(), m = read(), p = read();
for (int i = 0; i <= n; ++i) fa[i] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {
int l, r, c;
l = read(), r = read(), c = read();
--l;
int fl = find(l), fr = find(r);
if (fl == fr) { //结果已知
if ((cnt[l] - cnt[r] + p) % p == c) continue;
else {
printf("%d\n", i - 1);
return;
}
} else
merge(l, r, c);
}
printf("%d\n", m);
}
}
int main() {
steven24::main();
return 0;
}
/*
10 5 2
1 2 0
3 4 1
5 6 0
1 6 0
7 10 1
*/
J.小明反击
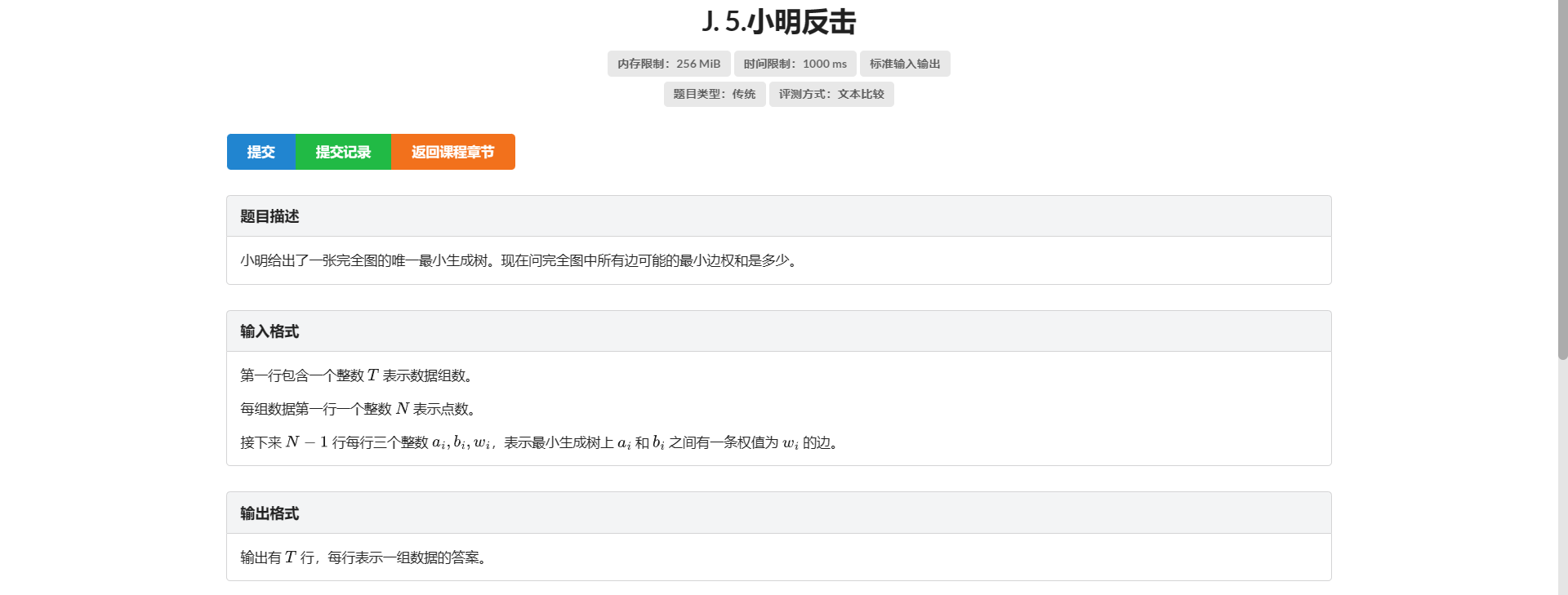
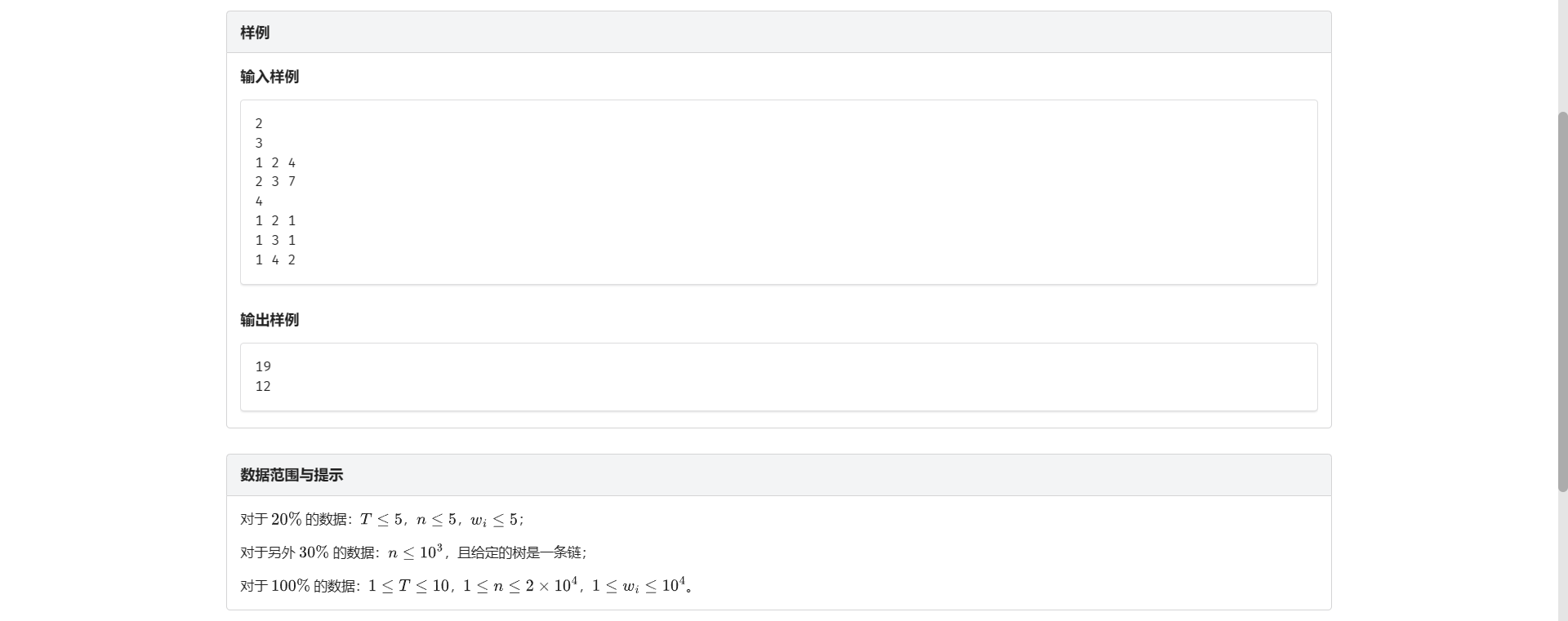
不是这为啥还有重题啊
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 0721;
int siz[N], fa[N];
int n;
int T;
ll ans;
struct node {
int u, v, w;
friend bool operator<(node a, node b) { return a.w < b.w; }
}edge[N];
int find(int x) {
if (x == fa[x])
return x;
else
return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--) {
ans = 0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; ++i) scanf("%d%d%d",&edge[i].u,&edge[i].v,&edge[i].w);
sort(edge + 1, edge + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
siz[i] = 1;
fa[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 1; ++i) {
int fx = find(edge[i].u), fy = find(edge[i].v);
if (fx == fy)
continue;
ans += ((ll)siz[fx] * siz[fy] - 1) * (edge[i].w + 1);
siz[fx] += siz[fy];
siz[fy] = 0;
fa[fy] = fx;
ans += edge[i].w;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号