YBTOJ 1.5广度搜索
A.走迷宫图
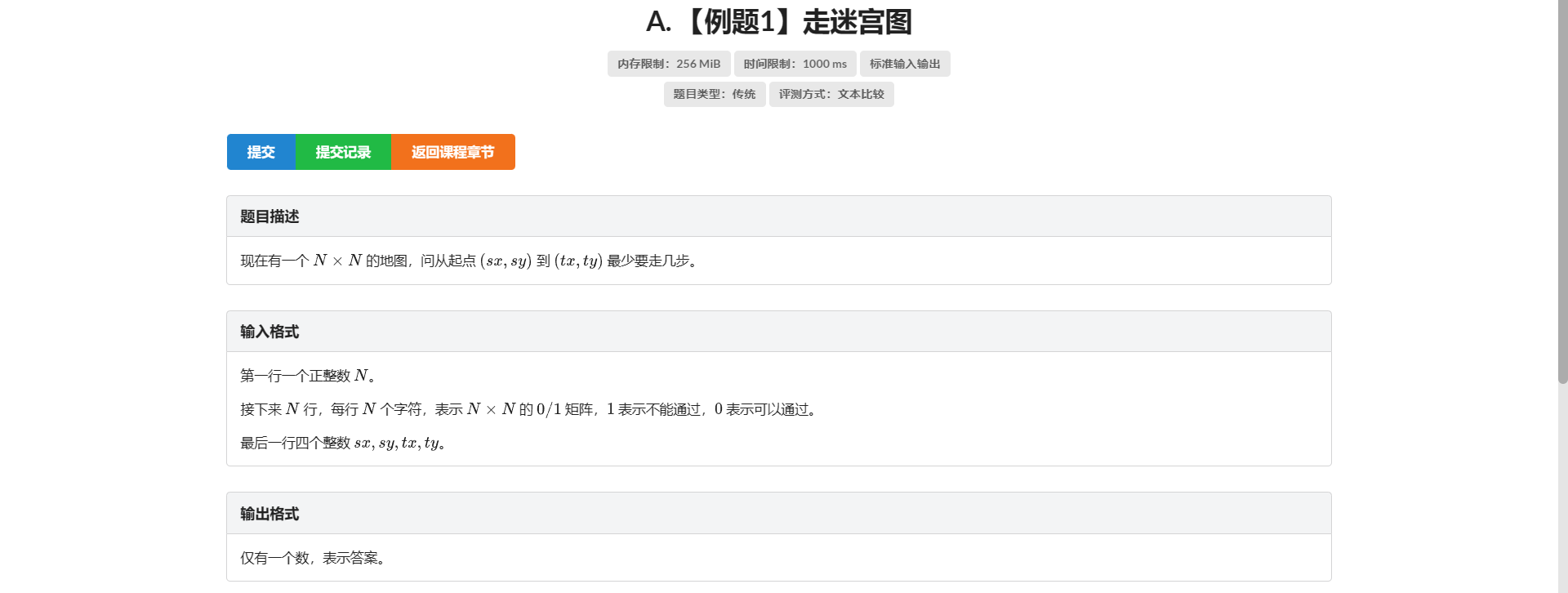
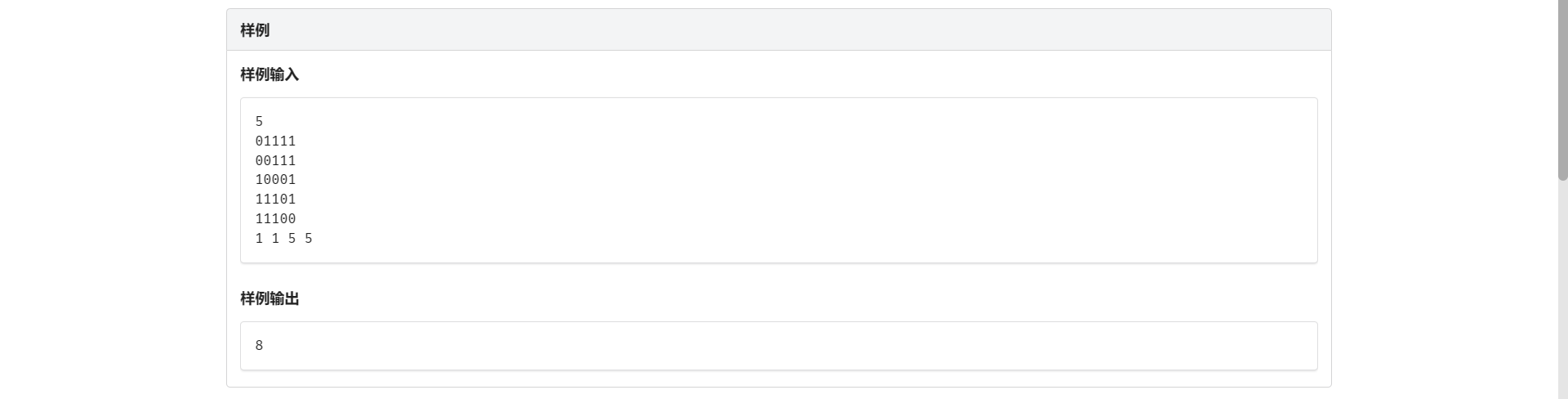

经典广搜题 但是记尊重 \(vis\) 数组
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 0x0d00;
int a[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
int stx, sty, endx, endy;
int n;
int dx[4] = { 1, 0, -1, 0 };
int dy[4] = { 0, 1, 0, -1 };
struct node {
int x, y, stp;
};
queue<node> q;
void bfs(int x, int y, int stp) {
vis[x][y] = 1;
q.push((node){ x, y, stp });
while (!q.empty()) {
int nowx = q.front().x;
int nowy = q.front().y;
int nowstp = q.front().stp;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int tox = nowx + dx[i];
int toy = nowy + dy[i];
if (tox == endx && toy == endy) {
printf("%d", nowstp + 1);
exit(0);
} else if (tox > 0 && tox <= n && toy > 0 && toy <= n && vis[tox][toy] == 0 && a[x][y] != 1)
q.push((node){ tox, toy, nowstp + 1 }), vis[tox][toy] = 1;
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
string s;
cin >> s;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
a[i][j] = s[j - 1] - '0';
if (a[i][j] == 1)
vis[i][j] = 1;
}
}
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &stx, &sty, &endx, &endy);
bfs(stx, sty, 0);
return 0;
}
B.山峰山谷
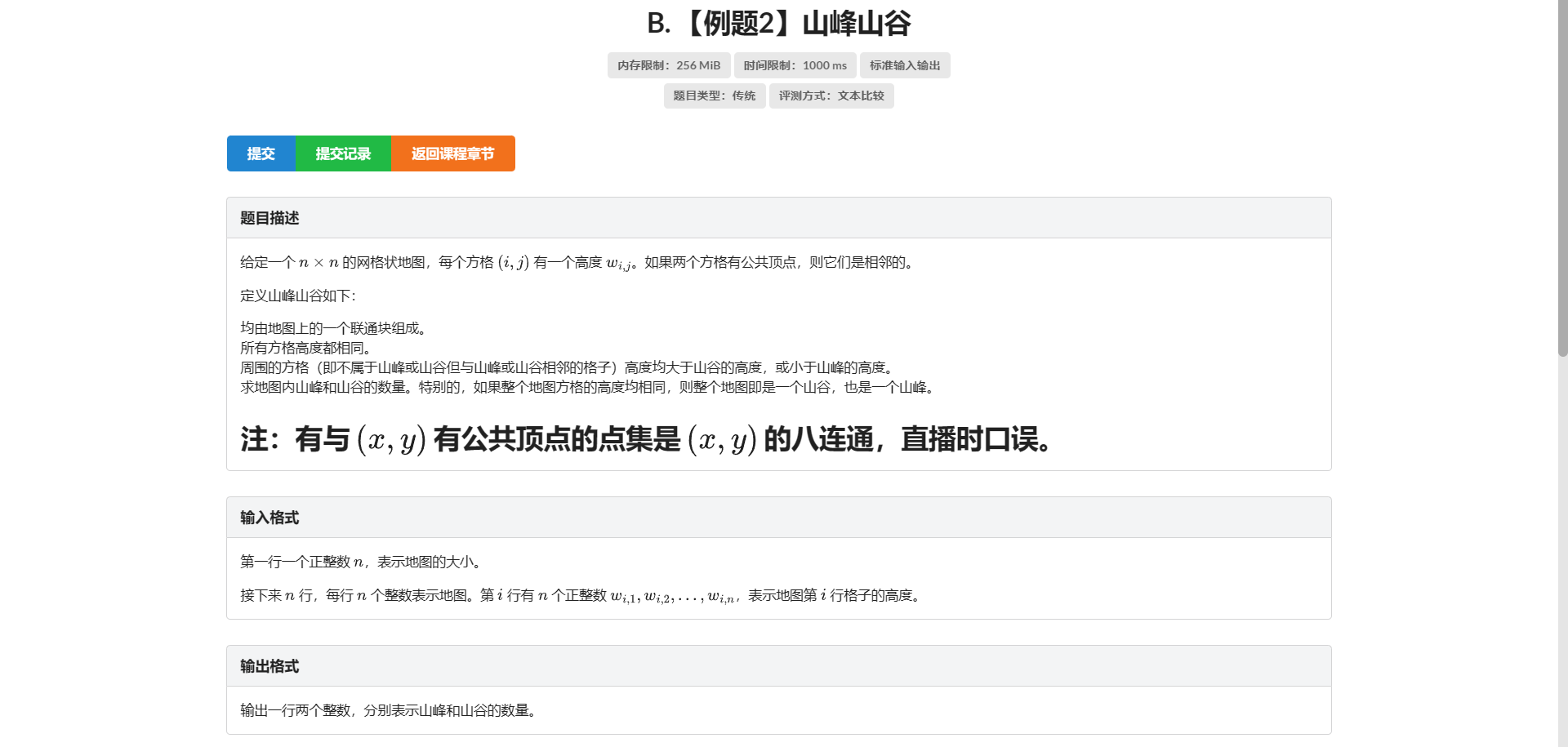
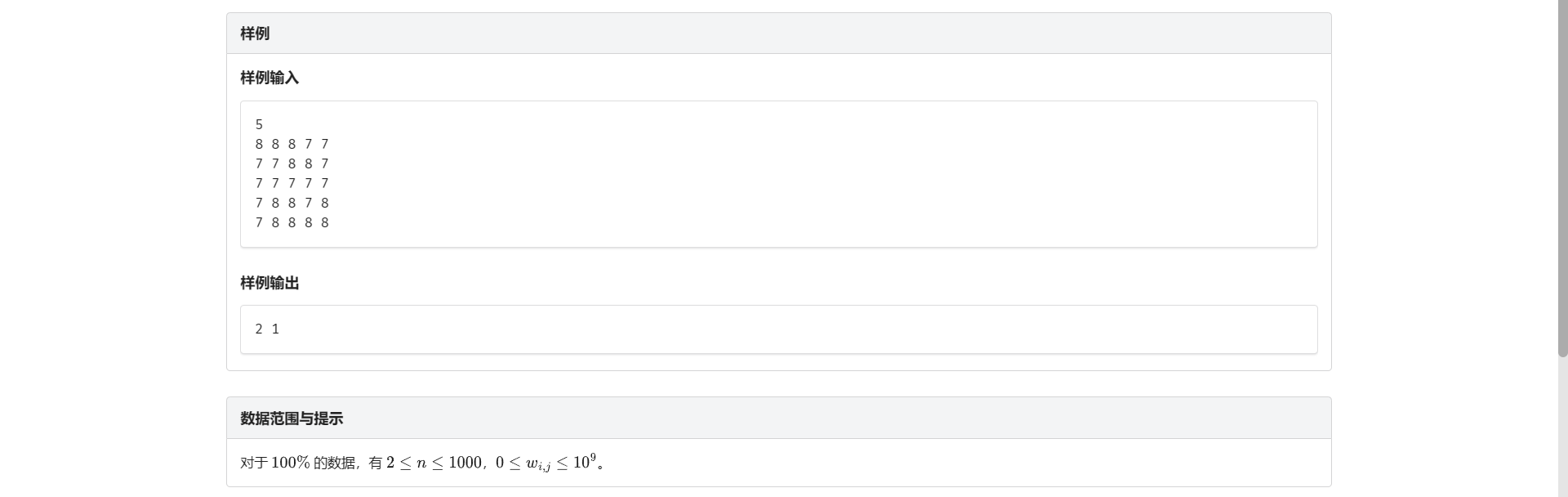
我们用广搜来搜每一个连通块 然后搜的时候分别记录块边界有没有比它大/小的数
进而判断它是不是山峰或者是山谷
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1001;
int a[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
int n, ans1, ans2;
int dx[8] = { 1, 1, -1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dy[8] = { 1, -1, 1, -1, 0, 0, -1, 1 };
struct node {
int x, y;
};
queue<node> q;
void bfs(int x, int y) {
vis[x][y] = 1;
q.push((node){ x, y });
bool flag1 = 1, flag2 = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int nowx = q.front().x;
int nowy = q.front().y;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tox = nowx + dx[i];
int toy = nowy + dy[i];
if (tox <= 0 || toy <= 0 || tox > n || toy > n)
continue;
if (a[tox][toy] != a[nowx][nowy]) {
if (a[tox][toy] > a[nowx][nowy])
flag1 = 0;
if (a[tox][toy] < a[nowx][nowy])
flag2 = 0;
} else if (vis[tox][toy])
continue;
else {
vis[tox][toy] = 1;
q.push((node){ tox, toy });
}
}
}
if (flag1)
++ans1;
if (flag2)
++ans2;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {
if (!vis[i][j])
bfs(i, j);
}
}
printf("%d %d", ans1, ans2);
return 0;
}
C.荆轲刺秦

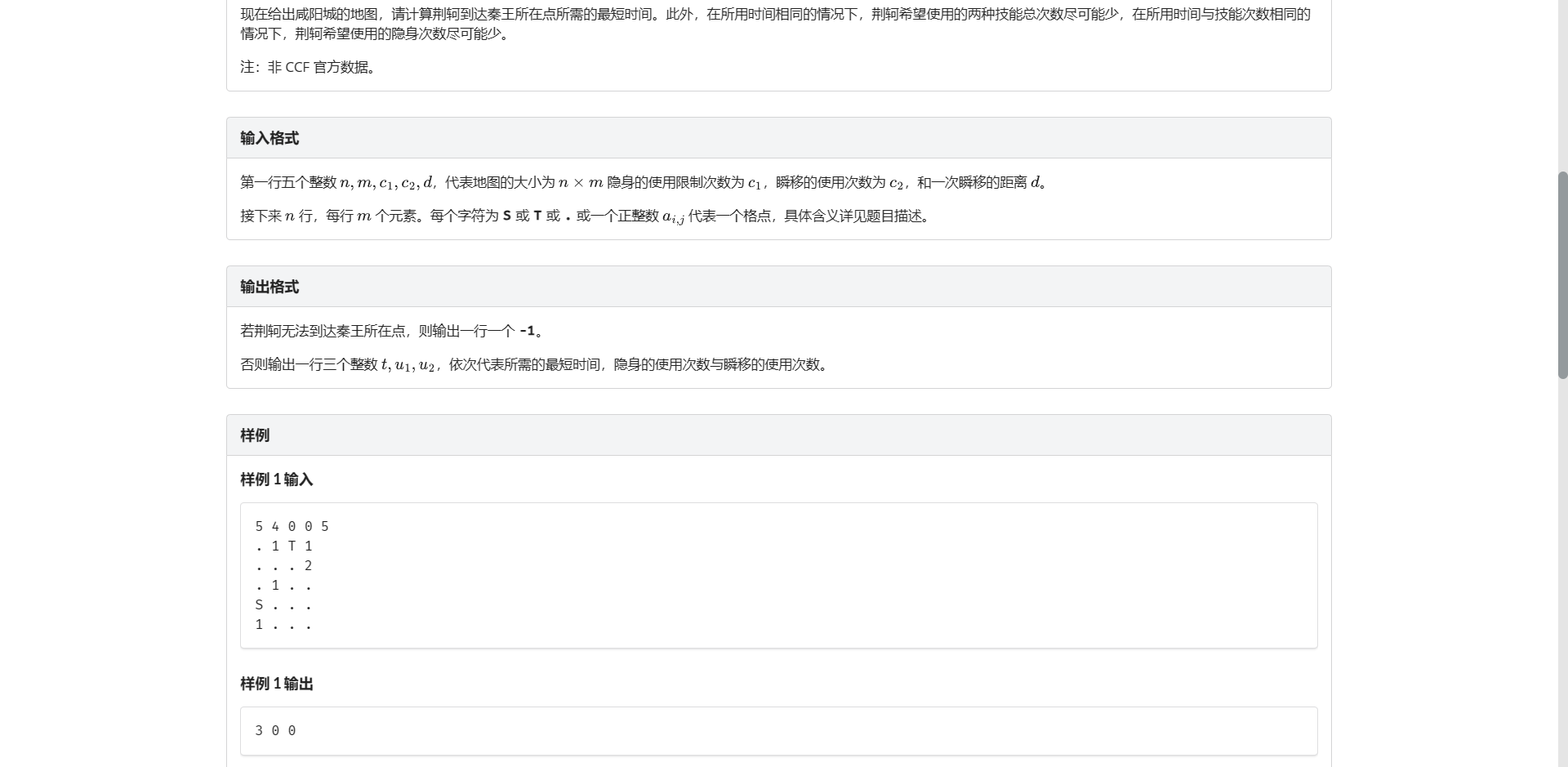
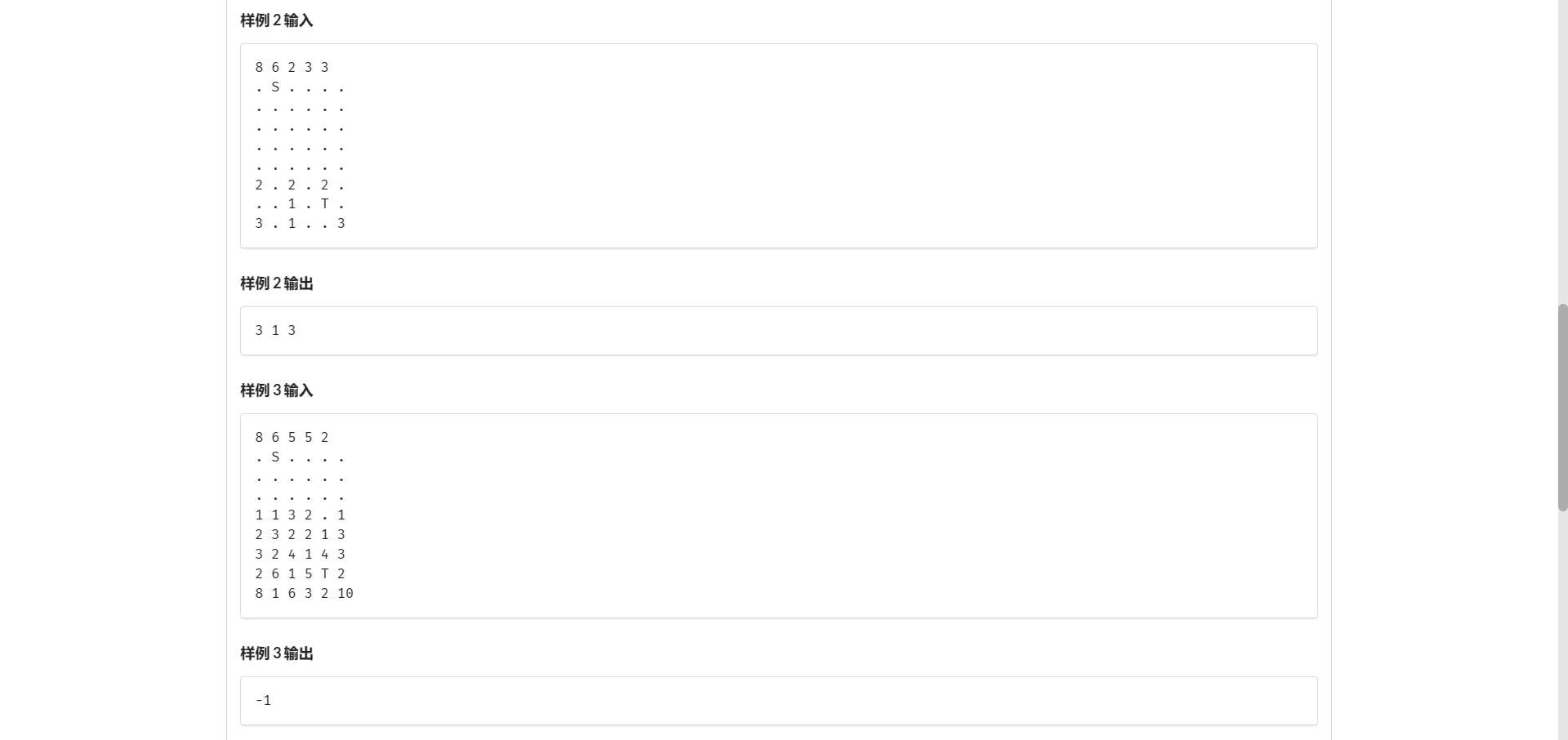
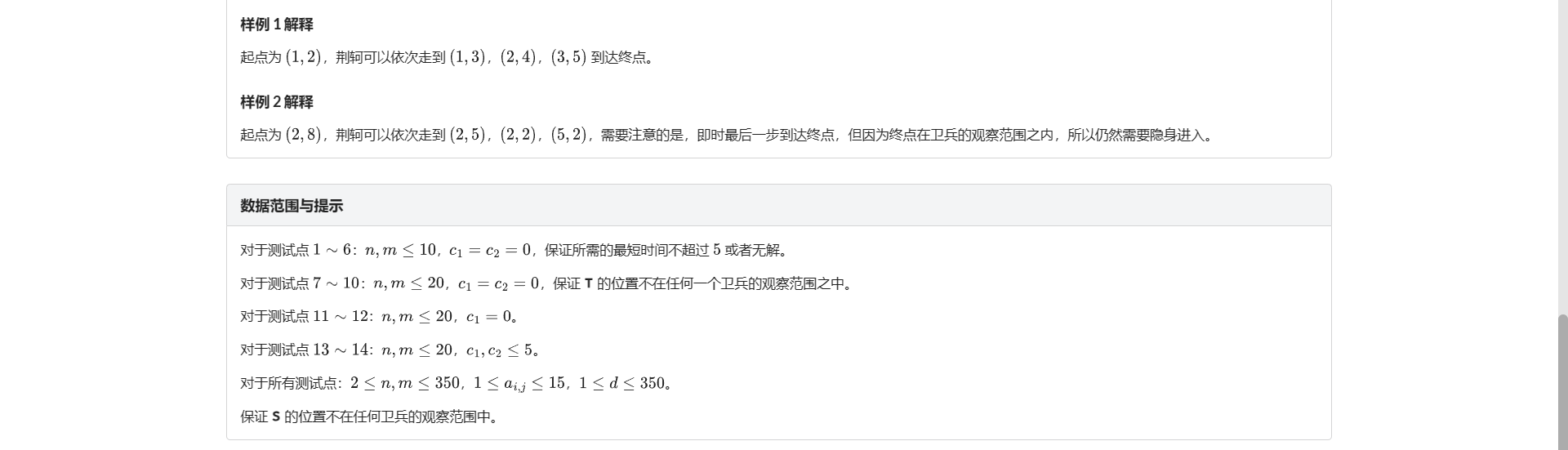
其实是个挺板的广搜 结果发现表示每个士兵视线范围内的点时 复杂度会出现问题
后来发现实际上可以转化为每一行用差分做 这样三次方复杂度就可以了
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 361;
int a[N][N], mp[N][N];
bool vis[N][N][16][16];
bool per[N][N];
int mindis, minc1 = 20, minc2 = 20;
int stx, sty, endx, endy;
int n, m, c1, c2, d;
int dx[8] = { 0, 0, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1 };
int dy[8] = { 1, -1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 1, -1 };
struct node {
int x, y, u1, u2, stp;
};
queue<node> q;
void init(int x, int y, int val) {
--val;
if (val <= 0)
return;
for (int i = x - val; i <= x + val; ++i) {
if (i >= 1 && i <= n) {
++mp[i][max(1, y - abs(val - abs(i - x)))];
--mp[i][min(m + 1, y + 1 + abs(val - abs(i - x)))];
}
}
}
void init2(void) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) mp[i][j] += mp[i][j - 1];
}
}
inline bool exist(int x, int y) { return x >= 1 && x <= n && y >= 1 && y <= m; }
void bfs(int x, int y) {
vis[x][y][0][0] = 1;
q.push((node){ x, y, 0, 0, 0 });
while (!q.empty()) {
int nowx = q.front().x, nowy = q.front().y, now1 = q.front().u1, now2 = q.front().u2,
nowstp = q.front().stp;
q.pop();
if (nowx == endx && nowy == endy) {
if (mindis == 0 || mindis == nowstp) {
mindis = nowstp;
minc1 = min(minc1, now1);
minc2 = min(minc2, now2);
} else {
cout << mindis << " " << minc1 << " " << minc2;
exit(0);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
int tox = nowx + dx[i], toy = nowy + dy[i];
if (exist(tox, toy) && !per[tox][toy]) {
if (mp[tox][toy] == 0) {
if (!vis[tox][toy][now1][now2])
q.push((node){ tox, toy, now1, now2, nowstp + 1 });
vis[tox][toy][now1][now2] = 1;
} else if (now1 < c1) {
if (!vis[tox][toy][now1 + 1][now2])
q.push((node){ tox, toy, now1 + 1, now2, nowstp + 1 });
vis[tox][toy][now1 + 1][now2] = 1;
}
}
}
if (now2 < c2) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int tox = nowx + dx[i] * d, toy = nowy + dy[i] * d;
if (exist(tox, toy) && !per[tox][toy]) {
if (mp[tox][toy] == 0) {
if (!vis[tox][toy][now1][now2 + 1]) {
q.push((node){ tox, toy, now1, now2 + 1, nowstp + 1 });
vis[tox][toy][now1][now2 + 1] = 1;
}
} else if (now1 < c1) {
if (!vis[tox][toy][now1 + 1][now2 + 1]) {
q.push((node){ tox, toy, now1 + 1, now2 + 1, nowstp + 1 });
vis[tox][toy][now1 + 1][now2 + 1] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
if (mindis != 0) {
cout << mindis << " " << minc1 << " " << minc2;
exit(0);
}
cout << "-1";
}
int main() {
// freopen("bandit18.in", "r", stdin);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> m >> c1 >> c2 >> d;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
char x;
cin >> x;
if (x == '.')
a[i][j] = 0;
else if (x == 'S')
stx = i, sty = j;
else if (x == 'T')
endx = i, endy = j;
else
a[i][j] = x - '0', per[i][j] = 1;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) init(i, j, a[i][j]);
}
init2();
bfs(stx, sty);
return 0;
}
upd:实际上这个写法还是有点问题 至少洛谷过不去
应该开结构体存每个格的状态 然后全搜完再打印答案
D.电梯维修
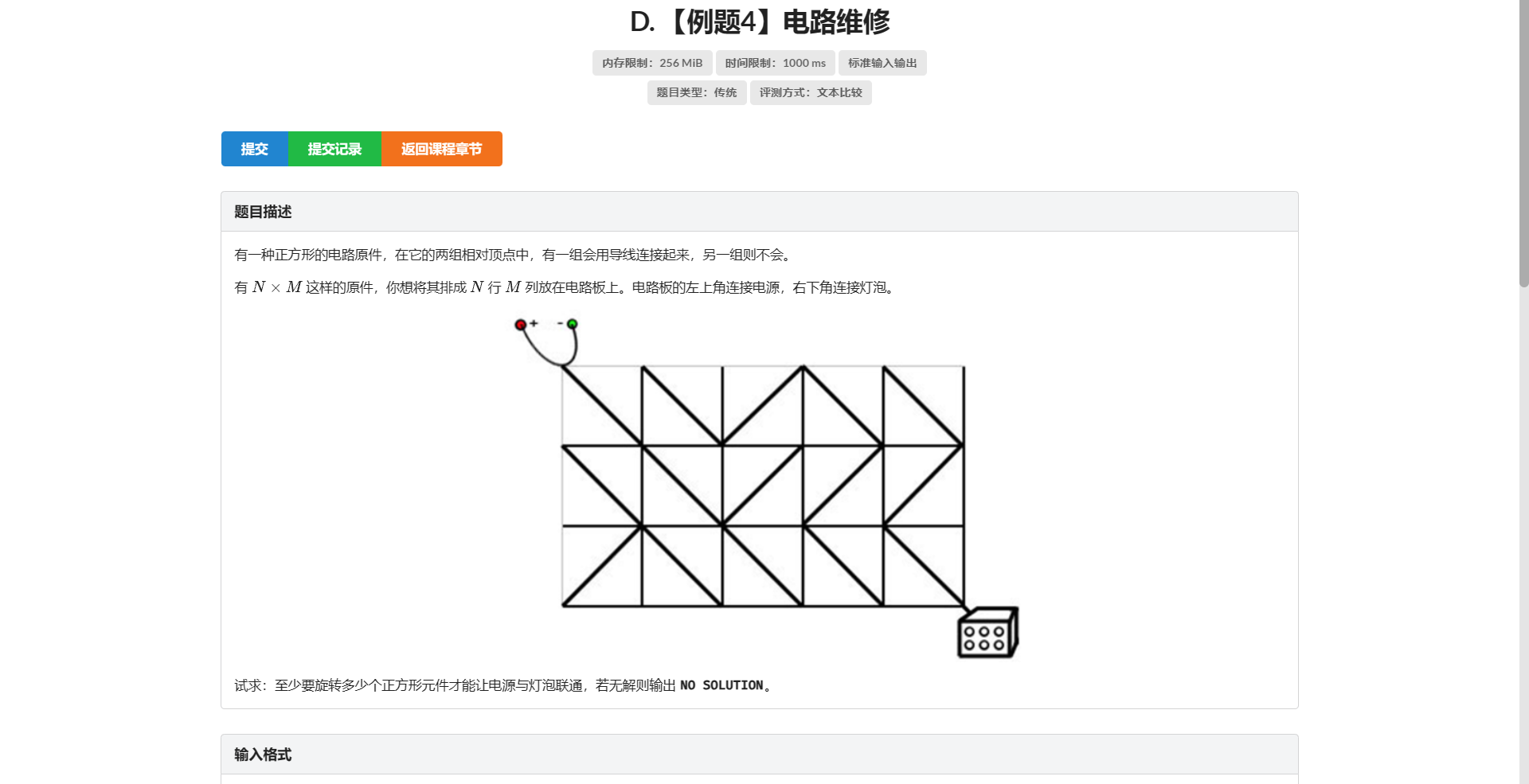
这题乍一看确实没什么思路
我们思考如何进行状态转移
对于每根线我们有两种选择:转或者不转
进一步思考 如果我从左上角的点走到右下角 如果线正好是这么连的 我就不需要转 否则我就需要转一根线
那么我们可以把它看作一条由左上角连到右下角一根边权为 \(0\) / \(1\) 的边
然后你就会发现这题就是一个最短路
但实际上这题想说的是 \(01BFS\) 我们选择跑 \(dijkstra\) 但是不需要开优先队列去维护 而是换成一个双端队列 如果松弛操作边权为 \(0\) 就放到队首 否则放到队尾
(另外 如果用静态数组模拟双端队列 要开四倍空间)
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e6 + 0721;
int head[N], nxt[N], to[N], len[N], cnt;
int dis[N];
int maxn[1];
int n, m;
inline void cmb(int x, int y, int z) {
to[++cnt] = y;
len[cnt] = z;
nxt[cnt] = head[x];
head[x] = cnt;
}
inline int modify(int x, int y) {
return x * (m + 1) + y;
}
void dijkstra(int s) {
deque<int> q;
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof dis );
dis[s] = 0;
q.push_back(s);
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
q.pop_front();
for (int i = head[now]; i; i = nxt[i]) {
int y = to[i];
if (dis[y] > dis[now] + len[i]) {
dis[y] = dis[now] + len[i];
if (len[i] == 1)
q.push_back(y);
else
q.push_front(y);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
memset(maxn, 0x3f, sizeof maxn );
while (T--) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
memset(head, 0, sizeof head );
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {
char c;
cin >> c;
if (c == '\\') {
cmb(modify(i - 1, j - 1), modify(i, j), 0);
cmb(modify(i, j), modify(i - 1, j - 1), 0);
cmb(modify(i - 1, j), modify(i, j - 1), 1);
cmb(modify(i, j - 1), modify(i - 1, j), 1);
}
else {
cmb(modify(i - 1, j - 1), modify(i, j), 1);
cmb(modify(i, j), modify(i - 1, j - 1), 1);
cmb(modify(i - 1, j), modify(i, j - 1), 0);
cmb(modify(i, j - 1), modify(i - 1, j), 0);
}
}
}
dijkstra(0);
if (dis[modify(n, m)] != maxn[0])
printf("%d\n",dis[modify(n, m)]);
else
printf("NO SOLUTION\n");
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号