磁盘性能测试(iops、)
磁盘性能测试
什么是IOPS?IOPS与吞吐、读写块大小、时延有什么关系?
IOPS(Input/Output Per Second)即每秒IO操作的次数(读写次数)。
读写块大小、IOPS、吞吐量、写入次数及时延的关系公式为:
吞吐量=IOPS*读写块大小;IOPS=读写次数/任务整体时延
例如,容量型NAS文件系统1 MiB写时延约为100 ms,8 KiB写时延约为15 ms,4 KiB写时延约为10 ms,最大支持128个并发任务。当您需要1s内写1 MiB数据时,可以有多种写入方案,如下列举其中几种:
| 序号 | 读写块大小 | 并发数 | 写入次数 | 任务整体时延 | IOPS | 吞吐量 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方案一 | 4 KiB | 1 | 250 | 10 ms*250=2.5s | 250/2.5s=100 | 4 KiB*100=400 KiB/s | 小块读写加上低并发数,导致吞吐和时延性能都很差,无法达到1 MiB/s的吞吐目标。 |
| 方案二 | 1 MiB | 1 | 1 | 100 ms | 1/0.1s=10 | 1 MiB*10=10 MiB/s | 相较方案一仅提高读写块大小,吞吐和时延性能有提升,达到了1 MiB/s的吞吐目标,但任务整体时延较长。 |
| 方案三 | 4 KiB | 125 | 250 | 10 ms*(250/125)=20 ms | 250/0.02s=12500 | 4 KiB*12500≈49 MiB/s | 相较方案一仅提高任务并发数,吞吐和时延性能有提升,达到了1 MiB/s的吞吐目标,任务整体时延也很短,但IOPS较高,容易触及文件系统的IOPS上限。 |
| 方案四 | 8 KiB | 125 | 125 | 15 ms*(125/125)=15 ms | 125/0.015s≈8333 | 8 KiB*8333≈65 MiB/s | 相较方案一同时提高读写块大小和任务并发数,吞吐和时延性能有提升,达到了1 MiB/s的吞吐目标,任务整体延时最短,IOPS较低,不容易触及文件系统的IOPS上限。 |
fio 吞吐量和iops测试
# 安装
yum install -y libaio-devel fio
测试脚本
fio -direct=1 -rw=write -bs=100m -size=20g -numjobs=16 -iodepth=16 -runtime=60 -group_reporting -name=test -ioengine=libaio -userspace_reap -filename=/storage/io --output=/home/big_write
fio -direct=1 -rw=read -bs=100m -size=20g -numjobs=16 -iodepth=16 -runtime=60 -group_reporting -name=test -ioengine=libaio -userspace_reap -filename=/storage/io --output=/home/big_read
fio -direct=1 -rw=write -bs=4k -size=20g -numjobs=16 -iodepth=16 -runtime=60 -group_reporting -name=test -ioengine=libaio -userspace_reap -filename=/storage/io --output=/home/4k_write
fio -direct=1 -rw=read -bs=4k -size=20g -numjobs=16 -iodepth=16 -runtime=60 -group_reporting -name=test -ioengine=libaio -userspace_reap -filename=/storage/io --output=/home/4k_read
示例
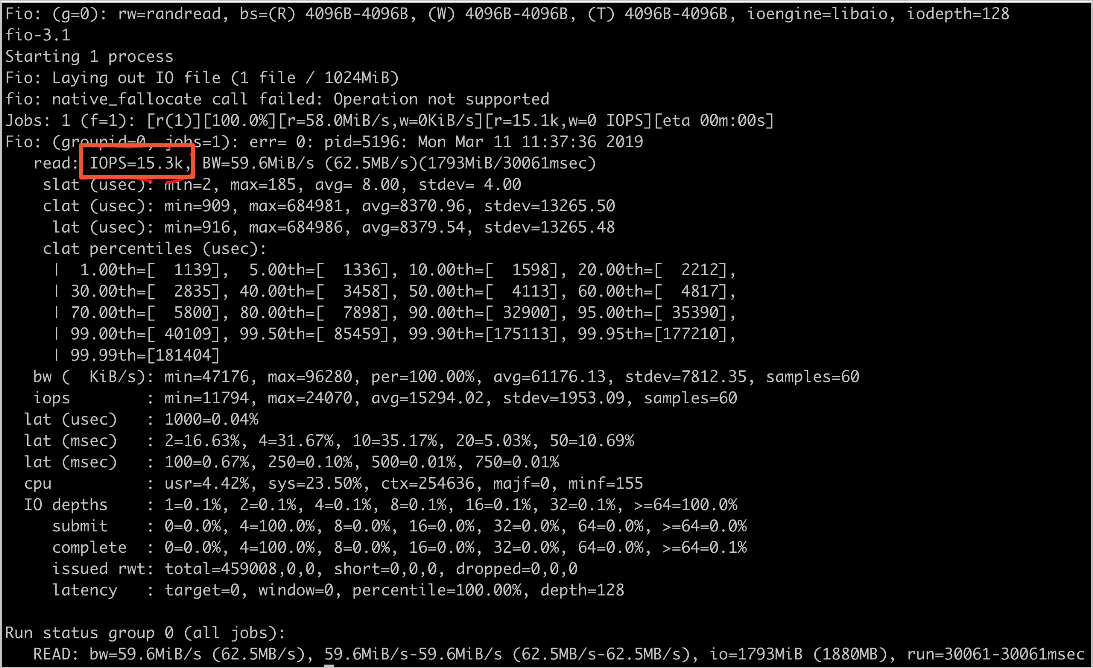
随机读IOPS设置。
fio -numjobs=1 -iodepth=128 -direct=1 -ioengine=libaio -sync=1 -rw=randread -bs=4K -size=1G -time_based -runtime=60 -name=Fio -directory=/mnt
单机预估值:14k
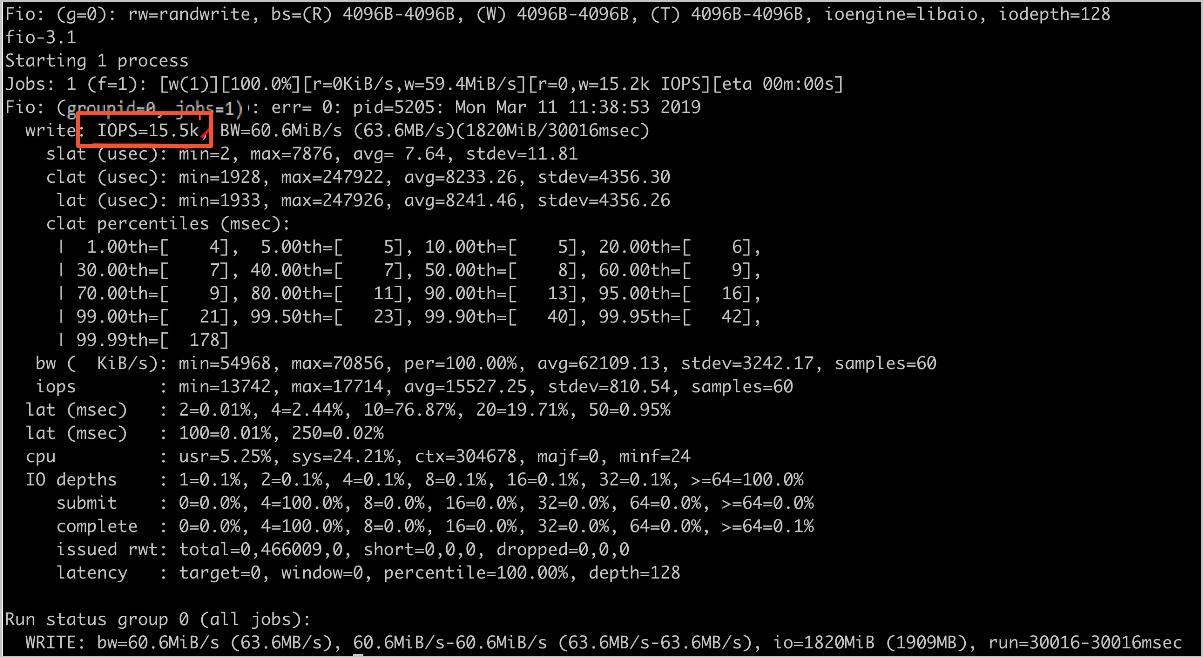
随机写IOPS设置
fio -numjobs=1 -iodepth=128 -direct=1 -ioengine=libaio -sync=1 -rw=randwrite -bs=4K -size=1G -time_based -runtime=60 -name=Fio -directory=/mnt
单机预估值:10k
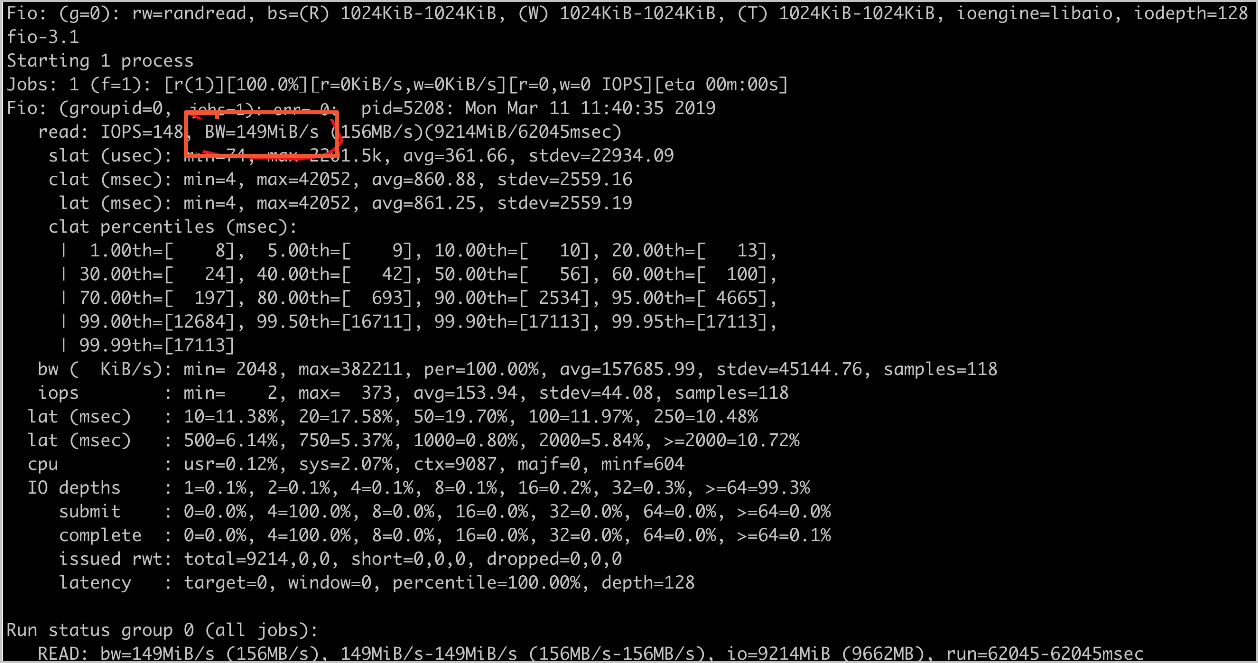
随机读吞吐
fio -numjobs=1 -iodepth=128 -direct=1 -ioengine=libaio -sync=1 -rw=randread -bs=1M -size=1G -time_based -runtime=60 -name=Fio -directory=/mnt
容量型单机预估值:150 MB/s
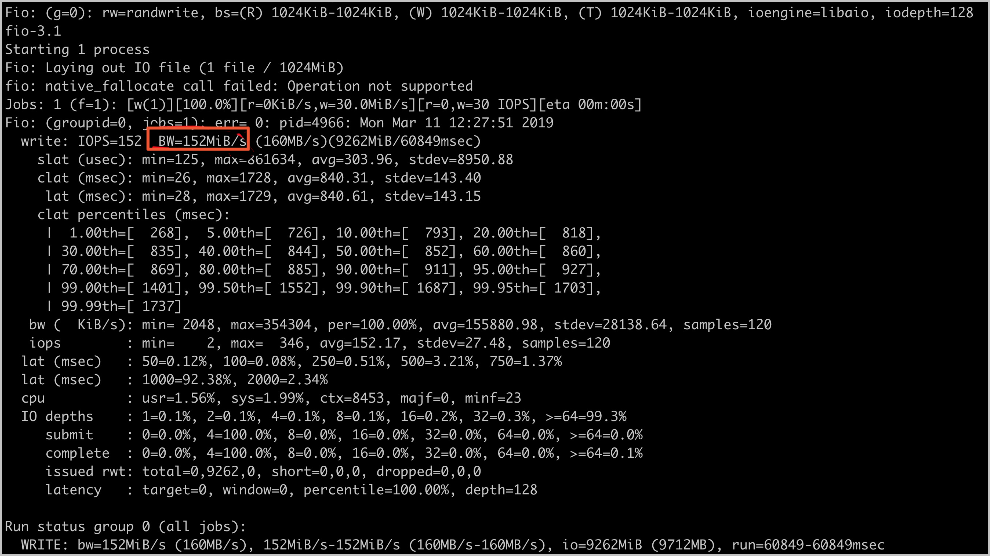
随机写吞吐
fio -numjobs=1 -iodepth=128 -direct=1 -ioengine=libaio -sync=1 -rw=randwrite -bs=1M -size=1G -time_based -runtime=60 -name=Fio -directory=/mnt
容量型单机预估值:150 MB/s
fio 参考说明
filename=/dev/sdb1 #测试文件名称,通常选择需要测试的盘的data目录
direct=1 #测试过程绕过机器自带的buffer。使测试结果更真实
rw=randwrite #测试随机写的I/O
rw=randrw #测试随机写和读的I/O
bs=16k #单次io的块文件大小为16k
bsrange=512-2048 #同上,提定数据块的大小范围
size=5G #本次的测试文件大小为5g,以每次4k的io进行测试
numjobs=30 #本次的测试线程为30个
runtime=1000 #测试时间1000秒,如果不写则一直将5g文件分4k每次写完为止
ioengine=psync #io引擎使用psync方式
rwmixwrite=30 #在混合读写的模式下,写占30%
group_reporting #关于显示结果的,汇总每个进程的信息
lockmem=1G #只使用1g内存进行测试
zero_buffers #用0初始化系统buffer
nrfiles=8 #每个进程生成文件的数量
#顺序读
fio -filename=/dev/sda -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=read -ioengine=psync -bs=16k -size=200G -numjobs=30 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -name=mytest
#顺序写
fio -filename=/dev/sda -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=write -ioengine=psync -bs=16k -size=200G -numjobs=30 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -name=mytest
#随机读
fio -filename=/dev/sda -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=randread -ioengine=psync -bs=16k -size=200G -numjobs=30 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -name=mytest
#随机写
fio -filename=/dev/sda -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=randwrite -ioengine=psync -bs=16k -size=200G -numjobs=30 -runtime=1000 -group_reporting -name=mytest
#混合随机读写
fio -filename=/dev/sda -direct=1 -iodepth 1 -thread -rw=randrw -rwmixread=70 -ioengine=psync -bs=16k -size=200G -numjobs=30 -runtime=100 -group_reporting -name=mytest -ioscheduler=noop
#复制下面的配置内容,将directory=/path/to/test修改为你测试硬盘挂载目录的地址,并另存为fio.conf
[global]
ioengine=libaio
direct=1
thread=1
norandommap=1
randrepeat=0
runtime=60
ramp_time=6
size=1g
directory=/path/to/test
[read4k-rand]
stonewall
group_reporting
bs=4k
rw=randread
numjobs=8
iodepth=32
[read64k-seq]
stonewall
group_reporting
bs=64k
rw=read
numjobs=4
iodepth=8
[write4k-rand]
stonewall
group_reporting
bs=4k
rw=randwrite
numjobs=2
iodepth=4
[write64k-seq]
stonewall
group_reporting
bs=64k
rw=write
numjobs=2
iodepth=4
#测试
fio fio.conf
fio 常用参数
filename: 指定文件(设备)的名称。可以通过冒号分割同时指定多个文件,如filename=/dev/sda:/dev/sdb。
directory: 设置filename的路径前缀。在后面的基准测试中,采用这种方式来指定设备。
name: 指定job的名字,在命令行中表示新启动一个job。
direct: bool类型,如果设置成true (1),表示不使用io buffer。
ioengine: I/O引擎,现在fio支持19种ioengine。默认值是sync同步阻塞I/O,libaio是Linux的native异步I/O。关于同步异步,阻塞和非阻塞模型可以参考文章“使用异步 I/O 大大提高应用程序的性能”。
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-async/
iodepth: 如果ioengine采用异步方式,该参数表示一批提交保持的io单元数。该参数可参考文章“Fio压测工具和io队列深度理解和误区”。
http://blog.yufeng.info/archives/2104
rw: I/O模式,随机读写,顺序读写等等。
bs: I/O block大小,默认是4k。
size: 指定job处理的文件的大小。
numjobs: 指定job的克隆数(线程)。
time_based: 如果在runtime指定的时间还没到时文件就被读写完成,将继续重复知道runtime时间结束。
runtime: 指定在多少秒后停止进程。如果未指定该参数,fio将执行至指定的文件读写完全完成。
group_reporting: 当同时指定了numjobs了时,输出结果按组显示。
参考链接
[性能说明FAQ (aliyun.com)](
本文来自博客园, 作者:Star-Hitian, 转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Star-Haitian/p/16964647.html


