LeetCode题解-07(简单图论)
目录
LeetCode题解
chap-17:图论
1、岛屿数量
// 并查集+坐标变换
class UnionFind{
public:
vector<int> parent;
UnionFind(int n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
parent.push_back(i);
}
int Find(int id){
if(parent[id] == id) return id;
parent[id] = Find(parent[id]);
return parent[id];
}
void Union(int a,int b){
int pa=Find(a);
int pb=Find(b);
parent[pb] = pa;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int encode(int i,int j, int m){
return i*m+j;
}
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
int dx[4]={-1,0,1,0}, dy[4]={0,1,0,-1};
int n=grid.size(), m=grid[0].size();
UnionFind UF(n*m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
for(int d = 0; d < 4; d++){
int di = dx[d], dj = dy[d];
if(i+di >=0 && i+di < n && j+dj >=0 &&
j+dj < m && grid[i+di][j+dj]=='1'){
UF.Union(encode(i, j, m), encode(i+di, j+dj, m));
}
}
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
int id=encode(i,j,m);
if(UF.Find(id) == id) ans++;
}
return ans;
}
};
// dfs
class Solution {
public:
int res = 0;
int dx[4] = {1,0,-1,0}, dy[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
int numIslands(vector<vector<char>>& grid) {
for(int i = 0;i<grid.size();i++){
for(int j = 0;j<grid[0].size();j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
res++;
dfs(grid,i,j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<char>>& g,int x,int y){
g[x][y] = '*';
for(int i = 0;i<4;i++){
int x_ = dx[i] + x, y_ = dy[i] + y;
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a >= 0 && a < g.size() && b >= 0 && b < g[a].size() && g[a][b] == '1')
dfs(g,a, b);
}
}
};
2、课程表 拓扑排序
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int n, vector<vector<int>>& p) {
vector<int> in(n,0);
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for(auto&t:p){
g[t[1]].push_back(t[0]);
in[t[0]]++;
}
queue<int> q;
vector<bool> f(n,false);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) if(in[i]==0) q.push(i);
while(q.size()){
auto t=q.front();
f[t]=true;
for(auto &c:g[t]) {
in[c]--;
if(in[c] == 0) q.push(c);
}
q.pop();
}
for(bool t:f) if(!t) return false;
return true;
}
};
3、课程表 II
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findOrder(int n, vector<vector<int>>& pres) {
vector<int> indegree(n,0);
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for(auto &t:pres){
g[t[1]].push_back(t[0]); indegree[t[0]]++;
}
queue<int> q;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) if(indegree[i]==0) q.push(i);
vector<bool> vis(n,false);
vector<int> ans;
while(q.size()){
auto t=q.front();
vis[t]=true;
ans.push_back(t); q.pop();
for(auto &c:g[t]){
indegree[c]--;
if(indegree[c]==0) q.push(c);
}
}
for(auto c:vis) if(!c) return vector<int>({});
return ans;
}
};
4、最小高度树 树形DP
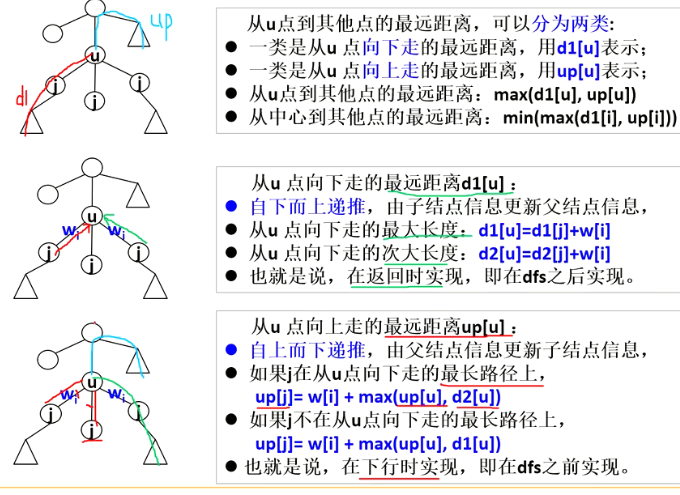
// 树形模板
class Solution {
public:
int n;
vector<vector<int>>g;
vector<int> d1,d2,p1,up;
void dfs1(int u,int father){ // 向下遍历
for(auto x:g[u]){
if(x==father) continue;
dfs1(x,u);
int d = d1[x]+1;
if(d>=d1[u]){
d2[u]=d1[u], d1[u]=d;
p1[u]=x;
}else if(d>d2[u]) d2[u]=d;
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int father){ // 向上遍历
for(auto x:g[u]){
if(x==father) continue;
if(p1[u]==x) up[x] = max(up[u], d2[u])+1;
else up[x] = max(d1[u], up[u])+1;
dfs2(x,u);
}
}
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int m, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
n=m; d1.resize(n); d2.resize(n); p1.resize(n); up.resize(n);
g.resize(n);
for(auto &t:edges) {
g[t[0]].push_back(t[1]);
g[t[1]].push_back(t[0]);
}
dfs1(0,-1);
dfs2(0,-1);
int mind=n-1;
vector<int> ans;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
auto t=max(d1[i],up[i]);
if(mind > t){
ans = vector<int>({});
ans.push_back(i);
mind = t;
}else if(mind == t) ans.push_back(i);
}
return ans;
}
};
// BFS
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findMinHeightTrees(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
if(n==1) return {0};
vector<int> degree(n); //节点对应的出度
vector<vector<int>> m(n); //邻接表
vector<int> res; //结果
for(auto &t:edges){
degree[t[0]]++; degree[t[1]]++;
m[t[0]].push_back(t[1]);
m[t[1]].push_back(t[0]);
}
queue<int> q;
//最外层叶子节点入栈
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) if(degree[i]==1) q.push(i);
//从外向内一层一层剥,每次加入的都是一层的
while(!q.empty()){
res.clear();
int sz=q.size();
for(int i=0;i<sz;i++){
int t=q.front(); q.pop();
res.push_back(t);
degree[t]--;
for(auto j:m[t]){
degree[j]--;
if(degree[j]==1) q.push(j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
5、重新安排行程 欧拉回路
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> ans;
unordered_map<string,multiset<string>> hash;
vector<string> findItinerary(vector<vector<string>>& tickets) {
for(auto &t:tickets){
hash[t[0]].insert(t[1]);
}
dfs("JFK");
return vector<string>(ans.rbegin(),ans.rend());
}
void dfs(string s){
while(hash[s].size()){
auto t=*hash[s].begin();
hash[s].erase(hash[s].begin());
dfs(t);
}
ans.push_back(s);
}
};
6、除法求值
class Solution {
public:
vector<double> calcEquation(vector<vector<string>>& es, vector<double>& vs, vector<vector<string>>& qs) {
// floyed
unordered_set<string> hash;
unordered_map<string,unordered_map<string,double>> g;
for(int i=0;i<es.size();i++){
auto a = es[i][0], b = es[i][1];
g[a][b] = vs[i], g[b][a] = 1 / vs[i];
hash.insert(a), hash.insert(b);
}
for(auto &k:hash)
for(auto &i:hash)
for(auto &j:hash)
if(g[i][k] && g[k][j])
g[i][j] = g[i][k]*g[k][j];
vector<double> ans;
for(auto q: qs) {
auto a = q[0], b = q[1];
if (g[a][b]) ans.push_back(g[a][b]);
else ans.push_back(-1);
}
return ans;
}
};
7、省份数量 【朋友圈】
// 并查集+坐标变换
class UnionFind{
public:
vector<int> parent;
UnionFind(int n){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
parent.push_back(i);
}
int Find(int id){
if(parent[id] == id) return id;
parent[id] = Find(parent[id]);
return parent[id];
}
void Union(int a,int b){
int pa=Find(a);
int pb=Find(b);
parent[pb] = pa;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected) {
int n=isConnected.size();
UnionFind Uf(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(isConnected[i][j]==1){
Uf.Union(i, j);
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(Uf.Find(i) == i) ans++;
return ans;
}
};
8、冗余连接 【并查集】
class Solution {
public:
int find(vector<int>&father, int id){
if(father[id]==id) return id;
father[id]=find(father,father[id]);
return father[id];
}
vector<int> findRedundantConnection(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n=edges.size();
vector<int> father(n+1);
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)father[i]=i;
vector<int> ans(2,0);
for(auto &edge:edges){
int fa=find(father,edge[0]), fb=find(father,edge[1]);
if(fa==fb) ans[0]=edge[0], ans[1]=edge[1];
father[fa]=fb;
}
return ans;
}
};
9、网络延迟时间
class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n, int c) {
int dp[n+1][n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
if(i==j) dp[i][j]=0;
else dp[i][j]=0x3f3f3f;
for(auto &t:times) dp[t[0]][t[1]]=t[2];
// floyd
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j], dp[i][k]+dp[k][j]);
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(dp[c][i]==0x3f3f3f) return -1;
else ans=max(ans,dp[c][i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
// spfa算法
class Solution {
public:
static const int N=110, M=6010, INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[N], e[M], w[M], ne[M];
int eidx,n;
int dist[N];
bool st[N];
void add(int a,int b,int c){
e[eidx]=b, w[eidx]=c, ne[eidx]=h[a], h[a]=eidx++;
}
void spfa(int start){
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
dist[start]=0;
while(q.size()){
int t=q.front();
q.pop();
st[t]=false;
for(int i=h[t];i!=-1;i=ne[i]){
if (dist[e[i]] > dist[t] + w[i]){
dist[e[i]] = dist[t] + w[i];
if (!st[e[i]])
{
st[e[i]] = true;
q.push(e[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int n_, int k) {
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
eidx=0; n=n_;
for(auto &t:times) add(t[0],t[1],t[2]);
memset(dist,0x3f,sizeof dist);
memset(st,0,sizeof st);
spfa(k);
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(dist[i]==INF) return -1;
else ans = max(ans,dist[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};
10、判断二分图 【×】
class Solution {
public:
bool isBipartite(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
int n=graph.size();
vector<int> st(n,-1);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(st[i]==-1)
if(!dfs(graph,st,i,0))
return false;
return true;
}
bool dfs(vector<vector<int>>& graph, vector<int>&st, int u,int c){
st[u]=c;
for(auto a:graph[u]){
if(st[a] != -1) {
if(st[a]==c) return false;
}
else if(!dfs(graph, st, a, 1-c)) return false;
}
return true;
}
};
// bfs
class Solution {
public:
bool bfs(int S, vector<int>& color, const vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
color[S] = 0;
queue<int> q; q.push(S);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (auto &v : graph[u]) {
if (color[v] == color[u])
return false;
if (color[v] == -1) {
color[v] = 1 - color[u];
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return true;
}
bool isBipartite(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
int n = graph.size();
vector<int> color(n, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (color[i] == -1) {
if (!bfs(i, color, graph))
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
11、所有可能的路径 dfs
class Solution {
public:
int n;
vector<bool> f;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
n=graph.size();
f.resize(n);
dfs(graph,0);
return ans;
}
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& graph, int u){
if(u == n-1 && !f[u]){
path.push_back(u);
ans.emplace_back(path);
path.pop_back();
}else if(!f[u]){
f[u]=true;
path.push_back(u);
for(auto t:graph[u]){
dfs(graph, t);
}
path.pop_back();
f[u]=false;
}
}
};
12、等式方程的可满足性
class Solution {
public:
int Find(vector<int>& father, int id){
if(father[id]==id) return id;
father[id]=Find(father, father[id]);
return father[id];
}
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations) {
vector<int> father(26);
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) father[i]=i;
for(auto &eq:equations){
int a = eq[0]-'a', b = eq[3]-'a';
if(eq[1]=='='){
int fa=Find(father, a);
int fb=Find(father, b);
father[fa]=fb;
}
}
for(auto &eq:equations){
int a = eq[0]-'a', b = eq[3]-'a';
if(eq[1]=='!'){
int fa=Find(father, a);
int fb=Find(father, b);
if(fa==fb) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
13、连接所有点的最小费用 【最小生成树】
class Solution {
private:
int calc(vector<int> &x, vector<int> &y) {
return abs(x[0] - y[0]) + abs(x[1] - y[1]);
}
public:
int minCostConnectPoints(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
// prim算法
const int n = points.size();
vector<bool> vis(n, false);
vector<int> dis(n, INT_MAX);
int ans = 0;
dis[0] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int mindis = INT_MAX;
int m = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (!vis[j] && mindis > dis[j]) {
mindis = dis[j];
m = j;
}
vis[m] = true;
ans += mindis;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
dis[j] = min(dis[j], calc(points[m], points[j]));
}
return ans;
}
};
[Go Back~](# LeetCode题解)
版权声明:本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接。


