之前一直用翻滚窗口,每条数据都只属于一个窗口,所有不需要考虑数据需要在多个窗口存的事情。
刚好有个需求,要用到滑动窗口,来翻翻 flink 在滑动窗口中,数据是怎么分配到多个窗口的
一段简单的测试代码:
val input = env.addSource(kafkaSource) val stream = input .map(node => { Event(node.get("id").asText(), node.get("createTime").asText()) }) .windowAll(SlidingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.minutes(1), Time.seconds(10))) .process(new ProcessAllWindowFunction[Event, Event, TimeWindow] { override def process(context: Context, elements: Iterable[Event], out: Collector[Event]): Unit = { val it = elements.iterator var xx: Event = null while (it.hasNext) { xx = it.next() } out.collect(xx) } }) stream.print()
定义了一个长度为1分钟,滑动距离 10秒的窗口,所以正常每条数据应该对应 6 个窗口
在 process 中打个断点就可以追这段处理的源码了
数据的流向和 TumblingEventTimeWindows 是一样的,所以直接跳到对应数据分配的地方
WindowOperator.processElement,代码比较长,这里就精简一部分
@Override public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {
// 对应的需要分配的窗口 final Collection<W> elementWindows = windowAssigner.assignWindows( element.getValue(), element.getTimestamp(), windowAssignerContext); //if element is handled by none of assigned elementWindows boolean isSkippedElement = true; final K key = this.<K>getKeyedStateBackend().getCurrentKey(); if (windowAssigner instanceof MergingWindowAssigner) { } else {
// 循环遍历,将数据放到对应的窗口状态的 namesspace 中 for (W window: elementWindows) { // drop if the window is already late if (isWindowLate(window)) { continue; } isSkippedElement = false; // 将数据放到对应的窗口中 windowState.setCurrentNamespace(window); windowState.add(element.getValue()); registerCleanupTimer(window); } } }
for 循环就是将数据放到多个窗口的循环,看下 dubug 信息

看对应的6个窗口,从后往前的
窗口分配的代码,就对应这个方法的第一句:
final Collection<W> elementWindows = windowAssigner.assignWindows( element.getValue(), element.getTimestamp(), windowAssignerContext);
assignWindows 的源码是根据 windowAssigner 的不同而改变的,这里是: SlidingProcessingTimeWindows,对应源码:
@Override public Collection<TimeWindow> assignWindows(Object element, long timestamp, WindowAssignerContext context) { timestamp = context.getCurrentProcessingTime(); List<TimeWindow> windows = new ArrayList<>((int) (size / slide)); long lastStart = TimeWindow.getWindowStartWithOffset(timestamp, offset, slide); for (long start = lastStart; start > timestamp - size; start -= slide) { windows.add(new TimeWindow(start, start + size)); } return windows; }
有个list 存储对应的窗口时间对象,list 的长度就是 窗口的长度 / 滑动的距离 (即一条数据会出现在几个窗口中)
这里用的是处理时间,所有Timestamp 直接从 处理时间中取,数据对应的 最后一个窗口的开始时间 lastStart 就用处理时间传到TimeWindow.getWindowStartWindOffset 中做计算
算出最后一个窗口的开始时间后,减 滑动的距离,就是上一个窗口的开始时间,直到 窗口的开始时间超出窗口的范围
对应的关键就是 lastStart 的计算,看源码:
/** * Method to get the window start for a timestamp. * * @param timestamp epoch millisecond to get the window start. * @param offset The offset which window start would be shifted by. * @param windowSize The size of the generated windows. * @return window start */ public static long getWindowStartWithOffset(long timestamp, long offset, long windowSize) { return timestamp - (timestamp - offset + windowSize) % windowSize; }
没指定 offset ,所以 offset 为0, lastStart = timestamp - (timestamp - offset + windowSize) % windowSize
windowSize 是 滑动的距离,这里画了个图来说明计算的公式:
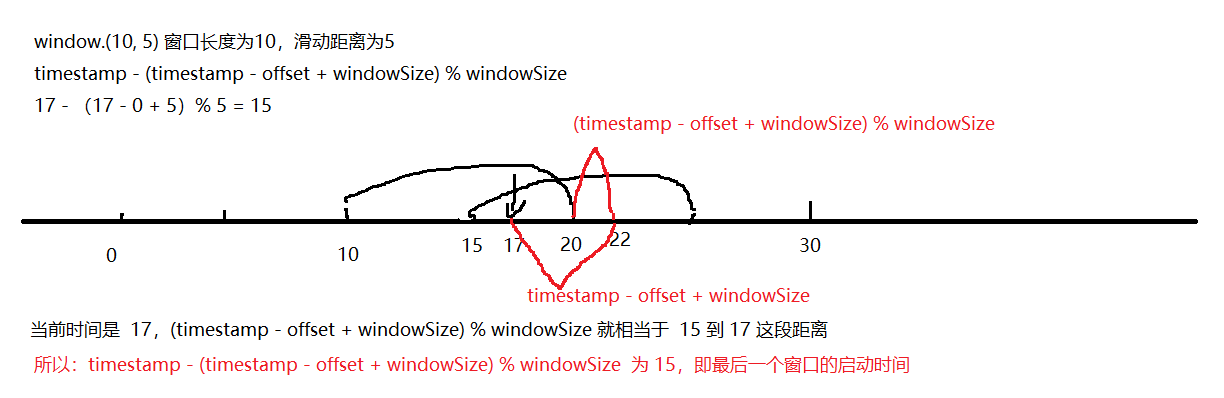
算出最后一个窗口的时间后,下面的 for 循环计算出数据对应的所有窗口,并创建一个时间窗口(这个时间窗口,并不是一个窗口,只是窗口的时间,表达一个窗口的开始时间和结束时间)
long lastStart = TimeWindow.getWindowStartWithOffset(timestamp, offset, slide); for (long start = lastStart; start > timestamp - size; start -= slide) { windows.add(new TimeWindow(start, start + size)); }
所以 17 对应的这条数据对应的窗口就有 (10-20), (15,25)
一条数据属于多少个窗口分配好了以后,就是把数据放到对应的窗口中了,flink 的窗口对应 state 的 namespace , 所以放到多个窗口,就是放到多个 namespace 中,对应的代码是:
windowState.setCurrentNamespace(window);
windowState.add(element.getValue());
选择 namespace,把数据放到对应的 state 中,后面窗口 fire 的时候,会从对应的 namespace 中 get 数据
欢迎关注Flink菜鸟公众号,会不定期更新Flink(开发技术)相关的推文




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号