Spring感知接口
一,感知接口的介绍
1.ResourceLoaderAware 资源加载器感知接口
2 .BeanNameAware Bean配置的的名字感知接口
3.ApplicationContextAware 应用上下文感知接口
4.BeanFactoryAware Bean工厂感知接口
5.MessageSourceAware MessageSource感知接口
6.ApplicationEventPublisherAware ApplicationEventPublisher感知接口
二,感知接口的使用
有如下类
package liusheng.spring.aware; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware; import org.springframework.context.MessageSource; import org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAware; import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware; import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader; /** * 输出传入所有参数的的全限定类名 * @author liusheng */ public class AwareImpl implements BeanNameAware,ResourceLoaderAware ,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,MessageSourceAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware{ public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) { System.out.println(applicationEventPublisher.getClass().getName()); } public void setMessageSource(MessageSource messageSource) { System.out.println(messageSource.getClass().getName()); } public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { System.out.println(applicationContext.getClass().getName()); } public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException { System.out.println(beanFactory.getClass().getName()); } public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) { System.out.println(resourceLoader.getClass().getName()); } public void setBeanName(String name) { System.out.println(name.getClass().getName()); } }
当调用感知容器启动时,会输出所有的参数的全类路径名字,于是:
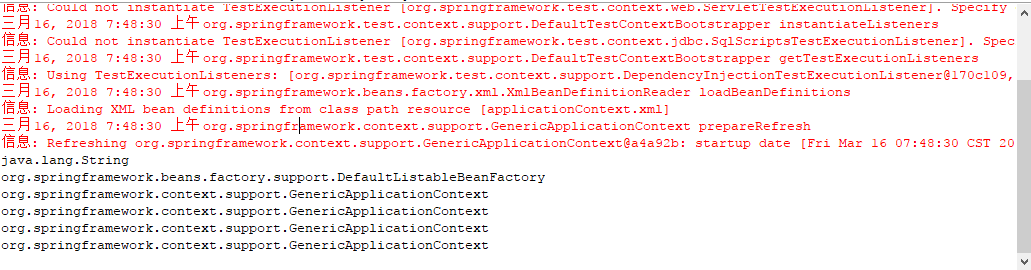
于是我查看这个org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext 实现的接口,它实现4个接口
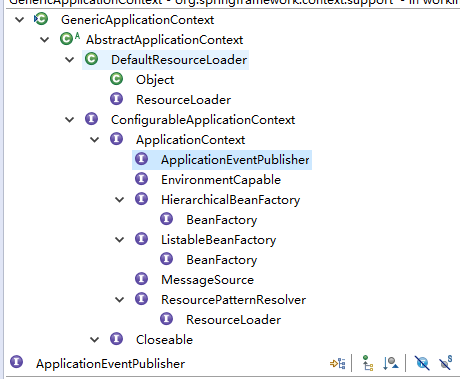
于是使用感知接口时从方法获得属性的值,都是ApplicationContext的对象,相当于还是在使用容器。
1.MessageSourceAware
MessageSourceAware 用来国际化的感知接口,这个接口默认读取Bean名字为messageSource
如下配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.1.xsd"> <bean class="liusheng.spring.aware.AwareImpl" />
<!--名字必须是这个-->
<bean name="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basename" value="message"/> </bean> </beans>
2.ApplicationEventPublisherAware
写个用来标识自己写的事件的标识性接口:
package liusheng.spring.aware; 就只有一个输出方法 public interface MyPrint { public void print(); }
则定义这个以下这个事件
package liusheng.spring.aware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; public class MyEvent extends ApplicationEvent implements MyPrint { private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * * 很显然这个不用向主配置文件注册 * 注册也行,对属性初始化 */ public MyEvent(Object source) { super(source); } public void print() { System.out.println(name+"发布了事件是:"+this.getSource().toString()); } }
事件发布器:
package liusheng.spring.aware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware; public class MyPublisher implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware { private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher; private ApplicationEvent event; public ApplicationEvent getEvent() { return event; } public void setEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { this.event = event; } public ApplicationEventPublisher getApplicationEventPublisher() { return applicationEventPublisher; } public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) { this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher; } public void publisher(){ applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(event); } }
事件监听器,这个一定要注册,因为是系统调用
package liusheng.spring.aware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; public class MyEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { if(event instanceof MyPrint){ MyPrint my=(MyPrint) event; my.print(); }else { System.out.println(event.getSource()); } } }
主配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util" xmlns:lang="http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang http://www.springframework.org/schema/lang/spring-lang-4.1.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util-4.1.xsd"> <bean class="liusheng.spring.aware.AwareImpl" /> <bean class="liusheng.spring.aware.MyEvent" name="event"> <constructor-arg name="source"> <value>我要用力学习Spring</value> </constructor-arg> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> </bean> <bean class="liusheng.spring.aware.MyEventListener"/> <bean class="liusheng.spring.aware.MyPublisher" > <property name="event" ref="event"></property> </bean> </beans>
测试:
package liusheng.spring.aware; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext2.xml") public class EventTest { @Autowired MyPublisher my; @Test public void test() throws Exception { my.publisher(); } }
结果:

从结果看一看出,Spring中还有许多内置的事件,故需要区分。
Spring中有许多的感知接口为我们提供方便,同时这个会让这些类成为Spring的专用的类



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号