java-循环结构
1.循环结构:
在某些条件满足的情况下,反复执行特定代码的功能。
2.JAVA循环语句分类:
(1)for循环
(2)while循环
(3)do-while循环
3.循环语句的四个组成部分
(1)初始化部分
(2)循环条件部分
(3)循环体部分
(4)迭代部分
4.for循环
一、For循环结构的使用
(1)初始化部分
(2)循环条件部分
(3)循环体部分
(4)迭代部分
二、For循环结构
for((1);(2);(3)){
(4)
}
三、For循环例子
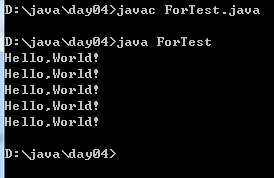
例1:输出五次HelloWorld
方法一:
import java.util.Scanner;
class ForTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++){
System.out.println("Hello,World!");
}
}
}
编译运行:
方法二:
import java.util.Scanner; class ForTest{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i=2;i<=10;i+=2){//i=1,2,3,4,5 System.out.println("Hello,World!"); } } }
例2:
import java.util.Scanner; class ForTest{ public static void main(String[] args){ //练习: int num=1; for(System.out.print('a');num<=3;System.out.print('c'),num++){ System.out.print('b'); //输出结果 abcbcbc } } }
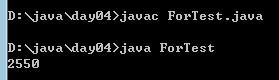
例3:求100以内的偶数之和。
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
class ForTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int sum = 0;
for(int i=2;i<=100;i++){
if(i%2==0)
sum+=i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
运行结果:
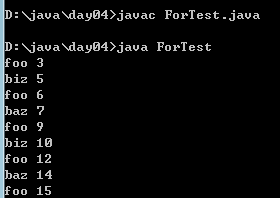
例4:编写程序从1-150,并在每行打印一个值,另外在每个3的倍数行上打印出“foo”,另外在每个5的倍数行上打印“biz”,在每个7的倍数行上打印输出"baz"。
代码实现:
import java.util.Scanner;
class ForTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=2;i<=150;i++){
if(i%3==0)
{System.out.println("foo"+" "+i);}
if(i%5==0)
{System.out.println("biz"+" "+i);}
if(i%7==0)
{System.out.println("baz"+" "+i);}
}
}
}
编译运行:
例5:输入两个正整数m和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。
比如:12和20的最大公约数是4,最小公倍数是60。
代码实现:
/*
12 20
除数不能超过两者的最小值
最大公约数:不能超过两个数的最大值(从大的往小的找)
最小公倍数:
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
class ForTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个正整数:");
int m=scan.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个正整数:");
int n=scan.nextInt();
//获取两个数中的最小值-找到一个就不用再往下找了
int min=(m<=n)?m:n;
for(int i=min;i>=1;i--)
if(m%i==0&&n%i==0){
System.out.println(i);//4
break;//跳出当前for循环
}
//获取最小公倍数-不能比它俩小(范围:max到两乘积之间)
int max=(m>=n)?m:n;//获取两个数中的较大值
for(int i=max;i>=m;i++)
if(i%m==0&&i%n==0){
System.out.println(i);//60
break;//跳出当前for循环
}
}
}
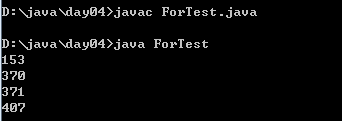
例6:输出所有的水仙花数,所谓水仙花数是一个三位数,其各个位上数立方和等于其本身。
代码实现:
class ForTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=100;i<=999;i++){
int p=i/100;//求出百位
int q=i%100/10;//求出十位
int r=i%10;//求出个位
int result=p*p*p+q*q*q+r*r*r;
if(i==result){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
编译运行:
5.while循环
一、while循环的使用
(1)初始化部分 (2)循环条件部分 (3)循环体部分 (4)迭代部分
二、while循环结构
(1)初始化条件
while((2)循环条件){
(3);
(4);
}
三、while循环的例子
遍历1-100以内的所有偶数
代码实现:
class WhileTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i=1;
while(i<=100){
if(i%2==0){
System.out.print(i);
}
i+=1;
}
}
}
6、for与while循环的转换说明
for和while的循环是可以相互转换的。
区别:for循环与while循环的初始化条件的范围不一样。
7.do-while循环
一、循环结构四要素(循环条件是布尔类型)
二、do-while循环结构
(1)
do{
(3);
(4);
}while((2))
执行过程:(3)-(4)-(2)......
三、例子-100以内偶数和
class DoWhileTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i=1;
do{
if(i%2==0){
System.out.print(i);
i+=1;
}while(i<=100)
}
}
}
8.while与do-while
class DoWhileTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
int i=10;
do{
System.out.print("hello:do-while");
i--;
}while(i>10)
}
while(i>10){
System.out.print("hello:while");
i++;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号