C# - 深拷贝与浅拷贝
前言
深浅拷贝的意义
当你New一个对象时,每New一次,都需要执行一个构造函数,如果构造函数的执行时间很长,那么多次New对象时会大大拉低程序执行效率,因此:一般在初始化信息不发生变化的前提下,克隆是最好的办法,这既隐藏了对象的创建细节,又大大提升了性能!
————《大话设计模式》
深浅拷贝意义在于 节省重复创建对象时所耗费的资源。
对于深浅拷贝的性能开销对比:C#原型模式(深拷贝、浅拷贝) - 也难熬
适用场合
值类型、引用类型
-
值类型:
- 结构类型:结构体、整型数值、浮点型数值、bool、char
- 枚举类型:enum
- 值元组
-
引用类型:
-
class、interface、delegate
-
dynamic、object、string
-
深拷贝
含义
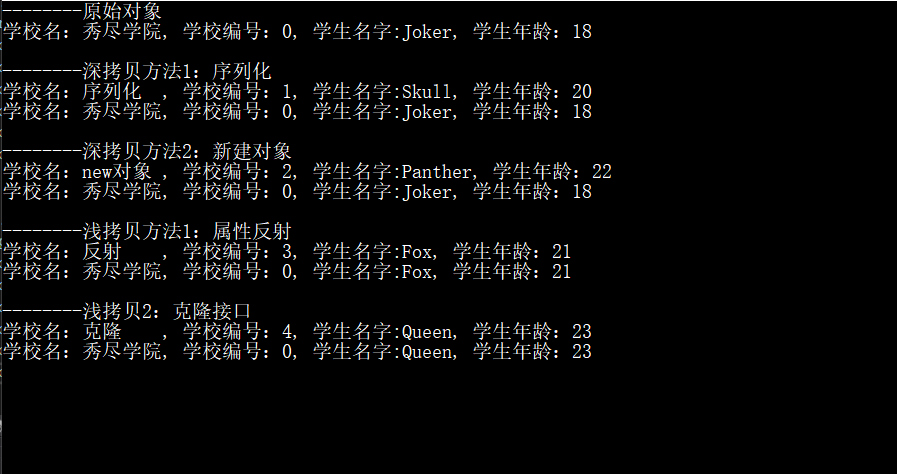
创建新对象,为其中的值类型和引用类型开辟新空间,并具有和被拷贝对象等值的属性及字段,不影响被拷贝对象中的内容。
- 对值类型的影响:新对象的值类型成员与被拷贝对象的值类型成员 值相同,但地址不同
- 对引用类型的影响:同理互不相干
实现方法
新建对象法
手动new进行对象的逐层新建。
public class School : ICloneable
{
public string Name { get; set; } = "init";
public int Number { get; set; } = -1;
public Student Student { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 深拷贝:新建对象实现克隆,如果属性是引用类型,需要一层层new赋值,直到属性是值类型为止
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public School NewClone()
{
return new School()
{
Name = this.Name,
Number = this.Number,
Student = this.Student.NewClone()
};
}
}
public class Student : ICloneable
{
public string Name { get; set; } = "xxx";
public int Age { get; set; } = 0;
public Student NewClone()
{
return new Student() { Age = this.Age, Name = this.Name };
}
}
序列化法
通过把对象序列化到内存然后再反序列化回来实现的深拷贝,不推荐
/// <summary>
/// 深拷贝:序列化
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
/// <param name="source"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static T SerializableClone<T>(T source)
{
if (!typeof(T).IsSerializable)
{
throw new ArgumentException("The type must be serializable.", source.GetType().ToString());
}
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(source, null))
{
return default(T);
}
IFormatter formatter = new BinaryFormatter();
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
{
formatter.Serialize(ms, source);
ms.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin);
return (T)formatter.Deserialize(ms);
}
}
浅拷贝
含义
将被拷贝的所有字段逐个复制到新对象,如果字段是值类型,则简单地复制一个副本到新对象;如果字段是引用类型,则复制的是引用,会影响被拷贝对象中的内容。
- 对值类型的影响:新对象的值类型成员与被拷贝对象的值类型成员 值相同,但地址不同
- 对引用类型的影响:拷贝与被拷贝对象为同一引用,成员变动相互关联
实现方法
ICloneable接口法
调用函数 protected object MemberwiseClone () ,返回Object的浅表副本
public class School : ICloneable
{
public string Name { get; set; } = "init";
public int Number { get; set; } = -1;
public Student Student { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 浅拷贝:实现ICloneable接口
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public object Clone()
{
return this.MemberwiseClone();
}
}
反射法
/// <summary>
/// 浅拷贝:反射
/// </summary>
/// <param name="t"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static T PropertyClone<T>(T t)
{
if (Object.ReferenceEquals(t, null))
{
return default(T);
}
Type type = t.GetType();
PropertyInfo[] propertyInfos = type.GetProperties();
Object obj = Activator.CreateInstance<T>();
Object p = type.InvokeMember("", BindingFlags.CreateInstance, null, t, null);
foreach (PropertyInfo propertyInfo in propertyInfos)
{
if (propertyInfo.CanWrite)
{
object value = propertyInfo.GetValue(t, null);
propertyInfo.SetValue(obj, value, null);
}
}
return (T)obj;
}
特殊情况
深浅拷贝原理简单,但经常遇到例外,例如拷贝时遇到 string或者关联类:
public class School : ICloneable
{
// 尽管string属于引用类型,但是由于该引用类型的特殊性,Object.MemberwiseClone方法仍旧为他创建了副本,
// 也就是说,在浅拷贝过程中,我们应该将 **string** 看成 **值类型**
// String 对象不可变(只读),其值在创建后无法修改。 用于修改 String 对象的方法实际上会返回一个包含修改的新 String 对象
public string Name { get; set; } = "init";
public int Number { get; set; } = -1;
// 注意:此处student是一个 引用类型,在浅拷贝时其内的 值类型将以 引用类型的形式进行拷贝
public Student Student { get; set; }
// 深拷贝
public School NewClone()
{
return new School()
{
Name = this.Name,
Number = this.Number,
Student = this.Student.NewClone()
};
}
// 浅拷贝
public object Clone(){ return this.MemberwiseClone(); }
}
public class Student : ICloneable
{
public string Name { get; set; } = "xxx";
public int Age { get; set; } = 0;
// 深拷贝
public Student NewClone(){ return new Student() { Age = this.Age, Name = this.Name }; }
/// 浅拷贝:实现ICloneable接口
public object Clone(){ return this.MemberwiseClone(); }
}
因此在对School类进行:
- 深拷贝时:字段、属性、关联类均不影响被拷贝对象
- 浅拷贝时:
- 值类型的Number和字符串类型的Name 不影响被拷贝对象
- 引用类型的Student会影响被拷贝对象(包括Student类中值类型的Age和字符串类型的Name)
源代码:深拷贝与浅拷贝示例.cs
总结
深拷贝,所有内容都是新的;
浅拷贝,直属值类型和string是新的,引用类型及其下属内容都是旧的。



