SpringBoot【六】 Shiro
Shiro
- Apache Shiro 是一个 java 的安全(权限)框架
- 可以容易的开发出足够好的应用,不仅可以用在 JavaSE 环境,也可以用在 JavaEE 环境
- 可以完成认证、授权、加密、会话管理、Web 集成、缓存等
功能

Shiro 架构
外部
从外部来看 Shiro,即从应用程序角度来观察如何使用 Shrio 完成工作

- Subject 用户
- SecurityManager 管理所有用户
- Realm 连接数据
内部

快速入门
参考:https://github.com/apache/shiro/tree/master/samples/quickstart
-
导入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.shiro/shiro-core --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-core</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency> <!-- configure logging --> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId> <version>1.7.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> -
配置文件
log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m %n # General Apache libraries log4j.logger.org.apache=WARN # Spring log4j.logger.org.springframework=WARN # Default Shiro logging log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro=INFO # Disable verbose logging log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.util.ThreadContext=WARN log4j.logger.org.apache.shiro.cache.ehcache.EhCache=WARNshiro.ini(IDEA 中要先加入 Ini 插件)
[users] # user 'root' with password 'secret' and the 'admin' role root = secret, admin # user 'guest' with the password 'guest' and the 'guest' role guest = guest, guest # user 'presidentskroob' with password '12345' ("That's the same combination on # my luggage!!!" ;)), and role 'president' presidentskroob = 12345, president # user 'darkhelmet' with password 'ludicrousspeed' and roles 'darklord' and 'schwartz' darkhelmet = ludicrousspeed, darklord, schwartz # user 'lonestarr' with password 'vespa' and roles 'goodguy' and 'schwartz' lonestarr = vespa, goodguy, schwartz # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- # Roles with assigned permissions # # Each line conforms to the format defined in the # org.apache.shiro.realm.text.TextConfigurationRealm#setRoleDefinitions JavaDoc # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- [roles] # 'admin' role has all permissions, indicated by the wildcard '*' admin = * # The 'schwartz' role can do anything (*) with any lightsaber: schwartz = lightsaber:* # The 'goodguy' role is allowed to 'drive' (action) the winnebago (type) with # license plate 'eagle5' (instance specific id) goodguy = winnebago:drive:eagle5 -
QuickStart.class 分析
一些常用方法:
// 获取当前用户对象 Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 根据当前用户拿到 session Session session = currentUser.getSession(); // 判断当前用户是否被认证 currentUser.isAuthenticated() currentUser.getPrincipal() currentUser.hasRole("schwartz") currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield") // 注销 currentUser.logout();
SpringBoot 集成 Shiro
环境搭建
-
新建 SpringBoot 项目,添加 web、thymeleaf 依赖
-
编写 Controller
@Controller public class MyController { @RequestMapping({"/","/index"}) public String toIndex(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg", "hello"); return "index"; } } -
前端页面
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>首页</h1> <p th:text="${msg}"></p> </body> </html> -
测试,环境 OK!
Shiro 核心配置
-
导入 shrio 整合 Spring 的依赖
<!--导入 shiro 整合 Spring --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.shiro</groupId> <artifactId>shiro-spring</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency> -
编写 Shiro 的配置类 ShiroConfig.class,配置三个 Bean,即三大核心要素(对应三大核心对象):
- ShiroFilterFactoryBean:过滤对象【第 3 步:连到前端】-------> Subject 用户
- DefaultWebSecurityManager:安全对象【第 2 步:接管】--------> SecurityManager 管理所有用户
- Realm 对象,需要自定义【第 1 步:创建对象】-------> Realm 连接数据
@Configuration public class ShiroConfig { // ShiroFilterFactoryBean:3 // DefaultWebSecurityManager:2 // 创建 realm 对象,需要自定义:1 } -
自定义 Realm 对象,需要继承 AuthorizingRealm,重写两个方法:认证和授权
// 自定义的realm extends AuthorizingRealm public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm{ // 授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了 授权 doGetAuthorizationInfo"); return null; } // 认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行了 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo"); return null; } } -
将自定义的 Realm 对象注入 Bean 中
// 创建 realm 对象,需要自定义:1 @Bean public UserRealm userRealm(){ return new UserRealm(); } -
创建 DefaultWebSecurityManager 对象并注入 Bean 中,需要关联 Realm 对象(通过传参实现),因为它要对 Realm 对象进行管理
// DefaultWebSecurityManager:2 @Bean(name = "securityManager") public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){ DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); // 关联 userRealm securityManager.setRealm(userRealm); return securityManager; } -
创建 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 对象并注入 Bean 中,需要关联 securityManager(通过传参)
// ShiroFilterFactoryBean:3 @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); // 设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager); return bean; }
登录拦截
-
编写两个前端页面 /user/add 和 /user/update
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>add</h1> </body> </html><!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>update</h1> </body> </html> -
Controller 跳转
@RequestMapping("/user/add") public String add(){ return "user/add"; } @RequestMapping("/user/update") public String update(){ return "user/update"; } -
首页加入两个跳转的超链接
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a> | <a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a> -
测试,点击首页的 add 和 update,两个页面都可以进去
-
增加需求:对于某个页面,有些用户可以访问,有些用户不可以访问
-
在 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 对象,添加 Shiro 的内置过滤器
anon:无需认证就可以访问 authc:必须认证才可以访问 user:必须拥有 记住我 功能才能用 perms: 拥有对某个资源的权限才能访问 role:拥有某个角色的权限才能访问Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // 登录拦截 filterMap.put("/user/add", "authc"); filterMap.put("/user/update", "authc"); // filterMap.put("/user/*", "authc"); // 总和上面两个的作用,*为通配符 bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);Shiro 的内置过滤器源码: 运行 Web 应用时,Shiro会创建一些有用的默认 Filter 实例,并自动地在 [main] 项中将它们置为可用, 这些可用的默认的 Filter 实例是被 DefaultFilter 枚举类定义的(枚举的名称字段就是可供配置的名称) public enum DefaultFilter { anon(AnonymousFilter.class), authc(FormAuthenticationFilter.class), authcBasic(BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter.class), authcBearer(BearerHttpAuthenticationFilter.class), logout(LogoutFilter.class), noSessionCreation(NoSessionCreationFilter.class), perms(PermissionsAuthorizationFilter.class), port(PortFilter.class), rest(HttpMethodPermissionFilter.class), roles(RolesAuthorizationFilter.class), ssl(SslFilter.class), user(UserFilter.class); } -
测试,点击 add 和 update 都会跳转到错误页码,证明拦截成功
-
想要拦截之后跳转到登录页面,需要先编写一个登录页面
<h1>登录</h1> <p th:text="${msg}" style="color:red;"></p> <form th:action="@{/login}"> <p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username"></p> <p>密码:<input type="text" name="password"></p> <p><input type="submit"></p> </form> -
对应的需要在 Controller 中进行跳转
@RequestMapping("/toLogin") public String toLogin(){ return "login"; } -
在 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 中配置,如果没有权限,让其跳转到登录页面
// 设置登录的请求 bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin"); -
测试成功,点击 add 和 update 都会被拦截,而且跳转到自己编写的登录页面
登录拦截的 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 中配置总结
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
// 登录拦截
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 添加 shiro 的内置过滤器
filterMap.put("/user/*", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
// 设置登录的请求
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
return bean;
}
用户认证
用户的认证和授权在 Realm 对象中进行设置,然后和其他两个核心对象进行联动。
-
在 Controller 中通过前端提交的表单数据,获取当前用户信息并封装为令牌,对令牌执行登录的方法,如果信息错误则抛出异常(这些异常是 Shiro 已经定义好的)
@RequestMapping("/login") public String login(String username, String password, Model model){ // 获取当前的用户 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // 封装用户的登录数据 UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password); try{ subject.login(token); // 执行登录的方法,如果没有异常就说明 OK 了 return "index"; // 登录成功,返回首页 } catch (UnknownAccountException e){ //用户名不存在 model.addAttribute("msg", "用户名错误"); return "login"; } catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice){ //密码不存在 model.addAttribute("msg", "密码错误"); return "login"; } } -
在登录页面的表单上方添加一个提示信息,如果用户名或密码错误会提示
<p th:text="${msg}" style="color:red;"></p> -
测试,在表单中填写信息,会提示错误信息,因为我们还没有认证用户名和密码
注意:IDEA 控制台会显示 “执行了 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo”,说明执行了 UserRealm 的认证方法!
源码分析:在使用 SecurityUtils 的静态方法返回 getSubject() 之前,静态变量 securityManager 已经被加载,因为 securityManager 中管理着 Realm 对象,所以会执行 Realm 中的方法,但是为什么是执行了认证方法呢?是因为执行了 login() 方法,会将 token 传到 Authentication 吧
// 源码: public abstract class SecurityUtils { private static SecurityManager securityManager; public static Subject getSubject() { ... return subject; } } /* @param token * the token encapsulating the subject's principals and credentials to be passed to the Authentication subsystem for verification. */ void login(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException; -
因为执行了认证方法,所以我们可以在该方法中做一些操作:取出数据库中真实的用户信息,用于和用户填写的信息进行比对
// 认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行了 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo"); // 用户名,密码,数据库中取 String name = "root"; String password = "123456"; UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; if (!userToken.getUsername().equals(name)){ return null; //抛出异常 UnknownAccountException } // 可以加密 MD5 、MD5盐值加密 // 密码认证 shiro 做,加密了 return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",password,""); } -
测试,用户名和密码分别填写 root 和 123456,登录成功可以访问 add 和 update 页面。
用户认证:连接数据库,整合 MyBatis
-
导入依赖,使用 Druid 数据源
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- Druid --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid</artifactId> <version>1.1.21</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.18.10</version> </dependency> <!-- mybatis-spring-boot-starter:整合 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.1</version> </dependency> -
Druid 数据源信息 application.yaml
spring: datasource: username: root password: root url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # 自定义数据源 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource #Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定 #druid 数据源专有配置 initialSize: 5 minIdle: 5 maxActive: 20 maxWait: 60000 timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000 validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL testWhileIdle: true testOnBorrow: false testOnReturn: false poolPreparedStatements: true #配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入 #如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority #则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j filters: stat,wall,log4j maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20 useGlobalDataSourceStat: true connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500 -
将数据库绑定到 IDEA 中
-
配置 MyBatis,application.properties
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.song.pojo mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml -
根据数据库表的信息编写实体类,提前导入 Lombok
@Data @AllArgsConstructor @NoArgsConstructor public class User { private int id; private String name; private String pwd; private String perms; } -
编写 mapper 接口 UserMapper.class
@Repository @Mapper public interface UserMapper { public User queryUserByName(String name); } -
编写对应的 mapper 配置文件 UserMapper.xml,放在 resources/mapper 文件夹下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.song.mapper.UserMapper"> <select id="queryUserByName" resultType="User" parameterType="String"> select * from User where name = #{name} </select> </mapper> -
编写 service 层,UserService 接口及实现类
public interface UserService { public User queryUserByName(String name); }@Service public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{ @Autowired UserMapper userMapper; @Override public User queryUserByName(String name) { return userMapper.queryUserByName(name); } } -
测试,成功输出数据库中的“张三”对象,说明前面编写的代码没有问题
@SpringBootTest class ShiroSpringbootApplicationTests { @Autowired UserService userService; @Test void contextLoads() { System.out.println(userService.queryUserByName("张三")); } } -
用户认证:Realm 的认证方法中使用连接的数据库中的真实的数据
@Autowired UserService userService; // 认证 @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("执行了 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo"); UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token; // 连接真实数据库 User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername()); if (user == null){ // 没有这个人 return null; //UnknownAccountException } // 密码可以加密: MD5 、MD5盐值加密 return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPwd(),""); } -
测试,成功
用户授权
-
在 ShiroFilterFactoryBean 设置权限,并设置跳转的未授权页面,当进入设置权限的页面 /user/add 和 /user/update 时,会自动执行 Rleam 中的授权方法,所以要在 Rleam 的授权方法中做具体的授权操作
// ShiroFilterFactoryBean:3 @Bean public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){ ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); // 设置安全管理器 bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager); Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>(); // 通过 shiro 的内置过滤器 // 授权,正常情况下没有授权会跳转到未授权页面 filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]"); filterMap.put("/user/update","perms[user:update]"); // 登录拦截 filterMap.put("/user/*", "authc"); bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap); // 设置登录的请求 bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin"); // 未授权页 bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/noauth"); return bean; } -
Controller 跳转到未授权页面
@RequestMapping("/noauth") @ResponseBody public String unauthrized(){ return "未经授权无法访问此页面"; } -
测试,点击 add 会跳转到未授权页面,并且所有用户都是未授权,接下来要给用户授予访问的权限!
-
ShiroFilterFactoryBean 只是设置了权限,但是怎么把这个权限赋给用户呢?真正的授权操作在 Rleam 的授权方法中
// 授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了 授权 doGetAuthorizationInfo"); // SimpleAuthorizationInfo SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); // 授权 info.addStringPermission("user:add"); return info; } -
测试,/user/add 页面每个用户都可以进去,因为每个用户进入授权方法后都被授予了访问的权限,而在实际中不应该这样硬编码授权操作,应该根据数据库中的权限信息进行授权操作!
-
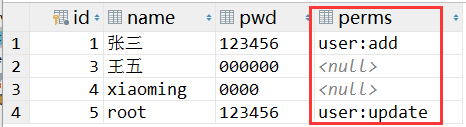
为数据库中的 User 表添加权限字段,对应实体类的属性字段也应该修改
![]()
-
根据数据库的 perms 字段设置权限
// 授权 @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) { System.out.println("执行了 授权 doGetAuthorizationInfo"); // SimpleAuthorizationInfo SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); // info.addStringPermission("user:add"); // 拿到当前登录的这个对象 Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); // user <= return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPwd(),""); // 第一个参数user,getPrincipal() 取出的是认证方法返回的对象中存的这个user User currentUser = (User) subject.getPrincipal(); // 拿到User对象 // 设置当前用户的权限 info.addStringPermission(currentUser.getPerms()); return info; }// SimpleAuthenticationInfo 源码 /* @param principal the 'primary' principal associated with the specified realm. * @param credentials the credentials that verify the given principal. * @param realmName the realm from where the principal and credentials were acquired. */ public SimpleAuthenticationInfo(Object principal, Object credentials, String realmName) { this.principals = new SimplePrincipalCollection(principal, realmName); this.credentials = credentials; } -
测试,用户“root”有访问 update 页面的权限,用户“张三”有访问 add 页面的权限,其他用户都不能访问这两个页面。
页面优化
让用户登录之后显示的信息不一样,比如:用户“root”登录之后只显示 update,而用户“张三”登录只显示 add,其他用户什么都不显示。可以使用 thymeleaf 进行操作。
-
导入 thymeleaf 整合包(和 Spring Security 很相似 thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity4)
<!--thymeleaf 和 shiro 整合包--> <dependency> <groupId>com.github.theborakompanioni</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiro</artifactId> <version>2.0.0</version> </dependency> -
在 ShiroConfig 中装配 Bean 来整合 shiro 和 thymeleaf
// 整合 ShiroDialect:用来整合 shiro thymeleaf @Bean public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){ return new ShiroDialect(); } -
修改前端 index.html 页面
先导入 shrio 的的命名空间
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro"修改之前的 add 和 update 页面
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:add"> <a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a> </div> <div shiro:hasPermission="user:update"> <a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a> </div> -
测试,需求实现,但是,当没有权限时 add 和 update 都没有,那么也就无法跳转到登录页面,说明缺少一个登录按钮,所以要增加一个登录按钮,让其在未登录时显示,登录之后不显示
-
编写前端代码,添加登录按钮
<!--从 session 中判断值--> <!--<div shiro:guest="true">--> <div th:if="${session.loginUser==null}"> <a th:href="@{/toLogin}" >登录</a> </div> -
在认证时查出来用户之后将信息传到前端,用来控制登录按钮的显示效果【这一步操作可以不写,可以在前端直接用 shiro 标签
shiro:guest="true"来实现】Subject currentSubject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); Session session = currentSubject.getSession(); session.setAttribute("loginUser",user); //前端可以拿到这个 user -
测试,登录按钮的显示效果成功实现
总结
1、Controller 层
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index"})
public String toIndex(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg", "hello");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/add")
public String add(){
return "user/add";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/update")
public String update(){
return "user/update";
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password, Model model){
// 获取当前的用户
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 封装用户的登录数据
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password);
try{
subject.login(token); // 执行登录的方法,如果没有异常就说明 OK 了
return "index";
} catch (UnknownAccountException e){ //用户名不存在
model.addAttribute("msg", "用户名错误");
return "login";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice){ //密码不存在
model.addAttribute("msg", "密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
@RequestMapping("/noauth")
@ResponseBody
public String unauthrized(){
return "未经授权无法访问此页面";
}
}
2、自定义的 Realm
// 自定义的realm extends AuthorizingRealm
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm{
@Autowired
UserService userService;
// 授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("执行了 授权 doGetAuthorizationInfo");
// SimpleAuthorizationInfo
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
// 每个用户都会被授予 user:add 权限
// info.addStringPermission("user:add");
// 拿到当前登录的这个对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// user <= return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPwd(),"");
// 第一个参数user,getPrincipal() 取出的就是认证方法返回的对象中存的这个user
User currentUser = (User) subject.getPrincipal();
// 设置当前用户的权限
info.addStringPermission(currentUser.getPerms());
return info;
}
// 认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("执行了 认证 doGetAuthenticationInfo");
/* // 用户名,密码,数据库中取,这里未连接数据可
String name = "root";
String password = "123456";
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
if (!userToken.getUsername().equals(name)){
return null; //抛出异常 UnknownAccountException
}
// 密码认证 shiro 做,加密了
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",password,"");*/
// 连接真实数据库
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) token;
User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername());
if (user == null){ // 没有这个人
return null; //UnknownAccountException
}
// 用于登录按钮是否显示
Subject currentSubject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
Session session = currentSubject.getSession();
session.setAttribute("loginUser",user); //前端可以拿到这个 user
// return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",user.getPwd(),"");
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPwd(),"");//第一个参数用于授权
}
}
3、ShrioConfig 配置类
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
// ShiroFilterFactoryBean:3
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
// 设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
// 添加 shiro 的内置过滤器
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 授权,正常情况下没有授权会跳转到未授权页面
filterMap.put("/user/add","perms[user:add]");
filterMap.put("/user/update","perms[user:update]");
// 登录拦截
// filterMap.put("/user/add", "authc");
// filterMap.put("/user/update", "authc");
filterMap.put("/user/*", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
// 设置登录的请求
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
// 未授权页面
bean.setUnauthorizedUrl("/noauth");
return bean;
}
// DefaultWebSecurityManager:2
@Bean(name = "securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
// 关联 userRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
return securityManager;
}
// 创建 realm 对象,需要自定义:1
@Bean
public UserRealm userRealm(){
return new UserRealm();
}
// 整合 ShiroDialect:用来整合 shiro thymeleaf
@Bean
public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){
return new ShiroDialect();
}
}
4、前端页面 index.html 和 login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:shiro="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>首页</h1>
<!--从 session 中判断值-->
<!--<div shiro:guest="true">-->
<div th:if="${session.loginUser==null}">
<a th:href="@{/toLogin}" >登录</a>
</div>
<p th:text="${msg}"></p>
<hr>
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:add">
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">add</a>
</div>
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:update">
<a th:href="@{/user/update}">update</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登录</h1>
<p th:text="${msg}" style="color:red;"></p>
<form th:action="@{/login}">
<p>用户名:<input type="text" name="username"></p>
<p>密码:<input type="text" name="password"></p>
<p><input type="submit"></p>
</form>
</body>
</html>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号