Axis2框架下SSL扩展开发
Axis2框架下SSL扩展开发
问题:
所有的SSL鉴权代码都是通过设置全局变量来指定需要使用的证书库和密钥库,然而我需要根据业务上的请求来指定访问其他服务器的证书和密钥。但是使用全局变量会导致冲突。
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStore", keyStoreFilePath);
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStorePassword", "mypassword");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.trustStoreType", "JKS");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStore", keyStoreFilePath);
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStorePassword", "mypassword");
System.setProperty("javax.net.ssl.keyStoreType", "JKS");
我的目的是能够自由的根据每一个请求线程获取的特定参数来决定所需要使用的指定证书和密钥。
Axis2帮我们做了什么?
(Axis2框架介绍)
http://www.cnblogs.com/cliffever/archive/2006/03/22/355753.html
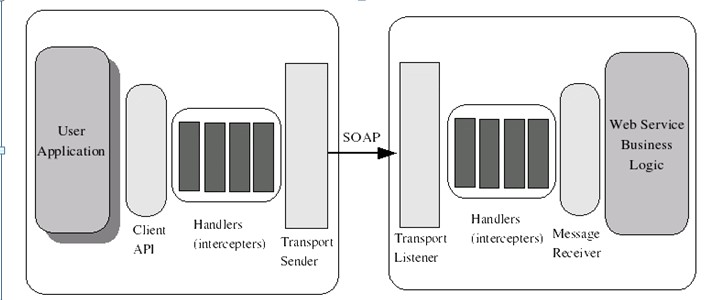
拥有自定义handler,可以写自己的拦截器,对消息体进行处理。
拥有可配置的Transport模块
SSL认证是怎么实现的
SSL是一个介于HTTP协议与TCP之间的一个可选层,其位置大致如下:
---------
| HTTP |
---------
| SSL |
---------
| TCP |
---------
| IP |
---------
如果利用SSL协议来访问网页,其步骤如下:
用户:在浏览器的地址栏里输入https://www.sslserver.com
HTTP层:将用户需求翻译成HTTP请求,如
GET /index.htm HTTP/1.1
Host http://www.sslserver.com
SSL层: 借助下层协议的的信道安全的协商出一份加密密钥,并用此密钥来加密HTTP请求。
TCP层:与web server的443端口建立连接,传递SSL处理后的数据。
接收端与此过程相反。
可见SSL协议是在HTTP协议层之下,那么Axis2中的handler模块如果只能够在HTTP层进行消息处理,那就无法控制SSL层的行为,即无法控制系统使用默认配置来执行SSL认证,使用全局的SSL证书和密钥(或许可以实现,后面再叙)所以我需要通过修改Axis2配置来替换Axis2中的transport模块,自行定制SSL协议使用证书和密钥的行为。
Axis2配置
让我们来看一下如何通过配置Axis2的配置文件来自定义扩展其中的transport sender模块
(Axis2配置指南(翻译))
http://fenghuolun.iteye.com/blog/144371
<transportSender name="https"
class="org.apache.axis2.transport.http.CommonsHTTPTransportSender">
<parameter name="PROTOCOL">HTTP/1.0</parameter>
<parameter name="Transfer-Encoding">chunked</parameter>
</transportSender>
上面的元素说明了如何在axis2.xml中定义传输接收端,这里,transportSender标签中的name属性标识指明传输接收端的类型,它可以是http,tcp,smtp,CommonsHTTP等。当系统启动或者你在客户端设置传输器(transport)的时候,你可以使用这些传输名字(transport names)装载合适的传输器。class属性是为了指明为该传输器实现需要的接口的实际的java类。
我只需要将其中的HTTPS类型协议所对应的处理类指定成我自定义的java类,然后在自定义的java类中定制SSL协议,既可以自行控制SSL协议如何处理证书了。
(或许如果这里的class为org.apache.axis2.transport.tcp.TCPTransportSender那么是否可以使用handler来自行处理HTTP和SSL层?没有考证,但是应该不简单,不是最佳路线)
如何定制SSL
(为高级 JSSE 开发人员定制 SSL)
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-customssl/
实现技术:
JSSE(Java Security Socket Extension)
是Sun为了解决在Internet上的安全通讯而推出的解决方案。它实现了SSL和TSL(传输层安全)协议。在JSSE中包含了数据加密,服务器验证,消息完整性和客户端验证等技术。通过使用JSSE,开发人员可以在客户机和服务器之间通过TCP/IP协议安全地传输数据
为了实现消息认证。
Server需要:
1)KeyStore: 其中保存服务端的私钥
2)Trust KeyStore:其中保存客户端的授权证书
同样,Client需要:
1)KeyStore:其中保存客户端的私钥
2)Trust KeyStore:其中保存服务端的授权证书
链接中有步骤自行查阅
(SSL双向认证java实现)
http://www.blogjava.net/stone2083/archive/2007/12/20/169015.html
主要目的是需要实现一个SSLcontext
SSLContext ctx = SSLContext.getInstance("SSL");
KeyManagerFactory kmf = KeyManagerFactory.getInstance("SunX509");
TrustManagerFactory tmf = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance("SunX509");
KeyStore ks = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
KeyStore tks = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
ks.load(new FileInputStream("data/kclient.keystore"), CLIENT_KEY_STORE_PASSWORD.toCharArray());
tks.load(new FileInputStream("data/tclient.keystore"), CLIENT_TRUST_KEY_STORE_PASSWORD.toCharArray());
kmf.init(ks, CLIENT_KEY_STORE_PASSWORD.toCharArray());
tmf.init(tks);
ctx.init(kmf.getKeyManagers(), tmf.getTrustManagers(), null);
return (SSLSocket) ctx.getSocketFactory().createSocket(DEFAULT_HOST, DEFAULT_PORT);
有了SSLContext后
可以按如下方式使用HttpClient
Protocol myhttps = new Protocol("https", new MySecureProtocolSocketFactory (), 443);
Protocol.registerProtocol("https", myhttps);
HttpClient httpclient=new HttpClient();
自定义transport Sender类(关键步骤)
<transportSender name="https" class="com.**.**.common.MyHTTPTransport">
<parameter name="PROTOCOL">HTTP/1.0</parameter>
<parameter name="Transfer-Encoding">chunked</parameter>
</transportSender>
创建java类MyHTTPTransport直接继承TransportSender,并且复制其中的方法。
在其中的writeMessageWithCommons方法中会使用到AbstractHTTPSender和HttpSender,同样的方法,继承并复制其中的方法创建MyAbstractHTTPSender和MyHttpSender类。
配置了自定义的处理类后,剩下的是如何传入定制的SSLcontext和如何在httpsender中使用它
在HttpSender中的getHostConfiguration方法中会看到这么一段话:(Axis2的开发人员很幽默)
// I assume the 90% case, or even 99% case will be no protocol handler case.
if (protocolHandler == null) {
config.setHost(targetURL.getHost(), port, targetURL.getProtocol());
} else {
config.setHost(targetURL.getHost(), port, protocolHandler);
}
如此则可以将上面自定的protocol(包含配置好的sslcontext)传进来即可,通过configContext传入
String path = FileUtil.getWebInfPath();
ConfigurationContext configContext = ConfigurationContextFactory
.createConfigurationContextFromFileSystem(path, path + "conf/axis2.xml");
AuthSSLProtocolSocketFactory sslProtocalFactory = new AuthSSLProtocolSocketFactory(vdiConfig.getCertStream(),vdiConfig.getPk());
ProtocolSocketFactory socketFactory = (ProtocolSocketFactory)sslProtocalFactory;
Protocol authhttps = new Protocol("https",socketFactory,443);
configContext.setProperty("httpsProtocol", authhttps);
vdistub = new VdsServiceStub(configContext,ItaURL);
然后在HttpSender中的getHostConfiguration方法中加入设置代码
Protocol authhttps = (Protocol)msgCtx.getConfigurationContext().getProperty("httpsProtocol");
protocolHandler = authhttps;




