洛谷链接&Atcoder 链接
本篇题解为此题较简单做法及较少码量,并且码风优良,请放心阅读。
从数轴的原点开始向正方向走。
第一次向前走 步,第二次向前走 ,以此类推。
求走过的最大位置。
首先直接模拟时间复杂度 ,看一下数据范围 得知此方法会超时。
那么就需要一点优化,用前缀和即可解决此题,没学过前缀和的建议看这个。通过前缀和求出前 项的和就很容易解决此题了:
先预处理前缀和,在预处理的过程中同步求最大值,但因为此题的答案即最大值有可能在过程中产生,故需要 遍历前缀和求最大,此时间复杂度可以接受。
经过以上分析和前缀和优化,很容易即可得出代码了:
提交记录
洛谷链接&Atcoder 链接
本篇题解为此题较简单做法及较少码量,并且码风优良,请放心阅读。
现在有一个字符串 ,每一次你可以选择一个 ,如果 。就可以将 设为
求最多能操作几次。
本题比较贪心,让我们先来造一个样例解释一下:
如 abbfioidddssabsaa 最优的方案是:
-
先操作 次变为 abbfioidddsssssss。
-
再操作 次变为 abbfioidddddddddd。
-
最后操作 次变为 abbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb。
这样最大总操作次数为 次。
从这个样例中可以发现贪心思路,要想总操作次数最大化,就需要从后到前去操作,如果从前到后操作那么后面可操作的连续字母就会被覆盖,这样总操作次数就不是最大了。
对于每次操作,最优的是把后面的所有不相同的字母变为一样,这就涉及到一个问题,如果后面有相同字母如何判断?其实不必再从当前位置往后搜,只需要定义一个 一维数组用 表示当前位置的后面字母 的个数。
对于 数组需要在搜的过程中处理。如果遇到可以替换的情况就把当前位置后的字母全变为当前字母,同时需清空 数组的记录,把当前位置的字母数记录即可。
替换后, 需增加 ,考虑到后面的相同字母,所以就需要用到我们维护的 数组了,所以操作数需减去 。
经过以上分析及优化后,很容易即可写出代码了:
提交记录
题目描述
北方之大德鲁伊天空之怒释放的大回复术是一等一的神术。大回复术之所以能够有极强的治疗效果,是因为该法术能够以人体经络为基本,并建立至多两条(也可以一条都不建立)用于疏通能量的经络。
人体的经络可以看作一张 个点的图,里面有 条已经连接好的经络。大回复术能够新建至多两条经络。如果每一个点都有偶数条经络与之相连,则经络中的能量会立刻循环往复生生不息,达到治疗的效果。现在你需要回答的是,对于一个给出的经络图,是否能够通过施展大回复术使得其中的能量生生不息。
输入格式
第一行两个整数 和 ,接下来 行每行两个整数表示一条已经存在的经络。
输出格式
输出一行,为 true 或者 false。
样例输入
样例输出
添加 4-5 即可。
样例输入
样例输出
添加 1-3、2-4 即可。
样例输入
样例输出
数据规模
点击查看代码
题目描述
一个雪花图是由两个大于 的整数 和 构成的:
从一个中心点开始
有 个点连接着中心点
个点中每个点都有y个点与其连接着
下面是当 时的一张雪花图:
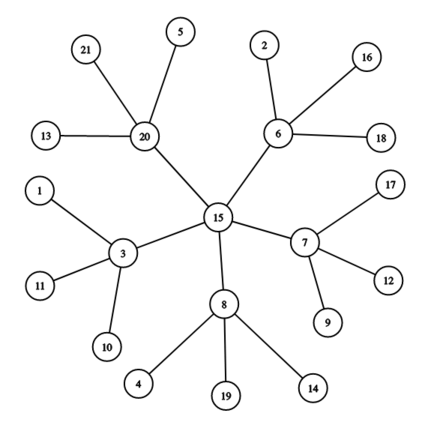
上图的中心点为 , 个 点分别为:,每个点都有 个点与其连着.
现在给你一张雪花图,请你确定该图 和 的值.
输入格式
第一行包含一个正整数 ,表示测试数据组数
对于每个测试数据,第一行包含两个整数 和 ,表示雪花图的点数和边数.
接下来 行每行包含两个整数 和 ,代表一条边.
数据保证没有重边和自环并且一定是一张雪花图, 和 均大于
输出格式
对于每个测试数据,每行空格输出 和 .
样例输入#1
样例输出#1
点击查看代码
题目描述
树是一种常见的数据结构.
一棵树的根节点只有一个,并且没有其他点指向它.从根节点遍历有向边,我们只会得到唯一的一个序列.
例如,下图中前两个例子是树,第三个不是:

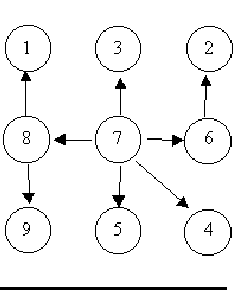
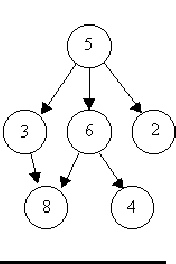
给你 张有向图,请你判断每张图是否是一颗树.
输入格式
第一行包含一个正整数 ,表示测试数据组数
对于每个测试数据,第一行包含两个整数 和 ,表示图的点数和边数.
接下来 行每行包含两个整数 和 ,代表一条 指向 的边.
数据保证没有重边和自环.
对于所有测试数据,数据总量不超过 .
输出格式
对于每个测试数据,输出 Case k is a tree.;如果第 个测试数据是一棵树,否则输出 Case k is not a tree.
样例输入#1
样例输出#1
点击查看代码
using namespace std;
int T, n, m, vis[200005], num = 0;
vector<int> v[200005];
void dfs(int x) {
vis[x] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < v[x].size(); i ++) {
if(vis[v[x][i]]) continue;
dfs(v[x][i]);
}
return;
}
void f(int Case) {
bool flag;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) v[i].clear(), vis[i] = false;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
int from, to;
cin >> from >> to;
v[from].push_back(to);
v[to].push_back(from);
}
dfs(1);
if(count(vis + 1, vis + n + 1, true) == n) flag = true;
else flag = false;
if(m != n - 1) flag = false;
if(flag) printf("Case %d is a tree.\n", Case);
else printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n", Case);
return;
}
int main() {
cin >> T;
for(int j = 1; j <= T; j ++) f(j);
return 0;
}
编译结果
compiled successfully
time: 456ms, memory: 15532kb, score: 100, status: Accepted
> test 1: time: 2ms, memory: 8224kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 2: time: 46ms, memory: 8280kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 3: time: 35ms, memory: 8168kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 4: time: 16ms, memory: 8292kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 5: time: 37ms, memory: 8272kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 6: time: 45ms, memory: 8160kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 7: time: 47ms, memory: 8284kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 8: time: 47ms, memory: 8048kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 9: time: 53ms, memory: 8180kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
> test 10: time: 128ms, memory: 15532kb, points: 10, status: Accepted
__EOF__





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】