Ajax
Ajax
Ajax优点与精髓
1、精髓
1、异步提交
2、局部刷新
2、优点
不重新加载整个页面的情况下,可以与服务器交换数据并更新部分网页内容。(这一特点给用户的感受是在不知不觉中完成请求和响应过程)
AJAX 不需要任何浏览器插件,但需要用户允许JavaScript在浏览器上执行。
同步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,需要等待服务器响应结束后,才能发出第二个请求;
异步交互:客户端发出一个请求后,无需等待服务器响应结束,就可以发出第二个请求。
Ajax基本语法
<script>
// 先给按钮绑定一个点击事件
$('#btn').click(function () {
// 朝后端发生ajax请求
$.ajax({
// 指定朝那个后端发请求
url:'', //不写就是朝当前地址提交
//请求方式
type:'post', //不指定默认是get 都是小写
// 数据
data:{'i1':$('#d1').val(), 'i2':$('#d2').val()},
// 回调函数(异步回调机制):当后端给你返回结果的时候自动触发,args接受后端的返回结果
success:function (args) {
{#alert(args)#}
$('#d3').val(args)
}
})
})
</script>
小练习
代码
views.py文件
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse
# Create your views here.
def ab_ajax(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.POST)
i1 = request.POST.get('i1')
i2 = request.POST.get('i2')
i3 = int(i1) + int(i2)
print(i3)
return HttpResponse(i3)
return render(request, 'index.html')
html文件
<body>
<input type="text" id="d1">+
<input type="text" id="d2">=
<input type="text" id="d3">
<div>
<button id="btn">点击</button>
</div>
<script>
// 先给按钮绑定一个点击事件
$('#btn').click(function () {
// 朝后端发生ajax请求
$.ajax({
// 指定朝那个后端发请求
url:'', //不写就是朝当前地址提交
//请求方式
type:'post', //不指定默认是get 都是小写
// 数据
data:{'i1':$('#d1').val(), 'i2':$('#d2').val()},
// 回调函数(异步回调机制):当后端给你返回结果的时候自动触发,args接受后端的返回结果
success:function (args) {
{#alert(args)#}
$('#d3').val(args)
}
})
})
</script>
</body>
效果
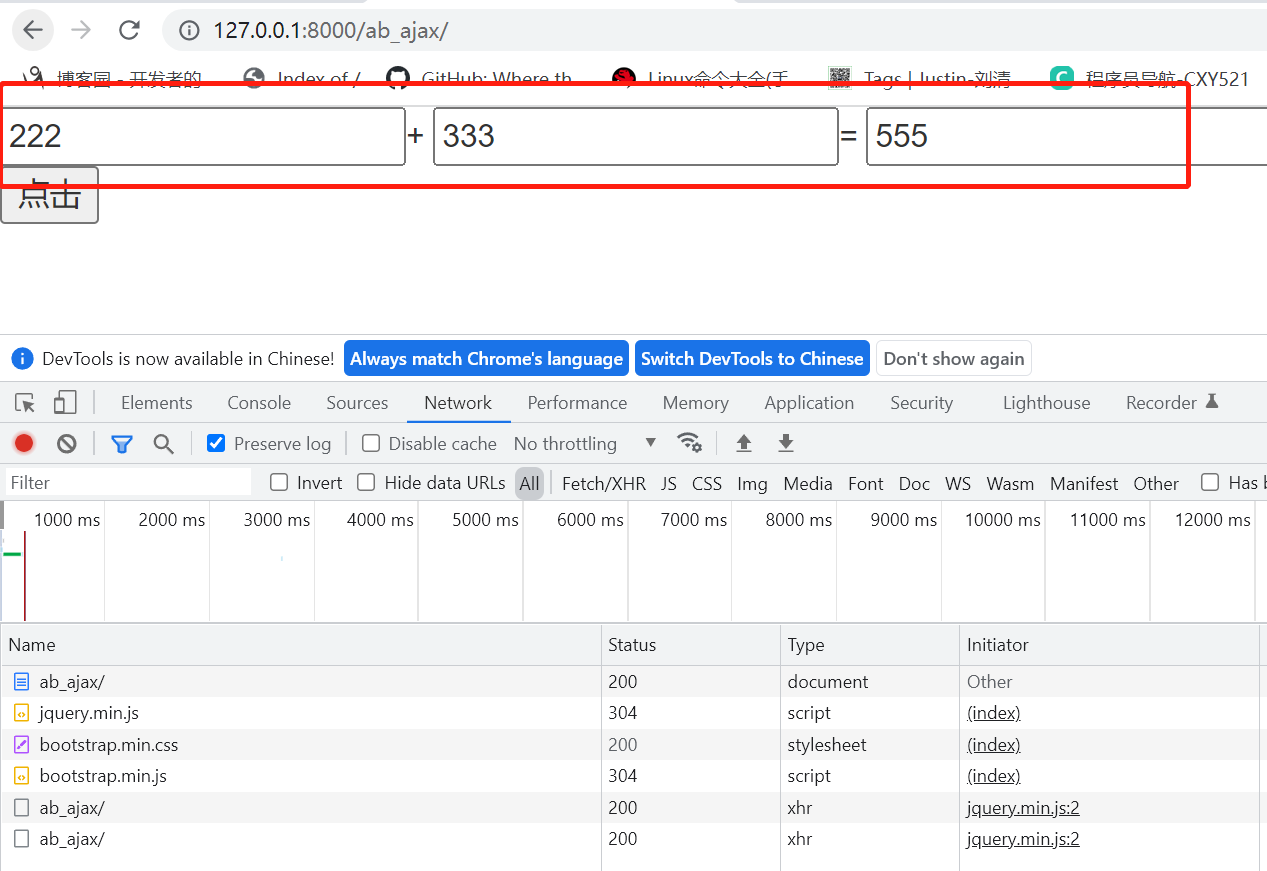
注意事项
1、后端使用HttpResponse,前端使用下面的方式
// 反序列化
res = JSON.parse(res) // {}
console.log(res.username);
2、后端使用JsonResponse,前端使用下面的方式
// 反序列化 console.log(res.username);
3、 指定请求方式
// 指定后端返回的数据格式 dataType:'json',
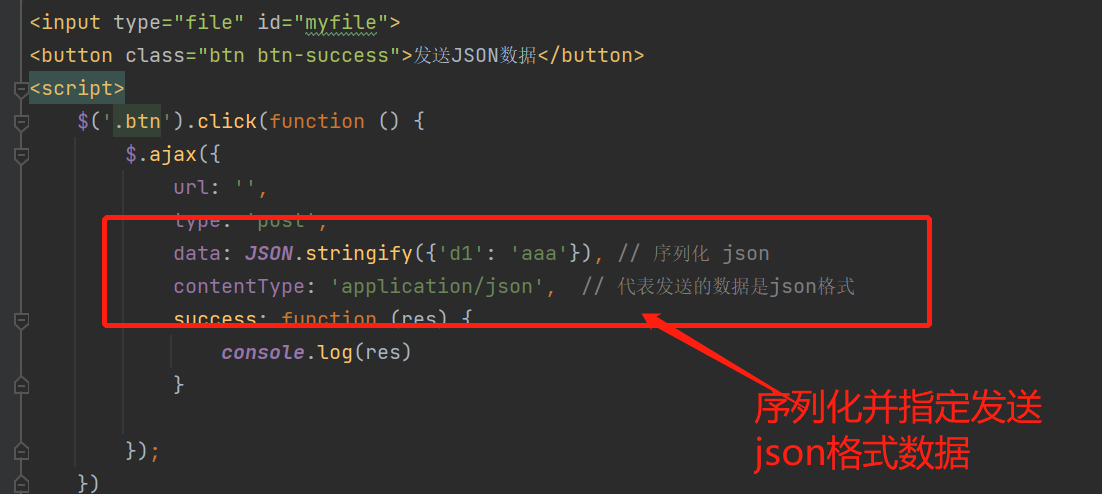
Ajax发送json格式数据
前端html
<input type="file" id="myfile">
<button class="btn btn-success">发送JSON数据</button>
<script>
$('.btn').click(function () {
$.ajax({
url: '',
type: 'post',
data: JSON.stringify({'d1': 'aaa'}), // 序列化 json
contentType: 'application/json', // 代表发送的数据是json格式
success: function (res) {
console.log(res)
}
});
})
</script>
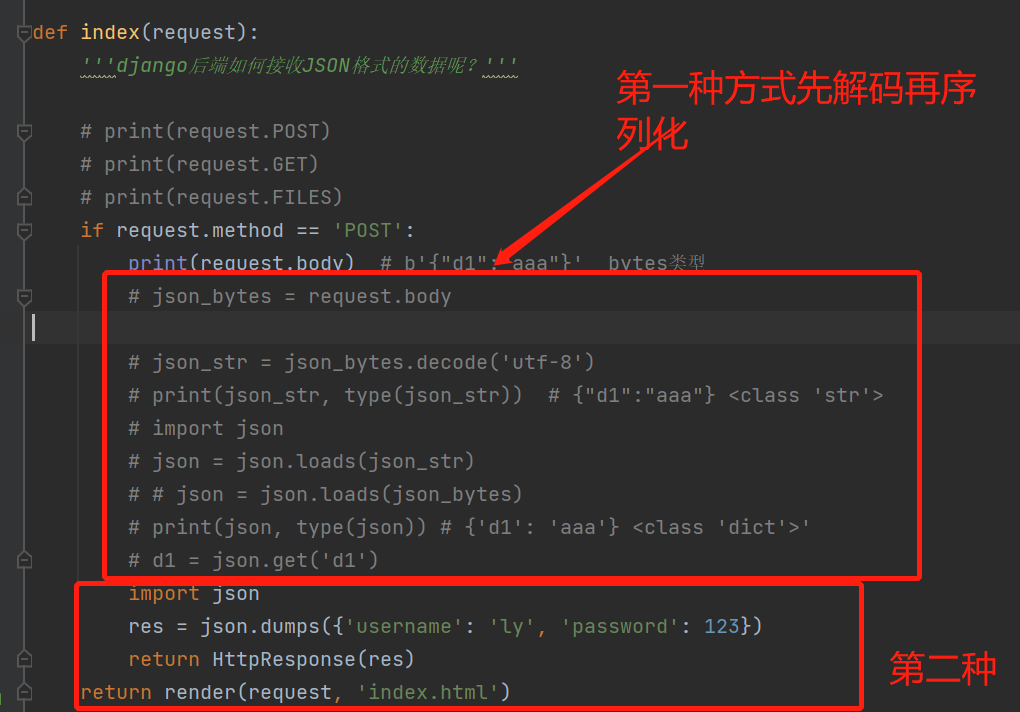
后端
def index(request):
'''django后端如何接收JSON格式的数据呢?'''
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.body) # b'{"d1":"aaa"}' bytes类型
第一种方式
# json_bytes = request.body
# json_str = json_bytes.decode('utf-8')
# print(json_str, type(json_str)) # {"d1":"aaa"} <class 'str'>
# import json
# json = json.loads(json_str)
# # json = json.loads(json_bytes)
# print(json, type(json)) # {'d1': 'aaa'} <class 'dict'>'
# d1 = json.get('d1')
第二种方式
import json
res = json.dumps({'username': 'ly', 'password': 123})
return HttpResponse(res)
return render(request, 'index.html')
json.dumps括号内如果传入了一个二进制格式的数据那么内部自动解码(编码)再反序列化
api工具
Ajax发送文件数据
form表单
前端html
<p>username:
<input type="text" id="d1">
</p>
<p>password:
<input type="text" id="d2">
</p>
<p><input type="file" id="d3">
</p>
<button class="btn btn-info" id="d4">点我</button>
<script>
// 点击按钮超后端发送普通键值对和文件数据
$('#d4').on('click', function () {
// 需要先利用FormData内置对象
let formDataObj = new FormData();
// 添加普通的键值对
formDataObj.append('username', $('#d1').val())
formDataObj.append('password', $('#d2').val())
// 添加文件对象
formDataObj.append('myfile', $('#d3')[0].files[0])
// 将对象基于Ajax发送给后端
$.ajax({
url:'',
type:'post',
data:formDataObj, // 直接将对象放在data后面即可
// ajax发送文件必须要指定的两个参数
contentType:false, // 不需要使用任何编码,django后端能够自动识别formdata对象
processData:false, // 告诉浏览器不要对你的数据进行任何处理
success:function (args) {
}
})
})
</script>
后端
def ab_file(request):
if request.is_ajax():
if request.method == 'POST':
print(request.POST)
print(request.FILES)
return render(request, 'ab_file.html')
总结
1、需要利用内置对象FormData
// 添加普通的键值对
formDataObj.append('username', $('#d1').val())
formDataObj.append('password', $('#d2').val())
// 添加文件对象
formDataObj.append('myfile', $('#d3')[0].files[0])
2、需要指定两个关键参数
// ajax发送文件必须要指定的两个参数
contentType:false , // 不需要使用任何编码,django后端能够自动识别formdata对象
processData: false, // 告诉浏览器不要对你的数据进行任何处理
3、Django后端能够直接识别到formdata对象并且能够将内部的普通键值自动解析并封装到request.POST中,文件数据自动解析并封装到request.FILES中



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号