自定义注解实现接口鉴权以及日志打印
自定义注解的使用
1.项目中我们经常使用到之定义注解,主要原理就是 通过反射获取注解对象,从而获取到注解的属性值,然后通过注解对象的属性来进行一些业务操作
2.注解通常只定义了一些成员方法,成员变量,或者枚举类
3.只有注解被使用时,那些方法或者变量或者枚举类才被真正意义上赋值;
4.然后通过反射的方式拿到注解上定义的属性,然后再执行业务代码
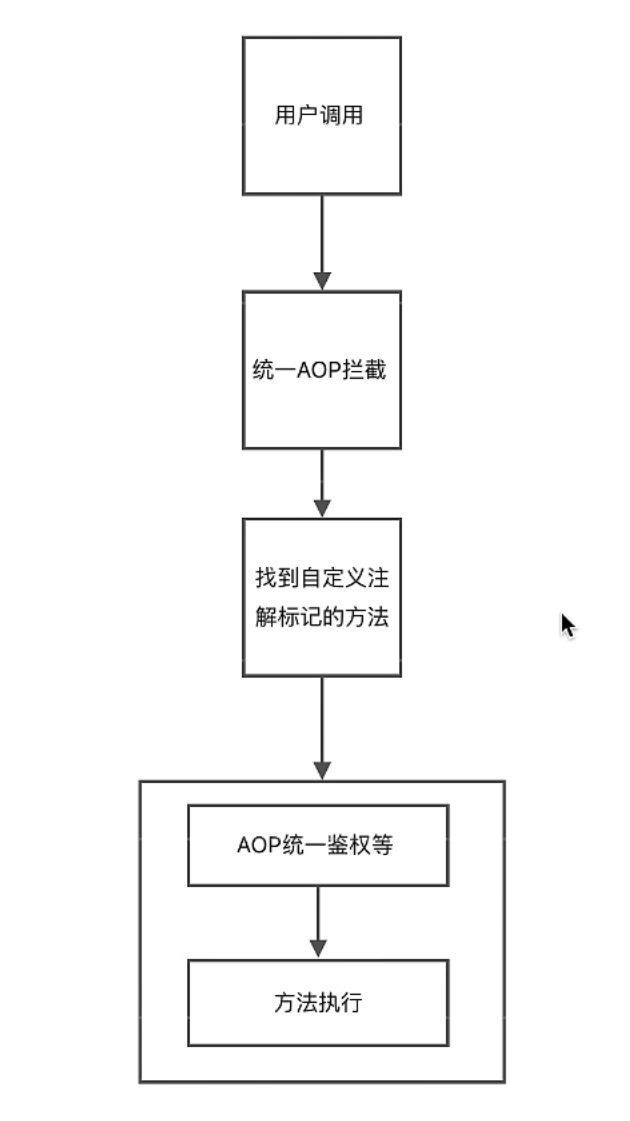
自定义注解
package com.villagechief;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author: villageChief
* @date: 2022/7/27
* @Description: Enjoy your work today! A better you a bigger world!
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MethodAuthLog {
//方法的说明
String logInfo();
//执行方法的权限
String auth();
}
注解执行类,aop打印日志
package com.villagechief; /**
* @author: villagechief
* @date: 2022/7/27
* @Description: Enjoy your work today! A better you a bigger world!
*/
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @Version V1.0
* @Author: leo
* @Date: 2022/7/27 22:30
* @Description:Enjoy your work today! A better you a bigger world!
*/
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MethodAuthLogAspect {
private static final String ACCOUNT_NAME = "张三";
@Around("@annotation(com.villagechief.MethodAuthLog)")
public Object processPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
//获取切入点上面的注解对象
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
MethodAuthLog annotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, MethodAuthLog.class);
//判断这个方法是否有这个注解
MethodAuthLog annotation = null;
boolean isMethodAuthLog = method.isAnnotationPresent(MethodAuthLog.class);
if (isMethodAuthLog) {
annotation = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(method, MethodAuthLog.class);
} else {
return point.proceed();
}
//获取注解上的属性对象
String methodLog = annotation.logInfo();
String auth = annotation.auth();
//获取织入方法的参数数组
Object[] args = point.getArgs();
System.out.println("===========取钱人的账号是=============");
Arrays.stream(args).forEach(System.out::println);
String account = (String) args[0];
// 模拟鉴权
Boolean aBoolean = authCheck(account, auth);
if (!aBoolean) {
throw new RuntimeException("没有权限");
}
log.info(methodLog + "#" + account);
Object proceed = point.proceed();
log.info(methodLog + "#" + account + "取钱执行完成");
return proceed;
}
private Boolean authCheck(String account, String auth) {
if (ACCOUNT_NAME.equals(account)) {
System.out.println("account" + account + " 是正确的账号,真的取到了钱");
return true;
} else {
System.out.println("account" + account + " 是错误的账号,不能取钱");
return false;
}
}
}
使用注解的任务类
package com.villagechief;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @Version V1.0
* @Author: leo
* @Date: 2022/7/27 22:37
* @Description:Enjoy your work today! A better you a bigger world!
*/
@Component
public class ServiceTask {
private static final String ACCOUNT_NAME="张三";
/**
* 注解应用
* @param account
* @return
*/
@MethodAuthLog(logInfo = "ServiceTask执行了", auth = "admin")
public void getMoney(String account) {
System.out.println(account+"取了" + 100000);
}
}
springboot 测试类
package com.villagechief;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = HelloworldMainApplication.class)
public class AnnotionUseTest {
public AnnotionUseTest() {
}
@Autowired
ServiceTask annotionTask;
@Test
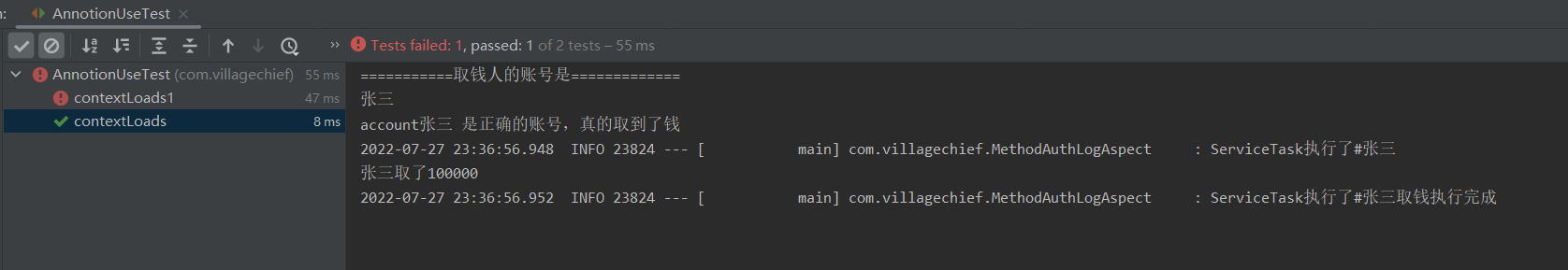
public void contextLoads() {
annotionTask.getMoney("张三");
}
@Test
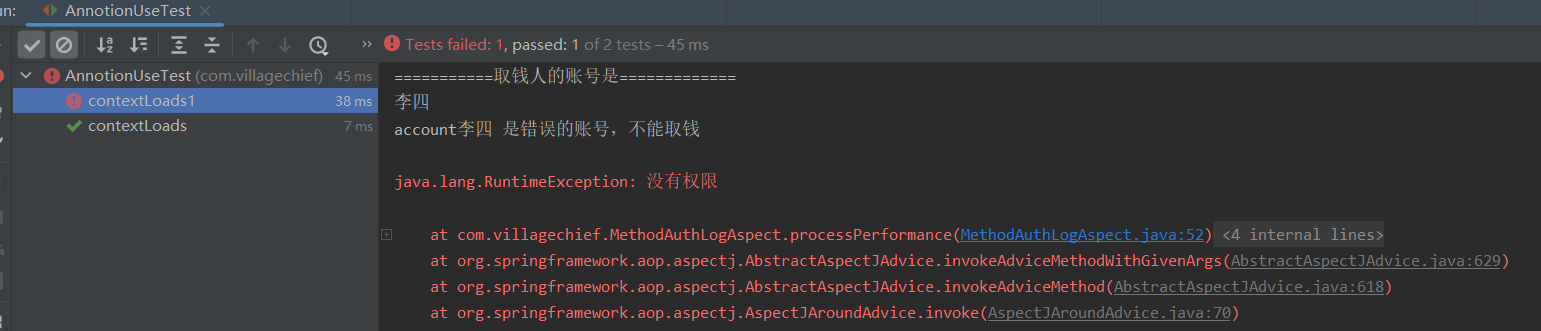
public void contextLoads1() {
annotionTask.getMoney("李四");
}
}
执行结果


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号