十大经典排序排序算法学习总结(C++实现)
常用算法总结记录一下,否则会变得只记得算法名,也可能名都记不住。
图片和动图(我不会画),但我从网上找到了资源。
代码我用C/C++实现的,运行结果都有验证。
时间复杂度和空间复杂度我还没有研究,各种地方抄到的,以后有时间再研究,如果有错误,还请指正。

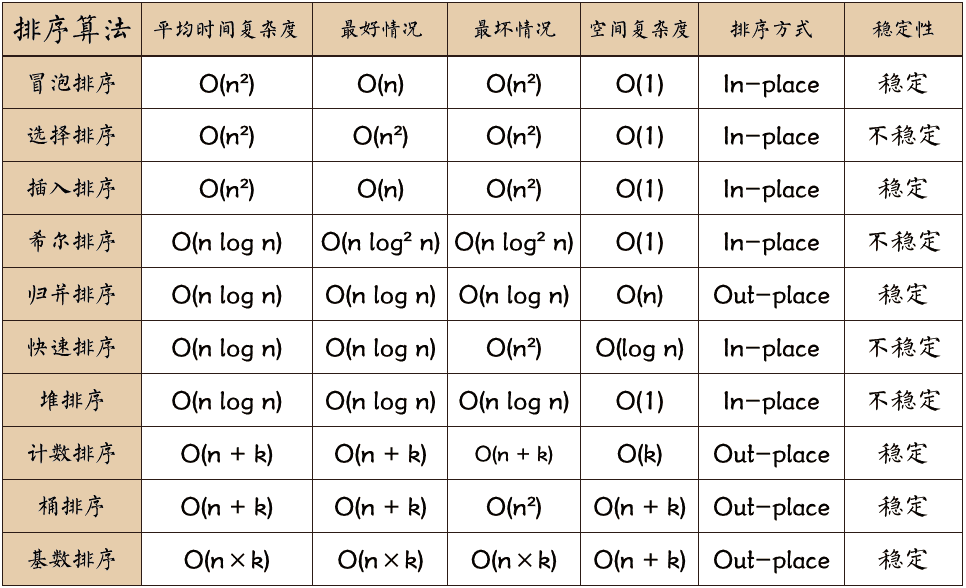
In/out-place: 不占/占额外内存
1.冒泡排序
冒泡排序算法原理:
比较相邻的元素。如果第一个比第二个大,就交换他们两个。
循环重复以上步骤,直到没有任何一对元素需要比较。
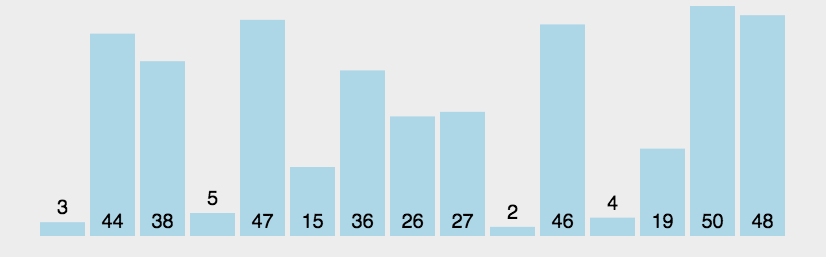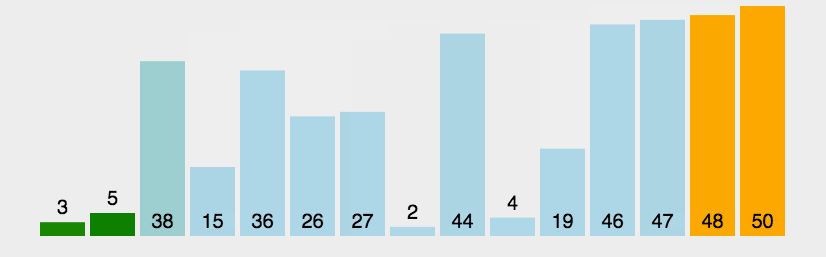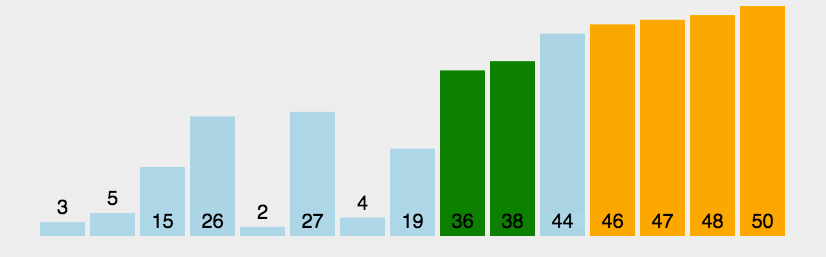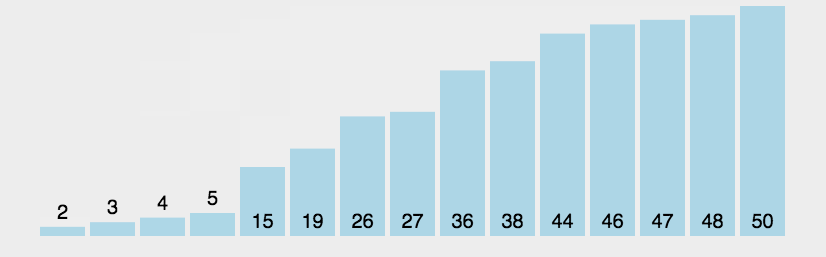
还有位前辈也画的挺好,我也把图贴过来了。

冒泡排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
冒泡排序时间复杂度:最好 O( n) 最坏 O( n2 ) ,平均 O( n2 ) 。
冒泡排序空间复杂度:O( 1 ) 。
冒泡排序是一种稳定排序算法。
冒泡排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 template <typename T> 6 void BubbleSort(T arr[], int len) 7 { 8 if (NULL == arr || 0 >= len) 9 return; 10 11 int i = 0, j = 0, nFlag = 0; 12 13 for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) 14 { 15 nFlag = 0; 16 17 for (j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++) 18 { 19 if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) 20 { 21 arr[j] = arr[j] ^ arr[j + 1]; 22 arr[j + 1] = arr[j] ^ arr[j + 1]; 23 arr[j] = arr[j] ^ arr[j + 1]; 24 nFlag = j + 1; // 记录最大交换位置 25 } 26 } 27 28 if (0 == nFlag) 29 return; 30 31 // len - i = nFlag 32 i = len - nFlag - 1; // 循环后 i 会 + 1,此处要把当前 i - 1,然后进行下一次循环 33 } 34 } 35 36 37 int main() 38 { 39 system("color 02"); 40 41 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 42 int len = _countof(arr); 43 44 cout << "原始数组:"; 45 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 46 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 47 cout << endl; 48 49 cout << "---------- Begin BubbleSort ----------" << endl; 50 BubbleSort(arr, len); 51 cout << "========== End BubbleSort ==========" << endl; 52 53 cout << "排序数组:"; 54 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 55 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 56 cout << endl; 57 58 system("pause"); 59 return 0; 60 }
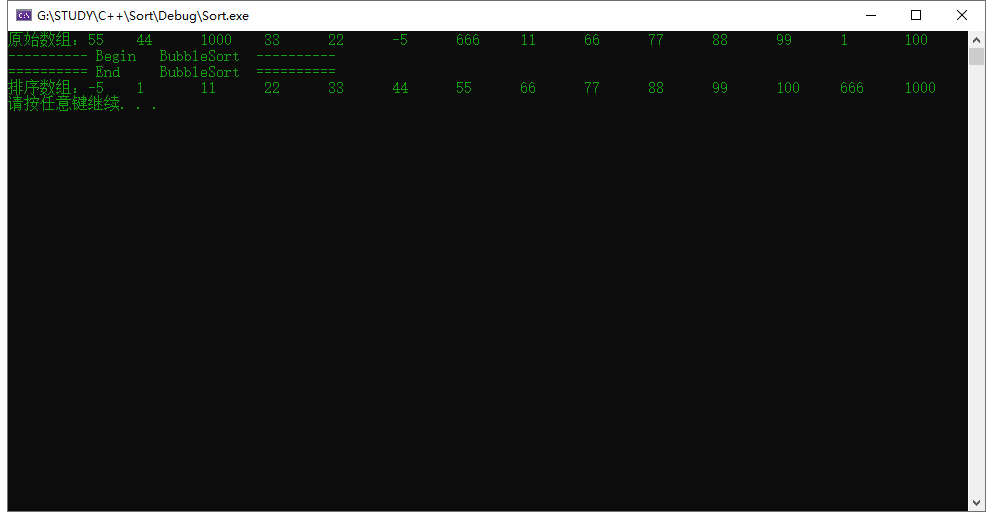
运行结果:
2.选择排序
选择排序算法原理:
第一次从未排序数组中选出最小的一个元素,存放在数组的起始位置。
然后再从剩余的未排序部分中寻找到最小元素,放到已排序部分的末尾。
循环重复以上步骤,直到全部未排序部分的元素个数为零。
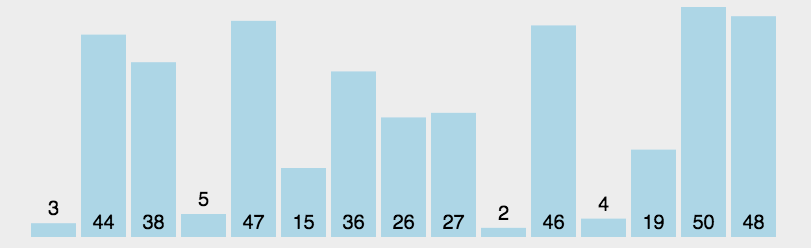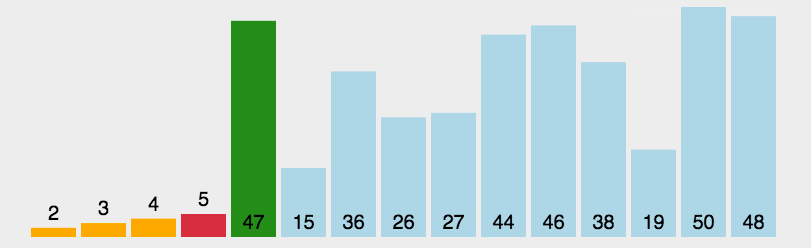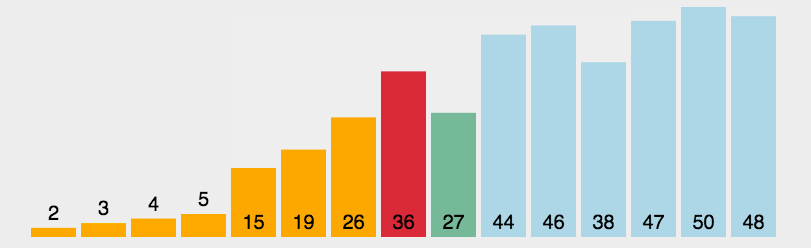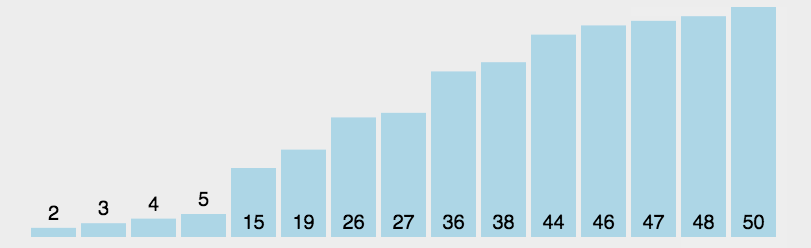
选择排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
选择排序时间复杂度为:最好 O( n2 ),最坏 O( n2 ) ,平均 O( n2 ) 。
选择排序空间复杂度为:O( 1 ) 。
选择排序是一种不稳定的排序算法。
选择排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 template <typename T> 6 void SelectSort(T arr[], int len) 7 { 8 if (NULL == arr || 0 >= len) 9 return; 10 11 int i = 0, j = 0, nMin = 0; 12 13 for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) 14 { 15 nMin = i; 16 17 for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++) 18 { 19 if (arr[j] < arr[nMin]) 20 nMin = j; 21 } 22 23 if (nMin != i) 24 { 25 arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[nMin]; 26 arr[nMin] = arr[i] ^ arr[nMin]; 27 arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[nMin]; 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 system("color 02"); 36 37 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 38 int len = _countof(arr); 39 40 cout << "原始数组:"; 41 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 42 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 43 cout << endl; 44 45 cout << "---------- Begin SelectSort ----------" << endl; 46 SelectSort(arr, len); 47 cout << "========== End SelectSort ==========" << endl; 48 49 cout << "排序数组:"; 50 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 51 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 52 cout << endl; 53 54 system("pause"); 55 return 0; 56 }
运行结果:

3.插入排序
插入排序算法原理:
插入算法把要排序的数组分成两部分:第一部分包含数组的已排序部分(第一次就是第一个元素)。第二部分包含数组的未排序部分(即剩余所有元素,也就是待插入元素)。
然后将数组的未排序部分逐一插入到数组的已排序的部分合理位置。
循环重复以上步骤,直到所有未排序部分的所有元素全部插入到已排序部分中。
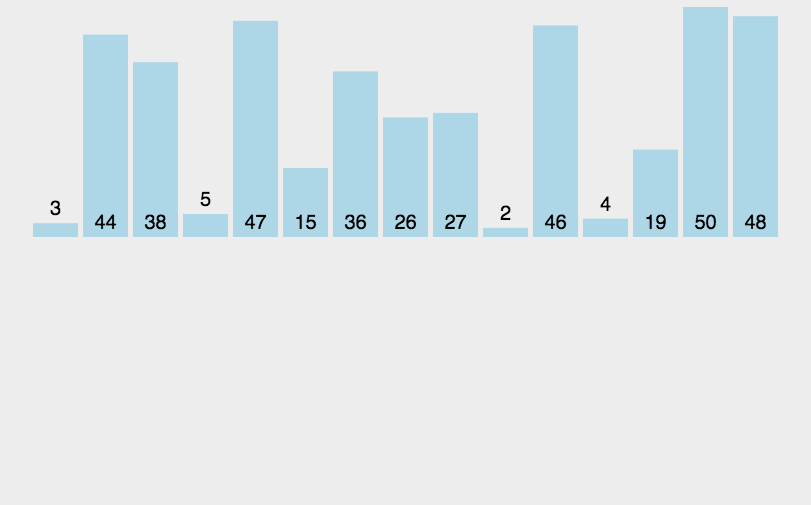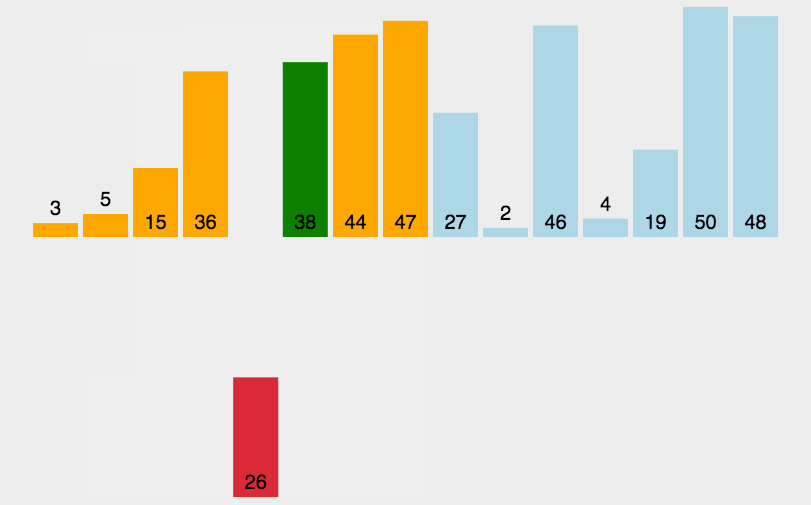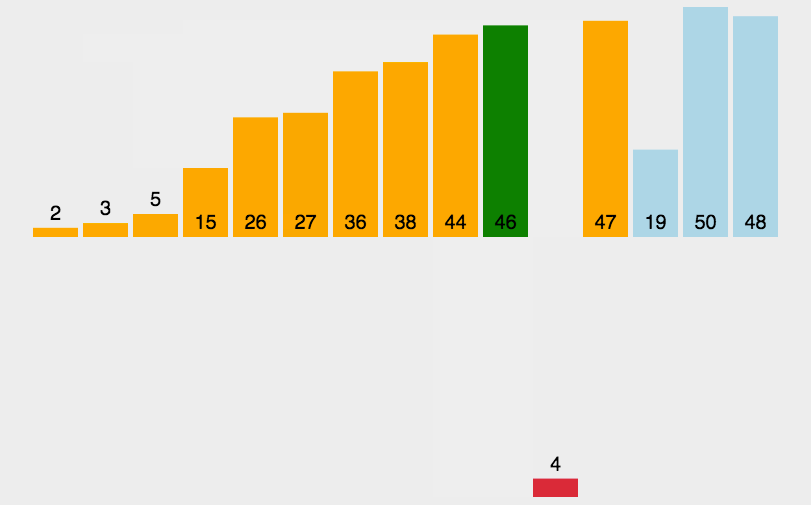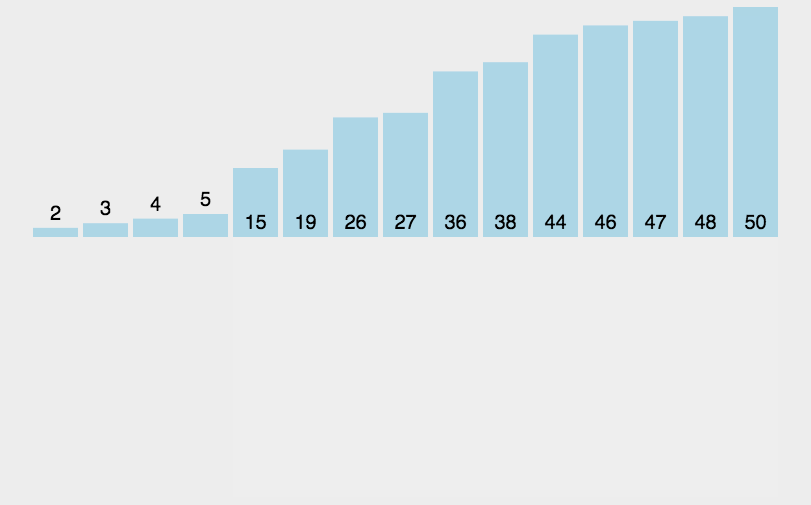
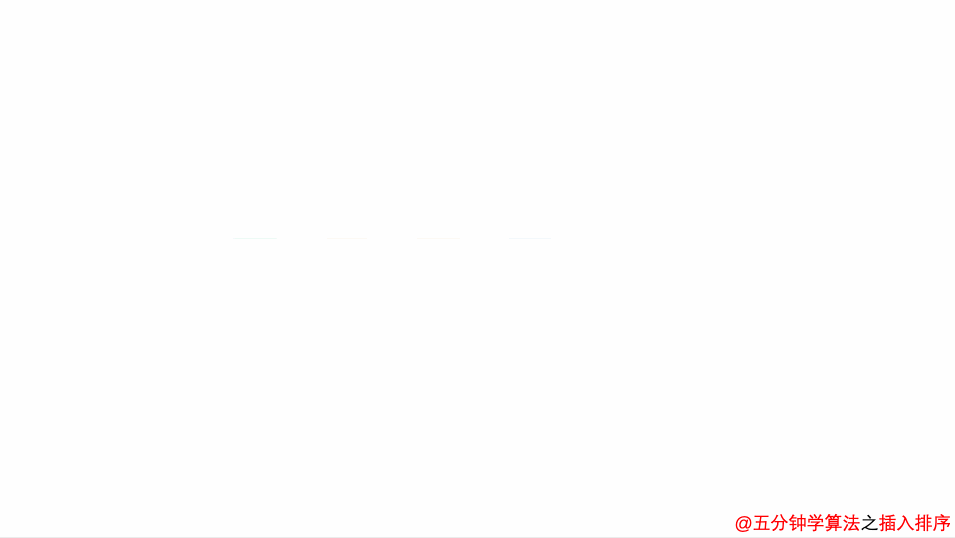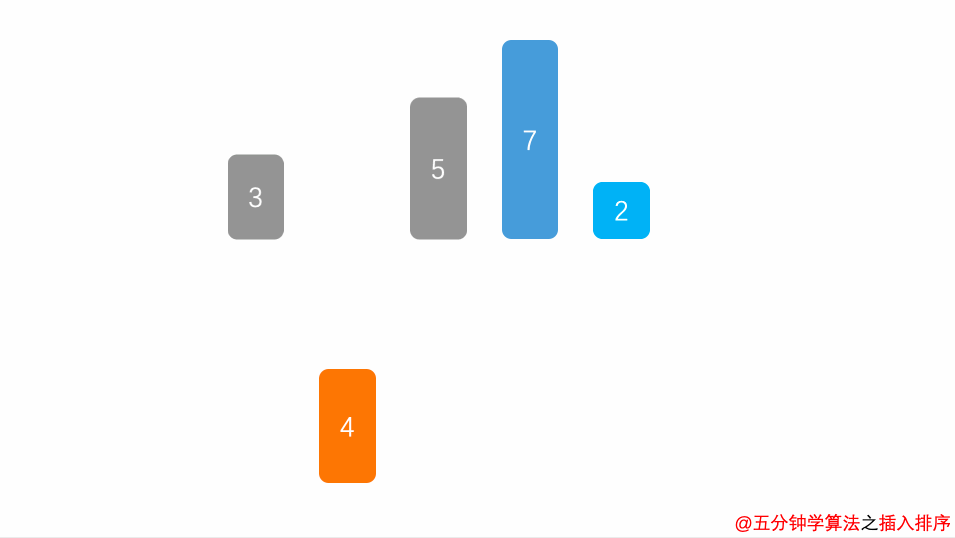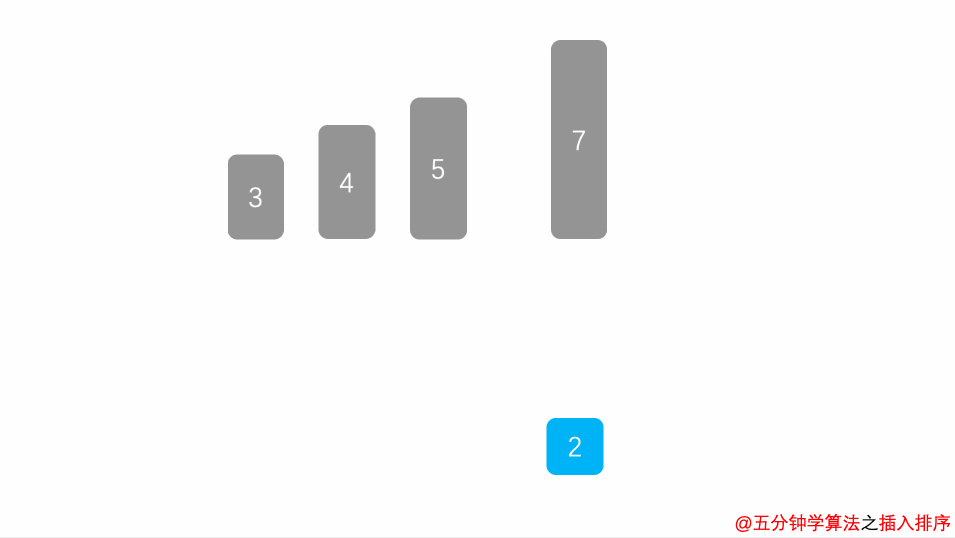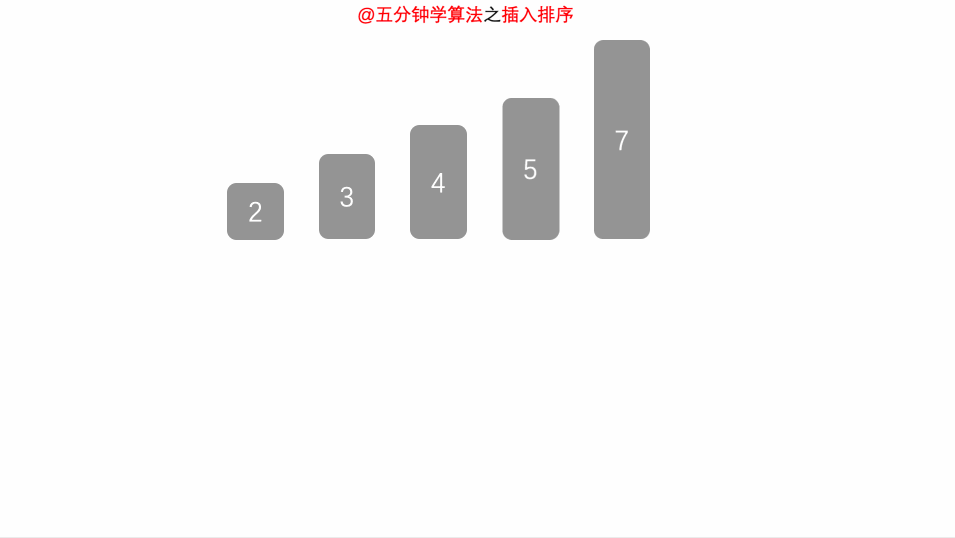
插入排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
插入排序时间复杂度: 最好 O( n ),最坏 O( n2 ),平均 O( n2 )。
插入排序空间复杂度: O( 1 ) 。
插入排序是一种稳定的排序算法。
插入排序源码实现(包括直接插入排序和二分法插入排序)
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 //// 直接法插入排序 6 //template <typename T> 7 //void InsertSort(T arr[], int len) 8 //{ 9 // if (NULL == arr || 0 > len) 10 // return; 11 // 12 // int i = 0, j = 0; 13 // T temp; 14 // 15 // for (i = 1; i < len; i++) 16 // { 17 // j = i - 1; // 记录已排序部分最后一个位置 18 // 19 // temp = arr[i]; // 记录未排序部分的第一个元素 20 // 21 // // 将未排序部分的每次循环的第一个元素插入到已排序部分的合理位置 22 // while (temp < arr[j] && j >= 0) 23 // { 24 // arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; 25 // 26 // --j; 27 // } 28 // 29 // arr[j + 1] = temp; 30 // } 31 //} 32 33 34 // 二分法插入排序 35 template <typename T> 36 void InsertSort(T arr[], int len) 37 { 38 if (NULL == arr || 0 >= len) 39 return; 40 41 int i = 0, j = 0, left = 0, mid = 0, right = 0; 42 T temp; 43 44 for (i = 1; i < len; i++) 45 { 46 mid = 0; 47 left = 0; 48 right = i - 1; // 记录已排序部分最后一个位置 49 temp = arr[i]; // 记录未排序部分的第一个元素 50 51 while (left <= right) 52 { 53 mid = (left + right) / 2; // mid 指向已排序部分中间位置 54 55 if (temp < arr[mid]) 56 right = mid - 1; 57 else 58 left = mid + 1; 59 } 60 61 // 已排序部分left之后的部分,后移一个位置 62 for (j = i - 1; j >= left; j--) 63 arr[j + 1] = arr[j]; 64 65 // 将未排序部分的第一个元素插入到已排序部分的合理位置 66 if (left != i) 67 arr[left] = temp; 68 } 69 } 70 71 72 int main() 73 { 74 system("color 02"); 75 76 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 77 int len = _countof(arr); 78 79 cout << "原始数组:"; 80 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 81 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 82 cout << endl; 83 84 cout << "---------- Begin InsertSort ----------" << endl; 85 InsertSort(arr, len); 86 cout << "========== End InsertSort ==========" << endl; 87 88 cout << "排序数组:"; 89 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 90 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 91 cout << endl; 92 93 system("pause"); 94 return 0; 95 }
运行结果:

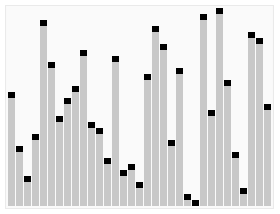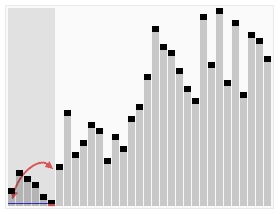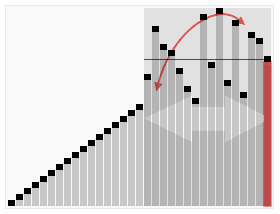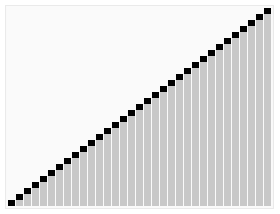
4.快速排序
快速排序算法原理:
首先设定一个分界值,通过该分界值将数组分成左右两部分。
将大于等于分界值的数据集中到数组右边,小于分界值的数据集中到数组的左边。
左边和右边的数据可以独立排序。对于左侧的数组数据,又可以取一个分界值,将该部分数据分成左右两部分,同样在左边放置较小值,右边放置较大值。右侧的数组数据也可以做类似处理。
递归以上步骤,数组最终排序完成。


我自己认为上面这个图不是很直观,所以又加了一个
快速排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
快速排序时间复杂度:最好 O( n log2 n ) ,最坏 O( n2 ),平均 O( n log2 n )。
快速排序空间复杂度:O( log2 n ) 。
快速排序是一种不稳定的排序算法。
快速排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 template <typename T> 6 void QuickSort(T arr[], int left, int right) 7 { 8 if (NULL == arr || left >= right || 0 > left || 0 > right) 9 return; 10 11 int i = left; 12 int j = right; 13 int key = arr[left]; 14 15 while (i < j) 16 { 17 while (i < j && key <= arr[j]) // 从右往左找大的 18 j--; 19 arr[i] = arr[j]; 20 21 while (i < j && key >= arr[i]) // 从左往右找小的 22 i++; 23 arr[j] = arr[i]; 24 } 25 26 arr[i] = key; 27 QuickSort(arr, left, i - 1); 28 QuickSort(arr, i + 1, right); 29 } 30 31 32 int main() 33 { 34 system("color 02"); 35 36 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 37 int len = _countof(arr); 38 39 cout << "原始数组:"; 40 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 41 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 42 cout << endl; 43 44 cout << "---------- Begin QuickSort ----------" << endl; 45 QuickSort(arr, 0, len - 1); // 参数为数组下标 46 cout << "========== End QuickSort ==========" << endl; 47 48 cout << "排序数组:"; 49 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 50 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 51 cout << endl; 52 53 system("pause"); 54 return 0; 55 }
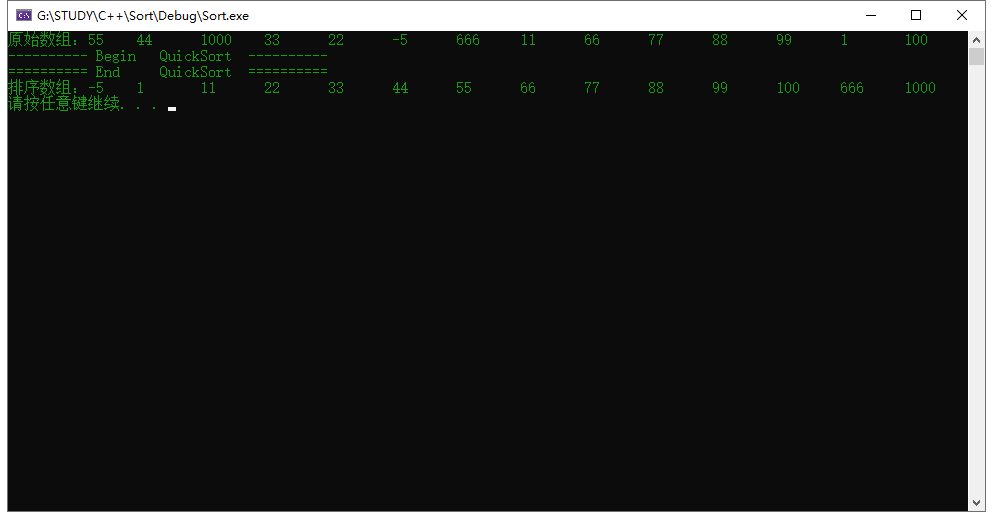
运行结果:
5.计数排序
计数排序算法原理:
计数排序不是基于比较的排序算法,其核心在于将输入的数据值转化为键存储在额外开辟的数组空间中。
作为一种线性时间复杂度的排序,计数排序要求输入的数据必须是有确定范围的整数(本例只能确保正整数正确演示排序算法的实现,如果数组中出现负整数,会需要考虑更多的逻辑处理)。
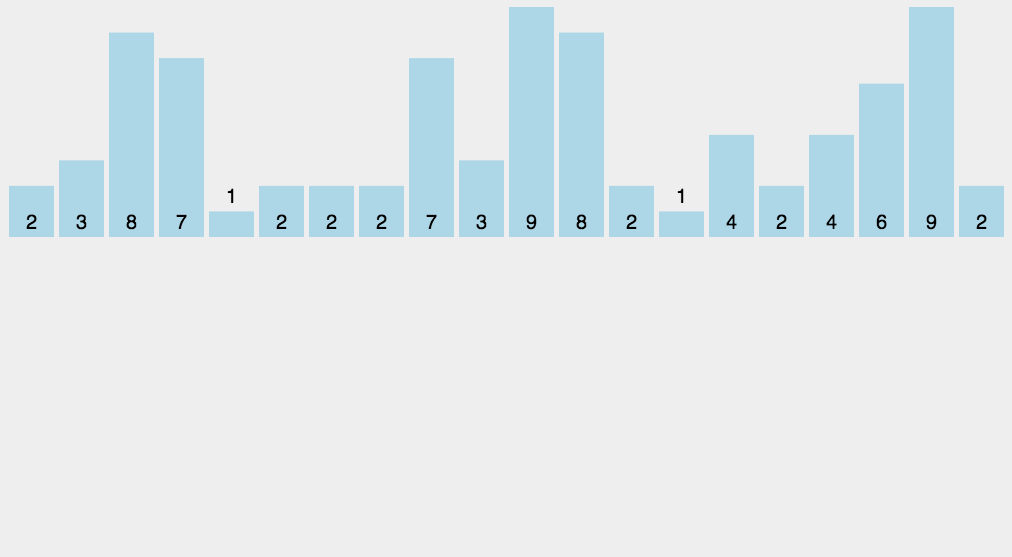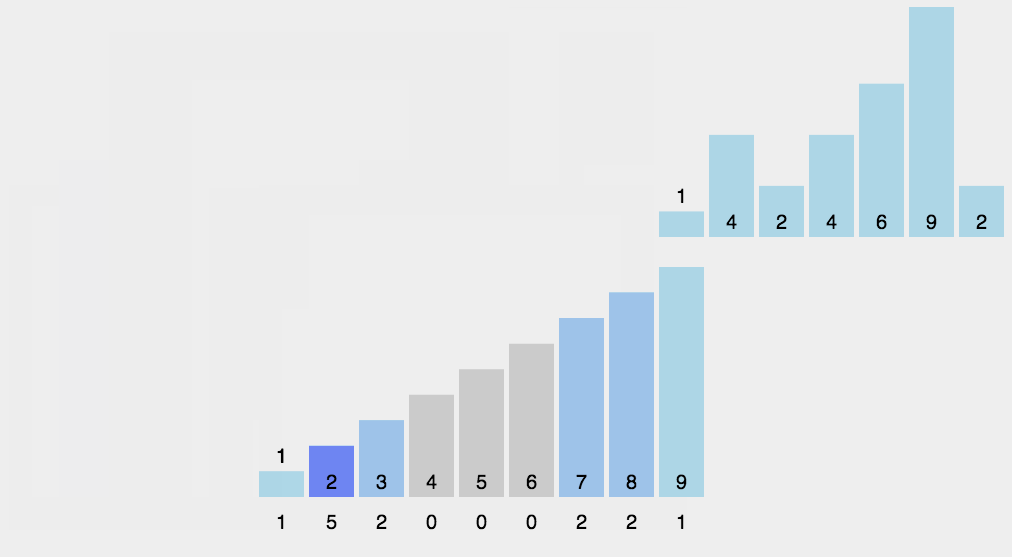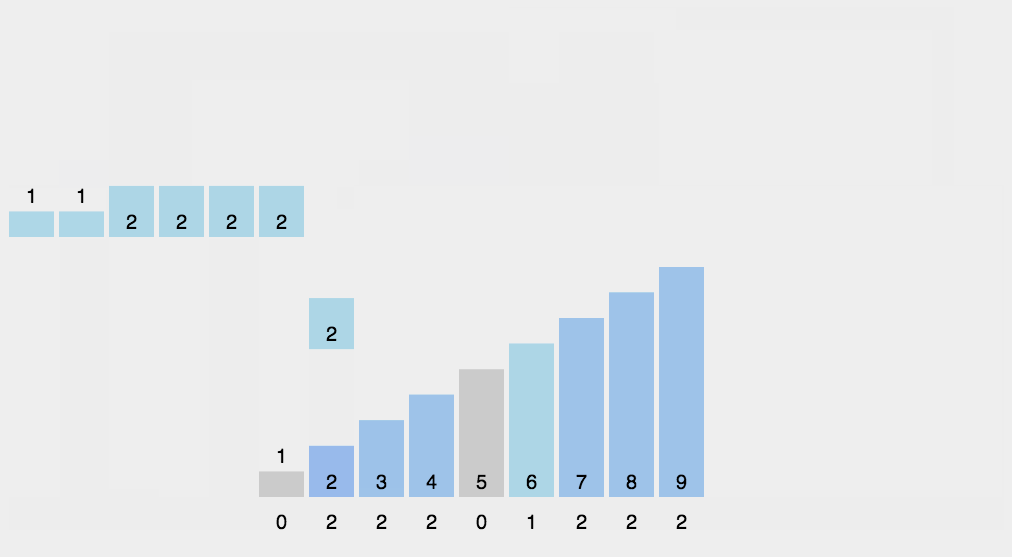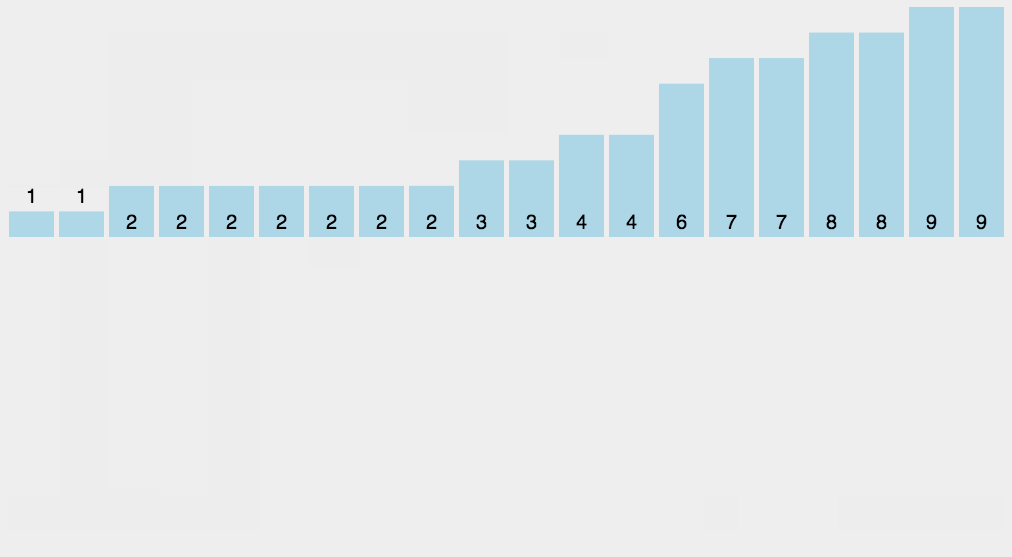
计数排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
计数排序时间复杂度:最好 O( n ),最坏 O( n ),平均 O( n )。
计数排序空间复杂度:O( n ) 。
计数排序是一种稳定的排序算法。
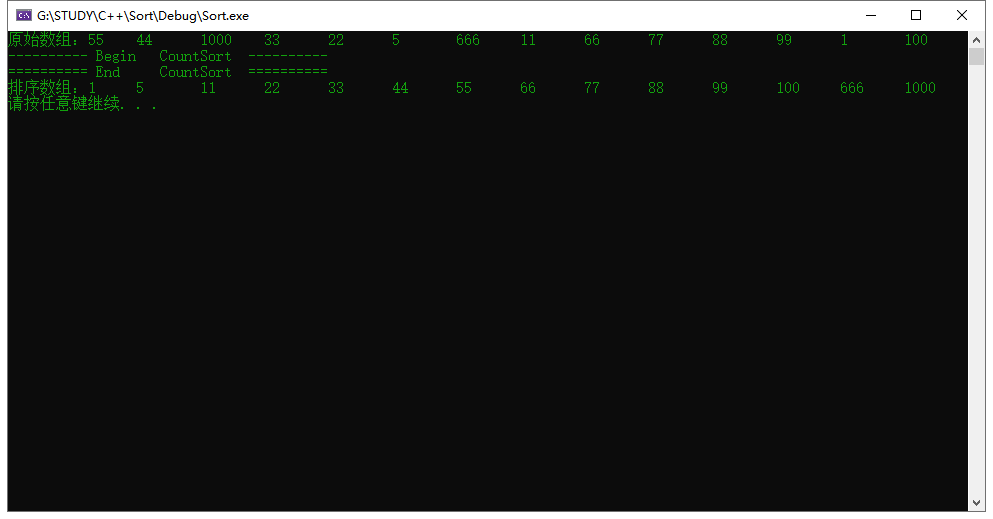
计数排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 template <typename T> 6 void CountSort(T arr[], int len) 7 { 8 T *pCount = NULL, max; 9 int i = 0, j = 0; 10 if( NULL == arr || 0 >= len ) 11 return; 12 13 // 找最大值 14 max = arr[0]; 15 for(i = 1; i<len; i++) 16 { 17 if(arr[i] > max) 18 max = arr[i]; 19 } 20 21 // 开辟计数数组 22 pCount = new T[max + 1]; 23 memset(pCount, 0, sizeof(T) * (max + 1)); 24 25 // 计数 26 for(i = 0; i < len; i++) 27 pCount[ arr[i] ]++; 28 29 j = 0; 30 // 根据计数数组,将原数组排序 31 for(i = 0; i <= max; i++) 32 { 33 while(pCount[i]) 34 { 35 arr[j] = i; 36 pCount[i]--; 37 j++; 38 } 39 } 40 41 // 清空 42 delete[] pCount; 43 pCount = NULL; 44 } 45 46 47 int main() 48 { 49 system("color 02"); 50 51 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, 5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 52 int len = _countof(arr); 53 54 cout << "原始数组:"; 55 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 56 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 57 cout << endl; 58 59 cout << "---------- Begin CountSort ----------" << endl; 60 CountSort(arr, len); 61 cout << "========== End CountSort ==========" << endl; 62 63 cout << "排序数组:"; 64 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 65 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 66 cout << endl; 67 68 system("pause"); 69 return 0; 70 }
运行结果:
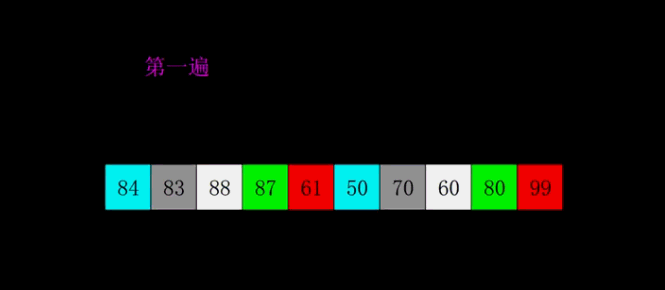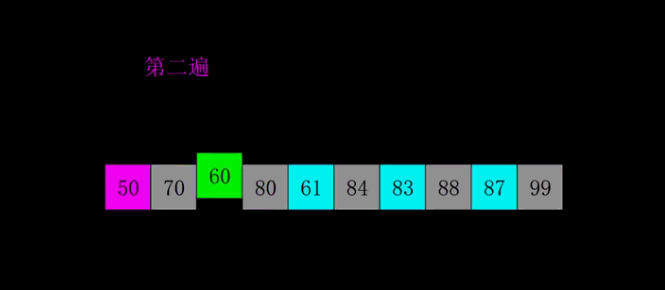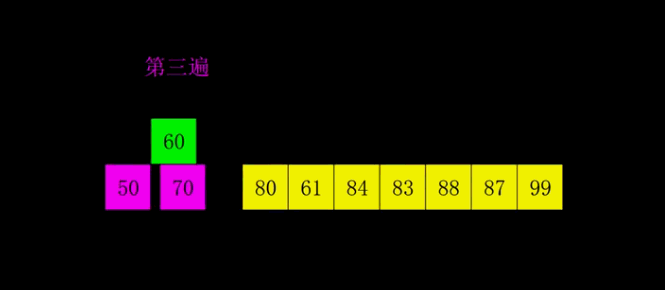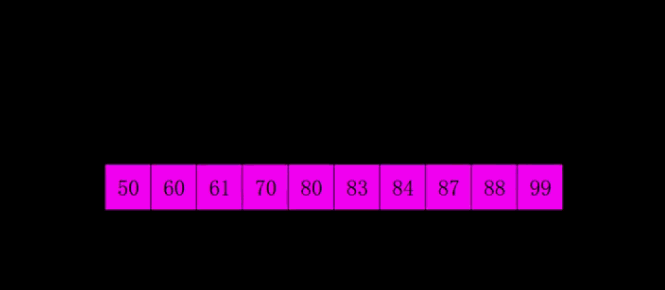
6.希尔排序
希尔排序算法原理:
先将整个待排序的记录序列分割成为若干子序列分别进行直接插入排序
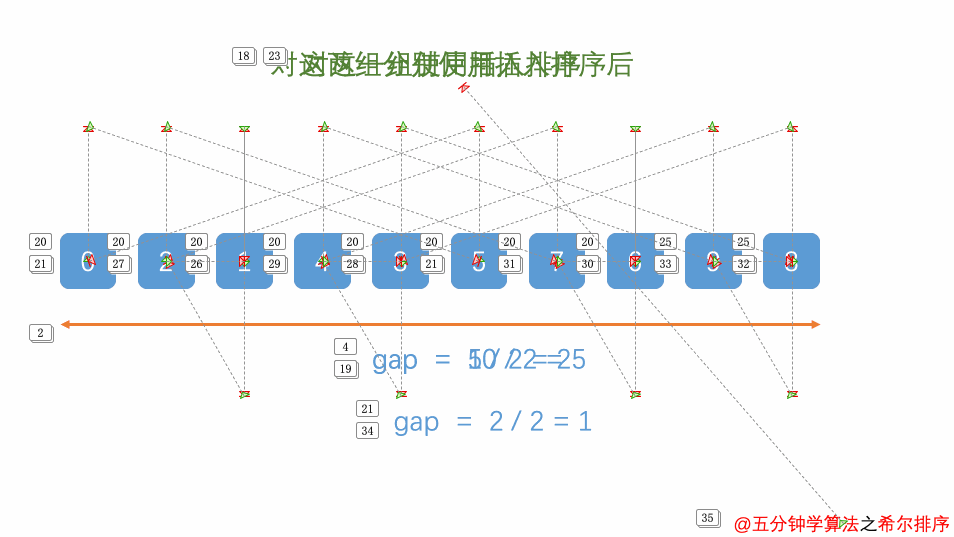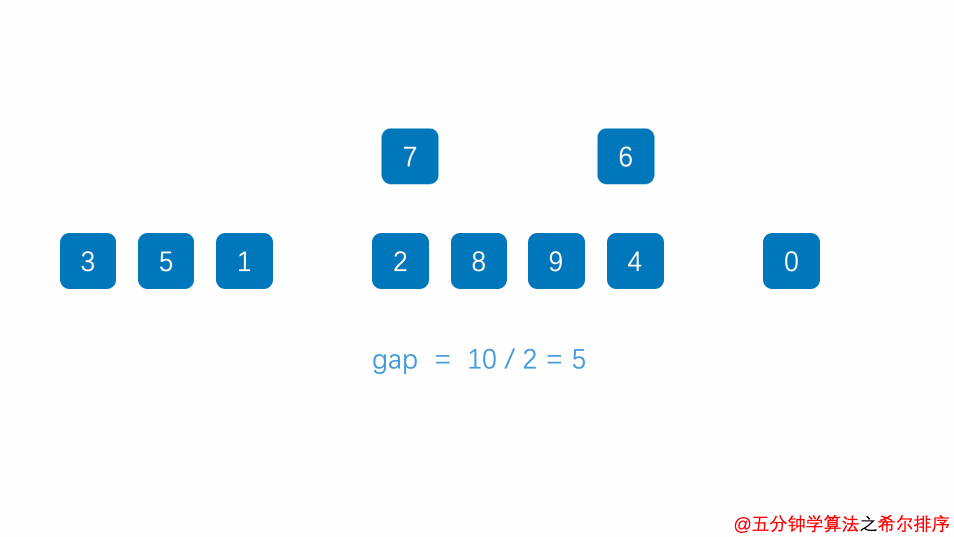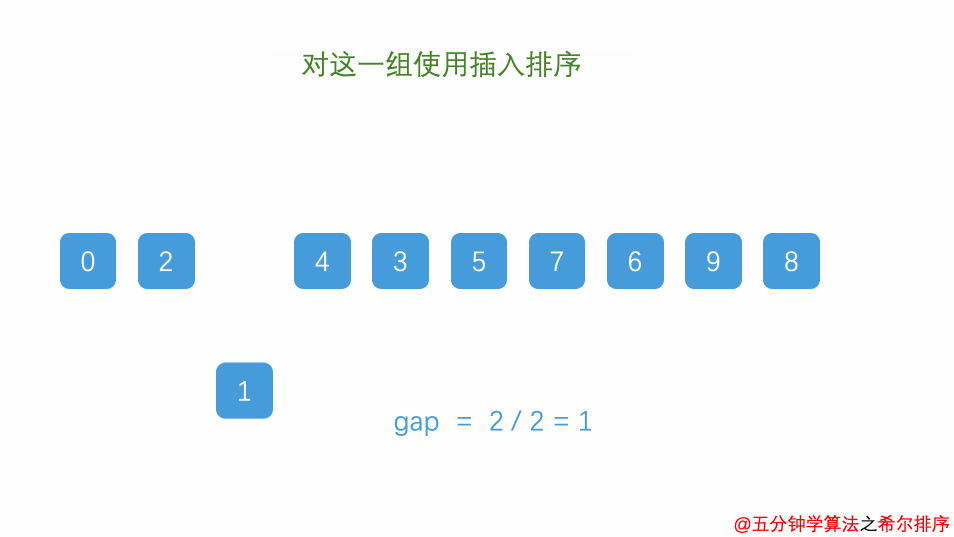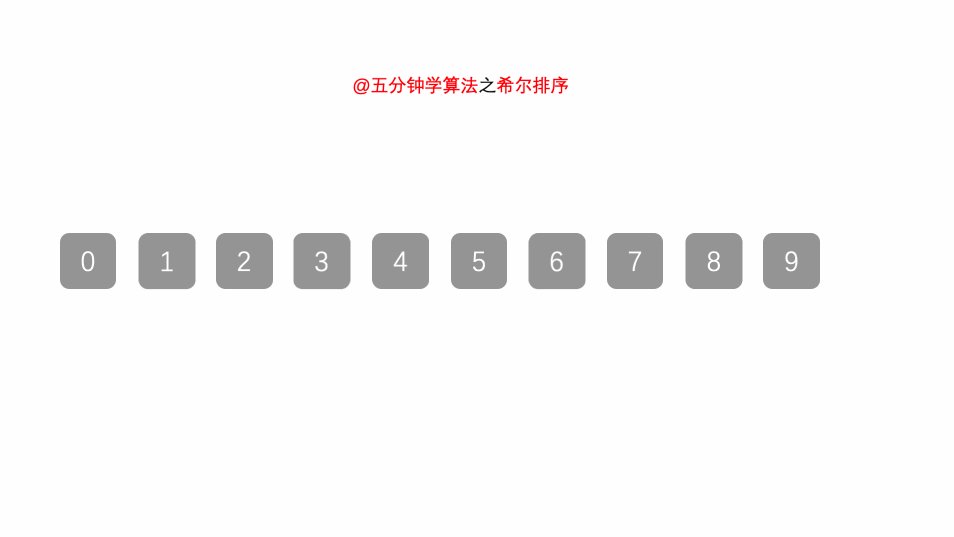
希尔排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
希尔排序时间复杂度:最好 O( n ),最坏 O( n2 ),平均 O( n1.3 )。
希尔排序空间复杂度:O( 1 ) 。
希尔排序是一种不稳定的排序算法。
希尔排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 template <typename T> 6 void ShellSort(T arr[],int len) 7 { 8 int gap = 0; // 步长 9 int j = 0; 10 int k = 0; 11 T temp; 12 13 if(NULL == arr || 0 >= len )return; 14 15 // 定步长 16 for(gap = len / 2; gap > 0; gap /= 2) 17 { 18 // 根据步长分组(步长是几 就有几组) 19 // 各组内插入排序 20 for(j = gap; j < len; j++) 21 { 22 k = j - gap; // 记住有序数组的最后一个 23 temp = arr[j]; // 保存无序数组的第一个 24 25 // 将无序数组的第一个元素插入到有序数组中 26 while(temp < arr[k] && k >= 0) 27 { 28 arr[k + gap] = arr[k]; 29 k -= gap; 30 } 31 32 arr[k + gap] = temp; 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 37 38 int main() 39 { 40 system("color 02"); 41 42 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 43 int len = _countof(arr); 44 45 cout << "原始数组:"; 46 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 47 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 48 cout << endl; 49 50 cout << "---------- Begin ShellSort ----------" << endl; 51 ShellSort(arr, len); 52 cout << "========== End ShellSort ==========" << endl; 53 54 cout << "排序数组:"; 55 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 56 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 57 cout << endl; 58 59 system("pause"); 60 return 0; 61 }
运行结果:
7.归并排序
归并排序算法原理:
归并排序是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。
将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;
即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。
若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。

归并排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
归并排序时间复杂度:最好 O( n log2 n ) ,最坏 O( n log2 n ),平均 O( n log2 n )。
归并排序空间复杂度:O( n ) 。
归并排序是一种稳定的排序算法。
归并排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 // 将a开头的长为n的数组和b开头长为right的数组合并len为数组长度,用于最后一组 6 template <typename T> 7 void Merge(T data[], int a, int b, int n, int len) 8 { 9 int right = 0; 10 if (b + n - 1 >= len - 1) 11 right = len - b; 12 else 13 right = n; 14 T* temp = new T[n + right]; 15 int i = 0, j = 0; 16 while (i <= n - 1 && j <= right - 1) 17 { 18 if (data[a + i] <= data[b + j]) 19 { 20 temp[i + j] = data[a + i]; 21 i++; 22 } 23 else 24 { 25 temp[i + j] = data[b + j]; 26 j++; 27 } 28 } 29 30 //a中还有元素,且全都比b中的大,a[i]还未使用 31 if (j == right) 32 memcpy(temp + i + j, data + a + i, (n - i) * sizeof(int)); 33 else if (i == n) 34 memcpy(temp + i + j, data + b + j, (right - j) * sizeof(int)); 35 36 memcpy(data + a, temp, (right + n) * sizeof(int)); 37 38 delete[] temp; 39 } 40 41 template <typename T> 42 void MergeSort(T data[], int len) 43 { 44 if (NULL == arr || 0 >= len)return; 45 46 int step = 1; 47 while (step < len) 48 { 49 for (int i = 0; i <= len - step - 1; i += 2 * step) 50 Merge(data, i, i + step, step, len); 51 // 将i和i+step这两个有序序列进行合并 52 // 序列长度为step 53 // 当i以后的长度小于或者等于step时,退出 54 // 在按某一步长归并序列之后,步长加倍 55 step *= 2; 56 } 57 } 58 59 60 int main() 61 { 62 system("color 02"); 63 64 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 65 int len = _countof(arr); 66 67 cout << "原始数组:"; 68 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 69 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 70 cout << endl; 71 72 cout << "---------- Begin MergeSort ----------" << endl; 73 MergeSort(arr, len); 74 cout << "========== End MergeSort ==========" << endl; 75 76 cout << "排序数组:"; 77 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 78 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 79 cout << endl; 80 81 system("pause"); 82 return 0; 83 }
运行结果:
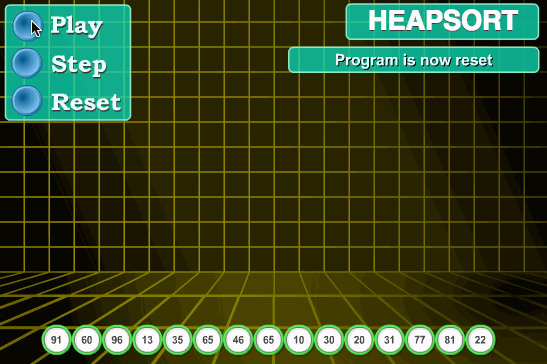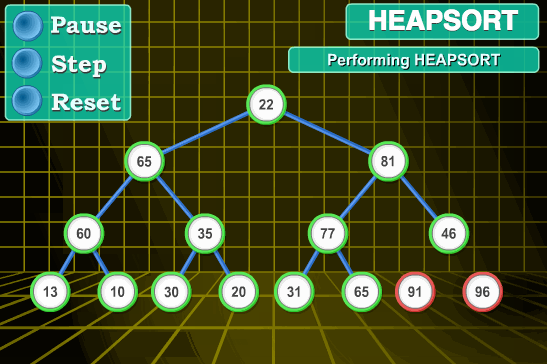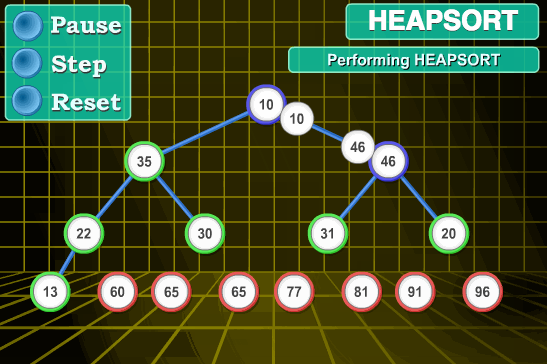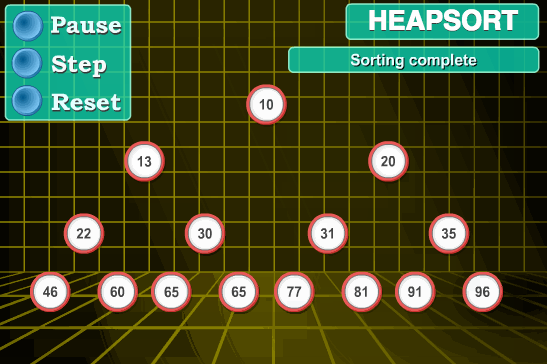
8.堆排序
堆排序算法原理:
堆排序是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法。堆是一个近似完全二叉树的结构,并同时满足堆积的性质:即子结点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点。

堆排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
堆排序时间复杂度:最好 O( n log2 n ) ,最坏 O( n log2 n ),平均 O( n log2 n )。
堆排序空间复杂度:O( 1 ) 。
堆排序是一种不稳定的排序算法。
堆排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 #define left (2 * root + 1) 5 #define right (2 * root + 2) 6 7 8 template <typename T> 9 void Adjust(T arr[], int len, int root) 10 { 11 int max = 0; 12 for(max = left; max < len; max = left) 13 { 14 //两个孩子 15 if(right < len) 16 { 17 //比较孩子大小 18 if(arr[right] > arr[left]) 19 max = right; 20 } 21 22 //拿较大的和根比较 23 if(arr[max] > arr[root]) 24 { 25 arr[max] = arr[root] ^ arr[max]; 26 arr[root] = arr[root] ^ arr[max]; 27 arr[max] = arr[root] ^ arr[max]; 28 29 //继续向下层调整 30 root = max; 31 continue; 32 } 33 34 break; 35 } 36 } 37 38 template <typename T> 39 void HeapSort(T arr[],int len) 40 { 41 if(NULL == arr || 0 >= len)return; 42 43 //建初始堆 44 //从最后一个父亲节点向前调整 45 for(int i = len / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) 46 { 47 //调整 48 Adjust(arr, len, i); 49 } 50 51 //选择排序 52 for(int i = len - 1; i > 0; i--) 53 { 54 //交换 和根交换 55 arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[0]; 56 arr[0] = arr[i] ^ arr[0]; 57 arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[0]; 58 59 //重新调整根节点 60 Adjust(arr, i, 0); 61 } 62 } 63 64 65 int main() 66 { 67 system("color 02"); 68 69 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 70 int len = _countof(arr); 71 72 cout << "原始数组:"; 73 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 74 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 75 cout << endl; 76 77 cout << "---------- Begin HeapSort ----------" << endl; 78 HeapSort(arr, len); 79 cout << "========== End HeapSort ==========" << endl; 80 81 cout << "排序数组:"; 82 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 83 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 84 cout << endl; 85 86 system("pause"); 87 return 0; 88 }
运行结果:

9.桶排序
桶排序算法原理:
将数组分到有限数量的桶子里。
每个桶子再个别排序。
桶排序是鸽巢排序的一种归纳结果。
当要被排序的数组内的数值是均匀分配的时候,桶排序使用线性时间 O(n) 。但桶排序并不是 比较排序,他不受到 O(n log n) 下限的影响。

桶排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
桶排序时间复杂度:最好 O( n ),最坏 O( n + c ),平均 O( n + c ),其中 c = n * ( log n - log m) , m 桶数量。
桶排序空间复杂度:O( n + m ) 。
桶排序是一种稳定的排序算法。
桶排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 typedef struct node 6 { 7 int nValue; 8 node *pNext; 9 }Bucket; 10 11 void Bubble(Bucket *pHead) 12 { 13 Bucket *pMark = NULL; 14 Bucket *pNode = NULL; 15 16 if(NULL == pHead)return; 17 18 pMark = pHead; 19 pNode = pMark; 20 21 while(pMark->pNext != NULL) 22 { 23 pNode = pHead; 24 while(pNode->pNext != NULL) 25 { 26 if(pNode->nValue > pNode->pNext->nValue) 27 { 28 int temp = pNode->nValue; 29 pNode->nValue = pNode->pNext->nValue; 30 pNode->pNext->nValue = temp; 31 } 32 pNode = pNode->pNext; 33 } 34 pMark = pMark->pNext; 35 } 36 } 37 38 void BucketSort(int arr[],int len) 39 { 40 int i = 0, j = 0, max = 0, min = 0, count = 0, base = 0, maxIndex = 0, minIndex = 0; 41 Bucket **pBucket = NULL, * pTemp = NULL, * pMark = NULL, * pDel = NULL; 42 43 if(NULL == arr || 0 >= len)return; 44 45 // 查找数组的最大值和最小值 46 max = arr[0]; 47 min = arr[0]; 48 for(i = 1; i < len; i++) 49 { 50 if(arr[i] > max) 51 max = arr[i]; 52 53 if(arr[i] < min) 54 min = arr[i]; 55 } 56 57 // 分析位数 58 base = max; 59 while(base) 60 { 61 base /= 10; 62 count++; 63 } 64 65 base = 1; // 除数 66 while(count > 1) 67 { 68 base *= 10; 69 count--; 70 } 71 72 maxIndex = max / base; 73 minIndex = min / base; 74 75 // 申请表头 76 pBucket = new Bucket*[maxIndex - minIndex + 1]; 77 memset(pBucket, 0, sizeof(Bucket*) * (maxIndex - minIndex + 1)); 78 79 //将数据元素入桶 80 for(i = 0; i < len; i++) 81 { 82 count = arr[i] / base - minIndex; // 对应的桶的下标 83 84 pTemp = new Bucket; 85 pTemp->nValue = arr[i]; 86 87 pTemp->pNext = pBucket[count]; 88 pBucket[count] = pTemp; 89 } 90 91 // 各桶内部进行排序 92 for(i = 0; i < maxIndex - minIndex + 1; i++) 93 Bubble(pBucket[i]); 94 95 // 将桶内元素按顺序倒回原数组 96 j = 0; 97 for(i = 0; i < maxIndex - minIndex + 1; i++) 98 { 99 pMark = pBucket[i]; 100 while(pMark) 101 { 102 arr[j] = pMark->nValue; 103 pMark = pMark->pNext; 104 j++; 105 } 106 } 107 108 // 回收空间 109 for(i = 0; i < maxIndex - minIndex + 1; i++) 110 { 111 pMark = pBucket[i]; 112 while(pMark) 113 { 114 pDel = pMark; 115 pMark = pMark->pNext; 116 117 delete pDel; 118 pDel = NULL; 119 } 120 } 121 122 // 释放表头 123 delete[] pBucket; 124 pBucket = NULL; 125 } 126 127 128 int main() 129 { 130 system("color 02"); 131 132 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, -5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 133 int len = _countof(arr); 134 135 cout << "原始数组:"; 136 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 137 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 138 cout << endl; 139 140 cout << "---------- Begin BucketSort ----------" << endl; 141 BucketSort(arr, len); 142 cout << "========== End BucketSort ==========" << endl; 143 144 cout << "排序数组:"; 145 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 146 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 147 cout << endl; 148 149 system("pause"); 150 return 0; 151 }
运行结果:

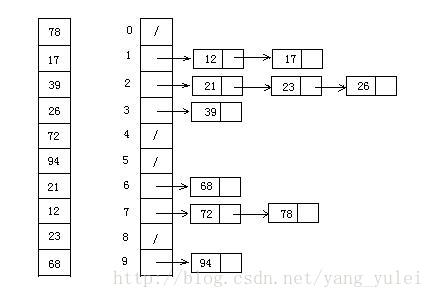
10.基数排序
基数排序算法原理:


基数排序时间复杂度、空间复杂度、稳定性
基数排序时间复杂度:最好 O( d * ( n + r ) ) ,最坏 O( d * ( n + r ) ),平均 O( d * ( n + r ) ),其中 d 最大数长度, r 桶数量。
基数排序空间复杂度:O( n + r ) 。
基数排序是一种稳定的排序算法。
基数排序源码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 5 typedef struct node 6 { 7 int nValue; 8 struct node *pNext; 9 }Radix; 10 11 int GetMax(int arr[], int len) 12 { 13 int max = arr[0]; 14 for(int i = 1; i < len; i++) 15 { 16 if(max < arr[i]) 17 { 18 max = arr[i]; 19 } 20 } 21 return max; 22 } 23 24 int GetLoop(int max) 25 { 26 int nCount = 0; 27 while(max) 28 { 29 max /= 10; 30 nCount++; 31 } 32 return nCount; 33 } 34 35 void Sort(int arr[], int len, int num) 36 { 37 38 int i = 0, j = 0, index = 0, base = 1; 39 Radix** pRadix = NULL, *pTemp = NULL, *pMark = NULL, *pDel = NULL; 40 41 // 计算被除数 基数 42 while(num > 1) 43 { 44 base *= 10; 45 num--; 46 } 47 48 // 申请表头空间 49 pRadix = new Radix*[10]; 50 memset(pRadix, 0, sizeof(Radix*) * 10); 51 52 for(i = 0; i < len; i++) 53 { 54 // 获得下标 55 index = arr[i] / base % 10; 56 57 pTemp = new Radix; 58 pTemp->nValue = arr[i]; 59 pTemp->pNext = NULL; 60 61 // 尾添加 62 pMark = pRadix[index]; 63 if(pRadix[index] == NULL) 64 pRadix[index] = pTemp; 65 else 66 { 67 // 找尾 68 while(pMark->pNext) 69 pMark = pMark->pNext; 70 71 pMark->pNext = pTemp; 72 } 73 } 74 75 // 将桶内元素放回原数组 76 j = 0; 77 for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) 78 { 79 pMark = pRadix[i]; 80 while(pMark) 81 { 82 arr[j] = pMark->nValue; 83 j++; 84 pMark = pMark->pNext; 85 } 86 } 87 88 // 清空 89 for(i = 0; i < 10; i++) 90 { 91 pMark = pRadix[i]; 92 while(pMark) 93 { 94 pDel = pMark; 95 pMark = pMark->pNext; 96 delete pDel; 97 pDel = NULL; 98 } 99 } 100 101 delete[] pRadix; 102 pRadix = NULL; 103 } 104 105 void RadixSort(int arr[], int len) 106 { 107 int max = 0, loop = 0; 108 if (NULL == arr || 0 >= len)return; 109 110 // 找到当前数组最大值 111 max = GetMax(arr,len); 112 113 // 分析最大值位数 114 loop = GetLoop(max); 115 116 // 按照各位进行入桶操作 117 for(int i = 1; i <= loop; i++) 118 Sort(arr,len,i); // 按位处理 119 } 120 121 122 int main() 123 { 124 system("color 02"); 125 126 int arr[] = { 55, 44, 1000, 33, 22, 5, 666, 11, 66, 77, 88, 99, 1, 100 }; 127 int len = _countof(arr); 128 129 cout << "原始数组:"; 130 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 131 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 132 cout << endl; 133 134 cout << "---------- Begin RadixSort ----------" << endl; 135 RadixSort(arr, len); 136 cout << "========== End RadixSort ==========" << endl; 137 138 cout << "排序数组:"; 139 for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) 140 cout << arr[i] << "\t"; 141 cout << endl; 142 143 system("pause"); 144 return 0; 145 }
运行结果:
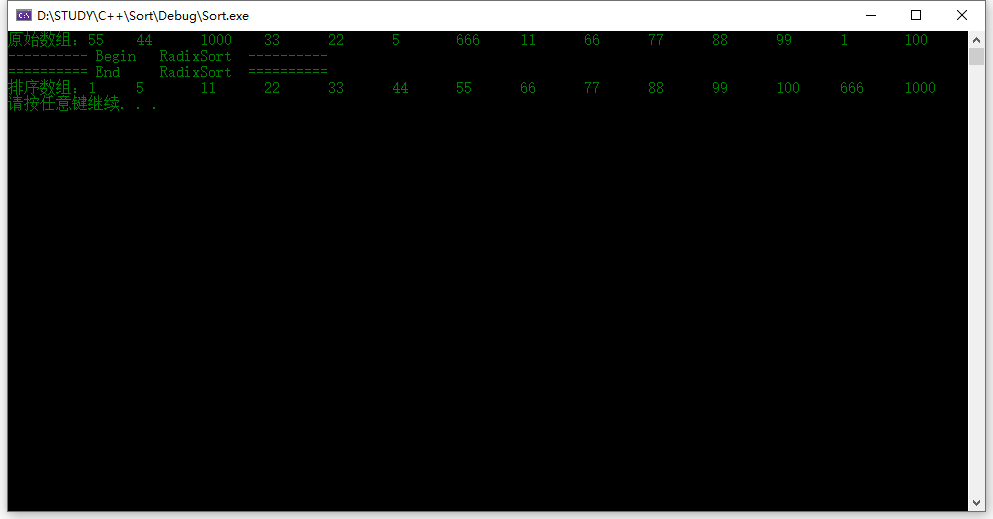
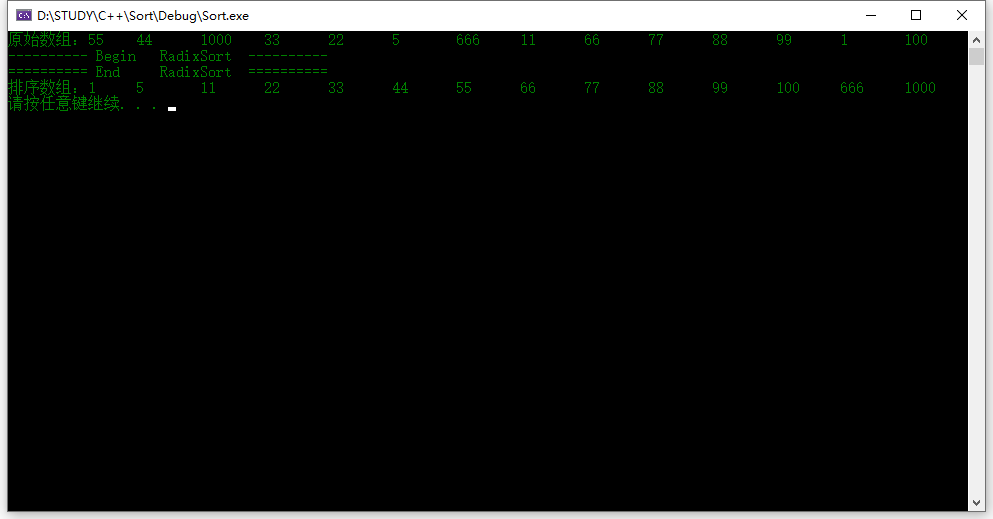
至此经典十大排序算法都已经总结完了,还请批评指正。。。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号