React18学习笔记
目录
- 使用Create-React-App创建项目
- 使用Vite创建项目
- JSX语法基础
- 组件
- Props组件通讯
- Hooks
- CSS Module
- CSS-in-JS
- Context
- useReducer
使用Create-React-App创建项目
npx create-react-app xxx项目名 (--template typescript)
使用Vite创建项目
yarn create vite react-demo-vite --template react-ts
JSX语法基础
标签
-
首字母大小写的区别,大写是自定义组件
<header></header> // HTML标签 <Header /> // 自定义组件 -
标签必须闭合,如<input>在JSX中是非法的
-
每段JSX只能有一个根节点
//JSX片段 const list1 = [ <div> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> <p>hello</p> </div>, ]; //如果不想用div作为根节点,可以使用<></> const list2 = [ <> <ul> <li></li> <li></li> <li></li> </ul> <p>hello</p> </>, ];
属性
-
class要改为className
避免与js中的关键字class进行混淆,标签中的class需要改为className
<div className="App"></div> -
style要使用JS对象(不能是string)而且key用驼峰写法
<a style={{ color: "red", backgroundColor: "pink" }}>一条链接</a> -
for要改为htmlFor
避免与js中的关键字for进行混淆,标签中的for需要改为htmlFor
<div> <label htmlFor="input">姓名</label> <input type="text" id="input" /> </div>
事件
- 使用onXxx的形式
- 必须传入一个函数(是fn而非fn())
- 注意Typescript类型
function App() {
const fn = () => {
console.log("点击");
};
return (
<div className="App">
<button onClick={fn}>点击</button>
</div>
);
}
如果需要在函数获取event元素,需要添加Typescript类型,否则会报错
//从react中引入 Event 事件对象类型
import type { MouseEvent } from "react";
const fn = (event: MouseEvent<HTMLButtonElement>) => {
event.preventDefault();
console.log("点击");
};
插入JS变量和表达式
-
使用{ xxx }可以插入JS变量、函数、表达式
const style = { color: "red", backgroundColor: "pink" } <a style={ style }>一条链接</a> -
可插入普通文本、属性
<p>{12}</p> <p>{"我是一个p"}</p> -
可用于注释
<h1>{/* 一条注释 */}</h1>
条件判断
-
使用&&逻辑运算符
const flag = true; <div>{flag && <p>hello p</p>}</div> -
使用三元表达式
const flag = true; <div>{flag ? <p>hello p1</p> : <p>hello p2</p>}</div> -
使用函数和if语句
// 首字母大写->自定义组件 function Hello() { if (flag) return <p>hello p3</p>; return <p>hello p4</p>; } <Hello></Hello>
循环
- 使用数组map
- 每个item元素需要key属性
- key在同级别唯一(最好不要用index作为key)
function App() {
const list = [
{ username: "zzz1", name: "zzz1" },
{ username: "zzz2", name: "zzz2" },
{ username: "zzz3", name: "zzz3" },
];
return (
<div className="App">
<div>
{list.map((user) => {
const { username, name } = user;
return <li key={username}>{name}</li>;
})}
</div>
</div>
);
}
实践:列表页
function App() {
// 列表数据
const questionList = [
{ id: "q1", title: "问卷1", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q2", title: "问卷2", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q3", title: "问卷3", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q4", title: "问卷4", isPublished: true },
];
function edit(id: string) {
console.log("edit", id);
}
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>问卷列表页</h1>
<div>
{questionList.map((question) => {
const { id, title, isPublished } = question;
return (
<div key={id} className="list-item">
<strong>{title}</strong>
{/* 条件判断 */}
{isPublished ? (
<span style={{ color: "green" }}>已发布</span>
) : (
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>未发布</span>
)}
<button onClick={() => edit(id)}>编辑问卷</button>
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</div>
);
}
组件
在react16之前,组件分为函数组件和class组件,在react16以后,React推崇函数组件和Hooks
- 组件名称首字母必须大写
- 函数必须返回一段JSX,如果不需要渲染任何内容,返回一个null
将上面代码放到List1.tsx下,创建List1组件
import React, { FC } from "react";
import "./List1.css";
//FC就是FunctionComponent的缩写,是函数组件
const List1: FC = () => {
// 列表数据
const questionList = [
{ id: "q1", title: "问卷1", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q2", title: "问卷2", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q3", title: "问卷3", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q4", title: "问卷4", isPublished: true },
];
function edit(id: string) {
console.log("edit", id);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>问卷列表页</h1>
<div>
{questionList.map((question) => {
const { id, title, isPublished } = question;
return (
<div key={id} className="list-item">
<strong>{title}</strong>
{/* 条件判断 */}
{isPublished ? (
<span style={{ color: "green" }}>已发布</span>
) : (
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>未发布</span>
)}
<button onClick={() => edit(id)}>编辑问卷</button>
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default List1;
在App.tsx中引用该组件
import React from "react";
import List1 from "./List1";
function App() {
return (
<>
<List1></List1>
</>
);
}
export default App;
Props组件通讯
- props不必先定义后使用
- props可以传递任意数据类型
- props是只读的 - 类似vue中的单项数据流(修改需要调用父组件内的方法修改)
可以修改上面的代码,在App.tsx中将一些props传递给List1组件,例如title(页面标题)、questionList(列表数据)
//App.tsx
import React from "react";
import List1 from "./List1";
function App() {
// 列表数据
const questionList = [
{ id: "q1", title: "问卷1", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q2", title: "问卷2", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q3", title: "问卷3", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q4", title: "问卷4", isPublished: true },
];
return (
<>
<List1 title="问卷列表页1" questionList={questionList}></List1>
</>
);
}
export default App;
子组件在接收父组件的属性时,需要定义接收的属性类型PropsType
//List1.tsx
import React, { FC } from "react";
import "./List1.css";
type QuestionType = {
id: string;
title: string;
isPublished: boolean;
};
type PropsType = {
title: string;
questionList: Array<QuestionType>;
};
//FC就是FunctionComponent的缩写,是函数组件
// { title, questionList }其实就是props,等价于于从函数参数中读取属性title,questionList
const List1: FC<PropsType> = ({ title, questionList }) => {
function edit(id: string) {
console.log("edit", id);
}
return (
<div>
<h1>{title}</h1>
<div>
{questionList.map((question) => {
const { id, title, isPublished } = question;
return (
<div key={id} className="list-item">
<strong>{title}</strong>
...
</div>
);
})}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default List1;
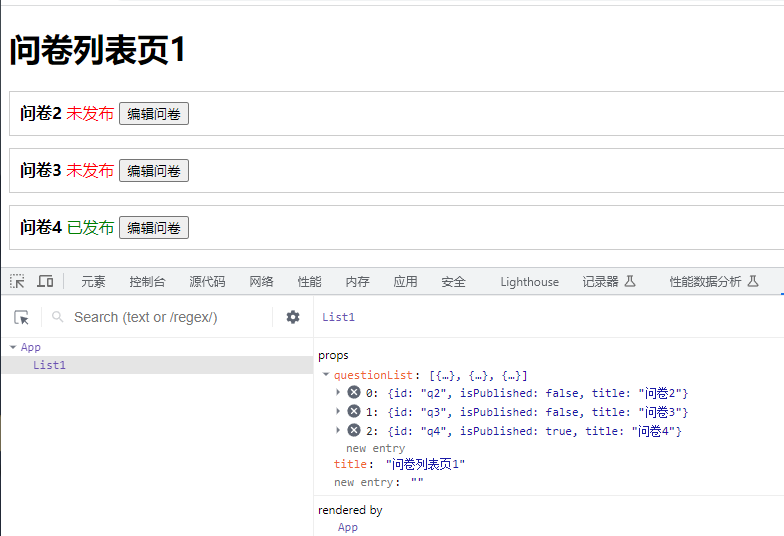
谷歌浏览器安装React Developer Tools插件可以清晰地看到组件间传递接收的props
Hooks
以use开头的函数称为Hooks。Hooks有很多规则,遇到错误时,先看是否违反规则。下面介绍几个比较常用的内置Hooks。
useState
基本使用
有这样的需求:点击一个button,累加数量。
let count = 0;
const add = () => {
count++;
console.log("count", count);
};
return (
<>
<div>
<button onClick={add}>add {count}</button>
</div>
</>
);
用普通的变量无法实现,虽然打印时count在变化,但是无法触发组件的更新。
用useState即可实现,它的作用是用来声明状态变量。useState会返回一个 state,以及更新 state 的函数。
import React, { useState } from "react"; // 引入useState Hook
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const add = () => {
// count++;
setCount(count + 1);
};
return (
<>
<div>
<button onClick={add}>add {count}</button>
</div>
</>
);
}
export default App;
state变化会触发组件更新,重新渲染render页面。
特点
- 异步更新
import React, { useState } from "react"; // 引入useState Hook
function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const add = () => {
// count++;
setCount(count + 1);
console.log("count", count); // 打印的是之前的count
};
return (
<>
<div>
<button onClick={add}>add {count}</button>
</div>
</>
);
}
export default App;
useState为异步更新,无法拿到最新的state值。但是组件会显示它的最新值。所以如果一个变量不用于JSX中显示,那就不要用useState来管理,而是用useRef。
- 可能会被合并
如果让它点击一次按钮,以传入新值的方式触发5次更新,会发现结果都是1。由于异步更新的原因,传入的新值可能都是当前的旧值+1,所以可能会被合并成一句。
function add() {
setCount(count + 1);
setCount(count + 1);
setCount(count + 1);
setCount(count + 1);
setCount(count + 1);
}
如果在setCount用函数更新count值,可以解决这个问题
function add() {
// setCount(count + 1);
// setCount(count + 1);
// setCount(count + 1);
// setCount(count + 1);
// setCount(count + 1);
setCount((count) => count + 1);
setCount((count) => count + 1);
setCount((count) => count + 1);
setCount((count) => count + 1);
setCount((count) => count + 1);
}
- 不可变数据
不可变数据就是不去修改state的值,而是传入一个新的值。
function App() {
const [userInfo, setUserInfo] = useState({ name: "zzz", age: 18 });
const changeAge = () => {
// userInfo.age++; //错误示范
setUserInfo({
...userInfo, //解构语法,避免传入新值遗漏state的其他属性
age: 19,
});
};
return (
<>
<div>{JSON.stringify(userInfo)}</div>
<button onClick={changeAge}>change Age</button>
</>
);
}
export default App;
如果是改变一个数组的长度,可以这样写
import React, { useState } from "react";
function App() {
const [list, setList] = useState(["x", "y"]);
function addItem() {
setList(list.concat("z")); // concat返回的是一个新数组
// setList(list.push('z')) // 错误 push返回的是元素
// setList([...list,'z']) // 可行
}
return (
<>
<div>{JSON.stringify(list)}</div>
<button onClick={addItem}>add Item</button>
</>
);
}
export default App;
使用useState实现问卷的增删改
父组件List2.tsx
import React, { FC, useState } from "react";
import QuestionCard from "./components/QuestionCard";
const List2: FC = () => {
const [questionList, setQuestionList] = useState([
{ id: "q1", title: "问卷1", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q2", title: "问卷2", isPublished: true },
{ id: "q3", title: "问卷3", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q4", title: "问卷4", isPublished: true },
]);
const add = () => {
let newLen = questionList.length + 1;
setQuestionList(
questionList.concat({
id: `q${newLen}`,
title: `问卷${newLen}`,
isPublished: false,
})
);
};
const deleteQuestion = (id: string) => {
setQuestionList(
questionList.filter((q) => {
if (q.id !== id) return true;
else return false;
})
);
};
const publishQuestion = (id: string) => {
setQuestionList(
questionList.map((q) => {
if (q.id !== id) return q;
return {
...q,
isPublished: true,
};
})
);
};
return (
<div>
<h1>问卷列表页2</h1>
<div>
{questionList.map((question) => {
const { id, title, isPublished } = question;
return (
<QuestionCard
key={id}
id={id}
title={title}
isPublished={isPublished}
deleteQuestion={deleteQuestion}
publishQuestion={publishQuestion}
/>
);
})}
</div>
<div>
<button onClick={add}>新增问卷</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default List2;
子组件QuestionCard.tsx
import React, { FC } from "react";
import styles from "./QuestionCard.module.css";
// ts 自定义类型
type PropsType = {
id: string;
title: string;
isPublished: boolean;
deleteQuestion?: (id: string) => void;
publishQuestion?: (id: string) => void;
};
const QuestionCard: FC<PropsType> = (props) => {
const { id, title, isPublished, deleteQuestion, publishQuestion } = props;
function edit(id: string) {
console.log("edit", id);
}
function del(id: string) {
deleteQuestion && deleteQuestion(id);
}
function publish(id: string) {
publishQuestion && publishQuestion(id);
}
return (
<div key={id} className="list-item">
<strong>{title}</strong>
{/* 条件判断 */}
{isPublished ? (
<span style={{ color: "green" }}>已发布</span>
) : (
<span style={{ color: "red" }}>未发布</span>
)}
<button onClick={() => edit(id)}>编辑问卷</button>
<button onClick={() => publish(id)}>发布问卷</button>
<button onClick={() => del(id)}>删除问卷</button>
</div>
);
};
export default QuestionCard;
使用immer解决不可变数据问题
需要安装immer
npm install immer --save
每次修改复杂类型的state时,总是需要将对象的所有属性或数组的所有元素重新传进去,而使用immer可以只单独修改某个属性或元素
//ImmerDemo.tsx
import React, { FC, useState } from "react";
import { produce } from "immer";
const ImmerDemo: FC = () => {
const [userInfo, setUserInfo] = useState({ name: "zzz", age: 18 });
const changeAge = () => {
// userInfo.age++; //错误示范
// setUserInfo({
// ...userInfo, //解构语法,避免传入新值遗漏state的其他属性
// age: 19,
// });
setUserInfo(
produce((draft) => {
draft.age = 19;
})
);
};
return (
<>
<div>{JSON.stringify(userInfo)}</div>
<button onClick={changeAge}>change Age</button>
</>
);
};
export default ImmerDemo;
可以使用immer优化前面例子的增删改
//增加问卷
const add = () => {
let newLen = questionList.length + 1;
setQuestionList(
questionList.concat({
id: `q${newLen}`,
title: `问卷${newLen}`,
isPublished: false,
})
);
};
//删除问卷
const deleteQuestion = (id: string) => {
setQuestionList(
questionList.filter((q) => {
if (q.id !== id) return true;
else return false;
})
);
};
//发布问卷
const publishQuestion = (id: string) => {
setQuestionList(
questionList.map((q) => {
if (q.id !== id) return q;
return {
...q,
isPublished: true,
};
})
);
};
useEffect
使用useEffect可以监听组件生命周期(创建、更新、销毁)。使用场景如下:
- 当组件渲染时,加载一个Ajax网络请求
- 当某个state更新时,加载一个Ajax网络请求
在List3.tsx组件可以监听组件渲染以及某个state更新
import React, { FC, useState, useEffect } from "react";
import QuestionCard from "./components/QuestionCard";
import { produce } from "immer";
const List3: FC = () => {
useEffect(() => {
console.log("加载 ajax 网络请求");
}, []);
const [questionList, setQuestionList] = useState([
{ id: "q1", title: "问卷1", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q2", title: "问卷2", isPublished: true },
{ id: "q3", title: "问卷3", isPublished: false },
{ id: "q4", title: "问卷4", isPublished: true },
]);
useEffect(() => {
console.log("questionList changed");
}, [questionList]);
...
};
export default List3;
在QuestionCard 组件,当点击删除问卷时会监听该组件销毁
import React, { FC, useEffect } from "react";
import classnames from "classnames";
import styles from "./QuestionCard.module.css";
// ts 自定义类型
type PropsType = {
id: string;
title: string;
isPublished: boolean;
deleteQuestion?: (id: string) => void;
publishQuestion?: (id: string) => void;
};
const QuestionCard: FC<PropsType> = (props) => {
const { id, title, isPublished, deleteQuestion, publishQuestion } = props;
...
useEffect(() => {
console.log("question card mounted");
return () => {
console.log("question card unmounted", id);
};
}, []);
...
};
export default QuestionCard;
在这个过程中可以看到useEffect在组件渲染时都会执行两次,特别是添加了销毁语句后,可以发现组件第一次执行渲染后又销毁自身最后再渲染一遍。
- React18开始,
useEffect在开发环境下会执行两次 - 模拟组件创建、销毁、再创建的完整流程,及早暴露问题
- 生产环境下会执行一次
useRef
-
一般用于操作DOM
import React, { FC, useRef } from "react"; const UseRefDemo: FC = () => { const inputRef = useRef<HTMLInputElement>(null); function selectInput() { const inputElem = inputRef.current; // 当前指向的dom节点 if (inputElem) inputElem.select();// DOM节点,DOM操作API } return ( <div> <input type="text" ref={inputRef} defaultValue={"hello world"} /> <button onClick={selectInput}>选中 input</button> </div> ); }; export default UseRefDemo; -
也可传入普通JS变量,但更新不会触发rerender
const UseRefDemo: FC = () => { const nameRef = useRef("water"); // 不是DOM节点,普通的JS变量 const changeName = () => { nameRef.current = "apple"; // 修改ref值不会触发rerender console.log(nameRef.current); }; return ( <div> <p>name {nameRef.current}</p> <div> <button onClick={changeName}>change name</button> </div> </div> ); }; -
要和Vue3的ref区分开
useMemo
- 函数组件,每次state更新都会重新执行函数
- useMemo可以缓存数据,不用每次执行函数都重新生成
- 可用于计算量较大的场景,缓存提高性能
useMemo(calculateValue, dependencies):calculateValue应该是一个没有任何参数的纯函数,并且可以返回任意类型。dependencies是依赖值构成的数组。
import React, { FC, useMemo, useState } from "react";
const UseMemoDemo: FC = () => {
console.log("update demo...");
const [num1, setNum1] = useState(10);
const [num2, setNum2] = useState(20);
const [text, setText] = useState("hello");
const sum = useMemo(() => {
console.log("update sum...");
return num1 + num2;
}, [num1, num2]); // 缓存num1和num2求和
return (
<>
<p>{sum}</p>
<p>
{num1} <button onClick={() => setNum1(num1 + 1)}>add num1</button>{" "}
</p>
<p>
{num2} <button onClick={() => setNum2(num2 + 1)}>add num2</button>{" "}
</p>
<div>
<input
type="text"
onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)}
value={text}
/>
</div>
</>
);
};
export default UseMemoDemo;
num1和num2更新时会触发sum 的更新,但是sum的生成没有因为text的更新而重新生成。
useCallback
useCallback和useMemo作用一样,但它是专门用于缓存函数。useCallback返回一个函数,只有在依赖项变化的时候才会更新(返回一个新的函数)。
例子讲解:传送门
自定义Hooks
如果需要抽离业务逻辑和UI逻辑,复用代码,需要自定义Hooks。
可以基于内置Hooks编写一个简单的自定义Hook。
- 修改页面标题
import React, { useEffect } from "react";
function useTitle(title: string) {
useEffect(() => {
document.title = title;
}, []);
}
export default useTitle;
App.tsx
import React from "react";
import useTitle from "./hooks/useTitle";
function App() {
useTitle("自定义Hook");
return (
<>
</>
);
}
export default App;
- 获取鼠标位置
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function useMouse() {
const [x, setX] = useState(0);
const [y, setY] = useState(0);
const mouseMoveHandler = (event: MouseEvent) => {
setX(event.clientX);
setY(event.clientY);
};
useEffect(() => {
//监听鼠标事件
window.addEventListener("mousemove", mouseMoveHandler);
//组件销毁时,一定要解绑DOM事件 可能会出现内存泄露问题
return () => {
window.removeEventListener("mousemove", mouseMoveHandler);
};
}, []);
return { x, y };
}
export default useMouse;
App.tsx
import React from "react";
import useTitle from "./hooks/useTitle";
import useMouse from "./hooks/useMouse";
function App() {
useTitle("自定义Hook");
const { x, y } = useMouse();
return (
<>
<p>x的位置:{x}</p>
<p>y的位置:{y}</p>
</>
);
}
export default App;
- 模拟异步加载数据
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
function getInfo(): Promise<string> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(Date.now().toString());
}, 1500);
});
}
const useGetInfo = () => {
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true);
const [info, setInfo] = useState("");
useEffect(() => {
getInfo().then((info) => {
setLoading(false);
setInfo(info);
});
}, []);
return { loading, info };
};
export default useGetInfo;
App.tsx
import React from "react";
import useTitle from "./hooks/useTitle";
import useMouse from "./hooks/useMouse";
import useGetInfo from "./hooks/useGetInfo";
function App() {
useTitle("自定义Hook");
const { x, y } = useMouse();
const { loading, info } = useGetInfo();
return (
<>
<p>x的位置:{x}</p>
<p>y的位置:{y}</p>
<p>{loading ? "加载中..." : info}</p>
</>
);
}
export default App;
第三方Hooks
Hooks使用规则
- 统一用useXxx来命名
- 只能在两个地方调用Hook(①组件内②其他Hook内)
- 必须保证每次的调用顺序一致(不能放在if/for内部)
Hooks闭包陷阱
- 当异步函数获取最新state时,可能不是当前最新的state
- 可使用useRef来解决
比如以下这种情况
import React, { FC, useState, useRef, useEffect } from "react";
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
function add() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
function alertFn() {
setTimeout(() => {
alert(count);
}, 3000);
}
return (
<>
<p>闭包陷阱</p>
<div>
<span>{count}</span>
<button onClick={add}>add</button>
<button onClick={alertFn}>alert</button>
</div>
</>
);
};
export default Demo;
当点击add按钮几次后,点击alert按钮后快速按add按钮几次,会发现alert输出的是前面的点击结果,不是当前最新的count。
使用useRef可以解决这个问题,拿到最新的count。
原理:使用对象的引用, 直接获取对象本身的数据。
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
const countRef = useRef(0);
useEffect(() => {
countRef.current = count;
}, [count]);
function add() {
setCount(count + 1);
}
function alertFn() {
setTimeout(() => {
alert(count); // state 值类型
alert(countRef.current); // ref 引用类型
}, 3000);
}
useRef 能解决闭包陷阱的原因是通过 ref.current,useRef 每次拿到的都是这个对象本身, 是同一个内存空间的数据, 所以可以获取到最新的值。
CSS Module
- 每个CSS文件都当作独立的模块,命名xxx.module.css
- 为每个className增加后缀名,不让它们重复
- Create-React-App原生支持CSS Module
例如:
QuestionCard.module.css
.list-item {
border: 1px solid #ccc;
padding: 10px;
margin-bottom: 16px;
}
.list-item .published-span {
color: green;
}
.published {
border-color: green;
}
List.tsx
import styles from "./QuestionCard.module.css";
<div key={id} className={styles['list-item']}>
...
</div>
CSS-in-JS
在JS中写CSS,带来极大的灵活性,它和内联Style不一样,也不会有内联Style的问题。
常用工具:styled-components
import React, { FC } from "react";
import styled, { css } from "styled-components";
// Button 组件
type ButtonPropsType = {
$primary?: boolean;
};
const Button = styled.button<ButtonPropsType>`
background: transparent;
border-radius: 3px;
border: 2px solid palevioletred;
color: palevioletred;
margin: 0 1em;
padding: 0.25em 1em;
${(props) =>
props.$primary &&
css`
background: palevioletred;
color: white;
`}
`;
// Container 组件
const Container = styled.div`
text-align: center;
`;
const Demo: FC = () => {
return (
<div>
<p>styled-components demo</p>
<Container>
<Button>Normal Button</Button>
<Button $primary>Primary Button</Button>
</Container>
</div>
);
};
export default Demo;
Context
- 可跨层级传递,而不像props层层传递
- 类似于Vue的Provide/Inject
- 应用场景:切换主题/语言
孙子组件ThemeButton.tsx
import React, { FC, useContext } from "react";
import { ThemeContext } from "./index";
const ThemeButton: FC = () => {
const theme = useContext(ThemeContext);
const style = {
color: theme.fore,
background: theme.background,
};
return <button style={style}>theme button</button>;
};
export default ThemeButton;
子组件Toolbar.tsx
import React, { FC } from "react";
import ThemeButton from "./ThemeButton";
const Toolbar: FC = () => {
return (
<>
<p>Toolbar</p>
<div>
<ThemeButton />
</div>
</>
);
};
export default Toolbar;
父组件index.tsx,当点击dark按钮时,button主题切换为dark
import React, { FC, createContext, useState } from "react";
import Toolbar from "./Toolbar";
const themes = {
light: {
fore: "#000",
background: "#eee",
},
dark: {
fore: "#fff",
background: "#222",
},
};
// 定义主题
export const ThemeContext = createContext(themes.light);
const Demo: FC = () => {
const [theme, setTheme] = useState(themes.light);
function toDark() {
setTheme(themes.dark);
}
return (
<ThemeContext.Provider value={theme}>
<div>
<div>
<span>Context Demo</span>
<button onClick={toDark}>dark</button>
</div>
<Toolbar />
</div>
</ThemeContext.Provider>
);
};
export default Demo;
useReducer
它是一个额外的hook,不经常用到。
- useState的代替方案
- 数据结构简单时使用useState,复杂时用useReducer
- 简化版的redux(状态管理器)
import React, { FC, useState, useReducer } from "react";
type StateType = { count: number };
type ActionType = { type: string };
const initialState: StateType = { count: 100 }; // 初始值
//根据传入的action返回新的state(不可变数据)
function reducer(state: StateType, action: ActionType) {
switch (action.type) {
case "increment":
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case "decrement":
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
throw new Error();
}
}
const CountReducer: FC = () => {
// const [count, setCount] = useState(100);
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, initialState);
return (
<>
<span>count:{state.count}</span>
{/* <button onClick={() => setCount(count+1)}>+</button> */}
{/* <button onClick={() => setCount(count-1)}>-</button> */}
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: "increment" })}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => dispatch({ type: "decrement" })}>-</button>
</>
);
};
export default CountReducer;


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号