Java集合类
将以以下形式记录常用的类信息:
1、继承关系
2、具体的底层实现
3、提供的初始化方法和方法
一、Map接口
二、Collection接口
public interface Collection<E>
{ int size();
boolean add(E element);
Iterator<E> iterator;
boolean isEmpty();
boolean contains(Object obj);
boolean containsAll(Collection<?> other);
boolean addAll(Collection< ? extends E > other);
boolean remove(Object obj);
void clear();
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> other); //删除other中存在的所有元素。如果这个调用改变了集合返回true。
Object[] toArray();
<T> T[] toArray(T[] arrayToFill);//如果arrayToFill足够大,则放在其中,剩余补null;否则,分配一个新数组,填装后返回。
}
1、List接口
2、Set接口
3、Queue接口
三、Array
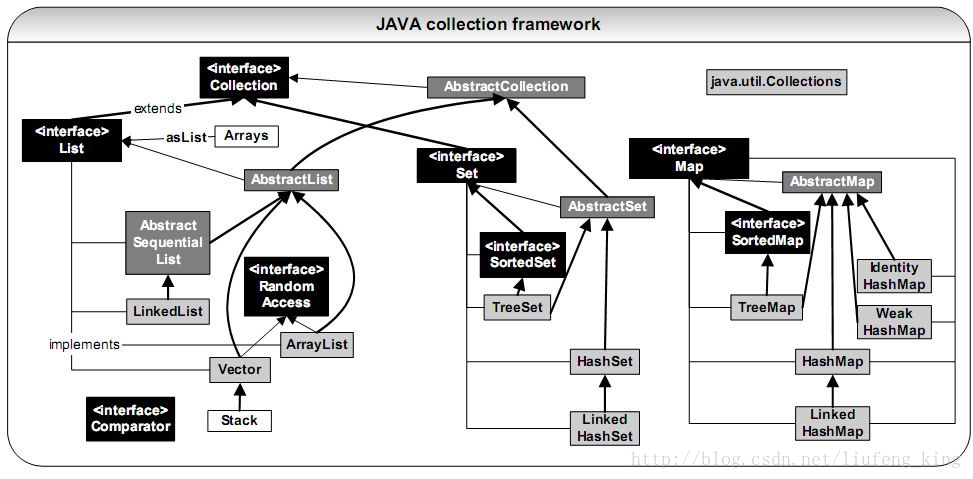

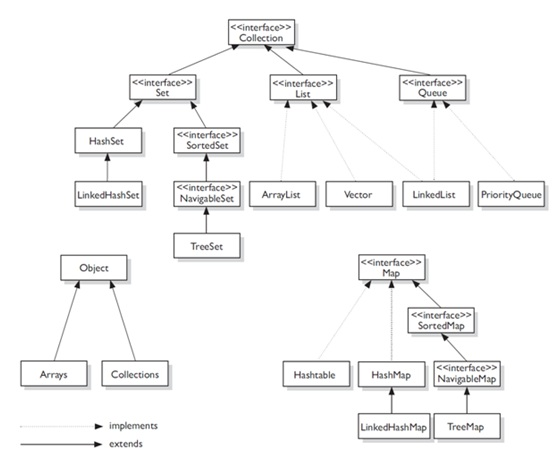
用“集合框架”设计软件时,记住该框架四个基本接口的下列层次结构关系会有用处:
- Collection 接口是一组允许重复的对象。
- Set 接口继承 Collection,但不允许重复。
- List 接口继承 Collection,允许重复,并引入位置下标。
- Map 接口既不继承 Set 也不继承 Collection, 存取的是键值对
我们以下面这个图表来描述一下常用的集合的实现类之间的区别:
|
Collection/Map |
接口 |
成员重复性 |
元素存放顺序(Ordered/Sorted) |
元素中被调用的方法 |
实现基于的数据结构 |
|
HashSet |
Set |
Unique elements |
No order |
equals() hashCode() |
Hash 表 |
|
LinkedHashSet |
Set |
Unique elements |
Insertion order |
equals() hashCode() |
Hash 表和双向链表 |
|
TreeSet |
SortedSet |
Unique elements |
Sorted |
equals() compareTo() |
平衡树(Balanced tree) |
|
ArrayList |
List |
Allowed |
Insertion order |
equals() |
数组 |
|
LinkedList |
List |
Allowed |
Insertion order |
equals() |
链表 |
|
Vector |
List |
Allowed |
Insertion order |
equals() |
数组 |
|
HashMap |
Map |
Unique keys |
No order |
equals() hashCode() |
Hash 表 |
|
LinkedHashMap |
Map |
Unique keys |
Key insertion order/Access order of entries |
equals() hashCode() |
Hash 表和双向链表 |
|
Hashtable |
Map |
Unique keys |
No order |
equals() hashCode() |
Hash 表 |
|
TreeMap |
SortedMap |
Unique keys |
Sorted in key order |
equals() compareTo() |
平衡树(Balanced tree) |
Reference:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_722e24e70100npaz.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/dingxiaoyue/p/4948267.html
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33326449/article/details/52741427
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_654189e00100mu3j.html


