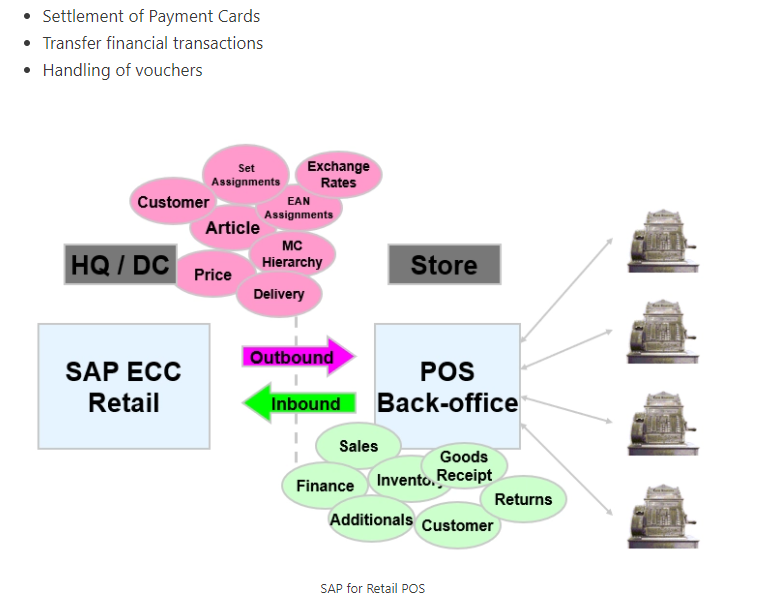
SAP CARR for retails solution SAP零售集成方案
- Customer-Centric Merchandising
- SAP Merchandising for Retail
- Inventory Valuation (e.g. Retail Method of Accounting)
- Perishables Procurement
- SAP Planning for Retail
- SAP Price Optimization
- SAP Promotion Management for Retail
- SAP Merchandising for Retail
- Customer-Driven Supply Chain
- Unified Customer Experience
- Business Process of Shopper Experience Management
- SAP Point of Sale
- SAP Point of Sale Data Management
- SAP Workforce Management
- In-Store Merchandise and Inventory Management & Mobile Employee Facing
- Analytics for SAP for Retail
- Loss Pevention Analytics for Retail
- In Store Fresh Item Management
- Enterprise Data Warehouse Service for POS
- Corporate Operations
- Business Process Platform
Cross Topics
Special Topics
- Global Data Synchronization
- ASAP Business Add-ons for Retail: Help to Lower Implementation Costs
- Run SAP for Retail - Best Practices for Solution Operations
- SAP Retail Technology Facts and Retail Switch
- Consequences of Activating the BF Set SAP Retail
Retail Value Map:
Customer-Centric Marketing and Merchandising
Build personalized shopping experiences with your customers. Develop targeted promotions and pricing strategies that give a high return on investment, while lowering inventory costs
Sourcing, Buying and Private Label
Efficiently source, buy, or produce products by collaborating with a global network of business partners

Supply Chain
Optimize customer service and profitability by balancing supply and inventory to meet dynamic demand at optimum cost
Omnicommerce Customer Experience
Truly understand customer needs to increase brand awareness, improve interaction, and utilize customer interaction channels that are consistent, personalized, and enjoyable
Please click on the boxes below to explore more Details
- Customer-Centric Merchandising
- SAP Merchandising for Retail
- Inventory Valuation (e.g. Retail Method of Accounting)
- Perishables Procurement
- SAP Planning for Retail
- SAP Price Optimization
- SAP Promotion Management for Retail
- SAP Merchandising for Retail
- Customer-Driven Supply Chain
- Unified Customer Experience
- Business Process of Shopper Experience Management
- SAP Point of Sale
- SAP Point of Sale Data Management
- SAP Workforce Management
- In-Store Merchandise and Inventory Management & Mobile Employee Facing
- Analytics for SAP for Retail
- Loss Pevention Analytics for Retail
- In Store Fresh Item Management
- Enterprise Data Warehouse Service for POS
- Corporate Operations
- Business Process Platform
Cross Topics
Special Topics
SAP for Retail Community Contributions
Whether they are best practices, lessons learned or success stories, share your experience with us. If you don't know where to start, please have a look at existing SAP for Retail Community page contributions (see the box SAP for Retail Community Contributions on the right side) to see what has been created by members of our Retail on SCN community.
Also, before you begin, read our page on how you can contribute so you can begin positioning yourself with your knowledge. Remember, it's you who makes the BPX community thrive! We welcome your input.
SAP Merchandising for Retail
SAP Merchandising for Retail is a real-time integrated solution for merchandise management that enables head office, stores as well as trading partners access to information and transactions that support best practice business processes across the entire retail merchandise lifecycle. It is based on SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning).
SAP Merchandising helps retailers execute the intelligent merchandising decisions that will set them apart from the competition. By understanding their customers and anticipating new trends, retailers can respond rapidly to consumer demands in ways that inspire customers to return to their stores, Website or call center - again and again. And with all the insight they need to make the best merchandising decisions, retailers can grow their business profitably.
Key Functions and Features
|
Key function |
Target in SAP Library |
Target in Solution Map for Retail |
Business Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Key function |
Target in SAP Library |
Target in Solution Map for Retail |
Business Scenario |
|
Operational Buying |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
• Source of Supply |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
• Purchase Orders |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
◊ Collective Purchase Orders |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
◊ Requirements Processing for Request for Quotations |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
◊ Processing Purchase Orders for Subcontracting |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
◊ Seasonal Procurement |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
|
||
|
• Order Optimization |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
||
|
• Open to Buy |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
|
|
|
• Invoicing |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
Verifying Logistics Invoices (Online/In Background) - Retail |
|
|
• Vendor Rebate Arrangements |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
|
|
|
• Consignment |
Supply Chain Management → Operational Buying |
|
|
|
• Retail Price Management & Execution |
Merchandise Lifecycle → Retail Price Management |
||
|
• Promotion Management & Execution |
Merchandise Lifecycle → Promotion Management |
|
|
|
• Markdown Management & Execution |
Merchandise Lifecycle → Markdown Management |
||
|
Distribution |
Supply Chain Management → Replenishment and Inventory Opt. |
|
|
|
• Allocation |
Supply Chain Management -> Replenishment and Inventory Opt. -> Allocation |
||
|
• Basic Replenishment |
Supply Chain Management -> Replenishment and Inventory Opt. -> Requirements Planning and Replenishment |
|
|
|
• Stock Relocation |
|
|
|
|
Inventory Management |
Supply Chain Management -> Replenishment and Inventory Opt. -> Chain Wide Inventory Management |
|
|
|
• Stock Management |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
• Retail Method of Accounting (RMA) |
|
||
|
• Stock Ledger (Cost, Retail, Hybrid) |
|
|
|
|
• Stock Relocation |
|
|
|
|
• Returns Management |
|
|
|
|
• Physical Inventory |
|
|
Getting started with SAP Merchandising for Retail
- SAP Retail Technology Facts of SAP Retail configuration (SMP credentials required): The objective of this document is to provide a solid understanding of the SAP Retail technology facts in the current release SAP ERP 6.0: activitation of SAP Retail with corresponding business function set, the enterprise extension Retail and the provision of innovations with Retail-related enterprise business function in enhancement packages. The document adresses business consultants and SAP customers to acquire deeper understanding of SAP Retail. Thus specialized knowledge about system installation or programming is not a prerequisite for reading this document.
(1) Access point: Access points in retails industry are where consumer touch to vendor or retailer. Now a day, access point can be POS (Point of Sales), E-Commerce website, Mobile Application, Telephone, Social Media, Facebook, … etc.
(2) Convertor: in first point (1), sales data can from many sources. SAP CAR provide standard EDI document format to help partners system can follow and provide data consistently. Conversion happened in partner’s system before send data to SAP CAR. There are two meaning of conversion, first convert and mapping master data, second convert from source structure to SAP CAR’s structure.
(3) IDOCs: IDOCs is one of the inbound methodology SAP CAR supported, partner’s system can supply data such as SAP CAR’s IDOC requirements without any deep knowledge about POS DTA processing.
(4) BAPI: BAPI is Business Application Programming Interface was provided by SAP. BAPI support SAP’s developer or technical consultant send transaction data to SAP CAR correctly.
(5) Master Data Loading: SAP CAR based on HANA technology, master data will be replicated from SAP S4 HANA to CAR through SAP SLT (System Landscape Transformation).
(6) Inbound Processing: Inbound processing is the first step in process sequence of POS DTA. Inbound processing help collect raw sales transaction data and put into queue. CAR Administrator can monitor queue (manual process / period process / Delete Queue).
(7) Sales Audit: When sales data came to inbound processing queue. Data audition will perform: master data validation, sales data logic validation. SAP CAR provided monitoring tools help operator can control sales data status. Operator can re-process error data after fixed issue.
(8) Aggregation: Aggregation is strongly recommend in Retails Industry, this procedure help system reduce amount of waste information. In retails landscape, SAP ERP system only need key objects. Example: In the supper market, hundred thousand of receipts send to SAP CAR, some key information in receipt will pass to ERP, some for reporting purpose only. Aggregation perform combine sales data as defined parameters help minimum number of inventory transaction to SAP ERP.
(9) Outbound Processing: After raw data aggregated, Outbound processing engine will performed to distribute aggregated transaction to destination system.
(10) Synchronize Transaction Data with SAP S4 HANA: invoke to retails landscape, it isn’t only sales transaction. Inventory, promotion campaign, Customer Relationship Management, Pricing, replenishment.. etc managed in SAP ERP, some objects need to be syn between CAR and SAP S4 HANA.
Example: Sales transaction happened on SAP CAR, Inventory movement happened on SAP ERP. Stock availability should be consistent between both system then all partners system can see near real-time. SAP BW reporting, reporting app can access inventory in SAP CAR also consistent.
(11) Outbound to SAP ERP: SAP ERP receive sales aggregated and Payment Aggregated data from SAP CAR.
(12) Outbound raw data to SAP BW: SAP BW receive sales raw data from SAP CAR to do detail reporting.
(13) (14) (15) outbound data to third-party systems as business requirements.
本文来自博客园,作者:Slashout,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/SlashOut/p/15216201.html







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号