栈和队列——用数组实现栈和队列
用数组结构实现大小固定的栈 (较简单)
栈是先进后出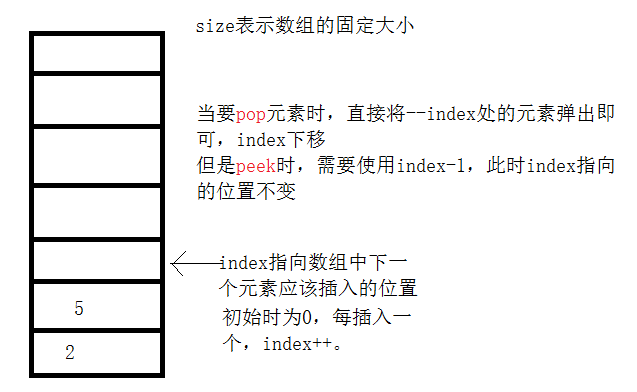
public class ArrayStack{
private int size;
private int [] arraySta;
private int index = 0;
public ArrayStack(int size) {
if(size < 0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException( "size must be positive" );
}
this.size = size;
this.arraySta = new int[this.size];
}
public void push(int num){
if(index == size) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException( "this stack is full" );
}
arraySta[index++] = num;
}
public int pop(){
if(index == 0){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException( "this stack is empty" );
}
return arraySta[--index];
}
public int peek(){
if(index == 0){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("this stack is empty");
}
return arraySta[index - 1];
}
}
用数组结构实现大小固定的队列 (较复杂)
队列是先进先出
注意:不要试图使用head和tail两个指针之间的关系进行判断,很复杂
head和tail分别从头开始,触底就从头开始,
只利用它们与size之间的关系,size==0时,出队列poll()抛出异常,size==array.length时,入队列offer()抛出异常
以及与数组的长度head==array.length时,tail==array.length时,从头开始

//数组实现队列 先进先出 head指向出元素端,tail直线进元素端
public class ArrayQueue{
private int size;
private int[] arrayQue;
private int head;
private int tail;
public ArrayQueue(int size) {
this.arrayQue = new int[size];
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
//向队列中添加元素
public void offer(int num){
if(size == arrayQue.length){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("queue is full");
}
arrayQue[tail++] = num;
size++;
if(tail == arrayQue.length) tail = 0;
}
//从队列中弹出元素
public int poll(){
if(size == 0){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("queue is empty");
}
int num = arrayQue[head++];
size--;
if(head == arrayQue.length) head = 0;
return num;
}
//获取队列的头部元素
public int peek(){
if(size == 0){
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("queue is empty");
}
return arrayQue[head];
}
}




