ASP.NET 加密 Part.2(对称算法)
在理解了上一篇文章的基础上,本文将创建两个工具类,一个使用对称的加密算法,一个使用非对称的加密算法。
1. 管理秘密信息
必须采取某种措施来保护密钥,你当然可以对密钥本身进行加密,但这样就需要另一个加密密钥了,也会面临一样的问题。
Windows 提供了一个内置机制来保存和保护秘密数据。这个机制使用一个系统安装时创建的机器密钥来加密数据。只有本地的操作系统才可以访问这个机器密钥。当然,每一次安装时,这个机器密钥都是不同的。
Windows 支持 DPAPI 使用这个密钥来保护数据。当使用这个 API 的时候,你不能直接访问密钥,你只需要告诉系统使用机器密钥加密或者解密就可以了。因此,这解决了密钥管理的问题。
为此,.NET Framework 提供了 System.Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData 类,可以这样使用:
byte[] protData = ProtectedData.Protect(ClearBytes, null, DataProtectionScope.LocalMachine);
使用 DPAPI 非常容易,但不要用来加密数据库中的信息。如上述代码段中那样,使用了 DataProtectionScope.LocalMachine 设置,已加密的数据就是和这个机器绑定的。因此,如果这台机器崩溃了,而你必须在另一台机器上恢复数据,那你会丢失所有加密过的信息。如果你使用 DPAPI 加密密钥,你还应当在另一个安全的地方备份这个密钥。
2. 使用对称算法
对称加密算法使用同一个密钥来加密和解密数据。本例中,我们创建一个工具类,该类负责加密和解密敏感数据。然后,就可以在几个 Web 程序中重用这个类。这个工具类将具有如下所示的结构并且可以用于加密和解密字符串数据。
public static class SymmetricEncryptionUtility
{
public static bool ProtectKey { get; set; }
public static string AlgorithmName { get; set; }
public static void GenerateKey(string targetFile) { }
public static void ReadKey(SymmetricAlgorithm algorithm, string file) { }
public static byte[] EncryptData(string data, string keyFile) { }
public static string DecryptData(byte[] data, string keyFile) { }
}
这个类只是一个工具类,只有静态成员,可以将其作为一个静态类,这样就没有人可以创建它的实例了。这个类通过 AlgorithmName 属性提供了指定加密算法的名称(DES、TripleDES、RijnDael、RC2)。它还支持生成一个新的密钥、从指定的文件中读取密钥到某个算法实例所定义的密钥属性、加密和解密数据的操作。
要想使用这个类,必须正确设置算法名称;如果没有密钥,则生成一个新的密钥。然后,你只需要调用 EncryptData() 和 DecryptData(),这 2 个方法将调用 ReadKey() 方法初始化这个算法。ProtectKey 属性允许这个类的用户指定是否应当使用 DPAPI 来保护密钥。
通过加密算法类生成加密密钥,下面是 GenerateKey():
public static void GenerateKey(string targetFile)
{
// Create the algorithm
SymmetricAlgorithm Algorithm = SymmetricAlgorithm.Create(AlgorithmName);
Algorithm.GenerateKey();
// Now get the key
byte[] Key = Algorithm.Key;
if (ProtectKey)
{
Key = ProtectedData.Protect(Key, null, DataProtectionScope.LocalMachine);
}
// Store the key in a file called key.config
using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(targetFile,FileMode.Create))
{
fs.Write(Key, 0, Key.Length);
}
}
SymmetricAlgorithm 实例的 GenerateKey() 通过加密系统的强随机数算法生成一个新的密钥,并使用这个密钥初始化 Key 属性。如果调用的代码将工具类的 ProtectKey 标志设为 true,那么实现将用 DPAPI 来加密这个密钥。
ReadKey() 方法从 GenerateKey() 方法所产生的文件中读取密钥:
public static void ReadKey(SymmetricAlgorithm algorithm, string file)
{
byte[] Key;
using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(file, FileMode.Open))
{
Key = new byte[fs.Length];
fs.Read(Key, 0, (int)fs.Length);
}
if (ProtectKey)
{
algorithm.Key = ProtectedData.Unprotect(Key, null, DataProtectionScope.LocalMachine);
}
else
{
algorithm.Key = Key;
}
}
如果这个密钥之前被保护,ReadKey 从文件中读取密钥的时候,会使用 DPAPI 来解除对已加密密钥的保护。此外,这个方法还接收一个现存的对称加密算法的实例。ReadKey() 会初始化这个算法的 Key 属性,这样在后续的操作中会自动使用这个密钥。最后,这个函数本身被 EncryptData() 和 DecryptData() 调用。
public static byte[] EncryptData(string data, string keyFile) { }
public static string[] DecryptData(byte[] data, string keyFile) { }
可以看到,这两个方法都需要一个 keyFile 参数来指定存储密钥的文件路径,然后它们调用 ReadKey() 使用密钥初始化它们的算法实例。
public static byte[] EncryptData(string data, string keyFile)
{
// Convert string data to byte array
byte[] ClearData = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(data);
// Now create the algorithm
SymmetricAlgorithm Algorithm = SymmetricAlgorithm.Create(AlgorithmName);
ReadKey(Algorithm, keyFile);
// Encrypt information
MemoryStream target = new MemoryStream();
// Generate a random initialization vector (IV) to use for the algorithm
Algorithm.GenerateIV();
target.Write(Algorithm.IV, 0, Algorithm.IV.Length);
// Encrypt actual data
CryptoStream cs = new CryptoStream(target,
Algorithm.CreateEncryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cs.Write(ClearData, 0, ClearData.Length);
cs.FlushFinalBlock();
// Return the encrypt stream of data as a byte array
return target.ToArray();
}
首先,将引入的纯文本字符串值转化为一个字节数组,因为加密算法的加密函数需要字节数组作为参数。然后,根据类的 AlgorithmName 属性创建加密算法,这个值可以是 RC2、Rijndael、DES、TripleDES,SymmetricAlgorithm 的工厂方法会创建适当的实例。然后,创建了一个内存数据流加密操作的目标,它先生成一个 IV(Initialization Vector,初始化向量)并将其写入到目标数据流的第一个位置。IV 为加密的数据流增加了随机的数据。
如果程序在客户端和服务器端之间多次交换同样的信息,简单的加密总是产生相同的加密结果,这会使得暴力破解更加容易。为了增加一些随机信息,对称加密算法支持了 IV。这些 IV 不仅本身会被添加到已加密的字节流中,而且也被用作输入来加密第一个数据块。
当使用 CryptoStream 加密信息时,不要忘记调用 FlushFinalBlock() 来保证加密数据的最后一个数据块被正确写入目标中。
解密时依旧需要使用到这个 IV:
public static string DecryptData(byte[] data, string keyFile)
{
// Create the algorithm
SymmetricAlgorithm Algorithm = SymmetricAlgorithm.Create(AlgorithmName);
ReadKey(Algorithm, keyFile);
// Decrypt information
MemoryStream target = new MemoryStream();
// Read IV and initialize the algorithm with it
int readPos = 0;
byte[] IV = new byte[Algorithm.IV.Length];
Array.Copy(data, IV, IV.Length);
Algorithm.IV = IV;
readPos += Algorithm.IV.Length;
CryptoStream cs = new CryptoStream(target,
Algorithm.CreateDecryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cs.Write(data, readPos, data.Length - readPos);
cs.FlushFinalBlock();
// Get the bytes from the memory stream and convert them to text
return System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(target.ToArray());
}
解密函数的结构恰恰反了过来。它创建加密算法并为要解密的目标创建一个数据流。在开始解密数据之前,必须先从加密的数据流中读取 IV,因为加密算法需要它来执行最后的转换。
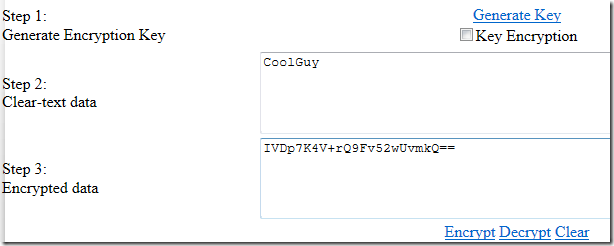
现在,创建一个页面来测试这个工具类。通过 Convert.ToBase64String() 可以很容易的将加密过的数据输出。通过 Convert.FromBase64String() 可以将已加密的字节传递给解密方法。
下面是测试页面的代码:
private string keyFileName;
private string algorithmName = "DES";
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SymmetricEncryptionUtility.AlgorithmName = algorithmName;
keyFileName = Server.MapPath("./") + "symmetric_key.config";
}
protected void GenerateKeyCommand_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SymmetricEncryptionUtility.ProtectKey = EncryptKeyCheck.Checked;
SymmetricEncryptionUtility.GenerateKey(keyFileName);
Response.Write("Key generated sucessfully!");
}
protected void EncryptCommand_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(keyFileName))
{
Response.Write("Missing encryption key. Please generate key!");
}
byte[] data = SymmetricEncryptionUtility.EncryptData(ClearDataText.Text, keyFileName);
EncryptedDataText.Text = Convert.ToBase64String(data);
}
protected void DecryptCommand_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(keyFileName))
{
Response.Write("Missing encryption key. Please generate key!");
}
byte[] data = Convert.FromBase64String(EncryptedDataText.Text);
ClearDataText.Text = SymmetricEncryptionUtility.DecryptData(data, keyFileName);
}
protected void ClearCommand_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
ClearDataText.Text = "";
EncryptedDataText.Text = "";
}
下面是加解密工具类的全部代码,并增加了中文注释:
using System;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.IO;
namespace EncryptionUtility
{
public static class SymmetricEncryptionUtility
{
public static bool ProtectKey { get; set; }
public static string AlgorithmName { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 生成加密密钥,并可选则是否对这个密钥进行保护
/// 保护的方式是使用 Windows 支持的 DPAPI
/// 最终,将密钥存放于 targetFile 中
/// </summary>
/// <param name="targetFile">指定存储密钥的文件路径</param>
public static void GenerateKey(string targetFile)
{
// Create the algorithm
SymmetricAlgorithm Algorithm = SymmetricAlgorithm.Create(AlgorithmName);
Algorithm.GenerateKey();
// Now get the key
byte[] Key = Algorithm.Key;
if (ProtectKey)
{
Key = ProtectedData.Protect(Key, null, DataProtectionScope.LocalMachine);
}
// Store the key in a file called key.config
using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(targetFile, FileMode.Create))
{
fs.Write(Key, 0, Key.Length);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 数据加密或解密只有使用相同的密钥才能配对成功
/// 因此,必需读取加密密钥来重置指定加密算法的 Key 属性
/// 如果是 DPAPI 方式保护过的密钥,则必需取消保护
/// </summary>
/// <param name="algorithm">对称算法的实例之一</param>
/// <param name="keyFile">保存密钥的文件路径</param>
public static void ReadKey(SymmetricAlgorithm algorithm, string keyFile)
{
byte[] Key;
using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(keyFile, FileMode.Open))
{
Key = new byte[fs.Length];
fs.Read(Key, 0, (int)fs.Length);
}
if (ProtectKey)
{
algorithm.Key = ProtectedData.Unprotect(Key, null, DataProtectionScope.LocalMachine);
}
else
{
algorithm.Key = Key;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 加密数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data">未加密的文本字符串</param>
/// <param name="keyFile">保存密钥的文件路径</param>
/// <returns>加密后的 byte[]</returns>
public static byte[] EncryptData(string data, string keyFile)
{
// 将文本字符串转换为 byte[],加密转换流需要用到
byte[] ClearData = System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(data);
// Now create the algorithm
SymmetricAlgorithm Algorithm = SymmetricAlgorithm.Create(AlgorithmName);
ReadKey(Algorithm, keyFile);
// Encrypt information
MemoryStream target = new MemoryStream();
// Generate a random initialization vector (IV) to use for the algorithm
Algorithm.GenerateIV();
// 将初始化向量写入内存流的第一个位置
// 因为许多算法的密钥长度包含了奇偶位,它们对加密强度并不起作用
// 在 DES 算法中,64 位密钥只使用 56 位,128 位的 TripleDES 密钥只使用 112 位
// 因此,在这里填充了初始化向量
target.Write(Algorithm.IV, 0, Algorithm.IV.Length);
// Encrypt actual data
// 加密转换流构造函数需要:
// Stream:对其执行加密转换的流
// ICryptoTransform:要对流执行的加密转换,这里由 CreateEncryptor() 提供
// CryptoStreamMode:指定加密流的模式
// CreateEncryptor():用指定算法的 Key 和 初始化向量 创建对称加密器对象
CryptoStream cs = new CryptoStream(target,
Algorithm.CreateEncryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
cs.Write(ClearData, 0, ClearData.Length);
cs.FlushFinalBlock();
// Return the encrypt stream of data as a byte array
return target.ToArray();
}
/// <summary>
/// 解密数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="data">可用 Convert.FromBase64String() 函数转换加密后的字符串得到 byte[]</param>
/// <param name="keyFile">保存密钥的文件路径</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static string DecryptData(byte[] data, string keyFile)
{
// Create the algorithm
SymmetricAlgorithm Algorithm = SymmetricAlgorithm.Create(AlgorithmName);
ReadKey(Algorithm, keyFile);
// Decrypt information
MemoryStream target = new MemoryStream();
// Read IV and initialize the algorithm with it
// 从已加密的数据中取出第一个位置的 IV(初始化向量)来重置当前算法的 IV
int readPos = 0;
byte[] IV = new byte[Algorithm.IV.Length];
Array.Copy(data, IV, IV.Length);
Algorithm.IV = IV;
// 将字节数组下标索引提升,以免解密时写入 IV 内容
readPos += Algorithm.IV.Length;
CryptoStream cs = new CryptoStream(target,
Algorithm.CreateDecryptor(), CryptoStreamMode.Write);
// 讲不包括第一个位置 IV 的真实加密数据解密后写入内存流
cs.Write(data, readPos, data.Length - readPos);
cs.FlushFinalBlock();
// Get the bytes from the memory stream and convert them to text
return System.Text.Encoding.UTF8.GetString(target.ToArray());
}
}
}





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架