静态 Top Tree 小记
Top Cluster 系列:
定义#
-
簇(Cluster):一个连通边集,每个簇有两个界点。
-
界点、内点:两个簇只会在界点处有交,除了界点外其他点为内点。
这两个定义也在 Top Cluster 树分块 解释过,下面用
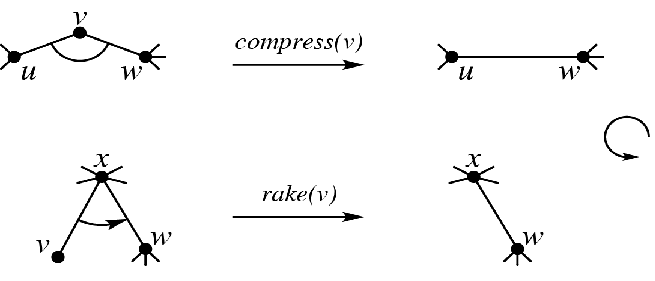
簇的两种合并操作#
对于两个边集无交、恰好有一个界点重合的簇,可以通过 Compress 操作或 Rake 操作将两者合并成一个新簇。
合并后的新簇的边集为原来两个簇的边集并集。
-
compress 操作:对于两个簇
-
rake 操作:对于两个簇
具体如下
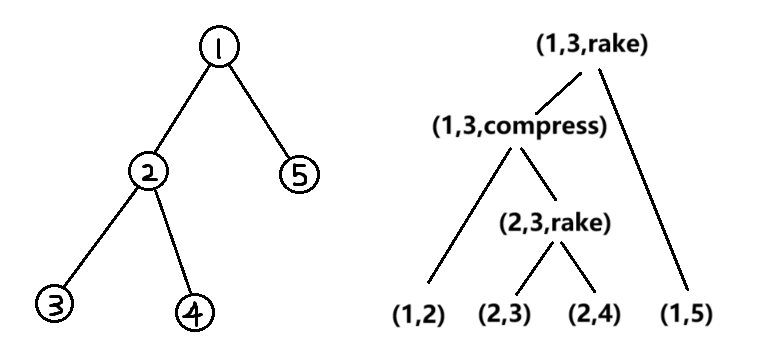
Top Tree#
定义#
对于一棵树的
我们通过不断进行 compress 和 rake 合并操作,将这
定义 Top Tree 为合并过程对应的树。例如:
静态 Top Tree 构建#
这里介绍一种方法,先重链剖分。
对于一条重链,先把每个重链上的点
然后只剩下重链上的簇了,通过 compress 操作依次合并即可。
为了保证复杂度,需要分治地合并。对于 compress 部分,可以类似于全局平衡二叉树,找到带权中点,注意这里是 Leafy 式的。
对于 rake 部分,同样根据每个轻儿子的子树大小找到带权中点,进行分治。
有分治部分保证,容易发现在 Top Tree 上每跳两次父亲,子树大小至少乘二。
这种构建方式还有一个性质,每个簇的两个界点一定是祖先关系。
点击查看代码
namespace Build {
ll tot, lc[maxn], rc[maxn], siz[maxn], son[maxn]; bool typ[maxn];
vector <ll> nd, nds; ll nowid[maxn], fa[maxn], ft[maxn];
void dfs1(ll u, ll f = 0) {
siz[u] = 1;
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v ^ f) {
dfs1(v, u), siz[u] += siz[v];
if(siz[v] > siz[son[u]]) son[u] = v;
}
}
ll build(ll l, ll r, bool Typ) { // Typ 表示合并操作为 Compress 还是 Rake
if(l == r) return nd[l];
ll w = nds[r] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0), lo = l, hi = r - 2;
while(lo <= hi) {
ll mid = lo + hi >> 1;
if((nds[mid] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0)) * 2 < w) lo = mid + 1;
else hi = mid - 1;
} ll x = lo, id = ++tot; typ[id] = Typ, ft[id] = ft[nd[Typ? r : l]];
return fa[lc[id] = build(l, x, Typ)]
= fa[rc[id] = build(x + 1, r, Typ)] = id;
}
void dfs2(ll u, ll f = 0, bool istp = true) {
nowid[u] = ft[u] = u;
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u] && v != f) dfs2(v, u);
if(son[u]) {
dfs2(son[u], u, false);
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
nd.pb(nowid[son[u]]), nds.pb(1);
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u] && v != f)
nd.pb(nowid[v]), nds.pb(siz[v]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[son[u]] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, false);
}
if(istp && son[u]) {
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
for(ll x = u; x; x = son[x])
nd.pb(nowid[x]), nds.pb(siz[x] - siz[son[x]]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[u] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, true);
}
}
} using namespace Build;
其实我们可以把 Top Tree 近似地看成线段树上树。
Top Tree 分治#
构建一棵 Top Tree,然后 DFS。
对于当前簇,找到所有跨越中间界点的所有询问,然后求解。
不难发现这是一个分治的过程,所以称为 Top Tree 分治。
例题#
[联合省选 2022] 填树#
标算为
考虑在移动区间
对于一个簇,维护六个量:
-
所有不包含上界点的路径上所有点权值乘积之和。
-
上界点到下界点路径上所有点权值乘积(不包含上界点)之和。
-
所有点(不包含上界点)到上界点的路径上所有点权值乘积之和。
-
所有点(不包含上界点)到下界点的路径上所有点权值乘积之和。
-
所有包含上界点的路径(路径两端不能是上界点)上所有点权值乘积之和。
-
其中一端为下界点的,所有包含上界点的路径(另一端不能是上界点)上所有点权值乘积之和。
这六者在两种合并操作中是容易求得的,时间复杂度降为
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
namespace Initial {
#define ll long long
#define ull unsigned long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mkp make_pair
#define pir pair <ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define i128 __int128
using namespace std;
namespace Read {
char buf[1 << 22], *p1, *p2;
// #define getchar() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, (1 << 22) - 10, stdin), p1 == p2)? EOF : *p1++)
template <class T>
const inline void rd(T &x) {
char ch; bool neg = 0;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))
if(ch == '-') neg = 1;
x = ch - '0';
while(isdigit(ch = getchar()))
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - '0';
if(neg) x = -x;
}
} using Read::rd;
const ll maxn = 410, inf = 1e18, mod = 1e9 + 7, iv = mod - mod / 2;
ll power(ll a, ll b = mod - 2) {
ll s = 1;
while(b) {
if(b & 1) s = s * a %mod;
a = a * a %mod, b >>= 1;
} return s;
}
template <class T>
const inline ll pls(const T x, const T y) { return x + y >= mod? x + y - mod : x + y; }
template <class T>
const inline void add(T &x, const T y) { x = x + y >= mod? x + y - mod : x + y; }
template <class T>
const inline void chkmax(T &x, const T y) { x = x < y? y : x; }
template <class T>
const inline void chkmin(T &x, const T y) { x = x > y? y : x; }
} using namespace Initial;
ll n, m, K, l[maxn], r[maxn], rt; vector <ll> to[maxn];
ll h[maxn], ht, op[maxn];
namespace Build {
ll tot, lc[maxn], rc[maxn], siz[maxn], son[maxn]; bool typ[maxn];
vector <ll> nd, nds; ll nowid[maxn], fa[maxn], ft[maxn];
void dfs1(ll u, ll f = 0) {
siz[u] = 1;
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v ^ f) {
dfs1(v, u), siz[u] += siz[v];
if(siz[v] > siz[son[u]]) son[u] = v;
}
}
ll build(ll l, ll r, bool Typ) {
if(l == r) return nd[l];
ll w = nds[r] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0), lo = l, hi = r - 2;
while(lo <= hi) {
ll mid = lo + hi >> 1;
if((nds[mid] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0)) * 2 < w) lo = mid + 1;
else hi = mid - 1;
} ll x = lo, id = ++tot; typ[id] = Typ, ft[id] = ft[nd[Typ? r : l]];
return fa[lc[id] = build(l, x, Typ)]
= fa[rc[id] = build(x + 1, r, Typ)] = id;
}
void dfs2(ll u, ll f = 0, bool istp = true) {
nowid[u] = ft[u] = u;
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u] && v != f) dfs2(v, u);
if(son[u]) {
dfs2(son[u], u, false);
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
nd.pb(nowid[son[u]]), nds.pb(1);
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u] && v != f)
nd.pb(nowid[v]), nds.pb(siz[v]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[son[u]] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, false);
}
if(istp && son[u]) {
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
for(ll x = u; x; x = son[x])
nd.pb(nowid[x]), nds.pb(siz[x] - siz[son[x]]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[u] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, true);
}
}
} using namespace Build;
struct Data {
ll a[maxn], b[maxn];
} f[maxn], d[maxn], a[maxn], b[maxn], p[maxn], q[maxn], w[maxn];
const Data operator + (const Data A, const Data B) {
Data C;
for(ll i = 1; i <= m; i++)
C.a[i] = pls(A.a[i], B.a[i]),
C.b[i] = pls(A.b[i], B.b[i]);
return C;
}
const Data operator * (const Data A, const Data B) {
Data C;
for(ll i = m; i; i--)
C.a[i] = A.a[i] * B.a[i] %mod,
C.b[i] = (A.a[i] * B.b[i] + A.b[i] * B.a[i]) %mod;
return C;
}
void compress(ll u) {
f[u] = f[lc[u]] + f[rc[u]] + b[lc[u]] * a[rc[u]] + p[rc[u]] * w[ft[lc[u]]];
d[u] = d[lc[u]] * d[rc[u]];
a[u] = a[lc[u]] + a[rc[u]] * d[lc[u]];
b[u] = b[rc[u]] + b[lc[u]] * d[rc[u]] + q[rc[u]] * w[ft[lc[u]]];
p[u] = p[lc[u]] + a[rc[u]] * q[lc[u]];
q[u] = q[lc[u]] * d[rc[u]];
}
void rake(ll u) {
f[u] = f[lc[u]] + f[rc[u]];
d[u] = d[lc[u]];
a[u] = a[lc[u]] + a[rc[u]];
b[u] = b[lc[u]];
p[u] = p[lc[u]] + p[rc[u]] + a[lc[u]] * a[rc[u]];
q[u] = q[lc[u]] + d[lc[u]] * a[rc[u]];
}
void pushup(ll u) {
if(typ[u]) compress(u);
else rake(u);
}
namespace Lagrange {
ll F[maxn], pre[maxn], suf[maxn], ifac[maxn];
void Init() {
ifac[0] = 1;
for(ll i = 1; i <= m; i++) ifac[i] = ifac[i - 1] * i %mod;
ifac[m] = power(ifac[m]);
for(ll i = m; i; i--) ifac[i - 1] = ifac[i] * i %mod;
}
ll Getval(ll *a, ll x) {
if(x <= 0) return 0;
for(ll i = 1; i <= m; i++) F[i] = pls(a[i], F[i - 1]);
if(x >= 1 && x <= m) return F[x];
ll ret = 0; pre[0] = suf[m + 1] = 1;
for(ll i = 1; i <= m; i++) pre[i] = pre[i - 1] * (x + mod - i) %mod;
for(ll i = m; i; i--) suf[i] = suf[i + 1] * (i + mod - x) %mod;
for(ll i = 1; i <= m; i++)
ret = (ret + pre[i - 1] * suf[i + 1] %mod * ifac[i - 1] %mod
* ifac[m - i] %mod * F[i]) %mod;
return ret;
}
} using Lagrange::Getval;
pir solve(ll k) {
h[0] = -inf; pir res = {};
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) w[i] = {};
for(ll u = 1; u <= tot; u++)
f[u] = d[u] = a[u] = b[u] = p[u] = q[u] = {};
h[ht + 1] = inf;
for(ll i = 0, j = 0; j < ht; ) {
ll st = max(h[j] + k, h[i]), ed = min(h[j + 1] - 1 + k, h[i + 1] - 1);
for(ll u = 1, nowop; u <= n; u++) {
if(i < l[u] || r[u] <= j) nowop = -1;
else if(l[u] <= j && i < r[u]) nowop = 0;
else if(j < l[u] && r[u] <= i) nowop = 1;
else if(j < l[u] && i < r[u]) nowop = 2;
else nowop = 3;
if(nowop == op[u]) continue; op[u] = nowop;
if(nowop == -1) w[u] = {};
if(nowop == 0)
for(ll x = 1; x <= m; x++) {
w[u].a[x] = k + 1;
w[u].b[x] = (2 * x - k + mod) * (k + 1) %mod * iv %mod;
}
if(nowop == 1)
for(ll x = 1; x <= m; x++) {
w[u].a[x] = pls(h[r[u]], mod - h[l[u]]);
w[u].b[x] = (h[r[u]] + h[l[u]] - 1)
* (h[r[u]] - h[l[u]] + mod) %mod * iv %mod;
}
if(nowop == 2)
for(ll x = 1; x <= m; x++) {
w[u].a[x] = pls(x + 1, mod - h[l[u]]);
w[u].b[x] = (x + h[l[u]])
* (x - h[l[u]] + 1 + mod) %mod * iv %mod;
}
if(nowop == 3)
for(ll x = 1; x <= m; x++) {
w[u].a[x] = (h[r[u]] - x + k) %mod;
w[u].b[x] = (x - k + h[r[u]] - 1 + mod)
* (h[r[u]] - x + k + mod) %mod * iv %mod;
}
f[u] = d[u] = a[u] = b[u] = w[u];
for(ll x = fa[u]; x; x = fa[x]) pushup(x);
}
if(i && st <= ed) {
add(res.fi, pls(Getval(f[rt].a, ed),
mod - Getval(f[rt].a, st - 1)));
add(res.se, pls(Getval(f[rt].b, ed),
mod - Getval(f[rt].b, st - 1)));
}
if(h[i + 1] - ed <= h[j + 1] + k - ed) ++i;
else ++j;
} return res;
}
signed main() {
freopen("tree.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("tree.out", "w", stdout);
rd(n), rd(K); m = n + 3;
memset(op, -1, sizeof op);
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; i++)
rd(l[i]), rd(r[i]), h[++ht] = l[i], h[++ht] = r[i] + 1;
sort(h + 1, h + 1 + ht);
ht = unique(h + 1, h + 1 + ht) - h - 1;
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; i++)
l[i] = lower_bound(h + 1, h + 1 + ht, l[i]) - h,
r[i] = upper_bound(h + 1, h + 1 + ht, r[i]) - h;
for(ll i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ll u, v; rd(u), rd(v);
to[u].pb(v), to[v].pb(u);
}
tot = n; dfs1(1), dfs2(1);
rt = nowid[1], Lagrange::Init();
pir ans1 = solve(K);
pir ans2 = solve(K - 1);
printf("%lld\n%lld\n", pls(ans1.fi, mod - ans2.fi), pls(ans1.se, mod - ans2.se));
return 0;
}
[NOI2022] 树上邻域数点#
第一个思路是 Top Tree 分治,然后每次询问就是两边合并。
但是一个簇内的邻域很难表示,这启示我们应该特殊考虑点
找到这样的一个簇
为了保证状态数,我们要求找的簇
那么
最后一点,此时每次询问我们仍然需要合并两次,考虑设
点击查看代码
#include"count.h"
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
namespace Initial {
#define ll int
#define ull unsigned long long
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mkp make_pair
#define pir pair <ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define i128 __int128
using namespace std;
namespace Read {
char buf[1 << 22], *p1, *p2;
// #define getchar() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, (1 << 22) - 10, stdin), p1 == p2)? EOF : *p1++)
template <class T>
const inline void rd(T &x) {
char ch; bool neg = 0;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))
if(ch == '-') neg = 1;
x = ch - '0';
while(isdigit(ch = getchar()))
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - '0';
if(neg) x = -x;
}
} using Read::rd;
const ll maxn = 4e5 + 10, inf = 1e9, mod = 1e9 + 7;
ll power(ll a, ll b = mod - 2) {
ll s = 1;
while(b) {
if(b & 1) s = s * a %mod;
a = a * a %mod, b >>= 1;
} return s;
}
template <class T>
const inline ll pls(const T x, const T y) { return x + y >= mod? x + y - mod : x + y; }
template <class T>
const inline void add(T &x, const T y) { x = x + y >= mod? x + y - mod : x + y; }
template <class T>
const inline void chkmax(T &x, const T y) { x = x < y? y : x; }
template <class T>
const inline void chkmin(T &x, const T y) { x = x > y? y : x; }
} using namespace Initial;
ll n, d[maxn], bz[maxn][20], rt; vector <ll> to[maxn];
namespace Build {
ll tot, lc[maxn], rc[maxn], siz[maxn], son[maxn]; bool typ[maxn];
ll df[maxn][20], dep[maxn], tp[maxn];
vector <ll> nd, nds; ll nowid[maxn], fa[maxn], ft[maxn];
ll len[maxn], len_tp[maxn], len_ft[maxn];
void dfs1(ll u) {
siz[u] = 1;
for(ll i = 1; i < 20; i++) df[u][i] = df[df[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v) {
df[v][0] = u, dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;
dfs1(v), siz[u] += siz[v];
if(siz[v] > siz[son[u]]) son[u] = v;
}
}
ll build(ll l, ll r, bool Typ) {
if(l == r) return nd[l];
ll w = nds[r] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0), lo = l, hi = r - 2;
while(lo <= hi) {
ll mid = lo + hi >> 1;
if((nds[mid] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0)) * 2 < w) lo = mid + 1;
else hi = mid - 1;
} ll x = lo, id = ++tot; typ[id] = Typ;
ft[id] = ft[nd[Typ? r : l]], tp[id] = tp[nd[l]];
fa[lc[id] = build(l, x, Typ)] = fa[rc[id] = build(x + 1, r, Typ)] = id;
if(Typ) {
d[id] = d[lc[id]] + d[rc[id]];
len[id] = max(max(len[lc[id]], len[rc[id]]), len_ft[lc[id]] + len_tp[rc[id]]);
len_tp[id] = max(len_tp[lc[id]], len_tp[rc[id]] + d[lc[id]]);
len_ft[id] = max(len_ft[lc[id]] + d[rc[id]], len_ft[rc[id]]);
}
else {
d[id] = d[lc[id]];
len[id] = max(max(len[lc[id]], len[rc[id]]), len_tp[lc[id]] + len_tp[rc[id]]);
len_tp[id] = max(len_tp[lc[id]], len_tp[rc[id]]);
len_ft[id] = max(len_ft[lc[id]], d[lc[id]] + len_tp[rc[id]]);
}
return id;
}
void dfs2(ll u, bool istp = true) {
len[u] = len_tp[u] = len_ft[u] = d[u] = 1;
nowid[u] = ft[u] = u, tp[u] = df[u][0];
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u]) dfs2(v);
if(son[u]) {
dfs2(son[u], false);
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
nd.pb(nowid[son[u]]), nds.pb(1);
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u])
nd.pb(nowid[v]), nds.pb(siz[v]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[son[u]] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, false);
}
if(istp && son[u]) {
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
for(ll x = u > 1? u : son[u]; x; x = son[x])
nd.pb(nowid[x]), nds.pb(siz[x] - siz[son[x]]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[u] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, true);
}
}
} using namespace Build;
using namespace std;
ll dist(ll u, ll v) {
if(dep[u] < dep[v]) swap(u, v);
ll t = dep[u] - dep[v], P = dep[u] + dep[v];
for(ll i = 0; i < 20; i++)
if(t & (1 << i)) u = df[u][i];
if(u == v) return P - dep[u] * 2;
for(ll i = 19; ~i; i--)
if(df[u][i] ^ df[v][i])
u = df[u][i], v = df[v][i];
return P - dep[u] * 2 + 2;
}
vector <info> f[maxn][2], g[maxn][2], h[maxn];
info e[maxn];
info F(ll u, ll c, ll i) { return i <= 0? emptyinfo : f[u][c][min(i, len[u])]; }
info G(ll u, ll c, ll i) { return i <= 0? emptyinfo : g[u][c][min(i, len[fa[u]])]; }
info H(ll u, ll i) { return i < 0? emptyinfo : h[u][min(i, len[fa[u]])]; }
info C(const info a, const info b) {
if(isempty(a)) return b;
if(isempty(b)) return a;
return MC(a, b);
}
info R(const info a, const info b) {
if(isempty(a)) return b;
if(isempty(b)) return a;
return MR(a, b);
}
void Dfs1(ll u) {
bz[u][0] = fa[u];
for(ll i = 1; i < 20; i++) bz[u][i] = bz[bz[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
f[u][0].resize(len[u] + 1), g[u][0].resize(len[fa[u]] + 1);
f[u][1].resize(len[u] + 1), g[u][1].resize(len[fa[u]] + 1);
f[u][0][0] = f[u][1][0] = g[u][0][0] = g[u][1][0] = emptyinfo;
if(u <= n)
return f[u][0][1] = f[u][1][1] = e[u], d[u] = 1, void();
Dfs1(lc[u]), Dfs1(rc[u]);
if(typ[u]) {
for(ll i = 1; i <= len[u]; i++) {
f[u][0][i] = C(F(lc[u], 0, i), F(rc[u], 0, i - d[lc[u]]));
f[u][1][i] = C(F(rc[u], 1, i), F(lc[u], 1, i - d[rc[u]]));
}
} else {
for(ll i = 1; i <= len[u]; i++) {
f[u][0][i] = R(F(lc[u], 0, i), F(rc[u], 0, i));
f[u][1][i] = R(F(lc[u], 1, i), F(rc[u], 0, i - d[lc[u]]));
}
}
}
void Dfs2(ll u) {
h[u].resize(len[fa[u]] + 1);
for(ll i = 0; i <= len[fa[u]]; i++)
h[u][i] = C(F(u, 0, len[u]), G(u, 0, i));
if(u <= n) return;
if(typ[u]) {
for(ll i = 1; i <= len[u]; i++) {
g[lc[u]][0][i] = G(u, 0, i);
g[lc[u]][1][i] = C(F(rc[u], 0, i), G(u, 1, i - d[rc[u]]));
g[rc[u]][0][i] = C(F(lc[u], 1, i), G(u, 0, i - d[lc[u]]));
g[rc[u]][1][i] = G(u, 1, i);
}
} else {
for(ll i = 1; i <= len[u]; i++) {
g[lc[u]][0][i] = R(G(u, 0, i), F(rc[u], 0, i));
g[lc[u]][1][i] = G(u, 1, i);
g[rc[u]][0][i] = R(G(u, 0, i), C(F(lc[u], 0, i), G(u, 1, i - d[lc[u]])));
g[rc[u]][1][i] = emptyinfo;
}
}
Dfs2(lc[u]), Dfs2(rc[u]);
}
void init(ll T, ll N, ll Q, vector <ll> Fa, vector <info> E, ll M) {
n = tot = N;
for(ll i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
to[Fa[i]].pb(i + 2), e[i + 2] = E[i];
dfs1(1), dfs2(1), rt = nowid[1];
Dfs1(rt), Dfs2(rt);
}
info ask(ll u, ll k){
if (k == 0) return emptyinfo;
ll x = max(u, 2);
for(ll i = 19; ~i; i--)
if(bz[x][i] && len[bz[x][i]] <= k) x = bz[x][i];
return C(H(x, k - dist(tp[x], u)), G(x, 1, k - dist(ft[x], u)));
}
广义串并联图上邻域数点#
建立 Top Tree,和填树一题一样,每个簇维护六类信息,一些信息需要同时维护个数和权值和。
询问可以直接做 Top Tree 合并,和线段树合并类似,可以做到强制在线。
点击查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
namespace Initial {
#define ll int
#define ull unsigned int
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mkp make_pair
#define pir pair <ll, ll>
#define pb push_back
#define i128 __int128
using namespace std;
namespace Read {
char buf[1 << 22], *p1, *p2;
#define getchar() (p1 == p2 && (p2 = (p1 = buf) + fread(buf, 1, (1 << 22) - 10, stdin), p1 == p2)? EOF : *p1++)
template <class T>
const inline void rd(T &x) {
char ch; bool neg = 0;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))
if(ch == '-') neg = 1;
x = ch - '0';
while(isdigit(ch = getchar()))
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + ch - '0';
if(neg) x = -x;
}
} using Read::rd;
const ll maxn = 4e5 + 10, inf = 1e9, mod = 1e9 + 7, iv = mod - mod / 2;
ll power(ll a, ll b = mod - 2) {
ll s = 1;
while(b) {
if(b & 1) s = s * a %mod;
a = a * a %mod, b >>= 1;
} return s;
}
template <class T>
const inline ll pls(const T x, const T y) { return x + y >= mod? x + y - mod : x + y; }
template <class T>
const inline void add(T &x, const T y) { x = x + y >= mod? x + y - mod : x + y; }
template <class T>
const inline void chkmax(T &x, const T y) { x = x < y? y : x; }
template <class T>
const inline void chkmin(T &x, const T y) { x = x > y? y : x; }
} using namespace Initial;
ll n, m, a[maxn], rt[maxn]; vector <ll> to[maxn];
ll idcnt, sid[maxn * 20], ls[maxn * 20], rs[maxn * 20];
ull w[maxn * 20], sum[maxn * 20], sumtp[maxn * 20], sumft[maxn * 20];
ull d[maxn], ftw[maxn * 20], cnt[maxn * 20], sz[maxn * 20];
ull kcnt[maxn * 20], ksum[maxn * 20], hcnt[maxn * 20], hsum[maxn * 20];
namespace Build {
ll tot, lc[maxn], rc[maxn], siz[maxn], son[maxn]; bool typ[maxn];
vector <ll> nd, nds; ll nowid[maxn], fa[maxn], ft[maxn];
void dfs1(ll u, ll f = 0) {
siz[u] = 1;
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v ^ f) {
dfs1(v, u), siz[u] += siz[v];
if(siz[v] > siz[son[u]]) son[u] = v;
}
}
ll build(ll l, ll r, bool Typ) {
if(l == r) return nd[l];
ll w = nds[r] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0), lo = l, hi = r - 2;
while(lo <= hi) {
ll mid = lo + hi >> 1;
if((nds[mid] - (l? nds[l - 1] : 0)) * 2 < w) lo = mid + 1;
else hi = mid - 1;
} ll x = lo, id = ++tot; typ[id] = Typ, ft[id] = ft[nd[Typ? r : l]];
fa[lc[id] = build(l, x, Typ)] = fa[rc[id] = build(x + 1, r, Typ)] = id;
d[id] = d[lc[id]] + (Typ? d[rc[id]] : 0);
return id;
}
void dfs2(ll u, ll f = 0, bool istp = true) {
nowid[u] = ft[u] = u;
d[u] = -a[u];
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u] && v != f) dfs2(v, u);
if(son[u]) {
dfs2(son[u], u, false);
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
nd.pb(nowid[son[u]]), nds.pb(1);
for(ll v: to[u])
if(v != son[u] && v != f)
nd.pb(nowid[v]), nds.pb(siz[v]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[son[u]] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, false);
}
if(istp && son[u]) {
nd.clear(), nds.clear();
for(ll x = u; x; x = son[x])
nd.pb(nowid[x]), nds.pb(siz[x] - siz[son[x]]);
for(ll i = 1; i < nds.size(); i++) nds[i] += nds[i - 1];
nowid[u] = build(0, nd.size() - 1, true);
}
}
} using namespace Build;
void frcp(ll x) {
if(ls[x] && rs[x]) return;
ll y = !ls[x]? lc[sid[x]] : rc[sid[x]];
w[0] = d[y], ftw[0] = -a[ft[y]];
}
void compress(ll x) {
frcp(x); ll u = ls[x], v = rs[x];
w[x] = w[u] + w[v], sz[x] = sz[u] + sz[v];
sum[x] = sum[u] + sum[v] + sumft[u] * sz[v] + cnt[u] * sumtp[v];
cnt[x] = cnt[u] + sz[v];
sum[x] += kcnt[v] * ftw[u] + ksum[v];
sumtp[x] = sumtp[u] + sumtp[v] + w[u] * sz[v];
sumft[x] = sumft[u] + sumft[v] + w[v] * cnt[u]
+ hsum[v] + hcnt[v] * ftw[u];
kcnt[x] = kcnt[u] + hcnt[u] * sz[v];
ksum[x] = ksum[u] + hsum[u] * sz[v] + hcnt[u] * sumtp[v];
hcnt[x] = hcnt[u], hsum[x] = hsum[u] + w[v] * hcnt[u];
ftw[x] = ftw[v];
}
void rake(ll x) {
frcp(x); ll u = ls[x], v = rs[x];
sum[x] = sum[u] + sum[v], w[x] = w[u];
sumtp[x] = sumtp[u] + sumtp[v], sumft[x] = sumft[u];
cnt[x] = cnt[u], sz[x] = sz[u] + sz[v];
kcnt[x] = kcnt[u] + kcnt[v] + sz[u] * sz[v];
ksum[x] = ksum[u] + ksum[v] + sumtp[u] * sz[v] + sz[u] * sumtp[v];
hcnt[x] = hcnt[u] + sz[v];
hsum[x] = hsum[u] + w[u] * sz[v] + sumtp[v];
ftw[x] = ftw[u];
}
void pushup(ll x) {
if(typ[sid[x]]) compress(x);
else rake(x);
}
ll Merge(ll p, ll q) {
if(!p || !q) return p | q;
ls[p] = Merge(ls[p], ls[q]);
rs[p] = Merge(rs[p], rs[q]);
pushup(p); return p;
}
ll New(ll x) {
if(x == 4)
--x, ++x;
ll p = ++idcnt; cnt[p] = sz[p] = 1;
sumtp[p] = sumft[p] = ftw[p] = w[p] = a[x], sid[p] = x;
for(ll y = x, q = p; x = fa[x]; pushup(p), y = x, q = p)
sid[p = ++idcnt] = x, lc[x] == y? (ls[p] = q) : (rs[p] = q);
return p;
}
signed main() {
rd(n), rd(m);
for(ll i = 1; i < n; i++) {
ll u, v; rd(u), rd(v);
to[u].pb(v), to[v].pb(u);
}
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) rd(a[i]);
tot = n, dfs1(1), dfs2(1);
for(ll i = 1; i <= n; i++) rt[i] = New(i);
while(m--) {
ll u, v; rd(u), rd(v);
rt[u] = Merge(rt[u], rt[v]);
printf("%u\n", 2 * sum[rt[u]]);
}
return 0;
}
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/Sktn0089/p/18615913
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」